Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
4EATDiagServ PDF
Caricato da
Йордан ВасилевDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
4EATDiagServ PDF
Caricato da
Йордан ВасилевCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Subaru
4EAT Diagnosis
and Service
Changing the engine oil would seem to
be such a simple procedure. Yet a mistake can yield catastrophic results. The
transmission in the photo above was
being replaced due to a differential failure. The differential failure was not
caused by a part failure, but rather by
operator error. The differential fluid had
been drained during an oil service, rather
than the engine oil. The drained fluid
was not replaced, and a few hundred
miles later, the differential was
destroyed.
This error may have been caused by
unfamiliarity with Subaru vehicles or simple inattentiveness. In any case, its not a
mistake any of us would want to make.
Although we ran this information in an
earlier End Wrench, seeing the destroyed
transaxle drove home the fact that some
technicians still need to be reminded of the
correct service procedures.
When performing an oil change service
on Subaru vehicles, dont confuse the
drain plugs and filters located under the
vehicle. Subaru models produced over the
past several years feature an under-engine
cover. This cover greatly reduces the accumulation of dirt and grime on the engine
and also reduces the overall coefficient of
drag of the vehicle. However, it does limit
the access to the engine oil drain plug and
engine oil filter.
Items to remember when performing
services on Subaru vehicles:
The engine oil filter is located at the
front of the engine.
The engine oil pan and 17 mm oil drain
plug are painted black and are located
directly under the engine above the
under-engine cover.
The engine oil dipstick is located
under the hood, on the front drivers
corner of the engine.
The transmission front differential is
bright aluminum with a gold-colored
21 mm drain plug. This housing is
bolted directly behind the engine and
is filled with GL-5 gear oil.
The differential dipstick is located
under the hood near the firewall, on
the passenger side of the differential
housing.
The transmission pan is black. Its 17
mm drain plug is located on the drivers side of the pan. The drain plug is
normally silver in color, but black
drain plugs have also been installed on
occasion. The transmission is filled
with Genuine Subaru factory
fill AT/PS Fluid P/N SOA868V9240.
1999 and later Subaru vehicles
Continued on page 16.
14
4EAT Diagnosis and Service
Continued on page 18.
equipped with automatic transmissions have a screw-on filter on the drivers side of the transmission. Do not
confuse this with the engine oil filter.
The transmission filter does not
require service under normal conditions.
The automatic transmission fluid dipstick is under the hood, on the drivers
side of the car near the firewall.
All three dipsticks have yellow handles for easy identification.
Always confirm proper lubricant levels
in each unit after performing any service.
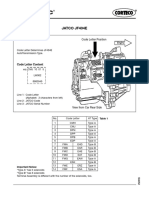
Transmission drain and filter
Engine oil drain plug (engine undercover in place)
Transmission dipstick
End Wrench
Differential drain plug
The
Differential dipstick (4EAT)
16
4EAT Diagnosis and Service
ATF and Differential
Level Inspection
ATF Level
1) Raise the ATF temperature to 60 to
80 degrees C (140 to 176 degrees F)
from 40 to 60 degrees C (104 to 140
degrees F) (when cold) by driving a distance of 5 to 10 km (3 to 6 miles).
Note: The ATF level
varies with fluid temperature. Pay attention
to the fluid temperature
when checking oil level.
Level Gauge
Measuring ATF level
2) Make sure the vehicle is level. After selecting all positions (P, R,
N, D, 3, 2,1), set the
selector lever in P
range. Measure fluid
level with the engine
idling.
Note: After running, idle the engine for
one or two minutes before measurement.
3) If the fluid level is below the center
between upper and lower marks, add
Genuine Subaru factory fill AT/PS Fluid
P/N SOA868V9240 until the fluid level
is found within the specified range
(above the center between upper and
lower marks). When the transmission is
hot, the level should be above the center of upper and lower marks, and when
it is cold, the level should be found
below the center of these two marks.
(32 degrees F is more than 25 minutes).
The time required for the transmission
fluid temperature to rise to 30 degrees C
(86 degrees F) when the atmospheric
temperature is 0 degrees C (32 degrees
F) is approximately eight minutes.
By running the vehicle
The time for the transmission fluid
temperature to rise to 60 degrees C (140
degrees F) with atmospheric temperature of 0 degrees C (32 degrees F) is
more than 10 minutes.
5) Method for checking fluid level upon
delivery or at periodic inspection:
Check fluid level after a warm-up run
of approximately 10 minutes. During
the warm-up period, the automatic
transmission functions can also be
checked.
Differential Gear Oil Level
1) Ensure the vehicle is on a level surface and the parking brake is set.
Note: Do not check the oil level nor add
oil to the case with the front end of the
vehicle raised; this will result in an
incorrect reading of the oil level.
2) Check whether the oil level is
between the upper (FF) and lower (LF)
marks. If it is below the lower limit
mark, add oil until the level reaches the
upper mark.
Oil Level Gauge
4) Time Required to Reach Proper Operating Temperature
By idling the engine
The time required for the transmission fluid temperature to rise to 60
degrees C (140 degrees F) when the
atmospheric temperature is 0 degrees C
Upper
Level
Lower
Level
Measuring differential gear oil level
Oil Leakage
It is difficult to accurately determine the precise position of an oil
leak, since the surrounding area
also becomes wet with oil. The
points listed below should be
checked for fluid leakage. Checking
Continued on page 20.
The
End Wrench
Caution:
Use care not to exceed the upper limit
level.
ATF level varies with temperature.
Remember that the addition of fluid to
the upper limit mark when the transmission is cold will result in the overfilling of fluid.
18
4EAT Diagnosis and Service
method is as follows:
(1) Place the vehicle on a lift, and
check whether the leaking oil is ATF
or not. The ATF is wine red in color,
and can be discriminated easily from
engine oil and gear oil.
(2) Wipe clean the leaking oil and
dust from a suspected area, using a
noninflammable organic solvent such
as carbon tetrachloride.
(3) Run the engine to raise the fluid
temperature, and set the selector
lever to D in order to increase the
fluid pressure and quickly detect a
leaking point. Also check for fluid
leaks while shifting select lever to
R, 2, and 1.
The places where oil seals and gaskets are applied are:
1) Jointing portion of the case
Transmission
case and oil pump
housing jointing
portion
Torque converter clutch case and
oil pump housing
jointing portion
Transmission
case and extension case jointing
portion
Differential gear breather
4) Automatic transmission case
Transmission case (defective casting)
Mating surface of oil pan
O-ring on the test plugs
Oil supply pipe connector
ATF cooler pipe connector and gasket
Oil pan drain plug
O-ring on the transmission harness
holder
Oil pump plugs
ATF breather
Shift lever oil seal
O-ring on the vehicle speed sensor 2
(Front)
O-ring on the turbine revolution sensor
ATF filter oil seal
5) Extension case
Potential mating surface leakage areas
Extension case
3) Oil pump housing
Oil pump housing (defective casting)
O-ring on the test plugs
The
End Wrench
2) Torque converter clutch case
Engine crankshaft oil seal
Torque converter clutch impeller
sleeve oil seal
ATF cooler pipe
connector
Torque converter clutch
Torque converter clutch case
Axle shaft oil
Torque converter clutch case seal
O-ring on the
outside diameter of axle shaft oil seal
holder
O-ring on the differential oil gauge
Differential oil drain plug
Location of steel balls
20
Extension case (defective casting)
O-ring on the vehicle speed sensor 1
(Rear)
Rear drive shaft oil seal
O-ring on the test plugs
Self-Diagnostics
Abnormal Display On AT
Oil Temp Indicator
When any on-board diagnostics
item is malfunctioning, the display on
the AT OIL TEMP indicator light blinks
from the time the malfunction is detected after starting the engine until the
ignition switch is turned OFF. The malfunctioning part or unit can be determined by a trouble code during onboard diagnostics operation. Problems
which occurred previously can also be
identified through the memory function. If the AT OIL TEMP indicator
does not show a problem (although a
problem is occurring), the problem can
be determined by checking the performance characteristics of each sensor
using the Select Monitor. The indicator
signal is as shown in the figure below.
Reading Trouble Codes Using the
Indicator Light
The AT OIL TEMP indicator light
flashes the code corresponding to the
faulty part.
The long segment (1.2 sec on) indicates a ten, and the short segment
(0.2 sec on) signifies a one
Clear Memory
The current trouble codes shown on
the display are cleared by turning the
ignition switch OFF after conducting
on-board diagnostics operation. Previous trouble codes, however, cannot be
cleared since they are stored in the
TCM memory, which is operating on
the back-up power supply. These trouble codes can be cleared by removing
the specified fuse (located under the
right or left lower position of the
instrument panel).
Clear Memory: Removal of No. 4 fuse
(for at least one minute)
The No. 4 fuse is located in the line
to the memory back-up power supply
of the TCM. Removal of this fuse clears
the previous trouble codes stored in the
TCM memory.
Be sure to remove the No. 4 fuse for
at least the specified length of time.
Otherwise, trouble codes may not be
cleared.
Trouble Code Flash Sequence
Trouble Code
Item
Content of Diagnosis
11
Engine speed signal
Detects open or shorted input signal circuit
27
ATF temperature sensor
Detects open or shorted input signal circuit
31
Throttle position sensor
Detects open or shorted input signal circuit
33
Vehicle speed sensor 2 (front)
Detects open or shorted input signal circuit
36
Torque converter turbine
Detects open or shorted input signal circuit
speed sensor
38
Torque control signal
45
Intake manifold pressure signal
Detects open or shorted input signal circuit
Detects open or shorted input signal circuit
71
Shift solenoid 1
Detects open or shorted output signal circuit
72
Shift solenoid 2
Detects open or shorted output signal circuit
73
Low clutch timing solenoid
Detects open or shorted output signal circuit
74
2-4 brake timing solenoid
Detects open or shorted output signal circuit
75
Line pressure duty solenoid
Detects open or shorted output signal circuit
76
2-4 brake duty solenoid
Detects open or shorted output signal circuit
77
Lock-up duty solenoid
Detects open or shorted output signal circuit
79
Transfer duty solenoid
Detects open or shorted output signal circuit
93
Vehicle speed sensor 1 (rear)
Detects open or shorted input signal circuit
21
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- AC Catalogue80Documento859 pagineAC Catalogue80Йордан ВасилевNessuna valutazione finora
- BMW Mini FWD CVTDocumento2 pagineBMW Mini FWD CVTЙордан ВасилевNessuna valutazione finora
- Derale CatalogDocumento32 pagineDerale CatalogЙордан ВасилевNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Choice: Filter CatalogueDocumento44 pagineAutomatic Choice: Filter CatalogueЙордан ВасилевNessuna valutazione finora
- 5HP30Documento43 pagine5HP30David Rosado100% (1)
- AC Vehicle IndexDocumento73 pagineAC Vehicle IndexЙордан ВасилевNessuna valutazione finora
- Mercedes Trans 7G Tronic PlusDocumento6 pagineMercedes Trans 7G Tronic PlusEdwin C. Walke100% (1)
- Dorsoduro 1200 ABS-ATC - SM - 2010 - GB - 897263 PDFDocumento408 pagineDorsoduro 1200 ABS-ATC - SM - 2010 - GB - 897263 PDFЙордан ВасилевNessuna valutazione finora
- Blz. 346-349 62TEDocumento4 pagineBlz. 346-349 62TEcmtassoNessuna valutazione finora
- Yamaha FJR 1300 - Service Manual (06) - Inglés PDFDocumento586 pagineYamaha FJR 1300 - Service Manual (06) - Inglés PDFЙордан Василев100% (2)
- AB60E Transmission OperationDocumento1 paginaAB60E Transmission OperationЙордан ВасилевNessuna valutazione finora
- 5HP30 Spare Parts CatalogDocumento46 pagine5HP30 Spare Parts CatalogAlberto VicenteNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Cambio Automatico SorentoDocumento8 pagineManual Cambio Automatico SorentoDione FreireNessuna valutazione finora
- 54 Mitsubishi 2 R4A51 V4A51 R5A51Documento8 pagine54 Mitsubishi 2 R4A51 V4A51 R5A51Йордан ВасилевNessuna valutazione finora
- 01J & 0AN (Multitronic) : in Line FWD CVT (Electronic Control)Documento3 pagine01J & 0AN (Multitronic) : in Line FWD CVT (Electronic Control)Йордан Василев0% (1)
- 2012 GTR ManualDocumento21 pagine2012 GTR ManualAkrae Acr0% (1)
- JF404EDocumento8 pagineJF404EЙордан Василев50% (6)
- 4eat Late PDFDocumento4 pagine4eat Late PDFЙордан Василев100% (1)
- 04CVT 57Documento11 pagine04CVT 57mklimesh2600Nessuna valutazione finora
- Valve Body and Mechatronic Service PDFDocumento44 pagineValve Body and Mechatronic Service PDFSamuel Zuniga100% (1)
- 04CVT 57Documento11 pagine04CVT 57mklimesh2600Nessuna valutazione finora
- 04CVT 57Documento11 pagine04CVT 57mklimesh2600Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4HP24ADocumento4 pagine4HP24Aruss-porter-7077Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4at Auto Trans PDFDocumento60 pagine4at Auto Trans PDFЙордан ВасилевNessuna valutazione finora
- Transmision Automatica AW 60-40LE Manual de Despiece y ReparacionDocumento3 pagineTransmision Automatica AW 60-40LE Manual de Despiece y ReparacionJose Francisco79% (28)
- 5 L 40 eDocumento2 pagine5 L 40 eLiviu NedaNessuna valutazione finora
- ZF 5hp24Documento46 pagineZF 5hp24Davidoff Red100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Armadio Presentation-2019Documento45 pagineArmadio Presentation-2019Subhash Singh TomarNessuna valutazione finora
- Investigation of Skew Curved Bridges in Combination With Skewed Abutments Under Seismic ResponseDocumento5 pagineInvestigation of Skew Curved Bridges in Combination With Skewed Abutments Under Seismic ResponseEditor IJTSRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis Essay Coming To Grips With GenesisDocumento11 pagineSynthesis Essay Coming To Grips With Genesisapi-259381516Nessuna valutazione finora
- Adriano Costa Sampaio: Electrical EngineerDocumento3 pagineAdriano Costa Sampaio: Electrical EngineeradrianorexNessuna valutazione finora
- Dairy Products Theory XIIDocumento152 pagineDairy Products Theory XIIDskNessuna valutazione finora
- Raneem AlbazazDocumento33 pagineRaneem AlbazazGordana PuzovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Us Navy To Evaluate Anti Submarine Warfare Training SystemDocumento2 pagineUs Navy To Evaluate Anti Submarine Warfare Training SystemVictor PileggiNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Code:TEX3021 Course Title: Wet Processing Technology-IIDocumento20 pagineCourse Code:TEX3021 Course Title: Wet Processing Technology-IINakib Ibna BasharNessuna valutazione finora
- Tabla de Avances de AcesoriosDocumento3 pagineTabla de Avances de AcesoriosPedro Diaz UzcateguiNessuna valutazione finora
- Test09 Eoc Algebra2 ReducedDocumento33 pagineTest09 Eoc Algebra2 ReducedkristymadimikeNessuna valutazione finora
- Quartile1 PDFDocumento2 pagineQuartile1 PDFHanifah Edres DalumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lima Indiana Oil FieldDocumento32 pagineLima Indiana Oil FieldCHARLES PATULAYNessuna valutazione finora
- Rectifier 5G High Density Embedded Power (3U Power Rack, Three Phase Four Wire) E...Documento4 pagineRectifier 5G High Density Embedded Power (3U Power Rack, Three Phase Four Wire) E...Lintas LtiNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 Benefits of CyclingDocumento8 pagine15 Benefits of CyclingJoycs PintoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tokyo Guidelines 2018Documento115 pagineTokyo Guidelines 2018Alik Razi100% (1)
- Wcdma Idle Mode (Ericsson)Documento29 pagineWcdma Idle Mode (Ericsson)Hosein ShahbaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Valdez, Shenny RoseDocumento3 pagineValdez, Shenny Roseyeng botzNessuna valutazione finora
- SOPDocumento16 pagineSOPjerome marquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Coffee Quality Manual by Abra Rand Nig Use IDocumento25 pagineCoffee Quality Manual by Abra Rand Nig Use IIpungNessuna valutazione finora
- Iodide and Bromide Ions in Brackish Water, Seawater, and Brines D 3869 - 04Documento12 pagineIodide and Bromide Ions in Brackish Water, Seawater, and Brines D 3869 - 04stevgonNessuna valutazione finora
- B737-3 ATA 23 CommunicationsDocumento112 pagineB737-3 ATA 23 CommunicationsPaul RizlNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic St. Package PDFDocumento28 pagineAtomic St. Package PDFSatvik RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostic Imaging of The Pharynx and Esophagus: Key PointsDocumento33 pagineDiagnostic Imaging of The Pharynx and Esophagus: Key PointsChutcharwan JintasoponNessuna valutazione finora
- 9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowerDocumento6 pagine9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowersivabharathamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Region 1 - Concreting Works Materials Prices - PHILCON PRICESDocumento9 pagineRegion 1 - Concreting Works Materials Prices - PHILCON PRICESMark Gregory RimandoNessuna valutazione finora
- EDS-A-0101: Automotive Restricted Hazardous Substances For PartsDocumento14 pagineEDS-A-0101: Automotive Restricted Hazardous Substances For PartsMuthu GaneshNessuna valutazione finora
- 500 TransDocumento5 pagine500 TransRodney WellsNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Dopant Diffusion - IDocumento32 pagineChapter 7 Dopant Diffusion - I강준호Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ujian 1 THN 4Documento13 pagineUjian 1 THN 4Che Shuk ShukaNessuna valutazione finora
- Indoor Air Quality Standard Procedures - 2014 RevDocumento12 pagineIndoor Air Quality Standard Procedures - 2014 RevFioriAmeliaHathawayNessuna valutazione finora