Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Atomic - Structure - Multiple - Choice 2009 05 13 1 Slide Per Page PDF
Caricato da
lazarosDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Atomic - Structure - Multiple - Choice 2009 05 13 1 Slide Per Page PDF
Caricato da
lazarosCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Slide 1 / 49
What is the frequency, in Hz, of electromagnetic
radiation that has a wavelength of 0.55 m?
A
5.5 x 108
1.8 x 10-9
1.6 x 108
1.3 x 10-33
1.3 x 1033
Slide 2 / 49
What is the frequency of light, in Hz, that has a
wavelength of 1.23 x 10-6 cm?
A
3.69
2.44 x 1016
4.10 x 10-17
9.62 x 1012
1.04 x 10-13
Slide 3 / 49
What is the wavelength of light (nm) that has a
frequency of 3.22 x 1014 Hz?
A
932
649
8.66 x 1022
7.32 x 10-7
1.05 x 106
Slide 4 / 49
What is the wavelength of light (nm) that has a
frequency 4.25 x 1014 Hz?
A
932
706
2.39 x 1023
1.54 x 10-3
1.07 x 106
Slide 5 / 49
The wavelength of a photon that has energy of
5.65 x 10-19 J is __________ m.
A
3.59 x 10-7
2.64 x 106
2.38 x 1023
4.21 x 10-24
3.79 x 107
Slide 6 / 49
The energy of a photon that has a wavelength of
10 m is __________ J.
A
1.99 x 10-26
5.5 x 1025
6.0 x 10-23
2.7 x 109
4.5 x 10-25
Slide 7 / 49
The energy of a photon that has a frequency of
7.75 x 1014 Hz is __________ J.
A
8.08 x 10-50
1.99 x 10-25
5.12 x 10-19
1.24 x 1049
1.26 x 10-19
Slide 8 / 49
What is the frequency (Hz) of a photon that has
energy of 4.38 x 10-18 J?
A
436
6.61 x 1015
1.45 x 10-16
2.30 x 107
1.31 x 10-9
Slide 9 / 49
Of the following, ______ radiation has the longest
wavelength and ______ radiation has the greatest
energy:
X-ray
ultraviolet
visible
A
ultraviolet, X-ray
visible, ultraviolet
x-ray, x-ray
visible, X-ray
X-ray, visible
Slide 10 / 49
10 Which one of the following is correct?
A
f+=c
f/=c
f=c
= cf
f =c
Slide 11 / 49
11 The photoelectric effect is __________.
the total reflection of light by metals giving them
their typical luster
the production of current by silicon solar cells
when exposed to sunlight
the ejection of electrons by a metal when struck
with light of sufficient energy
the darkening of photographic film when
exposed to an electric field
a relativistic effect
Slide 12 / 49
12 The wavelength of light emitted from a traffic light
having a frequency of 6.15 x1014 Hz is _________.
A
702 nm
641 nm
674 nm
487 nm
583 nm
Slide 13 / 49
13 A radio station broadcasts at 101.5 MHz. The
wavelength of the signal is __________ m.
A
3.10
2.96
4.71
2.75
3.84
Slide 14 / 49
14 The de Broglie wavelength of a 12 gram bullet
traveling at the speed of sound is _________ m.
The speed of sound is 331 m/sec.
A
2.7 x10-34
1.67 x10-34
3.35 x10-33
2.7 x10-37
6.6 x10-31
Slide 15 / 49
15 The de Broglie wavelength of a __________ will
have the shortest wavelength when traveling at 30
m/s.
A
marble
car
earth
uranium atom
hydrogen atom
Slide 16 / 49
16 Electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength of ___
nm appears as green light to the human eye. The
frequency of this light is 5.71 x1014 Hz.
525
425
650
1550
571
Slide 17 / 49
17 An FM radio station broadcasts electromagnetic
radiation at a frequency of 99.5 MHz. The
wavelength of this radiation is __________ m.
A
3.01 x106
3.01
3.018 x1016
3.018 x1010
0.302
Slide 18 / 49
18 Electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength of
525 nm appears as green light to the human eye.
The energy of one photon of this light is
__________ J.
A
1.04 x10-31
3.79 x10-28
3.78 x10-19
1.04 x10-22
2.64 x1018
Slide 19 / 49
19 Electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength of
531 nm appears as green light to the human eye.
The energy of one photon of this light is
3.74 x10-19 J. Thus, a laser that emits 2.3 x10-2 J of
energy in a pulse of light at this wavelength
produces __________ photons in each pulse.
A
6.9 x10-17
6.2 x10-24
6.8 x1019
6.15 x1016
6.5 x1013
Slide 20 / 49
20 The de Broglie wavelength of an electron with a
velocity of 6.00 x108 cm/s is __________ m. The
mass of the electron is 9.11 x10-31 kg.
A
8.25 x109
8.25 x1012
1.21 x10-16
1.21 x10-13
1.21 x10-10
Slide 21 / 49
21 Which statement below correctly describes the
responses of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation to
an electric field?
Both beta and gamma are deflected in the same
direction, while alpha shows no response.
Both alpha and gamma are deflected in the
same direction, while beta shows no response.
Both alpha and beta are deflected in the same
direction, while gamma shows no response.
Alpha and beta are deflected in opposite
directions, while gamma shows no response.
Only alpha is deflected, while beta and gamma
show no response.
Slide 22 / 49
22 The subatomic particles in the nucleus are
A
Protons, electrons
Electrons, neutrons
Protons, neutrons
none of the above
Neutrons, only neutrons
Slide 23 / 49
23 The ______ and _________ reside in the nucleus of
an atom.
A
electrons
protons, neutrons, and electrons
protons and neutrons
protons and electrons
protons
Slide 24 / 49
24 Which one of the following is not true concerning
cathode rays?
A
They originate from the negative electrode.
They travel in straight lines in the absence of
electric or magnetic fields.
They impart a negative charge to metals
exposed to them.
They are made up of electrons.
The characteristics of cathode rays depend on
the material from which they are emitted.
Slide 25 / 49
25 The determination of charge of an electron is
related to which of the following?
A
cathode ray tube, by J. J. Thompson
Rutherford gold foil experiment
Millikan oil drop experiment
Dalton atomic theory
atomic theory of matter
Slide 26 / 49
26 Fast-moving electrons are ___________ particles.
A
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
none of the above
Slide 27 / 49
27 The gold foil experiment __________.
confirmed the plum-pudding model of the atom
led to the discovery of the atomic nucleus
was the basis for Thomson's model of the atom
utilized the deflection of beta particles by gold
foil
proved the law of multiple proportions
Slide 28 / 49
28 In the Rutherford nuclear-atom model,
__________.
the heavy subatomic particles, protons and
neutrons, reside in the nucleus
the three principal subatomic particles (protons,
neutrons, and electrons) all have essentially the
same mass
the light subatomic particles, protons and
neutrons, reside in the nucleus
mass is spread essentially uniformly throughout
the atom
the three principal subatomic particles (protons,
neutrons, and electrons) all have essentially the
same mass and mass is spread essentially
uniformly throughout the atom
Slide 29 / 49
29 Cathode rays are __________.
A
neutrons
x-rays
electrons
protons
atoms
Slide 30 / 49
30 Cathode rays are deflected away from a negatively
charged plate because __________.
A
they are not particles
they are positively charged particles
they are neutral particles
they are negatively charged particles
they are emitted by all matter
Slide 31 / 49
31 In the absence of magnetic or electric fields,
cathode rays __________.
A
do not exist
travel in straight lines
cannot be detected
become positively charged
bend toward a light source
Slide 32 / 49
32 Of the three types radioactivity characterized
by Rutherford, which one is/are charged?
A
-rays
-rays and -rays
-rays, -rays, and -rays
-rays
-rays and -rays
Slide 33 / 49
33 Of the three types of radiation, which one is/are
not electrically charged?
A
-rays
-rays, -rays, and -rays
-rays
-rays and -rays
-rays and -rays
Slide 34 / 49
34 Of the three types of radioactivity characterized by
Rutherford, which are particles?
A
-rays
-rays, -rays, and -rays
-rays
-rays and -rays
-rays and -rays
Slide 35 / 49
35 Of the three types of radioactivity characterized by
Rutherford, which is/are not particles?
A
-rays
-rays and -rays
-rays
-rays
-rays, -rays, and -rays
Slide 36 / 49
36 Of the following, the smallest and lightest
subatomic particle is the __________.
A
neutron
proton
electron
nucleus
alpha particle
Slide 37 / 49
37 All atoms of a given element have the same
__________
A
mass
number of protons
number of neutrons
density
number of electrons and neutrons
Slide 38 / 49
38 The nucleus of an atom does not contain
__________.
A
protons
protons or neutrons
neutrons
subatomic particles
electrons
Slide 39 / 49
39 The nucleus of an atom contains __________.
A
electrons
protons
neutrons
protons and neutrons
protons, neutrons, and electrons
Slide 40 / 49
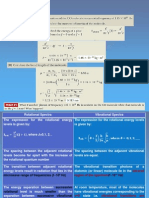
40 If r1 is the smallest orbital radius around a single
proton, then r4 is equal to
A
16 r1.
12 r1.
6 r 1.
2.45 r1.
0.17 r1.
Slide 41 / 49
41 The binding energy of the hydrogen atom in its
ground state is -13.6 eV. What is the energy when
it is in the n = 4 state?
2.72 eV
-2.72 eV
0.544 eV
-0.85 eV
5.44 eV
Slide 42 / 49
42 A hydrogen atom in the ground state absorbs a
photon of energy 12.09 eV. To which state will the
electron make a transition?
A
n=2
n=3
n=4
n=5
n=6
Slide 43 / 49
43 What is the ionization energy of the neutral
hydrogen atom?
A
27.2 eV
13.6 eV
6.8 eV
3.4 eV
none of the given answers
Slide 44 / 49
44 In making a transition from state n = 1 to state n =
2, the hydrogen atom must
A
absorb a photon of energy 10.2 eV.
emit a photon of energy 10.2 eV.
absorb a photon of energy 13.58 eV.
emit a photon of energy 13.58 eV.
none of the given answers
Slide 45 / 49
45 The electron of a hydrogen atom makes a
transition from the n = 5 state to the n = 2 state.
What is the wavelength of the emitted photon?
A
344 nm
430 nm
443 nm
523 nm
235 nm
Slide 46 / 49
46 In state n = 1, the energy of the hydrogen atom is
-13.58 eV. What is its energy in state n = 2?
A
-6.79 eV
-4.53 eV
-3.40 eV
-1.51 eV
-0.51 eV
Slide 47 / 49
47 The wavelength of a ruby laser is 694.3 nm. What
is the energy difference between the two energy
states involved in laser action?
A
1.537 eV
1.646 eV
1.786 eV
1.812 eV
1.951 eV
Slide 48 / 49
48 An electron is moving about a single proton in an
orbit characterized by n = 4. How many of the
electron's de Broglie wavelengths fit into the
circumference of this orbit?
A
16
32
Slide 49 / 49
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- CentralDocumento10 pagineCentralwondimuNessuna valutazione finora
- HP Board Class XII Physics Model Question PaperDocumento5 pagineHP Board Class XII Physics Model Question PaperJack DourNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY 142 (FAVOUR) QuestionsDocumento60 paginePHY 142 (FAVOUR) QuestionsAbdulganeey Horlarmilekan Muheez100% (1)
- Chapter 38 - Photons and Matter WavesDocumento12 pagineChapter 38 - Photons and Matter WavesVV Cephei100% (1)
- Chapter 35: Interference ExplainedDocumento11 pagineChapter 35: Interference ExplainedYuni Dwi LestariNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz Bootcamp08practicelightelectronconfigurationfa18 1Documento5 pagineQuiz Bootcamp08practicelightelectronconfigurationfa18 1api-233552637Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2Nd Edition by Zumdahl Isbn 1305079248 9781305079243 Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 pagineTest Bank For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2Nd Edition by Zumdahl Isbn 1305079248 9781305079243 Full Chapter PDFmarc.herman362100% (12)
- Gtse SolutionDocumento16 pagineGtse Solution1 AashuNessuna valutazione finora
- Short Questions on Interference and DiffractionDocumento11 pagineShort Questions on Interference and DiffractionNishi SinghalNessuna valutazione finora
- Wave Optics (QB)Documento12 pagineWave Optics (QB)Raju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Questions For Ch. 7: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocumento26 paginePractice Questions For Ch. 7: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionPaolo PepsNessuna valutazione finora
- Trial Physics STPM Sem 3 2013 TerengganuDocumento7 pagineTrial Physics STPM Sem 3 2013 TerengganuZuraini Arshad100% (1)
- Assignment 1 AtomicDocumento7 pagineAssignment 1 AtomicAman9692Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class XII 2023 2024 Prelims IDocumento10 pagineClass XII 2023 2024 Prelims ITanishkha RaajNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7Documento9 pagineChapter 7alexcw92Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 11th Edition Chang Test Bank DownloadDocumento21 pagineChemistry 11th Edition Chang Test Bank DownloadMatthew White100% (21)
- Atomic Structure and Periodic Table QuizDocumento16 pagineAtomic Structure and Periodic Table QuizGarvit GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- All India Test Series: FiitjeeDocumento16 pagineAll India Test Series: FiitjeeMP12Nessuna valutazione finora
- 000 - Problems1Documento2 pagine000 - Problems1Ijaz TalibNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Chemistry IIDocumento22 paginePhysical Chemistry IIJamaica FielNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Chemistry 4th Edition Bauer Test BankDocumento42 pagineIntroduction To Chemistry 4th Edition Bauer Test Bankericsimmonspasmcokyge100% (27)
- Quantum Physics Review QuestionsDocumento3 pagineQuantum Physics Review QuestionswondimuNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 12 Physic Question Paper 2020 Set 2Documento7 pagineCBSE Class 12 Physic Question Paper 2020 Set 2Rajendra SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter QuestionsDocumento13 pagineDual Nature of Radiation and Matter QuestionsRohit Karandikar0% (1)
- No Ans Regular Assignment of Atomic Structure XI Chapter 2Documento4 pagineNo Ans Regular Assignment of Atomic Structure XI Chapter 2manojwarlaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of Atom Bounceback 2.0Documento256 pagineStructure of Atom Bounceback 2.0Mamta SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Note 1Documento50 pagineNote 1Anand Muruganantham100% (1)
- Holiday Homework - Atomic Structure: o o o oDocumento8 pagineHoliday Homework - Atomic Structure: o o o oRajshri PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics NTSE Stage-1Documento11 paginePhysics NTSE Stage-1Sonal Gupta79% (19)
- Atomic StructureDocumento22 pagineAtomic StructureYash AkhauriNessuna valutazione finora
- Work Sheet OneDocumento3 pagineWork Sheet Onekaleb asegdewNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy PB Sample PaperDocumento7 paginePhy PB Sample Paperkomalkapri156Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Physics MCQDocumento6 pagineNuclear Physics MCQfreeuser3100% (1)
- CH17 Past Entry QuestionsDocumento2 pagineCH17 Past Entry QuestionsKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 7Documento10 pagineChang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 7haha_le12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry and Chemical Reactivity 9th Edition Kotz Test Bank DownloadDocumento15 pagineChemistry and Chemical Reactivity 9th Edition Kotz Test Bank DownloadTodd Dean100% (23)
- Homework Set3 ParticlenatureofmatterDocumento2 pagineHomework Set3 Particlenatureofmatteryobrosky0% (1)
- Atomic Structure MCQs & Short QuestionsDocumento2 pagineAtomic Structure MCQs & Short QuestionsTajammal AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 12 Chemistry Model ExamsDocumento11 pagineGrade 12 Chemistry Model ExamsErmias100% (1)
- National University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIDocumento11 pagineNational University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIKatto - Darling in the PianoNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQs For Chapter 7-12 KeyDocumento11 pagineMCQs For Chapter 7-12 KeyismahijNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Paper Physics PB I 2023-24Documento6 pagineQuestion Paper Physics PB I 2023-24rishirajkaran2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Canadian 2Nd Edition Silberberg Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 pagineChemistry Canadian 2Nd Edition Silberberg Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdolores.cook959100% (13)
- Wave-Particle Duality and Quantum PhysicsDocumento14 pagineWave-Particle Duality and Quantum PhysicsRodrigo S QuirinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nanyang Technological University Continuous Assessment Exam - I CBC111 – Principles of Modern Chemistry with Laboratory I CM1021 – Basic Inorganic Chemistry with Laboratory IDocumento4 pagineNanyang Technological University Continuous Assessment Exam - I CBC111 – Principles of Modern Chemistry with Laboratory I CM1021 – Basic Inorganic Chemistry with Laboratory IJoey Tay Wei YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit1 Gen Chemistry QnsDocumento16 pagineUnit1 Gen Chemistry QnsAbhishek KushwahNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure & Mole Concept (Question Paper)Documento5 pagineAtomic Structure & Mole Concept (Question Paper)Param shahNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 7 PTDocumento14 pagineCH 7 PTaaron.hartmanNessuna valutazione finora
- 102 Fundamentals of Radiology and ImagingDocumento15 pagine102 Fundamentals of Radiology and ImagingShivani YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- 102 Fundamentals of Radiology and ImagingDocumento14 pagine102 Fundamentals of Radiology and ImagingManisha khan100% (2)
- Vtu Be 1st Year Physics Question PaperDocumento4 pagineVtu Be 1st Year Physics Question PapermidhunmathewNessuna valutazione finora
- DPT-4 Chem & Zoo Neet 03.01.2024Documento8 pagineDPT-4 Chem & Zoo Neet 03.01.2024pinnaacleclasses salemNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Atomic StructureDocumento9 pagine10 Atomic StructurearcNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 42 - Nuclear PhysicsDocumento14 pagineChapter 42 - Nuclear PhysicsVV Cephei100% (3)
- Physics 3204: UNIT 3 - Test - Matter Energy InterfaceDocumento7 paginePhysics 3204: UNIT 3 - Test - Matter Energy InterfaceRaJA ViNoDNessuna valutazione finora
- Review - 2018 - Final ExamDocumento3 pagineReview - 2018 - Final ExamQuang LinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic StructureDocumento16 pagineAtomic StructureKaran100% (3)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyDa EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNessuna valutazione finora
- An Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation: Techniques and ApplicationsDa EverandAn Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation: Techniques and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercising Your Way To Lower Blood Pressure PDFDocumento2 pagineExercising Your Way To Lower Blood Pressure PDFlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Application Note: Microwave Heating Applications Part 3: Switch-Mode Resonant Power Supplies For Microwave GeneratorsDocumento4 pagineApplication Note: Microwave Heating Applications Part 3: Switch-Mode Resonant Power Supplies For Microwave GeneratorslazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Active Magnetic AntennasDocumento53 pagineActive Magnetic AntennaslazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Active Magnetic Antennas PDFDocumento6 pagineActive Magnetic Antennas PDFlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Tehillimsample PDFDocumento50 pagineTehillimsample PDFlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Buddhist ParablesDocumento495 pagineBuddhist ParablesRocío JM100% (1)
- 4005DDS DatasheetDocumento1 pagina4005DDS DatasheetlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Master RegardoDocumento2 pagineMaster RegardoRituraj KaushikNessuna valutazione finora
- RF 5thunit PDFDocumento61 pagineRF 5thunit PDFMani SriNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 Shishido CatalogDocumento24 pagine2016 Shishido CataloglazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Ajtr 1308004Documento8 pagineAjtr 1308004lazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Ξεπέρασε Την Ταχύτητα Του Φωτός Στις ΕπικοινωνίεςDocumento5 pagineΞεπέρασε Την Ταχύτητα Του Φωτός Στις ΕπικοινωνίεςlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 7Documento87 pagineChap 7lazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Pyramid PowerDocumento4 paginePyramid PowerUmeshNessuna valutazione finora
- AV02-4387EN DG Opto 2014-01-031Documento67 pagineAV02-4387EN DG Opto 2014-01-031lazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Application Note: Microwave Heating Applications Part 3: Switch-Mode Resonant Power Supplies For Microwave GeneratorsDocumento4 pagineApplication Note: Microwave Heating Applications Part 3: Switch-Mode Resonant Power Supplies For Microwave GeneratorslazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetismextrastudyquestions PDFDocumento80 pagineElectromagnetismextrastudyquestions PDFlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Some Alot of Circuits With DiscriptionDocumento47 pagineSome Alot of Circuits With DiscriptionlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Spherical Resonant Mass DetectorsDocumento88 pagineSpherical Resonant Mass DetectorslazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Vuk Stefanovic Karadzic: Srpski Rjecnik (1898)Documento935 pagineVuk Stefanovic Karadzic: Srpski Rjecnik (1898)krca100% (2)
- Water GuideDocumento17 pagineWater Guidelazaros100% (1)
- ARTECHE - NT - IVT For Line and Cap Bank Discharge - ENDocumento2 pagineARTECHE - NT - IVT For Line and Cap Bank Discharge - ENlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity From The SkyDocumento12 pagineElectricity From The Skyjester77200196% (27)
- 4915 Final Document PDFDocumento81 pagine4915 Final Document PDFlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- GeneralizedClassicalElectrodynamics PDFDocumento21 pagineGeneralizedClassicalElectrodynamics PDFlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are Scalar Waves - Horst Eckardt - Jan 2012 PDFDocumento9 pagineWhat Are Scalar Waves - Horst Eckardt - Jan 2012 PDFlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Scalar Resonator Manual PDFDocumento4 pagineScalar Resonator Manual PDFlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Nepenthes and Cannabis in Ancient Greece: Luigi ArataDocumento16 pagineNepenthes and Cannabis in Ancient Greece: Luigi AratalazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Insect and Pest Repellent CalendarDocumento40 pagineInsect and Pest Repellent CalendarlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- BatEcholocationResearch PDFDocumento174 pagineBatEcholocationResearch PDFlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Aetherometric Theory of Synchronicity - Encyclopedia NomadicaDocumento2 pagineAetherometric Theory of Synchronicity - Encyclopedia NomadicaMycoLogist4LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Alaska Support Industry Alliance: October 27, 2011 Anchorage, AKDocumento28 pagineAlaska Support Industry Alliance: October 27, 2011 Anchorage, AKVăn Đại - BKHNNessuna valutazione finora
- Giz2012 Trigeneration Igen enDocumento2 pagineGiz2012 Trigeneration Igen entfemilianNessuna valutazione finora
- Marine Current Turbines Generate Clean ElectricityDocumento23 pagineMarine Current Turbines Generate Clean ElectricityHasir Chelat82% (11)
- Properties of Saturated Steam - Pressure in BarDocumento6 pagineProperties of Saturated Steam - Pressure in Barmanpreetsodhi08Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rotational and Vibrational Spectra ExplainedDocumento7 pagineRotational and Vibrational Spectra ExplainedHarshit SuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth's Atmosphere LayersDocumento5 pagineEarth's Atmosphere LayersShawn SriramNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Physics I - Thomaz NotesDocumento42 pagineModern Physics I - Thomaz Notespineapple012Nessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook - Solar Water Heating Basics PDFDocumento111 pagineHandbook - Solar Water Heating Basics PDFmnt6176Nessuna valutazione finora
- 100RESDocumento309 pagine100RESJohn KiriakidisNessuna valutazione finora
- Evans The Atomic Nucleus PDFDocumento2 pagineEvans The Atomic Nucleus PDFKevinNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY491HW9Documento1 paginaPHY491HW9Andres MonroyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson1 WindenergycalcDocumento3 pagineLesson1 WindenergycalcLuis Augusto CarvalhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Synopsis of Solar Assembly Plant.Documento4 pagineSynopsis of Solar Assembly Plant.nazmul05Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet5 (Marine) - 1Documento2 pagineSheet5 (Marine) - 1AhmedTahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of AtomDocumento31 pagineStructure of Atomthinkiit100% (1)
- Atomic Structure and IsotopesDocumento24 pagineAtomic Structure and IsotopesRamon GasgasNessuna valutazione finora
- NUTRITIONAL STATUS TEMPLATE K VI EndlineDocumento87 pagineNUTRITIONAL STATUS TEMPLATE K VI Endlineサシンゴ ラアーニ83% (6)
- Design and Fabrication of Alternate Energy Storage Device Using PMCsDocumento40 pagineDesign and Fabrication of Alternate Energy Storage Device Using PMCsMujassamNazarKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Jabbaru Company ProfileDocumento19 pagineJabbaru Company ProfileSuryaTek100% (2)
- Solids Liquids and GasesDocumento25 pagineSolids Liquids and GasesJane Seymour100% (1)
- Eoy Final Exam Study GuideDocumento14 pagineEoy Final Exam Study Guideapi-324757649Nessuna valutazione finora
- Oil FlamDocumento8 pagineOil FlamDe DragobeteNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Energy Auditing For Electrical Appliances of A Residential HomeDocumento9 pagineSample Energy Auditing For Electrical Appliances of A Residential Homedarshak444Nessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocumento7 pagineNew Microsoft Word DocumentnirajmechgecNessuna valutazione finora
- Parametrization of The Woods-Saxon Potential For Shell-Model CalculationsDocumento19 pagineParametrization of The Woods-Saxon Potential For Shell-Model CalculationsGuillermo AlzagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Turbine Power PlantDocumento14 pagineGas Turbine Power PlantPradeep GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- An Assessment of The Renewable Energy Potential Using A Clustering Based Data Mining Method. Case Study in RomaniaDocumento14 pagineAn Assessment of The Renewable Energy Potential Using A Clustering Based Data Mining Method. Case Study in RomaniaMohamad MuhtaromiNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Clearances, Approvals Required For Power Projects in IndiaDocumento3 pagineList of Clearances, Approvals Required For Power Projects in Indiapandetarun100% (1)
- Dimensional FormulaDocumento4 pagineDimensional FormulaSurajguptarocksNessuna valutazione finora