Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chemistry Calculations A
Caricato da
KasunDilshanCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chemistry Calculations A
Caricato da
KasunDilshanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
IGCSE Chemistry
Chemistry Calculations A
22 RAMs and Moles
Relative Atomic Mass
Relative atomic mass is the average mass of the isotopes of an element
compared with one twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. It is also called
RAM or Ar
RAM = average mass of an atom of the element (in Kg)
1/12 x mass of an atom of carbon-12 (in Kg)
Q1 The average mass of an atom of Magnesium is 4.035943 x 10-26 Kg. Given that
the mass of an atom of carbon-12 is 1.9926 x 10-26, find the relative atomic mass
of Magnesium.
Q2 The relative abundances of the isotopes of Tungsten are:
180
W 0.12%
182
W 26.50%
183
W 14.31%
184
W 30.64%
185
W 28.43%
Find the relative atomic mass of Tungsten
Page 1 of 8
Relative Formula Mass (RFM of Mr)
Relative formula or relative molecular mass is the mass of a substance in relative
units.
Note: The term relative formula mass is used when calculating the mass of ionic
compounds
The term relative molecular mass is used when calculating the mass of covalent
compounds
To find the Mr of a compound, simply add the atomic masses.
e.g.: Mr of NaCl = 23 + 35.5 = 58.5
Q3 Find the Mr of the following compounds
a) Cr2(SO4)3
b) CuSO4.5H2O
c) CuCO3.Cu(OH)2
d) (NH4)2SO4.FeSO4.6H2O
Page 2 of 8
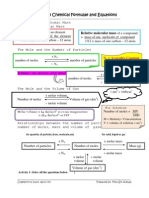
Moles (short form is mols)
Moles are the units used to measure the amount of a substance.
1 mole =
Amount of that substance that contains as many particles (atoms, ions or
molecules) as there are atoms in exactly 12g of carbon-12 = 6.02 x 1023
1 Mole
6.02 x 1023 Particles
6.02x1023 is called the Avogadros constant and
was named after the Italian scientist Amedeo
Avogadro in honour of his contributions to
Molecular theory
1 mole of sodium has 6.02x1023 sodium atoms.
1 mole of Na+ has 6.02x1023 sodium ions.
1 mole of CO2 has 6.02x1023 Carbon dioxide molecules.
1 mole of NaCl has 6.02x1023 Na+ ions and 6.02x1023 Cl- ions (A total of
1.204 x 1024 ions)
Q4 Calculate the no. of particles in:
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
0.5 mols of CO2
5 mols of FeSO4
0.1 mols of O2
6 mols of H2O
10 mols of Fe2+
Page 3 of 8
Relationship between moles, mass and molar mass
Molar mass mass of 1 mole of a substance
Molar mass = Mr but the only difference between them is Mr has no units and molar
mass has units grams per mole (gmol-1)
Moles =
Mass (grams)
Molar Mass (gmol-1)
Q5 Calculate the no. of moles (to 3 s.f. where necessary) in:
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
50 grams of Copper II sulphate crystals, CuSO4.5H2O
1 Kilogram of iron, Fe
0.032 grams of Sulphur Dioxide, SO2
50 milligrams of copper carbonate, CuCO3
1 tonne of Magnesium, Mg
Q6 Calculate the mass in grams of:
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
1 mol of Lead(II) Nitrate, Pb(NO3)2
4.3 mols of methane, CH4
0.24 mols of Na2CO3.10H2O
5.25 mols of Al2O3
4.1 mols of octacontane, C80H162
Using relative formula mass to find percentage composition
e.g.: Find the percentage by mass of copper in Copper (II) Oxide, CuO
Page 4 of 8
Q7 Find the percentage composition of Oxygen in each of the following compounds
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
CO(NH2)2
(NH4)2SO4
FeSO4.7H2O
Na2CO3.10H2O
CH3CH2COOH
Empirical formula and Molecular Formula
Empirical formula is the formula that shows the simplest ratio of elements in
a compound.
Molecular formula is the formula that shows the actual ratio of elements in a
compound.
Molecular Formula mass = Empirical formula mass x n
e.g.: An organic compound has the composition 38.7% Carbon, 9.70% Hydrogen and
51.6% Oxygen by mass. The relative formula mass of the compound is 62. Calculate
the empirical formula and the molecular formula of the compound.
Page 5 of 8
Q8 A gaseous compound of C and H contains 80% C by mass. Its molecular
mass is 30.2, Calculate its empirical formula and molecular formula.
Q9 The empirical formula of a compound is C3H6O. It has molar mass 58 gmol-1.
Calculate its molecular formula.
Q10 1.24g of phosphorus was burnt completely in oxygen to give 2.84 g of
phosphorus oxide. The molecular formula of the oxide is 284 gmol-1. Find its
empirical formula and molecular formula.
Concept of molar volume
Molar volume is the volume occupied by 1 mol of a gas
under room temperature and pressure conditions (r.t.p) conditions (25 C and
1atm pressure) , molar volume is
under standard temperature and pressure conditions (s.t.p) conditions (0 C
and 1atm pressure), molar volume is
Q11 Calculate the volumes of each of these in dm3 under r.t.p conditions
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
5 mols of O2
0.5 mols of CH4
0.25 mols of water vapour, H2O
50 grams of Nitrogen, N2
100 grams of Fluorine, F2
Q12 Calculate the volumes of the same moles of the above gases in dm3 under s.t.p
conditions
Q13 Calculate the mass in grams of the following volumes of gases:
a) 24dm3 of Chlorine gas
b) 200cm3 of Oxygen gas
c) 1.42dm3 of water vapour
Page 6 of 8
23 Calculations from equations
Consider the equation:
2CaCo3 (s) + 2SO2 (s) + O2 (g)
2CaSO4 (s) + 2CO2 (g)
Calculate the mass of CaSO4 (Calcium sulphate) formed from 100 grams of Calcium
Carbonate.
Page 7 of 8
Percentage Yield
% Yield =
Actual mass of product x 100%
Expected mass of product
e.g.:
Heating 12.4 grams of copper (II) carbonate in a crucible produced 7.0 g of copper
(II) Oxide. What is the percentage yield of Copper (II) Oxide?
The equation for the above mentioned reaction is:
CuCO3
CuO + CO2
Questions (1), (2), (4), (6) and (11) from text book
Page 8 of 8
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- GCE Chemistry Data Booklet Issue 2Documento35 pagineGCE Chemistry Data Booklet Issue 2purityplus89% (9)
- ASTM D5893-16 (Reapproved 2021)Documento6 pagineASTM D5893-16 (Reapproved 2021)anant11235Nessuna valutazione finora
- DABCO - Evonik Catalyst CatalogueDocumento9 pagineDABCO - Evonik Catalyst CataloguePhuong The Nguyen100% (1)
- Pre-Laboratory Activity: Chemical Activity and Corrosion of MetalsDocumento4 paginePre-Laboratory Activity: Chemical Activity and Corrosion of MetalsMigs MlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Iso 14644-6 2007Documento48 pagineIso 14644-6 2007JuanBorja50% (2)
- 03 Chemical Formulae & EquationDocumento15 pagine03 Chemical Formulae & EquationSathya RauNessuna valutazione finora
- Relative Masses of Atoms and MoleculesDocumento23 pagineRelative Masses of Atoms and MoleculesKris DookharanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mole Concept: Relative Atomic, Molecular and Formula Masses Relative Atomic Mass (RAM)Documento7 pagineMole Concept: Relative Atomic, Molecular and Formula Masses Relative Atomic Mass (RAM)Aria PersaudNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Handout 6Documento4 pagineChemistry Handout 6Naomi JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 4 Chemistry Chapter 3 NoteDocumento21 pagineForm 4 Chemistry Chapter 3 NoteSF CHENGNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1, Fundamental Concepts First Year MCATDocumento29 pagineTopic 1, Fundamental Concepts First Year MCATKhubaib Khan100% (1)
- Chemical Formulae and Equations: A Relative Atomic Mass (Ram) and Relative Molecular Mass (RMM)Documento19 pagineChemical Formulae and Equations: A Relative Atomic Mass (Ram) and Relative Molecular Mass (RMM)Kevin DanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 3 f4 KSSM - Student 2021Documento101 pagineChap 3 f4 KSSM - Student 2021Koo Rui CheeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocumento25 pagineChemical Formulae and EquationsirisNessuna valutazione finora
- MOLE NotesDocumento12 pagineMOLE NotesShanzay WaqarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryDocumento8 pagineChapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryTilak K C100% (1)
- Ncert Sol For Cbse Class 9 Sci Chapter 3 Atoms and MoleculesDocumento12 pagineNcert Sol For Cbse Class 9 Sci Chapter 3 Atoms and MoleculesShah RukhNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Form 4 Terminology and Concepts Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocumento7 pagineSPM Form 4 Terminology and Concepts Chemical Formulae and EquationsJedidah JongNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise - 3.1: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and MoleculesDocumento12 pagineExercise - 3.1: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and MoleculesMannat MadanNessuna valutazione finora
- Quick Notes: Relative Atomic MassDocumento20 pagineQuick Notes: Relative Atomic Massanwar9602020Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Chemical Calculations Calculat PDFDocumento37 pagineChapter 5 Chemical Calculations Calculat PDFAbdullah Sabry AzzamNessuna valutazione finora
- MATTER - KMTPHDocumento206 pagineMATTER - KMTPHMohamad Firdaus HarunNessuna valutazione finora
- Ccy 101 Topic 3Documento61 pagineCcy 101 Topic 3Leona TittleNessuna valutazione finora
- Atoms & Molecules SolutionsDocumento11 pagineAtoms & Molecules Solutionshkush78Nessuna valutazione finora
- IAL As Chemistry SN 4Documento116 pagineIAL As Chemistry SN 4Michael J George100% (2)
- ScienceDocumento43 pagineScienceHemang NityantNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Ar, MR and MolesDocumento11 pagine2 Ar, MR and MoleslfcluishoughtonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocumento6 pagineChapter 3 Chemical Formulae and EquationsArif AyepNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Relative Atomic MassDocumento7 pagine1 Relative Atomic MassHooi YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Atoms, Molecules & Stoichiometry RedoxDocumento189 pagineAtoms, Molecules & Stoichiometry RedoxPriscilla TjjNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide 1d Calculations With Exam Qs and MSDocumento22 pagineStudy Guide 1d Calculations With Exam Qs and MScammcbeanNessuna valutazione finora
- F4 Chapter 3 Relative Atomic MassDocumento28 pagineF4 Chapter 3 Relative Atomic MassSamuel LiewNessuna valutazione finora
- Moleblok 09Documento5 pagineMoleblok 09نور العينNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Module Form 4Documento32 pagineChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (3)
- 20171101131106chapter 5b - Mole and Stoichiometry PDFDocumento50 pagine20171101131106chapter 5b - Mole and Stoichiometry PDFShah100% (1)
- Atoms Molecules and StoichiometryDocumento28 pagineAtoms Molecules and StoichiometrySharneeshriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Important QuestDocumento12 pagineScience Important QuestSanjeev KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry, Form 4 Malaysia EducationDocumento7 pagineChemistry, Form 4 Malaysia EducationIkhwan AzimNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 7 StoichiometryDocumento59 paginePart 7 Stoichiometryjasumin91Nessuna valutazione finora
- PearsonDocumento12 paginePearsonTrishNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Stoichiometry ChemicalArithmeticDocumento44 pagineChapter 1 Stoichiometry ChemicalArithmetictrx9c96dgpNessuna valutazione finora
- Modul Kimia Skor ADocumento9 pagineModul Kimia Skor Aacik5596Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2013 Chem'l QuantitiesDocumento52 pagine2013 Chem'l Quantitiesapi-266061131Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Mole ConceptDocumento6 pagineIntroduction To Mole ConceptShari OliverNessuna valutazione finora
- Latihan Kimia Cuti Sekolah Part 1Documento7 pagineLatihan Kimia Cuti Sekolah Part 1FATIN MAISARAH BINTI AHMAD MISWAN MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Revision 2 For Test 2: Collision Theory and Rate of ReactionDocumento7 pagineChemistry Revision 2 For Test 2: Collision Theory and Rate of ReactionDaniel BerryNessuna valutazione finora
- Mole ConceptDocumento90 pagineMole ConcepthariniNessuna valutazione finora
- XI Chemistry Chapterwise Advanced Study MaterialDocumento537 pagineXI Chemistry Chapterwise Advanced Study MaterialregisNessuna valutazione finora
- Mole Concept Part 1Documento14 pagineMole Concept Part 1Heythere HiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equations - LATIHAN PENGUKUHANDocumento4 pagineChapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equations - LATIHAN PENGUKUHANSiti Aishah AzmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Form 4 - LisDocumento30 pagineChapter 3 Form 4 - LisStephenie Nilus Richard KulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9 Science Chapter 3Documento20 pagineClass 9 Science Chapter 3rupam baparyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch3 CompleteDocumento48 pagineCh3 CompleteAN NGUYENNessuna valutazione finora
- 05athemole 101129173016 Phpapp01Documento28 pagine05athemole 101129173016 Phpapp01Karm VeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Rams and Moles NotesDocumento8 pagineRams and Moles NotesHari VarshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch3 CompleteDocumento48 pagineCh3 CompleteAN NGUYENNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento104 pagineChapter 1Sarathy Hari KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Page No: 32: in Text QuestionsDocumento8 paginePage No: 32: in Text QuestionsVinod MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch3 CompleteDocumento48 pagineCh3 CompleteAN NGUYENNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesNessuna valutazione finora
- IAL Jan 2015 Grade BoundaryDocumento6 pagineIAL Jan 2015 Grade BoundaryAmorn JiralucksanawongNessuna valutazione finora
- EDEXCEL IGCSE Chemistry Practice Unit Test 1Documento7 pagineEDEXCEL IGCSE Chemistry Practice Unit Test 1KasunDilshan100% (1)
- Edexcel GCE Units Grade Boundaries - Summer 2010Documento14 pagineEdexcel GCE Units Grade Boundaries - Summer 2010goldsilvy100% (1)
- Edexcel IAL Mathematics Formula BookDocumento30 pagineEdexcel IAL Mathematics Formula BookThanuj Perera100% (3)
- IGCSE Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionDocumento9 pagineIGCSE Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- EDEXCEL IAL WBI06/01 Jan 2015Documento16 pagineEDEXCEL IAL WBI06/01 Jan 2015KasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Calculations DDocumento7 pagineChemistry Calculations DKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hookes Law DemonstrationDocumento7 pagineHookes Law DemonstrationKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Physics - Investigation On AccelerationDocumento7 pagineIGCSE Physics - Investigation On AccelerationKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Physics MomentsDocumento3 pagineIGCSE Physics MomentsKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- IAL Physics Unit 4 - Further Mechanics SummaryDocumento1 paginaIAL Physics Unit 4 - Further Mechanics SummaryKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Calculations BDocumento2 pagineChemistry Calculations BKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Calculations C PDFDocumento7 pagineChemistry Calculations C PDFKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 - ProbabilityDocumento3 pagineChapter 5 - ProbabilityKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 - RegressionDocumento2 pagineChapter 7 - RegressionKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 - CorrelationDocumento1 paginaChapter 6 - CorrelationKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapters 1 To 4 - Data Representation and Summarisation TechniquesDocumento8 pagineChapters 1 To 4 - Data Representation and Summarisation TechniquesKasunDilshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Standards For Insulation-Mineral Wool-RockwoolDocumento2 pagineTechnical Standards For Insulation-Mineral Wool-RockwooljaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Wall - Panel - KS1150 TF - NF - DatasheetDocumento4 pagineWall - Panel - KS1150 TF - NF - DatasheetMetlachisNessuna valutazione finora
- D and F PW New ModuDocumento32 pagineD and F PW New ModuIshant SankhalaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.HEA - Formation of Simple Crystal Structures in Cu-Co-Ni-Cr-Al-Fe-Ti-V Alloys With Multiprincipal Metallic PDFDocumento2 pagine1.HEA - Formation of Simple Crystal Structures in Cu-Co-Ni-Cr-Al-Fe-Ti-V Alloys With Multiprincipal Metallic PDFSudeep Kumar TNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Download Genetic Analysis An Integrated Approach 3rd Edition Sanders Test BankDocumento15 pagineFull Download Genetic Analysis An Integrated Approach 3rd Edition Sanders Test Bankdopemorpheanwlzyv100% (42)
- PH Lab ReportDocumento2 paginePH Lab Reportapi-252514594Nessuna valutazione finora
- Major Advances and Challenges in Heterogeneous CatalysisDocumento26 pagineMajor Advances and Challenges in Heterogeneous CatalysisJuan Lopez HernándezNessuna valutazione finora
- CarbonicAnhydrases Manuscript withDOIDocumento11 pagineCarbonicAnhydrases Manuscript withDOIFadhil MiftahulNessuna valutazione finora
- Item No. Photo Unit Price (RP) Product Description Material Size (C M) Available Color MinimumDocumento20 pagineItem No. Photo Unit Price (RP) Product Description Material Size (C M) Available Color Minimumrobiyanto wandooNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Displacement MatterDocumento20 pagineWater Displacement MatterJeannie Rose M. Sarabia IIINessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Carboxymethylcellulose and Starch As Thickening Agents On The Quality of Tomato KetchupDocumento7 pagineEffect of Carboxymethylcellulose and Starch As Thickening Agents On The Quality of Tomato KetchupAmir MehmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Lectr Online Clases Separation Processes - Prepared By:ms - Ammarah BatoolDocumento161 pagineRevision Lectr Online Clases Separation Processes - Prepared By:ms - Ammarah BatoolHajra AamirNessuna valutazione finora
- Soal Soal Yang Penting BangetDocumento7 pagineSoal Soal Yang Penting Bangetdexter137Nessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid OralsDocumento55 pagineLiquid OralsShraddha RNessuna valutazione finora
- Ijftr 27 (3) 290-306Documento17 pagineIjftr 27 (3) 290-306Ze MariNessuna valutazione finora
- Accumulation On and Extraction of Lead From Point-Of-Use Filters For Evaluating Lead Exposure From Drinking WaterDocumento26 pagineAccumulation On and Extraction of Lead From Point-Of-Use Filters For Evaluating Lead Exposure From Drinking WaterNermeen ElmelegaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Biodegradation NewDocumento37 pagineBiodegradation NewAyesha AbbasiNessuna valutazione finora
- A Theory of The EarthDocumento6 pagineA Theory of The EarthTeketel chemesaNessuna valutazione finora
- "Oil and Gas Processing Plant Design and Operation Training Course" " " 2002Documento10 pagine"Oil and Gas Processing Plant Design and Operation Training Course" " " 2002AjaykumarNessuna valutazione finora
- US4417079 KurarayDocumento16 pagineUS4417079 Kuraray黃英婷Nessuna valutazione finora
- Resin Based Restorative Dental Materials. Characteristics and Future PerspectivesDocumento13 pagineResin Based Restorative Dental Materials. Characteristics and Future PerspectivesDan MPNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Clinical Laboratory Chemistry SunheimerDocumento13 pagineTest Bank For Clinical Laboratory Chemistry SunheimerWilbur Penny100% (36)
- 3rd - Year - PPT - Chapter 4 PDFDocumento70 pagine3rd - Year - PPT - Chapter 4 PDFtolerakukuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Chapter 6Documento17 pagineChemistry Chapter 6Kashaf fatimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gregory D. Botsaris (Auth.), J. W. Mullin (Eds.) - Industrial Crystallization-Springer US (1976) PDFDocumento456 pagineGregory D. Botsaris (Auth.), J. W. Mullin (Eds.) - Industrial Crystallization-Springer US (1976) PDFAlan ConnorNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 5 - Light Sources - Written ReportDocumento110 pagineGroup 5 - Light Sources - Written ReportKEVIN JUGONessuna valutazione finora