Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
H2 Enzymes Questions
Caricato da
Wesley TanTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
H2 Enzymes Questions
Caricato da
Wesley TanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
Multiple Choice Questions
1.
Enzyme molecules with high optimum temperature will have
A
B
C
D
2.
less associated non-protein groups.
less hydrophobic amino acid residues.
more cysteine residues in their polypeptide chains.
more peptide bonds than other enzyme molecules.
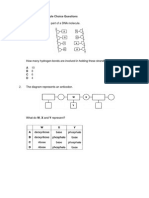
In an investigation to determine the effect of temperature on the activity of an enzyme,
the time taken for all the substrates to disappear from a standard solution was recorded.
Which graph shows the result of this investigation?
3.
The diagram below shows a simple metabolic pathway.
Enzyme 2
Enzyme 1
Enzyme 3
Which response shows feedback inhibition?
Metabolite
Binding site of metabolite
Active site of enzyme 1
Allosteric site of enzyme 1
Active site of enzyme 1
Allosteric site of enzyme 1
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
4.
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
The graph shows the results of an experiment in which samples containing the same
concentration of enzyme and substrate were kept at different temperatures for periods of
one, two and five hours. The quantities of product formed were then determined.
Which of the following options best explains why the optimum temperature is lower if the
quantity of product formed is measured after five hours rather than one hour?
A
B
C
D
Tertiary bonds are not broken at higher temperatures.
The enzyme has a range of optimum temperatures.
A longer time at high temperature denatures enzyme.
The optimum temperature for the enzymes is 45C.
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
5.
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
The diagram shows an enzyme molecule with its normal substrate and products. P and
Q are other molecules that can bind to the enzyme.
The graph shows the effect of P and Q on the rate of reaction of the enzyme at different
substrate concentrations.
Which statement correctly describes the activity of the enzyme?
A
B
C
D
P is a competitive inhibitor which binds to the active site, resulting in curve R.
P is a non-competitive inhibitor which distorts the shape of the enzyme, resulting in
curve S.
Q is a competitive inhibitor which distorts the shape of the enzyme, resulting in
curve R.
Q is a non-competitive inhibitor which binds to the active site, resulting in curve S.
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
6.
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
The monomers of both starch and cellulose are glucose molecules. Which of the
following best explains why amylase can only break down starch but not cellulose?
A
B
C
D
7.
Revision Package
The large number of cross-linkages between adjacent cellulose molecules that
prevents amylase from breaking down cellulose.
Amylase can only recognize -glycosidic linkages, which are present in starch but
not cellulose.
The glycosidic bonds between the monomers in cellulose are stronger than in
starch.
Cellulose is too large to be broken down by amylase.
Catalase is an enzyme that breaks down hydrogen peroxide. A scientist discovered a
new substance X, which will decrease the rate of enzymatic reaction of catalase when
added into the system. The addition of substrate, however, will increase the rate of
reaction again.
From the information given above, what can you conclude about substance X?
A
B
C
D
8.
It has similar molecular configuration to hydrogen peroxide.
It binds to a site away from the active site of the catalase enzyme.
It has the same configuration as the active site of catalase.
It increases the pH of the system.
The four unknown substances shown below form part of an enzyme-catalysed pathway.
The addition of substance V results in no change in the concentration of W, and an
accumulation of X, and a near absence of both Y and Z. Further addition of Y results in
the formation of Z.
What does this information indicate about substance V?
A
B
C
D
It is an inhibitor of enzyme 1
It is an inhibitor of enzyme 2
It is an inhibitor of enzyme 3
It catalyses the formation of X
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
9.
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
Which of the following statements about the function of enzymes is correct?
A
B
C
D
10.
Revision Package
Enzymes can speed up reaction but they cannot change the net energy output as
the activation energy cannot be changed.
Enzymes can speed up the reaction by increasing the activation energy of a
reaction.
Enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction and change the net energy
output.
Enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction but do not change the net energy
output..
In an experiment using starch and amylase, the concentrations of starch and maltose
present in the reacting mixture are measured every minute for 20 minutes. 1%
hydrochloric acid is added after 10 minutes and the mixture is heated to 60C at 14
minutes.
Which graph represents the results of this experiment?
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
11.
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
The diagram shows a metabolic pathway controlled by end product inhibition. As the
concentration of the end product increases above the set level, an enzyme in the
pathway leading to the end product is inhibited.
An increase in the concentration of end product 6 does not lead to a decrease in the
synthesis of end product 9.
Which enzyme is inhibited by end product 6?
A
B
C
Metabolite 1 Metabolite 2
Metabolite 2 Metabolite 3
Metabolite 3 Metabolite 4
Metabolite 3 Metabolite 7
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
12.
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
Lactose is a disaccharide present in milk. The enzyme -galactosidase catalyses the
breakdown of lactose to glucose and galactose.
10 cm3 of a 1% -galactosidase solution was added to 10 cm3 of milk. The graph shows
the total amount of glucose produced over the next ten minutes.
Then, 10 cm3 of a 2% galactosidase solution was added to 10 cm3 of milk.
Which graph shows the expected results?
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
13.
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
An enzyme is a globular protein held together by several different types of chemical
bond, giving the enzyme primary, secondary and tertiary levels of structure. Which
correctly summarises the types of bond involved in each level of structure?
A
B
C
D
14.
Revision Package
Disulfide Bonds
Hydrogen Bonds
Ionic Bonds
Peptide Bonds
Tertiary
Primary, Tertiary
Secondary
Primary
Secondary, Tertiary
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Tertiary
Secondary, Tertiary
Tertiary
Secondary
Primary
Secondary
Primary
Tertiary
Indinavir is a commercial HIV-1 protease inhibitor administered by doctors to treat AIDS
patients. It is supposed to act as a competitive inhibitor.
Which of the following shows the correct combination of the Km value and maximum
velocity (Vmax) of HIV-1 protease when Indinavir is added together with its substrate?
15.
Km
Maximum velocity (Vmax)
Remains the same
Increases
Remains the same
Decreases
Increases
Remains the same
Decreases
Decreases
The figure shows a series of reactions in a metabolic pathway.
D
A
3
J
Enzyme 3 catalyses the splitting of C into D and J. Assuming that product E is an
allosteric inhibitor of 3, which of the following would likely happen if E were not consumed
in a subsequent reaction?
A
B
C
D
The rate of production of D would increase.
The rate of production of E would remain the same.
The rate of production of L would remain the same.
The rate of production of all products D, E, J and K would decrease.
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
16.
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
Substance X (a mineral ion) is actively transported into cells. Equal-sized samples of
cells were placed in media containing different concentrations of X for an hour. The
intracellular concentration of X was then measured. All other metabolic conditions were
maintained at the optimum level. The graph below shows the results.
From the information given above, which one of the following would account for the level
region of the graph labelled Y?
A
B
C
D
17.
A respiratory inhibitor had been introduced.
All the active transport carriers had been operating at their maximum rate.
The active transport carriers had been inactivated by a non-competitive inhibitor.
As the internal concentration of X rose, more of the substance X was metabolised.
In the following branched metabolic pathway, a dotted arrow with a minus sign
symbolizes inhibition of a metabolic step by an end product:
Which reaction would prevail if both Q and S were present in the cell in high
concentrations?
A
B
C
D
LM
MO
LN
RS
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
18.
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
When investigating enzyme/substrate interactions, which one of the following would be
expected to show a linear relationship under constant conditions?
A
B
Amount of product against time, with the amount of substrate limited.
Rate of reaction against enzyme concentration, in the presence of excess
substrate.
Rate of reaction against enzyme concentration, with the amount of substrate
limited.
19.
Revision Package
Rate of reaction against substrate concentration, with the amount of enzyme
limited.
In the production of isoleucine from threonine in bacteria (Biochemical Pathway 1 [BP
1]), the end product acts as an inhibitor of the first enzyme in the pathway. In the
production of arginine (Biochemical Pathway 2[BP 2]), the end product has no influence
on other enzymes in the pathway. It is reasonable to conclude that in
A
B
C
D
BP 1, if the production of enzyme 3 stops there would be continuous production of
isoleucine.
BP 2, if the production of enzyme 3 stops there would be continuous production of
arginine.
BP 1, providing all enzymes are present, the production of isoleucine would be
continuous if there was a continuous supply of threonine.
BP 2, providing all enzymes are present, the production of arginine would be
continuous if there was a continuous supply of substrate.
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
20.
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
The graph shows the amount of product formed by a standard concentration of enzyme
and a standard concentration of substrate at a temperature of 15 C.
Which graph shows the effect on the activity of the enzyme of increasing the temperature
to 20 C?
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
Structured Questions
1 Lysozyme is an enzyme found in many places within the human body. It consists of a single
polypeptide folded into a complex shape. Fig. 1.1 shows a ribbon model of lysozyme.
Fig. 1.1
(a) With reference to Fig. 1.1, describe region X. [2]
Lysozyme is one of the many hydrolytic enzymes found within a lysosome. The lysosome enzymes
are only active over a narrow range of pH, with an optimum of pH 5. The pH of the cytoplasm is 7.2.
The internal pH of lysosomes is maintained by actively concentrating H+ ions in the lysosome using
proton pumps.
(b) Describe how H+ ions could be moved across the lysosome membrane. [3]
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
(c) Explain why enzymes from a leaky damaged lysosome may not destroy the cell contents. [2]
(d) Suggest why the lysosome membrane is not destroyed by the enzymes in the lysosome. [2]
[Total: 9 marks]
2 Detergent is a mixture that is used for cleaning purposes. Some of the components present in the
detergent include enzymes, preservatives, pH buffers, water softener and oxidizers.
(a) Suggest one enzyme that may be found in detergent and state its possible function. [1]
(b) (i) Suggest a reason why pH buffers are found in detergent. [1]
(ii) Explain what will happen if the pH deviates from the optimum pH for enzyme activity.[3]
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
(c) Explain why laundry should not be washed with ice-cold water. [3]
(d) Explain how the structure of the enzymes in the detergent is stabilized [2].
[Total: 10 marks]
3 Fig. 4.1 below shows a model of the enzyme chymotrypsin. Chymotrypsin catalyses the hydrolysis
of peptide bonds of proteins. The active site of chymotrypsin is located in a slight depression on
one side of the molecule. Three amino acids form the active site. These three amino acids are
some distance apart on the polypeptide chain but close together in the active site.
Fig. 4.1
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
(a) Describe how amino acid residues at different positions in the protein may be brought together
in the active site when the enzyme is synthesised. [2]
(b) Explain how a substrate may be attached to the enzyme. [3]
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
Fig. 4.2 shows the effects of increasing substrate concentration on the rate of an enzyme-catalysed
reaction at a temperature of 35C and a constant pH.
Graph 1
Graph 2
Graph 3
Fig. 4.2
(c) With reference to Fig. 4.2, explain why an increase in substrate concentration at low substrate
concentrations increases the rate of reaction but an increase at high substrate concentrations
does not have the same effect. [4]
[Total: 9 marks]
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
4
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
Enzymatic browning is one of the most important colour reactions that affect fruits. Cut apples
turned brown after exposure to air within minutes. This browning reaction is catalysed by the
enzyme polyphenol oxidase (PPO), which is abundant in the flesh of the apples. PPO converts ironcontaining phenol compounds in the presence of oxygen to melanin in a series of polymerization
reactions. Fig. 5.1 shows the structure of the PPO enzyme.
Fig. 5.1
(a) With reference to Fig. 5.1, describe the structure of the PPO enzyme. [3]
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
(b) Suggest the role of PPO in melanin synthesis in apples. [2]
Fig. 5.2 shows the results of tests to determine the optimum temperature for the activity of PPO.
Percentage of
phenols
converted into
melanin in 10
minutes / %
Fig. 5.2
(c) With reference to Fig. 5.2,
(i) state the optimum pH and temperature for the enzyme PPO. [1]
pH:
Temperature:
(ii) account for the curve at pH 8. [4]
[Total: 10 marks]
Anglo-Chinese Junior College
Revision Package
H2 & H1 Biology Enzymes
Essays
1
(a) Describe the roles of enzymes in DNA replication (KIV for DNA & Genomics)
[8]
(b) Explain the effect of a competitive inhibitor on the rate of enzyme activity.
[4]
(a) Describe the effects of pH and temperature on enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
[8]
(b) Distinguish between competitive and non-competitive inhibition of enzyme action.
[7]
(c) Explain the effect of enzyme and substrate concentration on the rate of enzyme catalyzed
reactions.
[5]
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Cell Structure and Function: Responses To Data Analysis ActivitiesDocumento2 pagineCell Structure and Function: Responses To Data Analysis ActivitiesWesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 Sem 1 Finals W AnsDocumento9 pagine2016 Sem 1 Finals W AnsWesley Tan100% (1)
- 15 Feb - VIVA Foundation X NUS Life Sciences Sharing On Paediatric OncologyDocumento7 pagine15 Feb - VIVA Foundation X NUS Life Sciences Sharing On Paediatric OncologyWesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Big List of MMI QuestionsDocumento15 pagineBig List of MMI QuestionsWesley Tan100% (4)
- NUS Scholarships Referee Information SheetDocumento2 pagineNUS Scholarships Referee Information SheetWesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Year 2013 in Review: Clinical A/Prof Tan Suat Hoon, DirectorDocumento4 pagineYear 2013 in Review: Clinical A/Prof Tan Suat Hoon, DirectorWesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ls Studyplan (AY1617)Documento1 paginaLs Studyplan (AY1617)Wesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiration EssaysDocumento4 pagineRespiration EssaysWesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2012 A Level Answers P1 and P2 Compiled FinalDocumento12 pagine2012 A Level Answers P1 and P2 Compiled FinalWesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 JC 1 Promos Revision Package - H1 - Revision Package 2 - ANS (Final)Documento19 pagine2014 JC 1 Promos Revision Package - H1 - Revision Package 2 - ANS (Final)Wesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- JC1 SSP 2014 (Redox + Atomic Structure) - Teachers (Final)Documento5 pagineJC1 SSP 2014 (Redox + Atomic Structure) - Teachers (Final)Wesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 J2 H1 Teaching Prog (Students)Documento2 pagine2015 J2 H1 Teaching Prog (Students)Wesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Https Doc 14 7c Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentDocumento5 pagineHttps Doc 14 7c Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentWesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture COPEG Qns (Last Lect)Documento8 pagineLecture COPEG Qns (Last Lect)Wesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- H2 Biomolecules QuestionsDocumento18 pagineH2 Biomolecules QuestionsWesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- H2 DNA and Genomics QuestionsDocumento18 pagineH2 DNA and Genomics QuestionsWesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- H2 Cell Division QuestionsDocumento18 pagineH2 Cell Division QuestionsWesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- H2 Evolution QuestionsDocumento27 pagineH2 Evolution QuestionsWesley Tan100% (1)
- Comparison Carbo Protein Lipids (Students)Documento6 pagineComparison Carbo Protein Lipids (Students)Wesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- H2 Cell Structure QuestionsDocumento15 pagineH2 Cell Structure QuestionsWesley Tan100% (2)
- Weekly Schedule - Daniel WongDocumento1 paginaWeekly Schedule - Daniel WongWesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- SSP Biomol QnsDocumento4 pagineSSP Biomol QnsWesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology SSP 2015 Govab AnsDocumento3 pagineBiology SSP 2015 Govab AnsWesley TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Quizbee 2019 Nutrition Month EasyDocumento4 pagineQuizbee 2019 Nutrition Month EasyJaenicaPaulineCristobalNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecules Are DNA Molecules Formed by Laboratory Methods of Genetic RecombinationDocumento2 pagineMolecules Are DNA Molecules Formed by Laboratory Methods of Genetic RecombinationMarygrace Broñola100% (2)
- Multiple Choice Questions: Patterns of Chromosome InheritanceDocumento10 pagineMultiple Choice Questions: Patterns of Chromosome InheritanceArwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Prefixes, Suffixes, Roots PDFDocumento37 paginePrefixes, Suffixes, Roots PDFVu SangNessuna valutazione finora
- Fig.1: Vegetative Morphology of EctocarpusDocumento21 pagineFig.1: Vegetative Morphology of EctocarpusAmrit Mund EducationalNessuna valutazione finora
- Debate: Gender Reassignment and Assisted ReproductionDocumento2 pagineDebate: Gender Reassignment and Assisted ReproductionArif Tri Prasetyo HarunNessuna valutazione finora
- Winkelman - Shamanism and The Origins of Spirituality and Ritual HealingDocumento32 pagineWinkelman - Shamanism and The Origins of Spirituality and Ritual Healinggustavo zelayaNessuna valutazione finora
- From Start To Phase 1 in 30 Months - Insilico MedicineDocumento9 pagineFrom Start To Phase 1 in 30 Months - Insilico MedicinejeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Divinicus PDF Ebook Version - 2019Documento250 pagineDivinicus PDF Ebook Version - 2019Frejya AuroraNessuna valutazione finora
- שיטות מעבדה ביולוגיה מולקולריתDocumento53 pagineשיטות מעבדה ביולוגיה מולקולריתKamal KabhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Smart Test Series: 1-Write Short Answers To Any 5 QuestionsDocumento1 paginaSmart Test Series: 1-Write Short Answers To Any 5 QuestionsYOUR FEARNessuna valutazione finora
- Bioremediation of PesticidesDocumento3 pagineBioremediation of PesticidesSunil VohraNessuna valutazione finora
- Historyof Genetics QuizDocumento2 pagineHistoryof Genetics QuizGelli NancaNessuna valutazione finora
- Davis 2017 Biology of ForgettingDocumento14 pagineDavis 2017 Biology of ForgettingWA YFNessuna valutazione finora
- Effectiveness of Fenbendazole and Metronidazole Against Giardia Infection in Dogs Monitored For 50-Days in Home-ConditionsDocumento7 pagineEffectiveness of Fenbendazole and Metronidazole Against Giardia Infection in Dogs Monitored For 50-Days in Home-ConditionsBrieNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrez Digital Tools and UtilitiesDocumento80 pagineEntrez Digital Tools and UtilitiesGeorge Sebastian AntonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Forensics 12-13 TestDocumento3 pagineForensics 12-13 Testmemmy3697Nessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Linkage, Recombination, Mapping - BIO231-FKDocumento9 pagineGenetic Linkage, Recombination, Mapping - BIO231-FKmalik husnainNessuna valutazione finora
- Macromolecules WorksheetDocumento6 pagineMacromolecules WorksheetMyka Zoldyck0% (1)
- Exam1 HighlightedDocumento19 pagineExam1 HighlightedCatherine FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestion and Absorption 111Documento6 pagineDigestion and Absorption 111Brijesh BalachandranNessuna valutazione finora
- Conservation of Embryo and Ovules 1Documento41 pagineConservation of Embryo and Ovules 1INDRA RACHMAWATINessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Concepts in Penicillium and Aspergillus ClassificationDocumento451 pagineModern Concepts in Penicillium and Aspergillus ClassificationThaina Araújo50% (2)
- An Introduction To Haematopoiesis Prof Vernon Louw Clinical Haematology University of Cape TownDocumento35 pagineAn Introduction To Haematopoiesis Prof Vernon Louw Clinical Haematology University of Cape TownAmmaarah IsaacsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Detritus Food-Web and The Diversity of Soil Fauna As Indicators of Disturbance Regimes in Agro-EcosystemsDocumento9 pagineThe Detritus Food-Web and The Diversity of Soil Fauna As Indicators of Disturbance Regimes in Agro-EcosystemsFábio Luís MostassoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Human RaceDocumento36 pagineThe Human RaceHazel HeramisNessuna valutazione finora
- Patient's Name:: Ms. Bharti PorwalDocumento1 paginaPatient's Name:: Ms. Bharti PorwalHimanshuNessuna valutazione finora
- High Sensitivity CRP - IMMULITE and IMMULITE 1000 - Rev 06 DXDCM 09017fe980297730-1538194293759Documento36 pagineHigh Sensitivity CRP - IMMULITE and IMMULITE 1000 - Rev 06 DXDCM 09017fe980297730-1538194293759Deqsa Corporativo0% (1)
- IUCN Redlist Categories and CriteriasDocumento38 pagineIUCN Redlist Categories and CriteriasMaria MahusayNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Case Study of Water Quality and Climate Change Resulting A Mass Mortality of Fish at Taj Boudi of BijapurDocumento7 pagineEnvironmental Case Study of Water Quality and Climate Change Resulting A Mass Mortality of Fish at Taj Boudi of BijapurIOSRjournalNessuna valutazione finora