Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
7 PDF
Caricato da
Ashish MeenaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
7 PDF
Caricato da
Ashish MeenaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
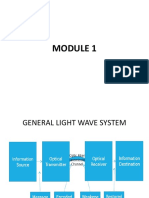
Guided Modes: Step-index and
Graded Index Fibers
Number of Modes:
2
Step index fiber: V /2
Graded index fiber (parabolic ref.index profile)
2
: V /4
Photonic Crystal Fibers
New optical fiber structure (1990s)
Initially called Holey fibers, later termed Photonic
crystal fibers, or microstructured fibers.
Basic difference between PCF and a conventional fiber
cladding region (and sometimes the core regions) of a
PCF contain air holes, which run along the entire length
of the fiber.
Differences in the light guiding properties:
Conventional fiber: material properties of the core and cladding
PCF fiber: the structural arrangement creates an internal
microstructure, which enables another dimension for light control
PCF fibers..
Light guiding characteristics: determined by the size
and spacing (pitch) of the holes in the microstructure
and the refractive index
PCF categories:
Index guiding fibers
Photonic bandgap fibers
Index guiding PCF: has a high index core surrounded
by a lower-index cladding; light transmission
mechanism similar to that in a conventional fiber.
Effective refractive index depends on the wavelength,
and the size and pitch of the holes
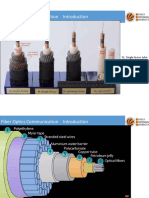
Index Guiding PCF
Fiber has a solid core
surrounded by a cladding
region containing air holes
running along the length of
the fiber
Core and cladding made of
the same material (say, pure
silica)
The air holes lower the
effective refractive index of
the cladding region (n=1 for
air, 1.45 for silica)
The above microstructural
arrangement creates a stepindex optical fiber
Source: Gerd Keiser, Optical
th
Fiber Communications, 4 ed.,
Tata McGraw-Hill, 2008:
Chapter 2.
Photonic Bandgap (PBG) Fiber
Source: Gerd Keiser, Optical
Fiber Communications, 4
Tata McGraw-Hill, 2008:
Chapter 2.
th
ed.,
Fiber has a hollow core
surrounded by a cladding
region which contains air
holes running along the
length of the fiber
Functional principle of PBG
fiber analogous to the role of
the periodic crystalline
lattice in a semiconductor
(blocks electrons from
occupying a bandgap
region)
Hollow core acts as a
defect in the photonic
bandgap structure creates
a region for the light to
propagate
Index Guiding PCF.
Advantages
Very low losses
High resistance to darkening effects from
nuclear radiation
- Can support single mode operation over
wavelengths in the range 300 nm to 2000 nm.
Mode field area of the PCF is much higher than
that of a conventional fiber
Can transmit high optical power levels
without encountering nonlinear effects
PBG Fiber .
Features (Source: John Senior, Optical Fiber Communications, 3rd
edition, Pearson Education, 2010, chapter 2.)
Periodic arrangement of cladding air holes provides for the
formation of a photonic bandgap in the transverse plane of the
fiber
Wavelengths within the bandgap cannot propagate
perpendicular to the fiber axis (i.e. in the cladding)
Light can be confined to propagate within a region where the ref
index is lower than the surrounding material
PBG fibers guide only in certain wavelength bands
Possible to have wavelengths at which higher order modes are
guided while the fundamental mode is not
Propagation losses are not as low as other fibers
Tend to be highly dispersive with narrow transmission windows
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Optics Ajay Ghatak, Optics, Tata McGraw Hill Education, 5th Edition, 2012Documento12 pagineOptics Ajay Ghatak, Optics, Tata McGraw Hill Education, 5th Edition, 2012Fadil N.Muhammad58% (12)
- ECE532 Sheet 2Documento1 paginaECE532 Sheet 2Mohamad El-MasryNessuna valutazione finora
- FTTH Basics and Network DesignDocumento43 pagineFTTH Basics and Network DesignJavier50% (2)
- 8501-00-9080 - F - 01 (1) User ManualDocumento109 pagine8501-00-9080 - F - 01 (1) User ManualRecep TorunNessuna valutazione finora
- Photonic Crystal FibersDocumento10 paginePhotonic Crystal FibersRajkeen ChamanshaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Phoyonic Crystal Fiber - Aziz MahfoudDocumento17 paginePhoyonic Crystal Fiber - Aziz MahfoudAna SimovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Fiber: By: Warqa'a Hashim Alkhaled Asst - Prof. DR Jinan.F.Mahdi April - 2020Documento25 pagineOptical Fiber: By: Warqa'a Hashim Alkhaled Asst - Prof. DR Jinan.F.Mahdi April - 2020noor deenNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Training in Signal Engineering and Telecommunication NCR, Lucknow Division, Kanpur CentralDocumento12 pagineIndustrial Training in Signal Engineering and Telecommunication NCR, Lucknow Division, Kanpur CentralPawan VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Photonic Crystal FibersDocumento10 paginePhotonic Crystal FibersnandiniNessuna valutazione finora
- RefDocumento8 pagineRefruhul aminNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter One Introduction To Fiber OpticDocumento28 pagineChapter One Introduction To Fiber OpticHogr RgohNessuna valutazione finora
- Photonic CrystalDocumento39 paginePhotonic CrystaldhanukrishnagNessuna valutazione finora
- Prof. Vipin Kumar JainDocumento35 pagineProf. Vipin Kumar JainDeepak SwamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement of The Attenuation of The OpDocumento9 pagineMeasurement of The Attenuation of The OpsuryaNessuna valutazione finora
- AP 2 Module 4Documento39 pagineAP 2 Module 4Anshuman NandanNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic: Optical Fiber: Design By: Rahul Ohlan IndiaDocumento33 pagineTopic: Optical Fiber: Design By: Rahul Ohlan IndiaArnela CamovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Fiber: By: V Jaithra Reddy PVG Madan Gopal B Srikanth ReddyDocumento12 pagineOptical Fiber: By: V Jaithra Reddy PVG Madan Gopal B Srikanth Reddymadan gopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Fiber PPT APDocumento14 pagineOptical Fiber PPT APSathwik PalnatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical FiberDocumento33 pagineOptical FiberUmesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Phys Fibre Optics MBADocumento45 paginePhys Fibre Optics MBAAYUSH MADHAURIYANessuna valutazione finora
- 9. bản tiếng anhDocumento37 pagine9. bản tiếng anhĐặng Thái NhậtNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber Optics-Understanding The BasicsDocumento7 pagineFiber Optics-Understanding The BasicsAmir SalahNessuna valutazione finora
- Holey Fibers: Suchita KaundinDocumento17 pagineHoley Fibers: Suchita KaundinIndra PrasetiyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer NetworkingDocumento3 pagineComputer NetworkingRanNa ArhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Dnyanasadhana College, Thane: Topic-Fiber OpticsDocumento16 pagineDnyanasadhana College, Thane: Topic-Fiber OpticscharlieNessuna valutazione finora
- Dnyanasadhana College, Thane: Topic-Fiber OpticsDocumento16 pagineDnyanasadhana College, Thane: Topic-Fiber OpticsShriram RautNessuna valutazione finora
- BSNL Training ReportDocumento33 pagineBSNL Training ReportAnil KamathNessuna valutazione finora
- Op Com SeminarDocumento16 pagineOp Com Seminarmuskan sNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Fiber SeminarDocumento20 pagineOptical Fiber Seminaryash patil100% (1)
- Chapter Twenty-Four: Fiber OpticsDocumento26 pagineChapter Twenty-Four: Fiber OpticsAkshay SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Twenty-Four: Fiber OpticsDocumento26 pagineChapter Twenty-Four: Fiber OpticsbhagNessuna valutazione finora
- OfcDocumento27 pagineOfcKulvinder SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Principal and Working of Optical FiberDocumento8 paginePrincipal and Working of Optical FiberminigamingindoNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical FiberDocumento17 pagineOptical FiberAkash MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Analysis of A 2D-Photoniccrystal Fiber Structure With Ultra-Flattened Dispersion and Single Mode Operation Over A Wide Range of WavelengthDocumento4 pagineDesign and Analysis of A 2D-Photoniccrystal Fiber Structure With Ultra-Flattened Dispersion and Single Mode Operation Over A Wide Range of WavelengthillyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Submitted To:-Er. Somesh Malhotra Er. Atul Agnihotri (Summer Training In-Charge)Documento22 pagineSubmitted To:-Er. Somesh Malhotra Er. Atul Agnihotri (Summer Training In-Charge)SagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Fiber CablesDocumento5 pagineOptical Fiber CablessoumikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Report About Optical Fiber CommunicationDocumento13 pagineReport About Optical Fiber CommunicationALI100% (1)
- PCF RussellDocumento3 paginePCF RussellhackerofxpNessuna valutazione finora
- Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited Regional Telecom Training Center LucknowDocumento26 pagineBharat Sanchar Nigam Limited Regional Telecom Training Center LucknowNischay UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Oc Module 1-6 PDFDocumento162 pagineOc Module 1-6 PDFTintu TrmNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber OpticsDocumento16 pagineFiber OpticsrajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec15 ES475 2023 Upload PDFDocumento31 pagineLec15 ES475 2023 Upload PDFEmad RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ofc PDFDocumento14 pagineOfc PDFLãkßhmáñ MødäláNessuna valutazione finora
- Optic FiberDocumento31 pagineOptic Fiberkeregi100% (1)
- Optical Fiber Communication: PrefaceDocumento11 pagineOptical Fiber Communication: PrefaceSushanth reddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber OpticsDocumento16 pagineFiber OpticsFarhan AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber OpticsDocumento154 pagineFiber Opticsboomar100% (2)
- Optical FiberDocumento47 pagineOptical FiberAbhijith S.SNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Fiber CommunicationDocumento71 pagineOptical Fiber CommunicationWasimul Haq WasimulNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber Optic Cable Core-How Much Do You Know About It?Documento16 pagineFiber Optic Cable Core-How Much Do You Know About It?UmairNessuna valutazione finora
- BEC701 - Fibre Optic Communication PDFDocumento201 pagineBEC701 - Fibre Optic Communication PDFMax DurendNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber Optics: Unit 3Documento16 pagineFiber Optics: Unit 3Vignesh AppavuNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical FiberDocumento9 pagineOptical Fiberbavip65344Nessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Optical Communications - SplauDocumento32 pagine02 Optical Communications - SplauFalco GalvanoNessuna valutazione finora
- QDT - CH 05 - Soi QuangDocumento162 pagineQDT - CH 05 - Soi QuangFlo NghẾchNessuna valutazione finora
- FIBER ClassDocumento26 pagineFIBER ClassSoumen ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber Optics and Laser Instrumentation - Module 1Documento35 pagineFiber Optics and Laser Instrumentation - Module 1maheshnaikm143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement of Attenuation of The Optical FiberDocumento38 pagineMeasurement of Attenuation of The Optical Fiberare you0% (1)
- Introduction To Nayatel TransmissionDocumento29 pagineIntroduction To Nayatel TransmissionmaryamNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber Optics PDFDocumento14 pagineFiber Optics PDFkariuki muneneNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook of Fiber Optics: Theory and ApplicationsDa EverandHandbook of Fiber Optics: Theory and ApplicationsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Coriolli'S Component Apparatus: Experiment No.1Documento5 pagineCoriolli'S Component Apparatus: Experiment No.1Ashish MeenaNessuna valutazione finora
- QrmethodDocumento13 pagineQrmethodAshish MeenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress (Mechanics) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaqDocumento34 pagineStress (Mechanics) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaqAshish MeenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Visual CommunicationDocumento33 pagineVisual CommunicationAshish MeenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress Concentration - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento6 pagineStress Concentration - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAshish MeenaNessuna valutazione finora
- This Course Will Be Taught by Three Faculty Members (From India and Japan) As FollowsDocumento2 pagineThis Course Will Be Taught by Three Faculty Members (From India and Japan) As FollowsAshish MeenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1Documento12 pagineExperiment 1Ashish Meena100% (1)
- Automator Marking LasersDocumento36 pagineAutomator Marking Laserskaniappan sakthivelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Systems DWDM Primer Oct03Documento87 pagineCisco Systems DWDM Primer Oct03anon-983826100% (5)
- IFE96Documento2 pagineIFE96MuhamadAprilialdiNessuna valutazione finora
- AQA PHYA2 W Specimen PaperDocumento13 pagineAQA PHYA2 W Specimen Paper04rchoudNessuna valutazione finora
- People - Details - EE5 Website PDFDocumento2 paginePeople - Details - EE5 Website PDFBanasshri SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drop Wire (DW) Cable - 4 Core - Specifications PDFDocumento3 pagineDrop Wire (DW) Cable - 4 Core - Specifications PDFinti lestariNessuna valutazione finora
- Laser Power PDFDocumento92 pagineLaser Power PDFصديقكالوفيNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Budget-Tx-Rx-dBmDocumento1 paginaOptical Budget-Tx-Rx-dBmpankajengNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Training ReportDocumento23 paginePractical Training Reportscolastica nyegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rre Ry Ry1 A2a MP014 Pe DD Tel A0 DWG 00144Documento1 paginaRre Ry Ry1 A2a MP014 Pe DD Tel A0 DWG 00144waz ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Photoelectric BannerDocumento12 paginePhotoelectric BannerEr2406Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber Optics NotesDocumento7 pagineFiber Optics NotesvarunkumargongallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Fibre: Kendriya Viyalaya No.2, Colaba, Mumbai - 05Documento16 pagineOptical Fibre: Kendriya Viyalaya No.2, Colaba, Mumbai - 05Prerna AmzareNessuna valutazione finora
- RRU3260 Hardware Description (02) (PDF) - enDocumento34 pagineRRU3260 Hardware Description (02) (PDF) - enАлексей АNessuna valutazione finora
- Free Space Optics and Submarine Laser Communication Systems For Egyptian Climate Weather in The Presence of Atmospheric TurbulenceDocumento12 pagineFree Space Optics and Submarine Laser Communication Systems For Egyptian Climate Weather in The Presence of Atmospheric TurbulenceijsretNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2: Basic Concepts Line Configuration - Defines The Attachment of Communication Link - A Physical Communication Pathway That Transfers DataDocumento13 pagineTopic 2: Basic Concepts Line Configuration - Defines The Attachment of Communication Link - A Physical Communication Pathway That Transfers Datashavali56Nessuna valutazione finora
- NR Electric Automation CatalogDocumento34 pagineNR Electric Automation CatalogmahnoorNessuna valutazione finora
- External Cavity Fiber LaserDocumento4 pagineExternal Cavity Fiber LaserAlok MehtaNessuna valutazione finora
- XDM-1000 IMM ETSI A08 8.1 enDocumento508 pagineXDM-1000 IMM ETSI A08 8.1 enVossKarr100% (1)
- 43 1821 NF 02 - Um - RapDocumento25 pagine43 1821 NF 02 - Um - RapfkkgđkjkNessuna valutazione finora
- Optct 2022Documento15 pagineOptct 2022ajaykumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ccna (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Certification and Training ProgramDocumento469 pagineCcna (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Certification and Training ProgramKulvir SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- OIF Co Packaging FD 01.0Documento53 pagineOIF Co Packaging FD 01.0Jason ChenNessuna valutazione finora
- FSW M 1x2 Mini Optical Switch Data Sheet 520401Documento5 pagineFSW M 1x2 Mini Optical Switch Data Sheet 520401GLsun MallNessuna valutazione finora
- M4NS, M4ysDocumento4 pagineM4NS, M4ysLuis LimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laser EfficiencyDocumento8 pagineLaser Efficiencykaushik4208100% (3)
- Translucent Concrete: Omkar KadamDocumento14 pagineTranslucent Concrete: Omkar KadamJakka hitheshiniNessuna valutazione finora