Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Hydralazine Drug Study
Caricato da
milkvCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Hydralazine Drug Study
Caricato da
milkvCopyright:
Formati disponibili
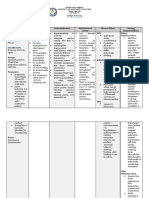
Name of Patient
F. S.
Age
35 y.o
Height
53
Diagnosis
G3P3 (3003) PU del. ceph. term live birth by 1oLSTCS +
BTL w/ variable deaceration; severe preeclampsia
M. M. Olmillo
Sex
Female
Weight
60 kg
Website
milkv.co.vu
A/N
youre welcome J
Author
DRUG DATA
Generic Name:
Hydralazine Hcl
CLASSIFICATION
Pharmacologic:
Peripheral
vasodilator
Trade name/s:
Apresoline
Patients dose:
50mg q15mins. x
2 doses for BP
MECHANISM OF
ACTION
Acts directly on
vascular smooth
muscle to cause
vasodilation, primarily
arteriolar, decreasing
peripheral resistance;
maintains or increases
renal and cerebral
blood flow
Therapeutic:
Antihypertensive
140/100
Maximum dose:
800mg repeated
as necessary
Pregnancy Category
Risk: C
Onset:
Rapid
Peak:
10-20mins
Minimum dose:
5-10mg
Duration:
2-4 hrs
Available forms:
Tablets 10, 25,
50, 100mg;
injection
20mg/mL
Metabolism:
Hepatic, 3-7 hr
Route: IVTT
Excretion: urine
Source: 2011
Lippincotts NDG
Distribution: crosses
placenta, may enter
breast milk
Source: 2011
Lippincotts NDG
Source: 2011
Lippincotts NDG
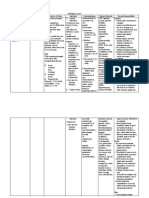
INDICATIONS
General:
> oral: essential
hypertension
alone or in
combination with
other drugs
> parenteral:
severe essential
hypertension
when drug cannot
be given orally or
when need to
lower BP is urgent
>unlabeled uses:
reducing afterload
in the treatment of
heart failure,
severe aortic
insufficiency, and
after valve
replacement
(doses up to
800mg TID)
Patients actual
indication:
Pregnancyinduced
hypertension
Source: 2011
Lippincotts NDG
CONTRAINDICATI
ON
Contraindicated with
hypersensitivity to
hydralazine, tartrazine;
CAD, mitral valvular
rheumatic heart disease
(implicated in MI)
Precaution:
Use cautiously with
CVAs, increased ICP,
severe hypertension with
uremia, advanced renal
damage, lactation,
pregnancy, pulmonary
hypertension
ADVERSE
EFFECTS
CNS: headace,
peripheral neuritis,
dizziness
CV: palpitations,
tachycardia,
angina pectoris
NURSING
RESPONSIBILITIE
S
Before:
> check doctors order
> wash hands before administering
the drug
> take the clients BP
> check the patency of the IV line
> educate the client about the
purpose and importance of the drug
GI: anorexia,
nausea, vomiting,
diarrhea
GU: difficult
micturation,
impotence
Hematologic: blood
dyscrasias
Hypersensitivity:
rash, urticaria,
pruritus
Interactions:
> drug-drug: increased
pharmacologic effect of
beta-adrenergic blockers
> drug-food: increased
bioavailability of oral
hydralazine given with
food
Other: nasal
congestion,
flushing, edema,
muscle cramps
Source: 2011
Lippincotts NDG
Source: 2011
Lippincotts NDG
During:
> Give drug exactly as prescribed
> Take with food
> discontinue if blood dyscrasias
> withdraw drug gradually and not at
once
> repeat the purpose of the drug
After:
> Monitor client for orthostatic
hypertension
> reevaluate therapy if patient
develops arthralgia, fever, chest pain,
or continued malaise.
> report persistent or severe
constipation
> report unexplained fever or
malaise, muscle or joint aching, rash,
numbness, tingling
> document and record.
Source: 2011 Lippincotts Nursing
Drug Guide
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 4.1 Genetic Counselling 222Documento12 pagine4.1 Genetic Counselling 222Sahar JoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento15 pagineDrug StudyCheyee MaeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Concise 48 Laws of Power PDFDocumento203 pagineThe Concise 48 Laws of Power PDFkaran kamath100% (1)
- Drug Study On CARBOPROSTDocumento4 pagineDrug Study On CARBOPROSTshadow gonzalez100% (1)
- Generic Name (Brand Name) Methergine (Methylergonovine Maleate)Documento3 pagineGeneric Name (Brand Name) Methergine (Methylergonovine Maleate)jennix_030883% (6)
- SAP Workflow Scenario: Maintenance Notification ApprovalDocumento6 pagineSAP Workflow Scenario: Maintenance Notification ApprovalPiyush BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- HNBBDocumento2 pagineHNBBSheen Ivashkov-Belikov100% (1)
- Magnesium SulfateDocumento1 paginaMagnesium SulfateIvanne Hisoler67% (3)
- Unit 5 - Simulation of HVDC SystemDocumento24 pagineUnit 5 - Simulation of HVDC Systemkarthik60% (10)
- Seventh Day Adventist Quiz by KnowingTheTimeDocumento4 pagineSeventh Day Adventist Quiz by KnowingTheTimeMiiiTheart100% (3)
- Drug Study - Ascorbic AcidDocumento6 pagineDrug Study - Ascorbic Acidalyssa marie salcedo100% (1)
- Drug Study (Oxytocin & HNBB)Documento6 pagineDrug Study (Oxytocin & HNBB)NE TdrNessuna valutazione finora
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineCefuroxime Drug Studymilkv93% (15)
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineCefuroxime Drug Studymilkv93% (15)
- Methyldopa Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaMethyldopa Drug Studychinchin ramosNessuna valutazione finora
- IsoxsuprineDocumento1 paginaIsoxsuprineAndrean EnriquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Evening PrimroseDocumento1 paginaEvening PrimroseMeranie Tiglao AlfonsoNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Drug StudyDocumento6 pagineDR Drug Studyslashmortred100% (5)
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaTramadol Drug Studymilkv82% (11)
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaTramadol Drug Studymilkv82% (11)
- Clozapine Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineClozapine Drug Studymilkv100% (8)
- OB Drug Study - MethylergonovineDocumento2 pagineOB Drug Study - MethylergonovineJustin Ancog0% (1)
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineMetoprolol Drug Studymilkv100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY - Calcium GluconateDocumento2 pagineDRUG STUDY - Calcium GluconateSiergs Smith Gervacio100% (2)
- Ceftriaxone Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaCeftriaxone Drug Studymilkv71% (7)
- Ceftriaxone Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaCeftriaxone Drug Studymilkv71% (7)
- Methyldopa Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineMethyldopa Drug Studymilkv100% (14)
- SD OverviewDocumento85 pagineSD OverviewSamatha GantaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento6 pagineDrug StudyBrix John PortellanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study HydralazineDocumento10 pagineDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyKrissy Java79% (14)
- Isoxilan Generic Name: Isoxsuprine: Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineIsoxilan Generic Name: Isoxsuprine: Drug StudyJohn Paolo Tamayo OrioNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUG CeftazidimeDocumento1 paginaDRUG Ceftazidimerholiboi0% (1)
- Celecoxib Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineCelecoxib Drug Studymilkv100% (2)
- Celecoxib Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineCelecoxib Drug Studymilkv100% (2)
- HydralazineDocumento2 pagineHydralazineShermayne Mallapre HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyErika ManubayNessuna valutazione finora
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaMefenamic Acid Drug Studymilkv70% (10)
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaMefenamic Acid Drug Studymilkv70% (10)
- Magnesium SulfateDocumento1 paginaMagnesium SulfateTrixie Anne Gamotin100% (1)
- Drug Study On DiazepamDocumento1 paginaDrug Study On DiazepamMaya Acosta BiruarNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnesium Sulfate Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineMagnesium Sulfate Drug StudyMaan Molinyawe81% (16)
- Delivery Room Drug StudyDocumento12 pagineDelivery Room Drug StudyJoe Anne Maniulit, MSN, RN100% (6)
- Tranexamic Acid Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineTranexamic Acid Drug Studymilkv93% (28)
- Tranexamic Acid Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineTranexamic Acid Drug Studymilkv93% (28)
- Azithromycin Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaAzithromycin Drug Studymilkv100% (6)
- Azithromycin Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaAzithromycin Drug Studymilkv100% (6)
- 6 MAGNESIUM SULFATE Drug StudyDocumento2 pagine6 MAGNESIUM SULFATE Drug StudyGwyn Rosales100% (2)
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaFurosemide Drug Studymilkv100% (12)
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaFurosemide Drug Studymilkv100% (12)
- Hydralazine Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineHydralazine Drug StudyErika Robella100% (1)
- Salazar Colleges of Science and Institute of TechnologyDocumento2 pagineSalazar Colleges of Science and Institute of TechnologyMark Keem Escuadro100% (3)
- HydralazineDocumento1 paginaHydralazineIvanne Hisoler75% (8)
- Barclays Global FX Quarterly Fed On Hold Eyes On GrowthDocumento42 pagineBarclays Global FX Quarterly Fed On Hold Eyes On GrowthgneymanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketorolac and NalbuphineDocumento4 pagineKetorolac and NalbuphineMaureen Campos-PineraNessuna valutazione finora
- Clindamycin Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineClindamycin Drug Studymilkv100% (4)
- Clindamycin Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineClindamycin Drug Studymilkv100% (4)
- MV + FeSO4 Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineMV + FeSO4 Drug Studymilkv71% (7)
- Ampicillin Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineAmpicillin Drug Studymilkv92% (12)
- Hyosine N ButylbromideDocumento1 paginaHyosine N ButylbromideJenny Vi CodenieraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ferrous Sulfate Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaFerrous Sulfate Drug Studymilkv82% (11)
- DRUG STUDY-Magnesium SulfateDocumento2 pagineDRUG STUDY-Magnesium SulfateCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada80% (5)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyMichael Baylon DueñasNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateDocumento4 pagineDRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateTempoNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnesium SulfateDocumento2 pagineMagnesium SulfateCecilia Cenas Bendol100% (2)
- Methyldopa Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineMethyldopa Drug StudyBea Dela Cena100% (1)
- Waterfront Development Goals and ObjectivesDocumento2 pagineWaterfront Development Goals and ObjectivesShruthi Thakkar100% (1)
- AMLODIPINEDocumento2 pagineAMLODIPINERye AnchNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Action Indication Side Effect Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsDocumento1 paginaDrug Action Indication Side Effect Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsRo-anne AkuNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocumento1 paginaDrug Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationSheng Gosep100% (3)
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocumento3 pagineLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Documento2 pagineDrug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Melinda Cariño Ballon100% (1)
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocumento6 pagineDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- CaptoprilDocumento2 pagineCaptoprilJohn Louie EscardaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study OxytocinDocumento1 paginaDrug Study OxytocinGil GanibanNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocumento3 pagineClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENessuna valutazione finora
- DRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFDocumento2 pagineDRUG STUDY Amoxicillin PDFMc SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- HYDRALAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE - (Apresoline)Documento1 paginaHYDRALAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE - (Apresoline)wen_pilNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyoscine ButylbromideDocumento2 pagineHyoscine ButylbromideEthan Merza EctoleNessuna valutazione finora
- BetamethasoneDocumento3 pagineBetamethasoneMichael KuzbytNessuna valutazione finora
- M Kaavya Sree Balaji Medical College and Hospital IndiaDocumento33 pagineM Kaavya Sree Balaji Medical College and Hospital IndiaNailahRahmahNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Mechanism of Action Side Effect/Adverse Effect/Contraindication Nursing InterventionsDocumento17 pagineDrugs Mechanism of Action Side Effect/Adverse Effect/Contraindication Nursing InterventionsJerome Vergel RubianesNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Failure ChiongDocumento4 pagineCardiac Failure ChiongJohn Miguel ChiongNessuna valutazione finora
- A Neural Network Based System For Intrusion Detection and Classification of AttacksDocumento6 pagineA Neural Network Based System For Intrusion Detection and Classification of AttacksbharadwajrohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2teeth and Its Care: Worksheet - 1Documento11 pagineChapter 2teeth and Its Care: Worksheet - 1RPJNessuna valutazione finora
- SKZ TrackDocumento6 pagineSKZ TrackOliviaNessuna valutazione finora
- An Equivalent Circuit of Carbon Electrode SupercapacitorsDocumento9 pagineAn Equivalent Circuit of Carbon Electrode SupercapacitorsUsmanSSNessuna valutazione finora
- 208 C - Algebras: Marc Rieffel Notes by Qiaochu Yuan Spring 2013Documento55 pagine208 C - Algebras: Marc Rieffel Notes by Qiaochu Yuan Spring 2013Nikos AthanasiouNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 13 ArqDocumento6 pagineCH 13 Arqneha.senthilaNessuna valutazione finora
- B2 First Unit 11 Test: Section 1: Vocabulary Section 2: GrammarDocumento1 paginaB2 First Unit 11 Test: Section 1: Vocabulary Section 2: GrammarNatalia KhaletskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart Rate Variability - Wikipedia PDFDocumento30 pagineHeart Rate Variability - Wikipedia PDFLevon HovhannisyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Of Bones and Buddhas Contemplation of TH PDFDocumento215 pagineOf Bones and Buddhas Contemplation of TH PDFCNessuna valutazione finora
- Lolita Enrico Vs Heirs of Spouses Eulogio Medinaceli and Trinidad MedinaceliDocumento3 pagineLolita Enrico Vs Heirs of Spouses Eulogio Medinaceli and Trinidad Medinacelichatmche-06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Roman Catholic Bishop of Jaro v. Dela PenaDocumento2 pagineRoman Catholic Bishop of Jaro v. Dela PenaBeltran KathNessuna valutazione finora
- ART 6 LEARNING PACKET Week2-3Documento10 pagineART 6 LEARNING PACKET Week2-3Eljohn CabantacNessuna valutazione finora
- Density Determination by PycnometerDocumento5 pagineDensity Determination by PycnometerAlexandre Argondizo100% (1)
- Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineCheat SheetFrancis TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Julien Freund - A TributeDocumento10 pagineJulien Freund - A TributeJuan Pablo SerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Sindhudurg Kokan All Tourism Spot Information WWW - Marathimann.inDocumento54 pagineSindhudurg Kokan All Tourism Spot Information WWW - Marathimann.inMarathi Mann92% (12)
- What Is Art?Documento14 pagineWhat Is Art?Sarvenaaz QaffariNessuna valutazione finora
- Why The Sea Is SaltDocumento3 pagineWhy The Sea Is SaltVictor CiobanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rule 107Documento8 pagineRule 107AlexNessuna valutazione finora
- AMU BALLB (Hons.) 2018 SyllabusDocumento13 pagineAMU BALLB (Hons.) 2018 SyllabusA y u s hNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Firewall SecurityDocumento133 pagineNetwork Firewall Securitysagar323Nessuna valutazione finora
- BS Assignment Brief - Strategic Planning AssignmentDocumento8 pagineBS Assignment Brief - Strategic Planning AssignmentParker Writing ServicesNessuna valutazione finora