Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Performance Analysis of A 6T SRAM Cell in 180nm CMOS Technology
Caricato da
IOSRjournalTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Performance Analysis of A 6T SRAM Cell in 180nm CMOS Technology
Caricato da
IOSRjournalCopyright:
Formati disponibili
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP)
Volume 5, Issue 2, Ver. I (Mar. - Apr. 2015), PP 20-22
e-ISSN: 2319 4200, p-ISSN No. : 2319 4197
www.iosrjournals.org
Performance Analysis of a 6T SRAM Cell in 180nm CMOS
Technology
Rohit Kumar Sah1, Inamul Hussain 2, Manish Kumar3
1,2,3
Department of ECE, North Eastern Regional Institute of Science & Technology, Nirjuli, India
Abstract : SRAM is a memory component and is used in various VLSI chips due to its unique capability to
retain data. This memory cell has become a subject of research to meet the demands for future communication
systems. In this paper a 6T SRAM cell is designed by using cadence virtuoso EDA tool in 180nm CMOS
technology. Its performance characteristics such as power dissipation, delay, and power delay product are
analysed. Power dissipation, delay, and power delay product of the designed 6T SRAM cell are 54.63 x10 -9 W,
19.96 x10-9s, and 1070.45 x 10-18 Ws respectively.
Keywords: Power, Delay, Power delay product, 6T SRAM cell.
I.
Introduction
Static random access memory (SRAM) is a static memory cell which is widely used in various
electronic systems. It is faster and consumes less power as compared to other memory cells [1-2]. It does not
require refreshing periodically. Because of this, SRAM is the most popular memory cell among VLSI designers.
Hence continuous evolution is going on for better performance of SRAM cells. Due to this, different types of
SRAM cells are available in the literature like 6T SRAM cell, 7T SRAM cell, 8T SRAM cell, 9T SRAM cell
etc. Most common SRAM cells used in digital system is the 6T SRAM cell. This cell can store 1-bit of data. The
bit remains in the cell as long as power is supplied. In this paper, design and performance analysis of a 6T
SRAM cell is discussed. Performance analysis is carried out by using Cadence Virtuoso in 180nm CMOS
technology.
A conventional 6T SRAM cell consists of two inverters which are connected back to back. Fig. 1
shows the basic structure of a 6T SRAM memory cell [3]. The data which has to be stored is latched in these
two inverters. The process of storing a data is known as Write operation and the process of recovering the data is
known as Read operation. Write operation is used for uploading the contents in a SRAM cell while Read
operation is used for fetching the contents. The read operation is done with the help of sense circuits which
sense BL and BLB data line before discharging it completely [4-5].
Fig. 1 A 6T SRAM cell
II.
Design Of A 6T SRAM CELL
The schematic diagram of the designed 6T SRAM cell is shown in Fig. 2. The 6T SRAM cell is
designed by using Cadence Virtuoso EDA tool in 180nm CMOS technology.
DOI: 10.9790/4200-05212022
www.iosrjournals.org
20 | Page
Performance Analysis of a 6T SRAM Cell in 180nm CMOS Technology
Fig. 2 Schematic of a 6T SRAM cell
III.
Results And Performance Analysis
Fig. 3 shows the transient waveform of the designed 6T SRAM cell for wordline, Bitline, Q and Q_bar.
Table 1 shows the performance characteristics such as power dissipation, delay, and power delay product of the
designed 6T SRAM cell in 180nm CMOS technology at power supply voltage (VDD) of 1.8V.
Table 1: Power dissipation, delay and power delay product of the designed 6T SRAM cell
Power dissipation
53.63 x 10-9 W
Delay
19.96 x 10-9s
Power delay product
1070.45 x 10 -18 Ws
Fig. 3 Transient waveforms of the designed 6T SRAM cell
DOI: 10.9790/4200-05212022
www.iosrjournals.org
21 | Page
Performance Analysis of a 6T SRAM Cell in 180nm CMOS Technology
IV.
Conclusion
A 6T SRAM cell is designed and its performance characteristics such as power, delay, and power delay
product are analysed in 180nm CMOS technology. Power dissipation, delay, and power delay product of the
designed 6T SRAM cell are 54.63 x10-9 W, 19.96 x10-9 s, and 1070.45 x 10-18 Ws respectively.
References
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
P. Athe, and S. Dasgupta, A Comparative Study of 6T, 8T and 9T Decanano SRAM cell, IEEE Symposium on Industrial
Electronics and Applications, 2, 2009, 889-894.
R. K. Sah, I. Hussain, and M. Kumar, Performance Comparison for Different Configurations of SRAM Cells, International Journal
of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology, 4, 2015, 18543-18546.
N. Rahman, and B. P. Singh, Design of Low Power SRAM Memory Using 8T SRAM Cell, International Journal of Recent
Technology and Engineering, 2, 2013, 123-127.
A. Agal, Pardeep, and B. Krishan, 6T SRAM Cell: Design and Analysis, Journal of Engineering Research and Applications, 4,
2014, 574-577.
D. Aggarwal, P. Kaushik, and N. Gujran, A Comparative Study of 6T, 8T and 9T SRAM Cell, International Journal of Latest
Trends in Engineering and Technology, 1, 2012, 44-52.
DOI: 10.9790/4200-05212022
www.iosrjournals.org
22 | Page
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Project Report Group1Documento91 pagineProject Report Group1api-332129590100% (2)
- Kinesics, Haptics and Proxemics: Aspects of Non - Verbal CommunicationDocumento6 pagineKinesics, Haptics and Proxemics: Aspects of Non - Verbal CommunicationInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sfa 5.22 PDFDocumento36 pagineSfa 5.22 PDFLuis Evangelista Moura PachecoNessuna valutazione finora
- Amt in A Nutshell - ExplainedDocumento2 pagineAmt in A Nutshell - ExplainedMis El100% (2)
- Design of 6T SRAM Cell Using Optimized 20 NM SOI Junctionless TransistorDocumento4 pagineDesign of 6T SRAM Cell Using Optimized 20 NM SOI Junctionless TransistorRaj sambhavNessuna valutazione finora
- A Comparative Study of 6T, 8T and 9T SRAM CellDocumento4 pagineA Comparative Study of 6T, 8T and 9T SRAM CellijaertNessuna valutazione finora
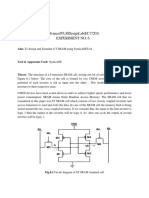
- Advanced Vlsi Design Lab (Ec17203) Experiment No. 6: Aim: To Design and Simulate 6-T Sram Using SymicadetoolDocumento4 pagineAdvanced Vlsi Design Lab (Ec17203) Experiment No. 6: Aim: To Design and Simulate 6-T Sram Using SymicadetoolHuzaifa AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Saun 2019 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 561 012093 PDFDocumento10 pagineSaun 2019 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 561 012093 PDFShruti DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Manage Enhancing Energy G.sakanaDocumento10 pagineManage Enhancing Energy G.sakanaBESTJournalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of 6T-SRAM Cell Using Dual Threshold Voltage TransistorDocumento4 pagineDesign of 6T-SRAM Cell Using Dual Threshold Voltage TransistorAbhijeet KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Analysis of CMOS Based 6T SRAM Cell at Different TechnologyDocumento6 pagineDesign and Analysis of CMOS Based 6T SRAM Cell at Different TechnologyRaj sambhavNessuna valutazione finora
- Designand Analysisof Low Power MTCMOSDocumento10 pagineDesignand Analysisof Low Power MTCMOSseshu bradyNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics 12 00834Documento15 pagineElectronics 12 00834Dat Nguyen ThanhNessuna valutazione finora
- A Highly Stable 8T SRAM Cell: P.Rama Koteswara Rao and D.Vijaya KumarDocumento6 pagineA Highly Stable 8T SRAM Cell: P.Rama Koteswara Rao and D.Vijaya KumarRakeshconclaveNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of A Low Power 10T SRAM Cell: Nternational Ournal of Nnovative Esearch in Cience, Ngineering and EchnologyDocumento3 pagineDesign of A Low Power 10T SRAM Cell: Nternational Ournal of Nnovative Esearch in Cience, Ngineering and EchnologySuyash KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Low Power Single Bitline 6T SRAM Cell With High Read StabilityDocumento6 pagineLow Power Single Bitline 6T SRAM Cell With High Read StabilitySanthoshReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Improved Stability SRAM Design For Low Power ApplicationsDocumento5 pagineImproved Stability SRAM Design For Low Power ApplicationsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- A 7T Security Oriented SRAM BitcellDocumento5 pagineA 7T Security Oriented SRAM BitcellUma MahiNessuna valutazione finora
- 6t Sram ThesisDocumento8 pagine6t Sram Thesisfjdqvrcy100% (2)
- Analysis of Low Power 6T SRAM Using 45 NM Technology: Shatrughan SinghDocumento5 pagineAnalysis of Low Power 6T SRAM Using 45 NM Technology: Shatrughan SinghShruti DasNessuna valutazione finora
- A Low Power 10T SRAM Cell With Extended Static Noise Margins Is Used To Implement An 8 by 8 SRAMDocumento10 pagineA Low Power 10T SRAM Cell With Extended Static Noise Margins Is Used To Implement An 8 by 8 SRAMIJRASETPublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Sram Utilization and Power Consumption Analysis For Low Power ApplicationsDocumento9 pagineSram Utilization and Power Consumption Analysis For Low Power ApplicationsHarshit RNessuna valutazione finora
- Low Power Sram ThesisDocumento5 pagineLow Power Sram ThesisBestWriteMyPaperWebsiteSingapore100% (2)
- Read/Write Stability Improvement of 8T Sram Cell Using Schmitt TriggerDocumento6 pagineRead/Write Stability Improvement of 8T Sram Cell Using Schmitt TriggerSasi Kiran SNessuna valutazione finora
- Ieee Report For VlsiDocumento4 pagineIeee Report For VlsiAmeyNessuna valutazione finora
- 6-T SRAM For MULTIMEDIADocumento5 pagine6-T SRAM For MULTIMEDIAUma MahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Variation Tolerant Differential 8T SRAM Cell For Ultralow Power ApplicationsDocumento10 pagineVariation Tolerant Differential 8T SRAM Cell For Ultralow Power ApplicationsSaimeena PiratlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Static RAMDocumento235 pagineStatic RAMAnjireddy ThatiparthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Venkata Lakshmi 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1804 012185Documento8 pagineVenkata Lakshmi 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1804 012185seshu bradyNessuna valutazione finora
- 8k Bit Using 6t SramDocumento8 pagine8k Bit Using 6t SramSwati Navdeep AggarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sram 6TDocumento5 pagineSram 6Taashish kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome To International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)Documento6 pagineWelcome To International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)IJERDNessuna valutazione finora
- The International Journal of Engineering and Science (The IJES)Documento7 pagineThe International Journal of Engineering and Science (The IJES)theijesNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Comparison For Different Configurations of SRAM CellsDocumento4 paginePerformance Comparison For Different Configurations of SRAM CellsSasi Kiran SNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Principles of SRAM Memory in Nano-CMOS Technologies: International Journal of Computer Applications May 2019Documento8 pagineDesign Principles of SRAM Memory in Nano-CMOS Technologies: International Journal of Computer Applications May 2019ROBI PAULNessuna valutazione finora
- Memory Trends in iSSCC ConferenceDocumento6 pagineMemory Trends in iSSCC Conferencekiranns1978Nessuna valutazione finora
- PRIYANKA KUMARI (Low Power SRAM)Documento15 paginePRIYANKA KUMARI (Low Power SRAM)Rekha KumariNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Simulation of Improved Memory Cell For Higher Read Stability, Mr. Kumar KeshamoniDocumento7 pagineDesign and Simulation of Improved Memory Cell For Higher Read Stability, Mr. Kumar KeshamoniKumar Goud.KNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of 6T SRAM Cell in Different TechnologiesDocumento4 pagineAnalysis of 6T SRAM Cell in Different TechnologiesRaj sambhavNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Evaluation of 6T, 7T & 8T SRAM at 180 NM TechnologyDocumento7 paginePerformance Evaluation of 6T, 7T & 8T SRAM at 180 NM TechnologyDr-Sanjeev KashyapNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Implementation of 64-Bit SRAM and CAM On Cadence and Open-Source EnvironmentDocumento9 pagineDesign and Implementation of 64-Bit SRAM and CAM On Cadence and Open-Source EnvironmentChandra Shekar MedarNessuna valutazione finora
- Low Power SRAM Project - Kushal 18ecu011 - Parth 18ecu016Documento17 pagineLow Power SRAM Project - Kushal 18ecu011 - Parth 18ecu016Parth BathlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stability and Performance Analysis of Low Power 6T SRAM Cell Using 45NM CMOS TechnologyDocumento1 paginaStability and Performance Analysis of Low Power 6T SRAM Cell Using 45NM CMOS TechnologySunil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 - Conclusion and Future ScopeDocumento5 pagine15 - Conclusion and Future ScopeMel Vin PinNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and VLSI Implementation of 8 MB Low Power SRAM in 90nmDocumento10 pagineDesign and VLSI Implementation of 8 MB Low Power SRAM in 90nmcnnprem_eeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Design AnalysisDocumento4 pagineDesign AnalysispradeepkarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of A Low Power SRAM Cell by Tanner Tool 45 NMDocumento6 pagineDesign of A Low Power SRAM Cell by Tanner Tool 45 NMEditor IJRITCCNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt 8Documento3 pagineExpt 8yuga.m.padhyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Simulation and Analysis of 5T-Sram Cell Using Different FoundriesDocumento6 pagineDesign Simulation and Analysis of 5T-Sram Cell Using Different FoundriesPreeti SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Vlsi Implementation of 32KB Sleepy Sram ThesisDocumento50 pagineVlsi Implementation of 32KB Sleepy Sram ThesisNikhil Manohar GhoradkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Designing Efficient and High-Performance AI AcceleDocumento13 pagineDesigning Efficient and High-Performance AI Accelepooja chandraboseNessuna valutazione finora
- Static Random-Access MemoryDocumento9 pagineStatic Random-Access MemorychahoubNessuna valutazione finora
- 6t SramDocumento13 pagine6t SramRekha KumariNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report Manu SirDocumento37 pagineProject Report Manu SirSai GaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Dayananda Sagar College of Engineering, Bangalore, Karnataka Department of Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocumento17 pagineDayananda Sagar College of Engineering, Bangalore, Karnataka Department of Electronics & Communication Engineeringsri harshaphaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Improvement in SRAM EmulatedTCAMDocumento7 paginePerformance Improvement in SRAM EmulatedTCAMIJRASETPublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Static-Noise-Margin Analysis of Modified 6T SRAM Cell During Read OperationDocumento5 pagineStatic-Noise-Margin Analysis of Modified 6T SRAM Cell During Read OperationidescitationNessuna valutazione finora
- Architecture of Static Random Access Memory Design Using 65nm TechnologyDocumento3 pagineArchitecture of Static Random Access Memory Design Using 65nm Technologyanil kasotNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of 6T, 5T and 4T SRAM Cell On Various Performance MetricsDocumento6 pagineDesign of 6T, 5T and 4T SRAM Cell On Various Performance MetricsNeha TripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- SRAM Circuit Design and Operation: Prepared By: Mr. B. H. NagparaDocumento49 pagineSRAM Circuit Design and Operation: Prepared By: Mr. B. H. NagparaBharatNessuna valutazione finora
- 8T Paper WTCM FinalDocumento11 pagine8T Paper WTCM Finaldeberjeet ushamNessuna valutazione finora
- Mohanty VLSI Integration 2012jan SRAMDocumento30 pagineMohanty VLSI Integration 2012jan SRAMPremkumar ChandhranNessuna valutazione finora
- Gain-Cell Embedded DRAMs for Low-Power VLSI Systems-on-ChipDa EverandGain-Cell Embedded DRAMs for Low-Power VLSI Systems-on-ChipNessuna valutazione finora
- The Role of Extrovert and Introvert Personality in Second Language AcquisitionDocumento6 pagineThe Role of Extrovert and Introvert Personality in Second Language AcquisitionInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- "I Am Not Gay Says A Gay Christian." A Qualitative Study On Beliefs and Prejudices of Christians Towards Homosexuality in ZimbabweDocumento5 pagine"I Am Not Gay Says A Gay Christian." A Qualitative Study On Beliefs and Prejudices of Christians Towards Homosexuality in ZimbabweInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Socio-Ethical Impact of Turkish Dramas On Educated Females of Gujranwala-PakistanDocumento7 pagineSocio-Ethical Impact of Turkish Dramas On Educated Females of Gujranwala-PakistanInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Attitude and Perceptions of University Students in Zimbabwe Towards HomosexualityDocumento5 pagineAttitude and Perceptions of University Students in Zimbabwe Towards HomosexualityInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Proposed Framework On Working With Parents of Children With Special Needs in SingaporeDocumento7 pagineA Proposed Framework On Working With Parents of Children With Special Needs in SingaporeInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Impact of Technologies On Society: A ReviewDocumento5 pagineThe Impact of Technologies On Society: A ReviewInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)100% (1)
- A Review of Rural Local Government System in Zimbabwe From 1980 To 2014Documento15 pagineA Review of Rural Local Government System in Zimbabwe From 1980 To 2014International Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Importance of Mass Media in Communicating Health Messages: An AnalysisDocumento6 pagineImportance of Mass Media in Communicating Health Messages: An AnalysisInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transforming People's Livelihoods Through Land Reform in A1 Resettlement Areas in Goromonzi District in ZimbabweDocumento9 pagineTransforming People's Livelihoods Through Land Reform in A1 Resettlement Areas in Goromonzi District in ZimbabweInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Investigation of Unbelief and Faith in The Islam According To The Statement, Mr. Ahmed MoftizadehDocumento4 pagineInvestigation of Unbelief and Faith in The Islam According To The Statement, Mr. Ahmed MoftizadehInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- An Evaluation of Lowell's Poem "The Quaker Graveyard in Nantucket" As A Pastoral ElegyDocumento14 pagineAn Evaluation of Lowell's Poem "The Quaker Graveyard in Nantucket" As A Pastoral ElegyInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Visual Analysis of Symbolic and Illegible Indus Valley Script With Other LanguagesDocumento7 pagineComparative Visual Analysis of Symbolic and Illegible Indus Valley Script With Other LanguagesInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of The Implementation of Federal Character in Nigeria.Documento5 pagineAssessment of The Implementation of Federal Character in Nigeria.International Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Relationship Between Social Support and Self-Esteem of Adolescent GirlsDocumento5 pagineRelationship Between Social Support and Self-Esteem of Adolescent GirlsInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Edward Albee and His Mother Characters: An Analysis of Selected PlaysDocumento5 pagineEdward Albee and His Mother Characters: An Analysis of Selected PlaysInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Lute Against Doping in SportDocumento5 pagineThe Lute Against Doping in SportInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Topic: Using Wiki To Improve Students' Academic Writing in English Collaboratively: A Case Study On Undergraduate Students in BangladeshDocumento7 pagineTopic: Using Wiki To Improve Students' Academic Writing in English Collaboratively: A Case Study On Undergraduate Students in BangladeshInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Madarsa Education in Empowerment of Muslims in IndiaDocumento6 pagineRole of Madarsa Education in Empowerment of Muslims in IndiaInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Human Rights and Dalits: Different Strands in The DiscourseDocumento5 pagineHuman Rights and Dalits: Different Strands in The DiscourseInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Substance Use and Abuse Among Offenders Under Probation Supervision in Limuru Probation Station, KenyaDocumento11 pagineSubstance Use and Abuse Among Offenders Under Probation Supervision in Limuru Probation Station, KenyaInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Classical Malay's Anthropomorphemic Metaphors in Essay of Hikajat AbdullahDocumento9 pagineClassical Malay's Anthropomorphemic Metaphors in Essay of Hikajat AbdullahInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Beowulf: A Folktale and History of Anglo-Saxon Life and CivilizationDocumento3 pagineBeowulf: A Folktale and History of Anglo-Saxon Life and CivilizationInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Women Empowerment Through Open and Distance Learning in ZimbabweDocumento8 pagineWomen Empowerment Through Open and Distance Learning in ZimbabweInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Micro Finance and Women - A Case Study of Villages Around Alibaug, District-Raigad, Maharashtra, IndiaDocumento3 pagineMicro Finance and Women - A Case Study of Villages Around Alibaug, District-Raigad, Maharashtra, IndiaInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On The Television Programmes Popularity Among Chennai Urban WomenDocumento7 pagineA Study On The Television Programmes Popularity Among Chennai Urban WomenInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Motivational Factors Influencing Littering in Harare's Central Business District (CBD), ZimbabweDocumento8 pagineMotivational Factors Influencing Littering in Harare's Central Business District (CBD), ZimbabweInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- An Exploration On The Relationship Among Learners' Autonomy, Language Learning Strategies and Big-Five Personality TraitsDocumento6 pagineAn Exploration On The Relationship Among Learners' Autonomy, Language Learning Strategies and Big-Five Personality TraitsInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Designing of Indo-Western Garments Influenced From Different Indian Classical Dance CostumesDocumento5 pagineDesigning of Indo-Western Garments Influenced From Different Indian Classical Dance CostumesIOSRjournalNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Management, A Business Tools' Package of Corporate Organizations: Bangladesh ContextDocumento6 pagineDesign Management, A Business Tools' Package of Corporate Organizations: Bangladesh ContextInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Food Quality Control ProgrammeDocumento75 pagineChapter 1 - Food Quality Control ProgrammeFattah Abu Bakar100% (1)
- Dell Online - Case AnalysisDocumento5 pagineDell Online - Case AnalysisMohit Agarwal0% (1)
- ISDM - Lab Sheet 02Documento4 pagineISDM - Lab Sheet 02it21083396 Galappaththi S DNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial MEP1553 - Insulation DiagnosticsDocumento4 pagineTutorial MEP1553 - Insulation DiagnosticsSharin Bin Ab GhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- ATH SR5BT DatasheetDocumento1 paginaATH SR5BT DatasheetspeedbeatNessuna valutazione finora
- LSM - Neutral Axis Depth CalculationDocumento2 pagineLSM - Neutral Axis Depth CalculationHimal KafleNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Start A Fish Ball Vending Business - Pinoy Bisnes IdeasDocumento10 pagineHow To Start A Fish Ball Vending Business - Pinoy Bisnes IdeasNowellyn IncisoNessuna valutazione finora
- Disaster Management in Schools: Status ReportDocumento28 pagineDisaster Management in Schools: Status ReportRamalingam VaradarajuluNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Marine Multispecies Hatchery Complex Plumbing Detailed BOQ - 23.10.2019Documento52 pagine03 Marine Multispecies Hatchery Complex Plumbing Detailed BOQ - 23.10.2019samir bendreNessuna valutazione finora
- Aperio CS2 BrochureDocumento3 pagineAperio CS2 BrochurelailaNessuna valutazione finora
- Submersible Sewage Ejector Pump: Pump Installation and Service ManualDocumento8 pagineSubmersible Sewage Ejector Pump: Pump Installation and Service Manualallen_worstNessuna valutazione finora
- Witness Affidavit of Emeteria B, ZuasolaDocumento4 pagineWitness Affidavit of Emeteria B, ZuasolaNadin MorgadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Gr7 3rd PeriodicalDocumento2 pagineGr7 3rd PeriodicalElle GonzagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapin Dance Syllabus 23-24Documento3 pagineChapin Dance Syllabus 23-24api-231581209Nessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering MetallurgyDocumento540 pagineEngineering Metallurgymadhuriaddepalli100% (1)
- 1ST Term S1 Physics-1Documento33 pagine1ST Term S1 Physics-1onos arereNessuna valutazione finora
- Material DevOps Essentials DEPC enDocumento88 pagineMaterial DevOps Essentials DEPC enCharlineNessuna valutazione finora
- SYLVANIA W6413tc - SMDocumento46 pagineSYLVANIA W6413tc - SMdreamyson1983100% (1)
- Thesis-Android-Based Health-Care Management System: July 2016Documento66 pagineThesis-Android-Based Health-Care Management System: July 2016Noor Md GolamNessuna valutazione finora
- Misurata UniversityDocumento11 pagineMisurata UniversityDustin EllisNessuna valutazione finora
- Funny AcronymsDocumento6 pagineFunny AcronymsSachinvirNessuna valutazione finora
- Ibps Po Mains Model Question Paper PDF Set 2Documento92 pagineIbps Po Mains Model Question Paper PDF Set 2DHIRAJNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study On DominoDocumento7 pagineCase Study On Dominodisha_pandey_4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Abhijit Auditorium Elective Sem 09Documento3 pagineAbhijit Auditorium Elective Sem 09Abhijit Kumar AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Area & Perimeter - CRACK SSC PDFDocumento10 pagineArea & Perimeter - CRACK SSC PDFSai Swaroop AttadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10 MSDN Download (Untouched)Documento5 pagineWindows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10 MSDN Download (Untouched)Sheen QuintoNessuna valutazione finora
- Synergy Elektrik (PVT.) LTD PDFDocumento3 pagineSynergy Elektrik (PVT.) LTD PDFMuhammad KashifNessuna valutazione finora
- Graphene/Metal Organic Framework Composites As Adsorbents For Adsorption Chiller ApplicationsDocumento88 pagineGraphene/Metal Organic Framework Composites As Adsorbents For Adsorption Chiller ApplicationsNajam Ul QadirNessuna valutazione finora