Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chemistry Calculations D
Caricato da
KasunDilshanCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chemistry Calculations D
Caricato da
KasunDilshanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
IGCSE Chemistry
Chemistry Calculations D
26 Titration Calculations
Measuring the concentration of a solution
Concentration of a solution can be measured in two ways:
grams per cubic decimetre (litre)
- gdm-3
Concentration = mass of substance (g)
Volume of solution (dm3)
mols per cubic decimetre (litre)
- moldm-3
Concentration = moles of substance (g)
Volume of solution (dm3)
C=n
v
(1) Find the concentrations of the following in grams per cubic decimetre
a) A solution containing 2.1 grams of NaHCO3 in 2 litres
b) A solution containing 5 grams of K2CO3 in 5000 cm3
c) A solution containing 120 grams of H2CO3 in 250 cm3
Page 1 of 7
d) A solution containing 2.5 Kilograms of Na2S2O3 in 1000000 cm3
e) A solution containing 2 tonnes of HCl gas dissolved in 2000 litres of water
(2) Convert the above concentrations to mols per cubic decimetre
Page 2 of 7
Calculations from equations involving solutions
(1) Ca(HCO3)2 decomposes when heated to form calcium carbonate, carbon dioxide
and water. The equation for this reaction is as follows:
Ca(HCO3)2 (aq)
CaCO3 (s) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
Calculate the mass of calcium carbonate which could be formed when 100dm3 of
0.002 moldm-3 Ca(HCO3)2 decomposes.
(2) Lime scale (CaCO3) can be removed from electric kettles by reacting it with
dilute ethanoic acid. The equation for this reaction is as follows:
CaCO3 (s) + 2CH3COOH (aq)
(CH3COO)2Ca (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
What mass of lime scale can be removed by 50cm3 of a solution containing
2moldm-3 of ethanoic acid? (RAMs: C = 12; O = 16; Ca = 40)
Page 3 of 7
Calculations from titrations
Titrations are done to find the concentration of a given solution using another
solution with known concentration and volume.
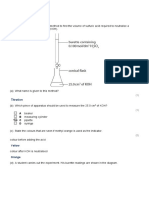
(1) List the equipment used when carrying out a titration.
(2) Explain how a titration is carried out.
A solution of the alkali is measured into a conical flask using a pipette. The acid is
run in from the burette swirling the flask constantly. Towards the end, the acid
is run in a drop at a time until the indicator just changes colour.
Note : When the titration is repeated, the average of the concordant results
are taken. Not all results are used to calculate the average. Concordant
results are the results that differ by 0.10 cm3
-
Calculations
a) Calculate the concentration of HCl when 23.5cm3 of dilute HCl is required to
neutralise 25.0 cm3 of 0.100 moldm-3 Sodium Hydroxide.
Page 4 of 7
b) 25cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution of unknown concentration was titrated
with dilute sulphuric acid of concentration 0.050 moldm-3. 20.0 cm3 of the
acid was required to neutralise the alkali. Find the concentration of the
sodium hydroxide.
c) Washing soda crystals have the formula Na2CO3.n H2O.
28.6 g of washing soda crystals were dissolved in pure water. More pure
water was added to make the total volume of the solution up to 1000 cm3. A
25.0 cm3 sample of this solution was neutralised by 40.0 cm3 of
0.125 moldm-3 hydrochloric acid using methyl orange as indicator.
Na2CO3 (aq) + 2HCl (aq)
2NaCl (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
(RAMs: H = 1; C = 12; O = 16; Na = 23)
I.
Calculate the concentration of the sodium carbonate solution in moles of
sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) per cubic decimetre.
Page 5 of 7
II.
Calculate the mass of Na2CO3 and mass of water in the washing soda
crystals, and use those results to find a value for n in the formula
Na2CO3.n H2O
d) Calculate the volume of 0.100 moldm-3 sodium hydrogen carbonate solution
needed to neutralise 20.0 cm3 of 0.125 moldm-3 hydrochloric acid.
NaHCO3 (aq) + HCl (aq)
NaCl (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
Page 6 of 7
e) A student was making up a solution of sodium hydroxide by dissolving 8.0 g
of sodium hydroxide in water. Unfortunately, the beaker broke and the
solution spilled onto the bench. All he had in hand to neutralise it was some
0.50 moldm-3 Sulphuric acid. What is the minimum volume of acid that he
would have to use?
2NaOH (aq) + H2SO4 (aq)
Na2SO4 (aq) + 2H2O (l)
(RAMs: H = 1; O = 16; Na = 23)
Page 7 of 7
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- S7 11012021 Acid Base Titrations WS With ANSWERSDocumento7 pagineS7 11012021 Acid Base Titrations WS With ANSWERSFatima Ahmed-VeriterNessuna valutazione finora
- Titation and Limiting ReagentDocumento27 pagineTitation and Limiting Reagentngah lidwine100% (1)
- Titration Questions and AnswersDocumento29 pagineTitration Questions and Answersngah lidwineNessuna valutazione finora
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocumento12 pagineSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryNikhil BhattNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (L) F 2 (L) - 1 (S) 2 (G) 2 (G) F 2 (G) - 1Documento27 pagine2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (L) F 2 (L) - 1 (S) 2 (G) 2 (G) F 2 (G) - 1SMJK KatholikNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Calculations and Chemical ReactionsDocumento7 pagineUnit 1 Calculations and Chemical ReactionsVeraNessuna valutazione finora
- CHE 123 HWK Back and Redox TitrationsDocumento3 pagineCHE 123 HWK Back and Redox TitrationsJuiloNessuna valutazione finora
- VOLUMETRIC AnalysisDocumento49 pagineVOLUMETRIC AnalysisLisa Dea SaryNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Titration Simple 1Documento69 pagine1 Titration Simple 1karokiNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Chemistry QuestionsDocumento22 paginePhysical Chemistry QuestionshanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions On StereochemistryDocumento2 pagineQuestions On StereochemistryShilajit BaruaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Volumetric LabDocumento20 pagineChemistry Volumetric Labsunil venkataNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Oxygen DemandDocumento11 pagineChemical Oxygen DemandikhwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysisofamixtureofcarbonateandbicarbonate 140328125044 Phpapp02 PDFDocumento12 pagineAnalysisofamixtureofcarbonateandbicarbonate 140328125044 Phpapp02 PDFBayu Maulida Naryo100% (1)
- Lab Manual-Total AlkalinityDocumento4 pagineLab Manual-Total AlkalinitySuvanka DuttaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM 1235 Volumetric QuizDocumento1 paginaCHEM 1235 Volumetric QuizJesseca Calaunan QuintoNessuna valutazione finora
- CHPracquiz CSEC Chemistry Multiple Choice Test 1Documento19 pagineCHPracquiz CSEC Chemistry Multiple Choice Test 1Atharva SatputeNessuna valutazione finora
- Iodimetric Titration: Aim: PrincipleDocumento2 pagineIodimetric Titration: Aim: PrincipleHarsh ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Assigned Problems-Chapter 4 AnswersDocumento8 pagineAssigned Problems-Chapter 4 Answersshaina leeNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths MCQ On Areas Related To Circles Chapter-12Documento11 pagineMaths MCQ On Areas Related To Circles Chapter-12Binode SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Practice Test Answers 4u1Documento1 paginaChapter 8 Practice Test Answers 4u1helloblargNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ ChemistryDocumento300 pagineMCQ Chemistryyase444Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction Kinetics NotesDocumento40 pagineReaction Kinetics Notesapi-234602673Nessuna valutazione finora
- Moles IB 1 PDFDocumento10 pagineMoles IB 1 PDFBita M100% (1)
- Questions and Answers of Acids, Bases and SaltsDocumento4 pagineQuestions and Answers of Acids, Bases and SaltsAryan BodkheNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 - Sample Titration ProblemsDocumento15 pagine8 - Sample Titration ProblemsGerald LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Treatment Lecture 4 EENVDocumento35 pagineWater Treatment Lecture 4 EENVEllina TehNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Lab# 3 (Completed)Documento3 pagineChemistry Lab# 3 (Completed)tahjsalmon100% (2)
- C3 Titration CalculationsDocumento1 paginaC3 Titration CalculationsYuones BalahNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Chemistry Study Guide: Chapter 14: Acids and Bases and Chapter 15, 16.1 and 21.3: Aqueous and Acid-Base EquilibriaDocumento8 pagineAP Chemistry Study Guide: Chapter 14: Acids and Bases and Chapter 15, 16.1 and 21.3: Aqueous and Acid-Base Equilibrialorraine_cuaNessuna valutazione finora
- PC PH DiagramsDocumento37 paginePC PH DiagramsKenny Pabón Cevallos100% (1)
- CAIE Chemistry A-Level: 24: ElectrochemistryDocumento8 pagineCAIE Chemistry A-Level: 24: ElectrochemistryahumanbeinginearthNessuna valutazione finora
- Energetics LabDocumento3 pagineEnergetics LabStudent Research100% (1)
- Back TitrationsDocumento3 pagineBack TitrationsChristine Angelica EvangelistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt01 HCL and NaOH AnsDocumento3 pagineExpt01 HCL and NaOH AnsaragpdNessuna valutazione finora
- Water TreatmentDocumento19 pagineWater TreatmentAnonymous 8ooQmMoNs1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hard Eness WaterDocumento4 pagineHard Eness WaterLaura OliverosNessuna valutazione finora
- Redox & Equivalent Concepts Chemistry Zenith 2022 A01 & A021591183372Documento53 pagineRedox & Equivalent Concepts Chemistry Zenith 2022 A01 & A021591183372SonalNessuna valutazione finora
- Cive3223 5 2015 2Documento4 pagineCive3223 5 2015 2Yannick HowNessuna valutazione finora
- H432-01-Periodic Table, Elements and Physical Chemistry/a Level Chemistry A H432 - H432-01 - QS13Documento5 pagineH432-01-Periodic Table, Elements and Physical Chemistry/a Level Chemistry A H432 - H432-01 - QS13Altay ShawNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effect of Concentration On The Rate of A ReactionDocumento7 pagineThe Effect of Concentration On The Rate of A Reactiongokul sNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM475 Exp10Documento4 pagineCHM475 Exp10Izzati HalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp7-Dissolution of BoraxDocumento7 pagineExp7-Dissolution of BoraxIzzy Ali67% (3)
- Chang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 5Documento8 pagineChang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 5haha_le12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Tutorial 3 Q1-Q10Documento7 pagineSolution Tutorial 3 Q1-Q10hoboslayer97Nessuna valutazione finora
- 13.1 Multiple-Choice Questions: Chapter 13 Properties of SolutionsDocumento43 pagine13.1 Multiple-Choice Questions: Chapter 13 Properties of SolutionsanonNessuna valutazione finora
- Buffers Complete Handout 2020 With Answer KeyDocumento14 pagineBuffers Complete Handout 2020 With Answer KeyRadhika RaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 09 - Flinn - Stoichiometric Ratio of A ReactionDocumento8 pagine09 - Flinn - Stoichiometric Ratio of A ReactionDerek Hammons100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Practice Test 4u1Documento1 paginaChapter 8 Practice Test 4u1helloblargNessuna valutazione finora
- Buffers Michaels CalculationDocumento5 pagineBuffers Michaels CalculationHassan Haider100% (1)
- MCQ Type QuestionsDocumento3 pagineMCQ Type QuestionsBhawana SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment # 4: Oxidation and Reduction of BenzaldehydeDocumento5 pagineExperiment # 4: Oxidation and Reduction of BenzaldehydeUsman GhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect 23 - Conductometric TitrationsDocumento5 pagineLect 23 - Conductometric TitrationsHarsh Kumar JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.3.4 Cis and Trans Potassium-Dioxalato Diaquo Chromate (III) K (CR (C O) (H O) ) .2H ODocumento3 pagine2.3.4 Cis and Trans Potassium-Dioxalato Diaquo Chromate (III) K (CR (C O) (H O) ) .2H OKiran YaqoobNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM 11 - Lesson 1 - Some Basic Concepts in ChemistryDocumento8 pagineCHEM 11 - Lesson 1 - Some Basic Concepts in ChemistryPrabhat Singh 11C 13Nessuna valutazione finora
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron in Vitamin TabletsDocumento13 pagineSpectrophotometric Determination of Iron in Vitamin TabletsSophie CroninNessuna valutazione finora
- MATTHEW CORREIA Acids Bases and Salts WORKSHEETDocumento4 pagineMATTHEW CORREIA Acids Bases and Salts WORKSHEETFrank MassiahNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 2 Standardization of Sodium Hydroxide With HCLDocumento2 pagineExperiment 2 Standardization of Sodium Hydroxide With HCLvafaashkNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 WorksheetDocumento6 pagineChapter 5 WorksheetJules BrunoNessuna valutazione finora
- Edexcel IAL Mathematics Formula BookDocumento30 pagineEdexcel IAL Mathematics Formula BookThanuj Perera100% (3)
- EDEXCEL IGCSE Chemistry Practice Unit Test 1Documento7 pagineEDEXCEL IGCSE Chemistry Practice Unit Test 1KasunDilshan100% (1)
- Edexcel GCE Units Grade Boundaries - Summer 2010Documento14 pagineEdexcel GCE Units Grade Boundaries - Summer 2010goldsilvy100% (1)
- IAL Jan 2015 Grade BoundaryDocumento6 pagineIAL Jan 2015 Grade BoundaryAmorn JiralucksanawongNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionDocumento9 pagineIGCSE Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- EDEXCEL IAL WBI06/01 Jan 2015Documento16 pagineEDEXCEL IAL WBI06/01 Jan 2015KasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Physics - Investigation On AccelerationDocumento7 pagineIGCSE Physics - Investigation On AccelerationKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Calculations C PDFDocumento7 pagineChemistry Calculations C PDFKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 - CorrelationDocumento1 paginaChapter 6 - CorrelationKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hookes Law DemonstrationDocumento7 pagineHookes Law DemonstrationKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Physics MomentsDocumento3 pagineIGCSE Physics MomentsKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Calculations ADocumento8 pagineChemistry Calculations AKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Calculations BDocumento2 pagineChemistry Calculations BKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- GCE Chemistry Data Booklet Issue 2Documento35 pagineGCE Chemistry Data Booklet Issue 2purityplus89% (9)
- Chapter 7 - RegressionDocumento2 pagineChapter 7 - RegressionKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 - ProbabilityDocumento3 pagineChapter 5 - ProbabilityKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapters 1 To 4 - Data Representation and Summarisation TechniquesDocumento8 pagineChapters 1 To 4 - Data Representation and Summarisation TechniquesKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- IAL Physics Unit 4 - Further Mechanics SummaryDocumento1 paginaIAL Physics Unit 4 - Further Mechanics SummaryKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cuckoo Clock: Sample TaskDocumento18 pagineCuckoo Clock: Sample TaskMohammad WorldNessuna valutazione finora
- StrippingDocumento9 pagineStrippingppalmacNessuna valutazione finora
- Procesos InglesDocumento4 pagineProcesos InglesMarcoDulongJaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Stoichiometry and Climate Change LessonDocumento4 pagineStoichiometry and Climate Change Lessonapi-366989204Nessuna valutazione finora
- Why Is It Important PH and AlkalinitDocumento4 pagineWhy Is It Important PH and Alkalinitibnu samsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Wastewater Treatment: Chemical PrecipitationDocumento34 pagineWastewater Treatment: Chemical PrecipitationDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (10)
- IJETR032728Documento5 pagineIJETR032728erpublicationNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 - Q2 ScienceDocumento21 pagine7 - Q2 Sciencemaximo meridaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitec 5000Documento1 paginaVitec 5000eduardoNessuna valutazione finora
- DPP - Acid, Base and Salts (Prashant Kirad)Documento10 pagineDPP - Acid, Base and Salts (Prashant Kirad)Abhinav SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 806 B 806 Bi Manual - v2.9.3Documento30 pagine806 B 806 Bi Manual - v2.9.3bmcpherson1982Nessuna valutazione finora
- E80dc1b2 01e9 4aee b425 C074a3d3649c Bukango Seed School Mid Term ExamsDocumento38 pagineE80dc1b2 01e9 4aee b425 C074a3d3649c Bukango Seed School Mid Term ExamsDaniel MarkNessuna valutazione finora
- 1,1,6 Precalciner KilnsDocumento39 pagine1,1,6 Precalciner KilnsMohamed Saad100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 1 2 3 4 Revision Questions and AnswersDocumento88 pagineChemistry Form 1 2 3 4 Revision Questions and AnswersOdero BravinNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ S For Moles CalculationDocumento9 pagineMCQ S For Moles CalculationLubzNessuna valutazione finora
- Foaming Capacity of SoapsDocumento6 pagineFoaming Capacity of SoapsPawan TandonNessuna valutazione finora
- Dissolution CaCO3 in Aqueous SolutionsDocumento2 pagineDissolution CaCO3 in Aqueous SolutionsYuni_Arifwati_5495Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sri Lanka's Mineral Resources Can Enrich Country's CoffersDocumento139 pagineSri Lanka's Mineral Resources Can Enrich Country's CoffersPrashan Francis100% (3)
- Demis MSC ThesisDocumento74 pagineDemis MSC ThesisMinilik Tikur SewNessuna valutazione finora
- Dowex Ion Exchange ResinsDocumento93 pagineDowex Ion Exchange ResinsJC PinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Float Grow TobaccoDocumento16 pagineFloat Grow TobaccodanspokerhandNessuna valutazione finora
- Master Thesis Marnix de JongDocumento94 pagineMaster Thesis Marnix de JongShashi Ranjan100% (1)
- The Manuf. of Paver BlockDocumento4 pagineThe Manuf. of Paver BlockMirtunjay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mahesh Tutorials: S.S.C. Batch: SB Marks: 30 Date: Time: 1 Hr. 15 MinDocumento10 pagineMahesh Tutorials: S.S.C. Batch: SB Marks: 30 Date: Time: 1 Hr. 15 MinHemantkumar YedeNessuna valutazione finora
- Y10 Moles Revision Questions AnswersDocumento4 pagineY10 Moles Revision Questions AnswersShougNessuna valutazione finora
- CACO3 PresentationDocumento17 pagineCACO3 PresentationakosiamagneNessuna valutazione finora
- Control of Odors in The Sugar Beet Processing Industry: Technical PaperDocumento7 pagineControl of Odors in The Sugar Beet Processing Industry: Technical PaperIrvan DwikiNessuna valutazione finora
- Techniques, Tips and Recipes: Soda FiringDocumento21 pagineTechniques, Tips and Recipes: Soda FiringCristiane SouzaNessuna valutazione finora
- BMC Work BookDocumento22 pagineBMC Work Bookankit kasanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Science 6888 (2021-23) (Original)Documento33 paginePhysical Science 6888 (2021-23) (Original)Blessing TshumaNessuna valutazione finora