Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Presentacion Oracle SQL
Caricato da
Danny PáezDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Presentacion Oracle SQL
Caricato da
Danny PáezCopyright:
Formati disponibili
2/5/2013
Objectives
Aftercompletingthislesson,youshouldbeableto
dothefollowing:
RetrievingDataUsing
theSQLSELECT Statement
LessonAgenda
BasicSELECT statement
ArithmeticexpressionsandNULL valuesintheSELECT
statement
Columnaliases
Useofconcatenationoperator,literalcharacterstrings,
alternativequoteoperator,andtheDISTINCT keyword
DESCRIBE command
d
ListthecapabilitiesofSQLSELECT statements
ExecuteabasicSELECT statement
CapabilitiesofSQLSELECT
Statements
Projection
Selection
Table1
Table1
Join
Table1
BasicSELECT Statement
SELECT *|{[DISTINCT] column|expression [alias],...}
FROM
table;
Table2
SelectingAllColumns
SELECT *
FROM
departments;
SELECT identifiesthecolumnstobedisplayed.
FROM identifiesthetablecontainingthosecolumns.
2/5/2013
SelectingSpecificColumns
SELECT department_id, location_id
FROM
departments;
WritingSQLStatements
SQLstatementsarenotcasesensitive.
SQLstatementscanbeenteredononeormorelines.
Keywordscannotbeabbreviatedorsplitacrosslines.
Clausesareusuallyplacedonseparatelines.
Indentsareusedtoenhancereadability.
In SQL Developer SQL statements can optionally be
InSQLDeveloper,SQLstatementscanoptionallybe
terminatedbyasemicolon(;).Semicolonsarerequired
whenyouexecutemultipleSQLstatements.
InSQL*Plus,youarerequiredtoendeachSQL
statementwithasemicolon(;).
ColumnHeadingDefaults
SQLDeveloper:
Defaultheadingalignment:Leftaligned
Defaultheadingdisplay:Uppercase
SQL*Plus:
CharacterandDatecolumnheadingsareleftaligned.
Numbercolumnheadingsareright
Number column headings are rightaligned
aligned.
Defaultheadingdisplay:Uppercase
ArithmeticExpressions
Createexpressionswithnumberanddatedatabyusing
arithmeticoperators.
Operator
BasicSELECT statement
ArithmeticexpressionsandNULL valuesintheSELECT
statement
ColumnAliases
Useofconcatenationoperator,literalcharacterstrings,
alternativequoteoperator,andtheDISTINCT keyword
DESCRIBE command
d
UsingArithmeticOperators
SELECT last_name, salary, salary + 300
FROM
employees;
Description
Add
Subtract
LessonAgenda
Multiply
/
Divide
2/5/2013
OperatorPrecedence
SELECT last_name, salary, 12*salary+100
FROM
employees;
DefiningaNullValue
1
Nullisavaluethatisunavailable,unassigned,unknown,
orinapplicable.
Nullisnotthesameaszeroorablankspace.
SELECT last_name, job_id, salary, commission_pct
FROM
O
e
employees;
p oyees;
SELECT last_name, salary, 12*(salary+100)
FROM
employees;
LessonAgenda
NullValuesinArithmeticExpressions
Arithmeticexpressionscontaininganullvalueevaluatetonull.
SELECT last_name, 12*salary*commission_pct
FROM
employees;
BasicSELECT statement
ArithmeticexpressionsandNULL valuesintheSELECT
statement
Columnaliases
Useofconcatenationoperator,literalcharacterstrings,
alternativequoteoperator,andtheDISTINCT keyword
DESCRIBE command
d
DefiningaColumnAlias
UsingColumnAliases
Acolumnalias:
Renamesacolumnheading
Isusefulwithcalculations
Immediatelyfollowsthecolumnname(Therecanalsobethe
optionalAS keywordbetweenthecolumnnameandalias.)
Requiresdoublequotationmarksifitcontainsspacesor
specialcharacters,orifitiscasesensitive
l h
f
SELECT last_name AS name, commission_pct comm
FROM
employees;
SELECT last_name "Name" , salary*12 "Annual Salary"
FROM
employees;
2/5/2013
LessonAgenda
BasicSELECT Statement
ArithmeticExpressionsandNULLvaluesinSELECT
statement
ColumnAliases
Useofconcatenationoperator,literalcharacterstrings,
alternativequoteoperator,andtheDISTINCT keyword
DESCRIBE command
d
ConcatenationOperator
Aconcatenationoperator:
Linkscolumnsorcharacterstringstoothercolumns
Isrepresentedbytwoverticalbars(||)
Createsaresultantcolumnthatisacharacterexpression
SELECT
FROM
last name||job id AS "Employees"
last_name||job_id
Employees
employees;
LiteralCharacterStrings
Aliteralisacharacter,anumber,oradatethatisincludedin
theSELECT statement.
Dateandcharacterliteralvaluesmustbeenclosedwithin
singlequotationmarks.
Eachcharacterstringisoutputonceforeachrowreturned.
UsingLiteralCharacterStrings
SELECT last_name ||' is a '||job_id
AS "Employee Details"
FROM
employees;
AlternativeQuote(q)Operator
Specifyyourownquotationmarkdelimiter.
Selectanydelimiter.
Increasereadabilityandusability.
SELECT department_name || ' Department' ||
q'['s Manager Id: ]'
|| manager_id
AS "Department and Manager"
FROM departments;
DuplicateRows
Thedefaultdisplayofqueriesisallrows,includingduplicate
rows.
SELECT department_id
FROM
employees;
SELECT DISTINCT department_id
FROM
employees;
2/5/2013
LessonAgenda
BasicSELECT statement
ArithmeticexpressionsandNULL valuesintheSELECT
statement
Columnaliases
Useofconcatenationoperator,literalcharacterstrings,
alternativequoteoperator,andtheDISTINCT keyword
DESCRIBE command
d
UsingtheDESCRIBE Command
DisplayingtheTableStructure
UsetheDESCRIBE commandtodisplaythestructure
ofatable.
Or,selectthetableintheConnectionstreeandusethe
Columnstabtoviewthetablestructure.
DESC[RIBE] tablename
Summary
Inthislesson,youshouldhavelearnedhowto:
DESCRIBE employees
WriteaSELECT statementthat:
Returnsallrowsandcolumnsfromatable
Returnsspecifiedcolumnsfromatable
Usescolumnaliasestodisplaymoredescriptivecolumn
headings
SELECT *|{[DISTINCT] column|expression [alias],...}
FROM table;
Practice1:Overview
Thispracticecoversthefollowingtopics:
Selectingalldatafromdifferenttables
Describingthestructureoftables
Performingarithmeticcalculationsandspecifying
columnnames
2/5/2013
RestrictingandSortingData
2/5/2013
Objectives
Aftercompletingthislesson,youshouldbeableto
dothefollowing:
Limittherowsthatareretrievedbyaquery
Sorttherowsthatareretrievedbyaquery
Useampersandsubstitutiontorestrictandsortoutput
at run time
atruntime
LimitingRowsUsingaSelection
EMPLOYEES
LessonAgenda
Limitingrowswith:
The WHERE clause
Thecomparisonconditionsusing=,<=,BETWEEN,IN,
LIKE,andNULL conditions
LogicalconditionsusingAND,OR,andNOT operators
Rulesofprecedenceforoperatorsinanexpression
p
p
p
SortingrowsusingtheORDER BY clause
Substitutionvariables
DEFINE andVERIFY commands
LimitingtheRowsthatAreSelected
RestricttherowsthatarereturnedbyusingtheWHERE
clause:
SELECT*|{[DISTINCT]column|expression [alias],...}
FROMtable
[WHEREcondition(s)];
TheWHERE
The WHERE clausefollowstheFROM
clause follows the FROM clause.
clause
retrieve all
employees in
department 90
UsingtheWHERE Clause
SELECTemployee_id,last_name,job_id,department_id
FROMemployees
WHEREdepartment_id=90;
CharacterStringsandDates
Characterstringsanddatevaluesareenclosedwith
singlequotationmarks.
Charactervaluesarecasesensitiveanddatevaluesare
formatsensitive.
ThedefaultdatedisplayformatisDD-MON-RR.
SELECTlast_name,job_id,department_id
FROMemployees
WHERElast_name='Whalen';
SELECTlast_name
FROMemployees
WHEREhire_date='17FEB96';
2/5/2013
ComparisonOperators
Operator
Meaning
Equal to
>
Greater than
>=
SELECTlast_name,salary
FROMemployees
WHEREsalary<=3000;
Greater than or equal to
<
Less than
<=
Less than or equal to
<>
Not equal to
BETWEEN
...AND...
Between two values (inclusive)
IN(set)
Match any of a list of values
LIKE
Match a character pattern
ISNULL
Is a null value
RangeConditionsUsingtheBETWEEN
Operator
UsetheBETWEEN operatortodisplayrowsbasedonarangeof
values:
Lower limit
UsetheIN operatortotestforvaluesinalist:
Upper limit
PatternMatchingUsingtheLIKE
Operator
UsetheLIKE operatortoperformwildcard
searchesofvalidsearchstringvalues.
Searchconditionscancontaineitherliteral
charactersornumbers:
% denoteszeroormanycharacters.
_ denotes
denotesonecharacter.
one character.
first_name
employees
first_nameLIKE'S%';
MembershipConditionUsingtheIN
Operator
SELECTemployee_id,last_name,salary,manager_id
FROMemployees
WHEREmanager_idIN(100,101,201);
SELECTlast_name,salary
FROMemployees
WHEREsalaryBETWEEN2500AND3500;
SELECT
FROM
WHERE
UsingComparisonOperators
CombiningWildcardCharacters
Youcancombinethetwowildcardcharacters(%,_)
withliteralcharactersforpatternmatching:
SELECTlast_name
FROMemployees
WHERElast_nameLIKE'_o%';
YoucanusetheESCAPE identifiertosearchforthe
actual% and_ symbols.
2/5/2013
UsingtheNULL Conditions
DefiningConditionsUsingtheLogical
Operators
TestfornullswiththeIS NULL operator.
Operator
SELECTlast_name,manager_id
FROMemployees
WHEREmanager_idISNULL;
Returns TRUE if both component conditions
are true
OR
Returns TRUE if either component condition
is true
NOT
UsingtheAND Operator
AND requiresboththecomponentconditionstobetrue:
SELECTemployee_id,last_name,job_id,salary
FROMemployees
WHEREsalary>=10000
ANDjob_idLIKE'%MAN%';
Meaning
AND
Returns TRUE if the condition is false
UsingtheOR Operator
OR requireseithercomponentconditiontobetrue:
SELECTemployee_id,last_name,job_id,salary
FROMemployees
WHEREsalary>=10000
ORjob_idLIKE'%MAN%';
UsingtheNOT Operator
LessonAgenda
Limitingrowswith:
TheWHERE clause
Thecomparisonconditionsusing=,<=,BETWEEN,IN,
LIKE,andNULL operators
LogicalconditionsusingAND,OR,andNOT operators
SELECTlast_name,job_id
FROMemployees
WHEREjob_id
NOTIN('IT_PROG','ST_CLERK','SA_REP');
Rulesofprecedenceforoperatorsinanexpression
p
p
p
SortingrowsusingtheORDER BY clause
Substitutionvariables
DEFINE andVERIFY commands
2/5/2013
RulesofPrecedence
Operator
RulesofPrecedence
SELECTlast_name,job_id,salary
FROMemployees
WHEREjob_id='SA_REP'
ORjob_id='AD_PRES'
ANDsalary>15000;
Meaning
Arithmetic operators
Concatenation operator
Comparison conditions
IS [NOT] NULL,
NULL LIKE,
LIKE [NOT] IN
[NOT] BETWEEN
Not equal to
NOT logical condition
AND logical condition
OR logical condition
SELECTlast_name,job_id,salary
FROMemployees
WHERE(job_id='SA_REP'
ORjob_id='AD_PRES')
ANDsalary>15000;
You can use parentheses to override rules of precedence.
UsingtheORDER BY Clause
LessonAgenda
Limitingrowswith:
SortretrievedrowswiththeORDER BY clause:
TheWHERE clause
Thecomparisonconditionsusing=,<=,BETWEEN,IN,
LIKE,andNULL operators
LogicalconditionsusingAND,OR,andNOT operators
Rulesofprecedenceforoperatorsinanexpression
p
p
p
SortingrowsusingtheORDER BY clause
Substitutionvariables
DEFINE andVERIFY commands
ASC:Ascendingorder,default
DESC:Descendingorder
TheORDER BY clausecomeslastintheSELECT statement:
SELECTlast_name,job_id,department_id,hire_date
FROMemployees
ORDERBYhire_date;
Sorting
Sorting
Sortingbyusingthecolumnsnumericposition:
Sortingindescendingorder:
SELECTlast_name,job_id,department_id,hire_date
FROMemployees
ORDERBYhire_dateDESC;
SELECTlast_name,job_id,department_id,hire_date
FROMemployees
ORDERBY3;
Sortingbymultiplecolumns:
SELECTemployee_id,last_name,salary*12annsal
Sortingbycolumnalias:
FROMemployees
ORDERBYannsal;
SELECTlast_name,department_id,salary
FROMemployees
ORDERBYdepartment_id,salaryDESC;
10
2/5/2013
LessonAgenda
SubstitutionVariables
Limitingrowswith:
TheWHERE clause
Thecomparisonconditionsusing=,<=,BETWEEN,IN,
LIKE,andNULL operators
LogicalconditionsusingAND,OR,andNOT operators
Rulesofprecedenceforoperatorsinanexpression
p
p
p
SortingrowsusingtheORDER BY clause
Substitutionvariables
DEFINE andVERIFY commands
SubstitutionVariables
Usesubstitutionvariablesto:
Temporarilystorevalueswithsingleampersand(&)anddouble
ampersand(&&)substitution
Usesubstitutionvariablestosupplementthefollowing:
WHERE conditions
ORDER BY clauses
Columnexpressions
Tablenames
EntireSELECT statements
UsingtheSingleAmpersand
SubstitutionVariable
... salary = ?
department_id = ?
... last_name = ? ...
I want
to query
different
values.
UsingtheSingleAmpersand
SubstitutionVariable
Useavariableprefixedwithanampersand(&)topromptthe
userforavalue:
SELECTemployee_id,last_name,salary,department_id
FROMemployees
WHEREemployee_id=&employee_num;
CharacterandDateValueswith
SubstitutionVariables
Usesinglequotationmarksfordateandcharactervalues:
SELECTlast_name,department_id,salary*12
FROMemployees
WHEREjob_id='&job_title';
11
2/5/2013
SpecifyingColumnNames,
Expressions,andText
SELECTemployee_id,last_name,job_id,&column_name
FROMemployees
WHERE&condition
ORDERBY&order_column;
UsingtheDoubleAmpersand
SubstitutionVariable
Usedoubleampersand(&&)ifyouwanttoreusethevariable
valuewithoutpromptingtheusereachtime:
SELECTemployee_id,last_name,job_id,&&column_name
FROMemployees
ORDERBY&column_name;
LessonAgenda
Limitingrowswith:
TheWHERE clause
Thecomparisonconditionsusing=,<=,BETWEEN,IN,
LIKE,andNULL operators
LogicalconditionsusingAND,OR,andNOT operators
Rulesofprecedenceforoperatorsinanexpression
p
p
p
SortingrowsusingtheORDER BY clause
Substitutionvariables
DEFINE andVERIFY commands
UsingtheDEFINE Command
UsetheDEFINE commandtocreateandassignavalue
toavariable.
UsetheUNDEFINE commandtoremoveavariable.
DEFINEemployee_num=200
SELECTemployee_id,last_name,salary,department_id
FROMemployees
WHEREemployee_id=&employee_num;
UNDEFINEemployee_num
UsingtheVERIFY Command
UsetheVERIFY commandtotogglethedisplayofthe
substitutionvariable,bothbeforeandafterSQL
Developerreplacessubstitutionvariableswithvalues:
SETVERIFYON
SELECTemployee_id,last_name,salary
FROM
FROMemployees
employees
WHEREemployee_id=&employee_num;
Summary
Inthislesson,youshouldhavelearnedhowto:
UsetheWHERE clausetorestrictrowsofoutput:
Usethecomparisonconditions
UsetheBETWEEN,IN,LIKE,andNULL operators
ApplythelogicalAND,OR,andNOT operators
UsetheORDER BY clausetosortrowsofoutput:
p
SELECT*|{[DISTINCT]column|expression [alias],...}
FROMtable
[WHEREcondition(s)]
[ORDERBY{column,expr,alias}[ASC|DESC]];
Useampersandsubstitutiontorestrictandsortoutput
at
runtime
12
2/5/2013
Practice2:Overview
Thispracticecoversthefollowingtopics:
Selectingdataandchangingtheorderoftherows
thataredisplayed
RestrictingrowsbyusingtheWHERE clause
SortingrowsbyusingtheORDER BY clause
Usingsubstitutionvariablestoaddflexibilitytoyour
Using substitution variables to add flexibility to your
SQLSELECT statements
13
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 1 Retrieving Data Using The SQL SELECT StatementDocumento16 pagine1 Retrieving Data Using The SQL SELECT StatementsjNessuna valutazione finora
- Retrieving Data PDFDocumento23 pagineRetrieving Data PDFYudiNessuna valutazione finora
- Retrieving Data Using The SQL SELECT StatementDocumento29 pagineRetrieving Data Using The SQL SELECT StatementWilson LimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Writing SELECT Queries: Module OverviewDocumento22 pagineWriting SELECT Queries: Module OverviewBobe DanutNessuna valutazione finora
- SQL I - 1x02 FRANZ 17Documento15 pagineSQL I - 1x02 FRANZ 17Freddy Andres NavarreteNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment #3: Retrieving Data Using The SQL SELECT StatementDocumento4 pagineExperiment #3: Retrieving Data Using The SQL SELECT StatementFeras TheReaperNessuna valutazione finora
- Database Systems Lecture2Documento20 pagineDatabase Systems Lecture2Humam Al-DhubhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Schedule: Timing Topic: 40 Minutes 25 Minutes Practice 65 Minutes TotalDocumento41 pagineSchedule: Timing Topic: 40 Minutes 25 Minutes Practice 65 Minutes TotalDaniiel ObandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced DBMS Course - ModuleDocumento42 pagineAdvanced DBMS Course - ModuleAli Sheikh AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Les 01Documento22 pagineLes 01Daniel Alejandro RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle - The Basic SelectDocumento28 pagineOracle - The Basic SelectVikas JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 - Retrieve Data Using The SQL SELECT StatementDocumento15 pagineUnit 2 - Retrieve Data Using The SQL SELECT StatementIulian NeagaNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Office Power Point PresentationDocumento59 pagineNew Microsoft Office Power Point PresentationalogargNessuna valutazione finora
- BDI LProyeccionDocumento21 pagineBDI LProyeccionjose garciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lession 01Documento24 pagineLession 01chandumistryNessuna valutazione finora
- Unitiii DBMSDocumento62 pagineUnitiii DBMSAnonymous DFpzhrRNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4Documento12 pagineUnit 4Satvick VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Retrieval Using Basic SELECT Statement: Module of InstructionDocumento15 pagineData Retrieval Using Basic SELECT Statement: Module of InstructionAlexander IbarretaNessuna valutazione finora
- SQL ProgrammingDocumento57 pagineSQL ProgrammingMrinaal MalhotraNessuna valutazione finora
- Dbms FileDocumento25 pagineDbms FileKanika JawlaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019-Cpe-27 DBMS Lab Manual 10Documento5 pagine2019-Cpe-27 DBMS Lab Manual 10Haalim MNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle TutorialsDocumento301 pagineOracle TutorialsPagdi SriniNessuna valutazione finora
- Expert Level SQLDocumento10 pagineExpert Level SQLHeet GandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- DBMS Lab ManualDocumento199 pagineDBMS Lab ManualMoulika Chowdary100% (1)
- Basic SELECT Statement: SELECT Identifies What Columns FROM Identifies Which TableDocumento21 pagineBasic SELECT Statement: SELECT Identifies What Columns FROM Identifies Which TableaaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rdbms Assignment 3Documento11 pagineRdbms Assignment 3DEEKSHITH RNessuna valutazione finora
- SQL Faq: What Is SQL and Where Does It Come From?Documento27 pagineSQL Faq: What Is SQL and Where Does It Come From?mohdsajjad25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To SQL: P212 Information ManagementDocumento30 pagineIntroduction To SQL: P212 Information Managementjohn kenneth cachero100% (1)
- OracleDocumento163 pagineOraclemousumiinderNessuna valutazione finora
- DBMS NotesDocumento31 pagineDBMS Notesjhalodwalaaliasgar53Nessuna valutazione finora
- Les01 PsDocumento56 pagineLes01 PsShinichi QuáchNessuna valutazione finora
- SQL Lab Manual Guide MaterialsDocumento15 pagineSQL Lab Manual Guide MaterialsBirhanu WorkuNessuna valutazione finora
- SQL 2Documento26 pagineSQL 2ይህየይስ ተአምኖNessuna valutazione finora
- Creating A User: System Privileges User PrivilegesDocumento33 pagineCreating A User: System Privileges User PrivilegesskdnfNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit II: Relational Data Model and Relational Database ConstraintsDocumento109 pagineUnit II: Relational Data Model and Relational Database ConstraintsShivakumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Hi Sir I Didn't Received Any T.interview Call From Your Side AboutDocumento18 pagineHi Sir I Didn't Received Any T.interview Call From Your Side AboutmkumarsejNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 5 - DDL QueriesDocumento12 pagineLab 5 - DDL QueriesJohn Philip DialaNessuna valutazione finora
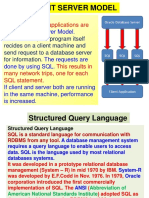
- Client Server Model: Many Databases Applications Are Built inDocumento52 pagineClient Server Model: Many Databases Applications Are Built inShriNessuna valutazione finora
- SQL Server NotesDocumento75 pagineSQL Server NotesShashiBTITNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle 10g - SQL (Fast N Final)Documento73 pagineOracle 10g - SQL (Fast N Final)manaenglishNessuna valutazione finora
- SQLDocumento62 pagineSQLsyamNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To SQLDocumento43 pagineIntroduction To SQLMichael AdegunwaNessuna valutazione finora
- SQLGDocumento6 pagineSQLGspeedmail71Nessuna valutazione finora
- Backup of DB2Documento1.297 pagineBackup of DB2Kamakshigari SureshNessuna valutazione finora
- SQL Server 2000 FaqsDocumento62 pagineSQL Server 2000 FaqsRamesh PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- SQL: Data Manipulation: Aisha BatoolDocumento54 pagineSQL: Data Manipulation: Aisha BatoolSaman PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Science Class 12 CBSE - Structure Query LanguageDocumento41 pagineComputer Science Class 12 CBSE - Structure Query LanguageSandeep YippieNessuna valutazione finora
- (M10-MAIN) - Other Schema ObjectsDocumento59 pagine(M10-MAIN) - Other Schema ObjectsMAEGAN THERESE GABRIANANessuna valutazione finora
- Database Development, Management & Administration: Course Lecturer: Denis Ssebuggwawo, Phd. Course Tutor: Ms L. TamaleDocumento31 pagineDatabase Development, Management & Administration: Course Lecturer: Denis Ssebuggwawo, Phd. Course Tutor: Ms L. TamaleDenisho DeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.SQL Queries DMLDocumento47 pagine4.SQL Queries DMLAnkit RajputNessuna valutazione finora
- Db2 Interview Questions - AdvertisementDocumento15 pagineDb2 Interview Questions - AdvertisementZakki Zain KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IV SQLDocumento156 pagineUnit IV SQLKhushi JainNessuna valutazione finora
- My-Sql: Learning ObjectivesDocumento22 pagineMy-Sql: Learning ObjectivesHarshit PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle9i Introduction To 9i SQL HandbookDocumento21 pagineOracle9i Introduction To 9i SQL Handbookemailtorakesh100% (2)
- DataBase Information Retriaval Syatem (DBIR)Documento52 pagineDataBase Information Retriaval Syatem (DBIR)Amit Chougule100% (1)
- Retrieving Data Using The SQL SELECT StatementDocumento22 pagineRetrieving Data Using The SQL SELECT StatementKim NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- SQL NotesDocumento40 pagineSQL Notessumanth vNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Visual Basic 6 (Database Programming SQL)Documento5 pagineMicrosoft Visual Basic 6 (Database Programming SQL)Abdul Majeed Khan100% (1)
- 2 Structured Query LanguageDocumento34 pagine2 Structured Query LanguageAli KhaidhirNessuna valutazione finora
- Deep LearningDocumento327 pagineDeep LearningThomazBarros100% (9)
- Social Science Computer ReviewDocumento18 pagineSocial Science Computer ReviewDanny PáezNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergence - From Chaos To Order - JHolland ReviewDocumento5 pagineEmergence - From Chaos To Order - JHolland ReviewMariana LourencoNessuna valutazione finora
- Facial Expression Recognition: A Brief Tutorial Overview: Claude C. Chibelushi, Fabrice BourelDocumento5 pagineFacial Expression Recognition: A Brief Tutorial Overview: Claude C. Chibelushi, Fabrice BourelDanny PáezNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 1 1 89 7369Documento8 pagine10 1 1 89 7369Danny PáezNessuna valutazione finora
- Specularity As A Mode of Knowledge and Agency in Richard Wright's Work.Documento20 pagineSpecularity As A Mode of Knowledge and Agency in Richard Wright's Work.Abdul JanmohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Obe Course Syllabus: Shariff Kabunsuan College, IncDocumento8 pagineObe Course Syllabus: Shariff Kabunsuan College, IncSai GuyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Making An Appointment and ReservationDocumento6 pagineMaking An Appointment and Reservationtuvan yega100% (2)
- Semi-Detailed LP in Language 5Documento7 pagineSemi-Detailed LP in Language 5Janella Marie BagtasNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 Text As A Connected DiscourseDocumento13 pagineLesson 1 Text As A Connected DiscourseAly SwiftNessuna valutazione finora
- Soal TKM B. Inggris Kls XI Des. 2013Documento8 pagineSoal TKM B. Inggris Kls XI Des. 2013Ahmad Rifa'i100% (1)
- Unit 1 Test: Why We Like To Gather Together: Groups and Human DevelopmentDocumento4 pagineUnit 1 Test: Why We Like To Gather Together: Groups and Human DevelopmentTrần Mỹ ThiNessuna valutazione finora
- libATA Developer's Guide PDFDocumento196 paginelibATA Developer's Guide PDFclu5t3rNessuna valutazione finora
- 3dof ModelDocumento14 pagine3dof ModelJennifer GonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- A Short History of The Mughal Empire - Fisher, H, Michael FisherDocumento1.026 pagineA Short History of The Mughal Empire - Fisher, H, Michael FisherNeha GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocumento2 pagineDetailed Lesson PlanJohnmel TrillesNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheat Sheet Final FinalDocumento2 pagineCheat Sheet Final FinalayoubNessuna valutazione finora
- Brahmayajnam: 1. Achamanam 2. Vighneswara Dhyanam 3. Pranayamam 4. SankalpamDocumento5 pagineBrahmayajnam: 1. Achamanam 2. Vighneswara Dhyanam 3. Pranayamam 4. SankalpamsudarshaniyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Edward Feser (@FeserEdward) TwitterDocumento1 paginaEdward Feser (@FeserEdward) TwittermatthewmayuiersNessuna valutazione finora
- Ex 145Documento3 pagineEx 145Quoc NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Questioned DocumentDocumento66 pagineQuestioned DocumentKienth Vincent LopeñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformation Assignment 5 Psyu 306 Summary Project Instructions and WorksheetDocumento4 pagineTransformation Assignment 5 Psyu 306 Summary Project Instructions and Worksheetapi-490946499Nessuna valutazione finora
- Filipino, The Language That Is Not OneDocumento7 pagineFilipino, The Language That Is Not OneRyan Christian BalanquitNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily-Lesson-Log GRADE-9 MAPEHDocumento7 pagineDaily-Lesson-Log GRADE-9 MAPEHMARY GRACE GAMBANessuna valutazione finora
- FasciDocumento11 pagineFasciLiza Dahan Andea-SaayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Shivansh Bhat - 19116071: Experiment-2Documento20 pagineShivansh Bhat - 19116071: Experiment-2Parth SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Binary-Decimal-HexaDecimal Conversion WorksheetDocumento3 pagineBinary-Decimal-HexaDecimal Conversion WorksheetSyed Umair AnwerNessuna valutazione finora
- Virtual KeyboardDocumento12 pagineVirtual KeyboardPriyatam Annam100% (2)
- 21st Century Lit Q2Documento5 pagine21st Century Lit Q2lyra colladoNessuna valutazione finora
- Absence REST UserDocumentationDocumento9 pagineAbsence REST UserDocumentationYonny Isidro RendonNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank: Class: Tycm Chapter No. 01 Introduction To AWTDocumento9 pagineQuestion Bank: Class: Tycm Chapter No. 01 Introduction To AWT332 Prathamesh SonawaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Using A Public CA Can Lead To A Man-In-The-Middle Attack TrueDocumento8 pagineUsing A Public CA Can Lead To A Man-In-The-Middle Attack TrueViviana LemusNessuna valutazione finora
- Magic Box LessonDocumento4 pagineMagic Box LessonJoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Emma Jane AustenDocumento4 pagineEmma Jane Austen4vrwqrtrd2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Loss-In-weight Feeder - Intecont TersusDocumento220 pagineLoss-In-weight Feeder - Intecont TersusneelakanteswarbNessuna valutazione finora