Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Granulation
Caricato da
maypeeeCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Granulation
Caricato da
maypeeeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
GRANULATION
primary powder particles are made to adhere to form larger multi-particle entities
commences after initial dry mixing of powders
typical size: 0.2 - 4.0 mm | tablet or capsule production : 0.2 - 0.5 mm
Reasons for granulation
prevent
segregation
of
the
constituents of the powder mix
control particle size distribution
machines fill by volume
improve flow properties of the mix
larger & isodiametric granules
improve compaction characteristics of
the mix
direct binder-binder bonding
reduce hazard of toxic materials
for slightly hygroscopic materials
convenient for storage & shipment
Granulation Methods
Dry Granulation
for drugs that do not compress well after wet granulation
for moisture-sensitive drugs
Slugging produce large tablet or slug by heavy-duty tableting press
Roller Compaction produce sheet of material by squeezing powder between 2 rollers
Wet Granulation
granulating fluid volatile & non-toxic
removed by drying
water, ethanol, isopropanol
water adv: non-flammable
disadv: affect drug stability (hydrolysis) ; longer drying time
Granulation Mechanisms
Pharmaceutical Granulation Equipment
Wet granulators
1) Shear granulators
have largely disappeared
traditional shear aka planetary
disadvantages:
long duration
need for several pieces of equipment
high material losses
2) High-speed mixer/granulators
mixing bowl stainless steel
three-bladed main impeller revolves horizontally
three-bladed auxiliary chopper breaker blade
revolves horizontally/vertically
switched on when moist mass is formed
break up wet mass
adv: powder blending, wet massing, granulation are all performed in same equipment
disadv: rapid progress from usable granule to unusable
High-speed
mixer/granulator
Collette UltimaGral
mixer
Oscillating
granulator
extensively used
two mixing shafts
granulate moist mass
type
Diosna type
variation of Diosna
type
mixing
bowl
1 L - 1250 L volumes
10 L - 200 L volumes
main blade
revolves horizontally; 150300 rpm
450-600 rpm (10 L)
150-200 rpm (200 L)
1500-3000 rpm
1500-300 rpm
60-100 rpm
wet mass: 300-500
kg/h
dry mass: 700-1200
kg/h
high-speed
chopper
rotor bars
optimum
fill capacity
3kg - 80kg batches
3) Fluidized-bed granulators
Fluidization air is blown/sucked through bed of unmixed powders to fluidize then mix
the particles
used extensively for fertilizers, herbicides, foodstuffs
granulating fluid sprayed from nozzle onto bed of powders
cause powder particles to adhere
exhaust filters prevents escape of material from granulation chamber
adv: all granulation processes are performed in one unit; process optimization
disadv: expensive; optimization of process needs extensive development work
4) Spray driers
dry granular product made from a solution/suspension
resultant granules: free-flowing hollow spheres
to make tablet granules
to convert hard elastic materials to ductile ones
adv: short drying time; minimal exposure to heat
for heat-sensitive materials
5) Spheronizers/pelletizers
pellets: for controlled drug release products
produce modified-release multiparticulates
Extrusion/Spheronization
make uniformly sized spherical particles
to produce multiparticulates for controlled drug release applications
adv: can incorporate high levels of active ingredients without producing large paticles;
minimal necessary excipients
Application
Controlled drug release pellets can contain 2 or more ingredients
incompatible ingredients can be manufactured in separate pellets
Processing increase bulk density
improve flow properties
reduce problems of dust
more labour-intensive process than other forms of granulation
last option to be considered for granulation methods
Desirable properties of pellets
uniform spherical shape
uniform size
good flow properties
reproducible packing
high strength
low friability
low dust
smooth surface
ease of coating
when coated: desired
drug release
Process/Main Steps
Dry mixing of ingredients achieve homogeneous powder dispersion
Wet massing produce sufficiently plastic wet mass
difference in granulation step: greater amount of granulation fluid;
importance of uniform dispersion of fluid
Extrusion form rod-shaped particles of uniform diameter
wet mass forced through dies
designs of extruder: 1) screw-feed (axial/endplate, dome, radial)
2) gravity-feed (cylinder roll, gear roll, radial
3) piston-feed
variables: 1) feed rate of wet mass
2) diameter of die
3) length of die
4) water content of wet mass
Spheronization round off the rods
dependent on frictional forces
spheres will not be formed if moist mass is too dry
Drying achieve desired moisture content
solute migration results to: 1) increased initial rate of dissolution
2) stronger pellets
3) modified surfaces
Screening (optional) achieve desired narrow size distribution
1) Melt granulation
heated extrusion of formulations
excipients melt & bind together
use of low melting point waxes
Rotorgranulation
direct manufacture of spheres from dry powder in one process
produce layered pellets
centrifugal force due to base plate high speed rotation
keeps moist mass at the edges of rotor
toroidal motion movement of mass
results in formation of spherical pellets
heated inlet air dries the resulting spheres
acts as positive-pressure seal
size range : 45 L 450 L
bowl & rotor disc diameters: 300-1400 mm
adjustable air gap manipulate resulting granule size
Dry Granulators
application of pressure to convert powders into granules
no use of a liquid
avoids heat/temperature combinations
necessary equipment: 1) machine for compressing dry powder into compacts/ flakes
2) mill for breaking intermediate products into granules
Slugging
large heavy-duty rotary press compact dry powders
slugs compacts made in the process
compacts are typically 25mm diameters by 10-15mm thick
hammer mill for breaking the compacts
disadv: work hardening results in poor compaction
compaction
powder mix squeezed between two counterrotating rollers
compressed sheet weak & brittle; breaks into flakes immediately
oscillating granulator convert flakes into granules
Protec or Hutt type vertical use feeder in the hopper for even flow of material
size range: 10-2000 kg/h
roller diameters: 100-450 mm
compaction forces: 16-64 kN/cm
roller lengths: 30-115 mm
advantages:
- economical
- low investment cost
- can cope with a wide range of materials
- process easily scaled up &
has uniform properties
Roller
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Art and Science of Granulation PresentationDocumento39 pagineThe Art and Science of Granulation PresentationumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Granulation إyu 2017Documento31 pagineGranulation إyu 2017Alaa AlzoubiNessuna valutazione finora
- GranulationDocumento32 pagineGranulationSantosh Payghan100% (1)
- Tablet PreparationDocumento51 pagineTablet PreparationNeha Dand100% (3)
- Granulation Machines Used For Dry Granulation and Wet GranulationDocumento18 pagineGranulation Machines Used For Dry Granulation and Wet GranulationShaban Danish100% (1)
- Tablet ManufacturingDocumento94 pagineTablet ManufacturingHamdi PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- L10 Size Enlargement - Part 2 PDFDocumento26 pagineL10 Size Enlargement - Part 2 PDFNhut NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Tablet Compression Consolidation and Compaction PhysicsDocumento7 pagineTablet Compression Consolidation and Compaction PhysicsYuppie Raj100% (1)
- Granulation TechniqueDocumento6 pagineGranulation TechniqueSrijonNessuna valutazione finora
- FiltrationDocumento50 pagineFiltrationDivya DharshiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Stability in PreformulationDocumento48 pagineStability in Preformulationmithaann2353Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmaceutical GranulesDocumento55 paginePharmaceutical GranulesWalaa abo fool100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Packaging TechnologyDocumento9 paginePharmaceutical Packaging TechnologyEditor IJTSRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Partech Size Enlargement PDFDocumento60 paginePartech Size Enlargement PDFPatricia de LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Granulation Part I PDFDocumento42 pagineGranulation Part I PDFSohib ZreegatNessuna valutazione finora
- Size EnlargementDocumento31 pagineSize EnlargementGladiador EdinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 5-FiltrationDocumento35 pagineLecture 5-FiltrationfathimashariffdeenNessuna valutazione finora
- Granulation ProcessDocumento5 pagineGranulation ProcessobrossaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tablet DefectsDocumento2 pagineTablet Defectsophelion2112Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 PDF Original PDFDocumento30 pagine3 PDF Original PDFDevang GondaliyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Granulation ProcessDocumento17 pagineGranulation ProcessSyed Waqas HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Granulation TechnologyDocumento32 pagineGranulation Technologysky.blueNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems and Remedies For Tablet CoatingDocumento7 pagineProblems and Remedies For Tablet CoatingAnowar HossainNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 - Disperse SystemsDocumento94 pagineLecture 2 - Disperse Systemsapi-370729792% (12)
- Tablet Technology EditedDocumento42 pagineTablet Technology EditedPramod Kc100% (1)
- FST 559 Unit Operations Mixing: Chapter OutcomesDocumento63 pagineFST 559 Unit Operations Mixing: Chapter OutcomesnajwaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1200i Engl Screen 04xDocumento14 pagine1200i Engl Screen 04xStreetRockFighterNessuna valutazione finora
- Size Reduction Unit OperationDocumento24 pagineSize Reduction Unit Operationashwinkumar4448Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dosage - Chapter 7Documento6 pagineDosage - Chapter 7kaukau4everNessuna valutazione finora
- GranulationDocumento32 pagineGranulationbalamuruganNessuna valutazione finora
- A Discussion On GranulationDocumento40 pagineA Discussion On Granulationtapasya50Nessuna valutazione finora
- Oral FormulationsDocumento10 pagineOral FormulationsSiddhartha MuppallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advance Granulation TechnologyDocumento81 pagineAdvance Granulation TechnologysyeedNessuna valutazione finora
- AssignmentDocumento12 pagineAssignmentAbdul Wahid OrakzaiNessuna valutazione finora
- T.Shivakumar: Kottam Institute of Pharmacy Jntu, A.PDocumento45 pagineT.Shivakumar: Kottam Institute of Pharmacy Jntu, A.PFree Escort ServiceNessuna valutazione finora
- APT-Pilot Plant Techniques-Capsules & Liquid OralsDocumento32 pagineAPT-Pilot Plant Techniques-Capsules & Liquid Oralssakumar5678Nessuna valutazione finora
- High Shear Granulation Scale UpDocumento36 pagineHigh Shear Granulation Scale Upckumar2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Particle Size EnlargementDocumento8 pagineParticle Size EnlargementZaid Bin GhaziNessuna valutazione finora
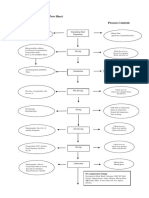
- Manufacturing Process Flow Sheet Manufacturing Step Process ControlsDocumento3 pagineManufacturing Process Flow Sheet Manufacturing Step Process ControlsHaroon RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmaceutical PelletsDocumento3 paginePharmaceutical PelletsMukesh TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Tablet Coating Process: Made byDocumento25 pagineTablet Coating Process: Made byYuppie RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Particle Size ReductionDocumento13 pagineParticle Size ReductionMarcel MrcNessuna valutazione finora
- Granulation: Ideal Characteristics of GranulesDocumento8 pagineGranulation: Ideal Characteristics of GranulesDr_Asma86100% (1)
- Pilot Plant Scale Up Techniques SeminarDocumento24 paginePilot Plant Scale Up Techniques Seminarsakumar5678Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class 1 Size Reduction ZZDocumento43 pagineClass 1 Size Reduction ZZZen EbeNessuna valutazione finora
- IpqcDocumento37 pagineIpqcAjitha AzhakesanNessuna valutazione finora
- Extraction-160805115400 2Documento141 pagineExtraction-160805115400 2Abdus SalamNessuna valutazione finora
- Extraction MethodsDocumento3 pagineExtraction MethodsMuhammadRafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- Uncoated TabletsDocumento1 paginaUncoated Tabletsfopcu91Nessuna valutazione finora
- Size ReductionDocumento9 pagineSize ReductionNur Muhammad Zam ZamNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Issues and Troubleshooting Fluid Bed GranulationDocumento6 pagineCurrent Issues and Troubleshooting Fluid Bed GranulationoanaciupercaNessuna valutazione finora
- Granulation Is Done ToDocumento9 pagineGranulation Is Done ToDebasmita KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Granulation Instruments PDFDocumento51 pagineGranulation Instruments PDFabdul hanan100% (1)
- Wet Granulation Process: Solvent (E.g. Ethanol, Isopropanol)Documento4 pagineWet Granulation Process: Solvent (E.g. Ethanol, Isopropanol)armstrongvinodrajNessuna valutazione finora
- CompoundingDocumento39 pagineCompoundingratanjeet pratap singhNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Khairul - Mixing PDFDocumento75 pagineDR Khairul - Mixing PDFMuhdAzrinNessuna valutazione finora
- Size Enlargement EquipmentDocumento43 pagineSize Enlargement EquipmentKeena Angeles100% (1)
- Spheronization - SlideDocumento36 pagineSpheronization - SlideNguyen PhuongNessuna valutazione finora
- Member 4 GranulationDocumento19 pagineMember 4 GranulationJoslin RozNessuna valutazione finora
- Spheronizer and Marumerisiers and Other Special Is Ed Granulation andDocumento56 pagineSpheronizer and Marumerisiers and Other Special Is Ed Granulation andNitu JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- TechnologyDocumento7 pagineTechnologymaypeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Clarification: Filtration Types of FiltrationDocumento4 pagineClarification: Filtration Types of Filtrationmaypeee100% (1)
- Organ SystemsDocumento4 pagineOrgan SystemsmaypeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Terms in Table Tennis: Juliefer May F. PleñosDocumento3 pagineTerms in Table Tennis: Juliefer May F. PleñosmaypeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- WrathDocumento1 paginaWrathmaypeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Banaue Rice TerracesDocumento1 paginaThe Banaue Rice TerracesmaypeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Prelim Reviewer HETARDocumento7 paginePrelim Reviewer HETARmaypeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ringer's Solution Stimulates The Blood Plasma of Frogs and Moistens The Exposed Muscle. Isotonic To Amphibians - Hypertonic To HumansDocumento2 pagineRinger's Solution Stimulates The Blood Plasma of Frogs and Moistens The Exposed Muscle. Isotonic To Amphibians - Hypertonic To Humansmaypeee100% (1)
- ZealotsDocumento3 pagineZealotsmaypeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Care - Quality (HETAR)Documento2 pagineCare - Quality (HETAR)maypeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Book FairDocumento1 paginaBook FairmaypeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Book FairDocumento1 paginaBook FairmaypeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Les MisérablesDocumento725 pagineLes MisérablesAnca Pop0% (1)
- Les MisérablesDocumento725 pagineLes MisérablesAnca Pop0% (1)
- Optimization and Analysis of NF3 in Situ Chamber Cleaning Plasmas 2004Documento12 pagineOptimization and Analysis of NF3 in Situ Chamber Cleaning Plasmas 2004Регина ШаяхметоваNessuna valutazione finora
- Carck WidthDocumento21 pagineCarck WidthPiyush VidyarthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bearing Capacity of Shallow Foundation by Terzhaghi TheoryDocumento13 pagineBearing Capacity of Shallow Foundation by Terzhaghi TheoryramNessuna valutazione finora
- MEM460 Report FoundryDocumento7 pagineMEM460 Report FoundrySiti Maizatul AkmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chile Wish List (Desmond Pilcher)Documento8 pagineChile Wish List (Desmond Pilcher)Ogalde LuisNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of Flaws in Pipe Girth WeldsDocumento17 pagineAssessment of Flaws in Pipe Girth Weldssherviny100% (1)
- Análisis de Ciclo de VidaDocumento12 pagineAnálisis de Ciclo de VidaOscar VicenteNessuna valutazione finora
- En 10008Documento40 pagineEn 10008TaTi Roecker100% (1)
- Mini Air BlowerDocumento19 pagineMini Air BlowerudaypavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sa 29 PDFDocumento26 pagineSa 29 PDFRaju SkNessuna valutazione finora
- Test For CARBOHYDRATESDocumento7 pagineTest For CARBOHYDRATESSoham N100% (2)
- Page From 651Documento1 paginaPage From 651palanaruvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Europrene INTOL POLIMERIDocumento28 pagineEuroprene INTOL POLIMERIRubik ArtNessuna valutazione finora
- HSN7471-75 R449A t0 - 35 TC 45Documento2 pagineHSN7471-75 R449A t0 - 35 TC 45KritsdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Homogeneous and Structured PCD-WC-Co Materials For DrillingDocumento9 pagineHomogeneous and Structured PCD-WC-Co Materials For Drillingdan_cunningham_15Nessuna valutazione finora
- Triboelectric NanogeneratorsDocumento537 pagineTriboelectric NanogeneratorsAviraj Limaye100% (1)
- GCSE Science 2011 Contents Guide Chemistry-1Documento12 pagineGCSE Science 2011 Contents Guide Chemistry-1airulyantiNessuna valutazione finora
- ESA MCQDocumento3 pagineESA MCQvamsikrishnamamidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Safety Data Sheet Visco XCDDocumento4 pagineMaterial Safety Data Sheet Visco XCDfs1640Nessuna valutazione finora
- 324-Chapter 1 Rock Bit Interactions PDFDocumento42 pagine324-Chapter 1 Rock Bit Interactions PDFBilge KaanNessuna valutazione finora
- European Steel and Alloy GradesDocumento2 pagineEuropean Steel and Alloy Gradesfarshid KarpasandNessuna valutazione finora
- Ficha Tecnica - Lana Mineral ThermafiberDocumento2 pagineFicha Tecnica - Lana Mineral ThermafiberJeshua Diego BarrientosNessuna valutazione finora
- C83600 PDFDocumento2 pagineC83600 PDFboccareddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Defects of Bricks: 2. Defects Due To FungiDocumento1 paginaDefects of Bricks: 2. Defects Due To FungiRayNessuna valutazione finora
- Bitumen Phenomenal Hau KauDocumento5 pagineBitumen Phenomenal Hau Kautariq wazedNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermometer Exp 1Documento11 pagineThermometer Exp 1hayder alaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Internship On Vermicomposting Edit NewDocumento12 pagineInternship On Vermicomposting Edit NewApoorva JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Metrology and Surface EngineeringDocumento2 pagineMetrology and Surface EngineeringnvemanNessuna valutazione finora
- Is 651Documento27 pagineIs 651sach24iitNessuna valutazione finora
- Wek MeDocumento6 pagineWek MeZoila FigueroaNessuna valutazione finora