Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Pervasive Communications Handbook 30
Caricato da
JasmeetDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pervasive Communications Handbook 30
Caricato da
JasmeetCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1-10
Pervasive Communications Handbook
After forwarding a packet, the forwarder waits to receive a response for time 2TTL1,
where TTL1 is computed from TTL1=(traveling time for one hop)(updated number of
hops).
If the forwarder receives RRP, it just forwards it on the reverse path and keeps the
route information.
If the forwarder receives Fail, it also forwards it on the same reverse path and
keeps the route information.
If it does not receive any response and its waiting time exceeds TTL1, it generates
Fail and forwards it on the reverse path.
Destination: The destination checks EM of RRQ to confirm the destination of RRQ.
Finally, it replies by RRP and keeps the route information.
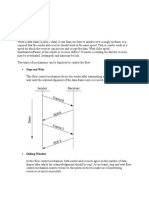
1.3.2.3 Working Principle
Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) [14] is used as the
channel-access mechanism for control messages. A sender (a source or a forwarder) of
an RRQ transmits the RRQ after sensing the channel and finding idle time for a distributed inter frame space (DIFS). When there is a collision, the sender retransmits the RRQ
after a short inter frame space (SIFS). The same procedure is applicable for any node for
the RRP as well as Fail.
Initial Procedure: A source makes a signed position request to the PS, and receives
required information CK, destinations position information, Auth, Token, and
PK of the destination from the PS.
Sources Working Procedure: The source generates an RRQ and sends it to its radio
region and waits to receive a response for time 2TTL.
If it receives the following response:
If source receives RRP, then it compares Auth with RRPMsg by decrypting it.
If it matches, then source sends data in the path and at last sends the
Token.
If it does not match, then source discards this RRP and estimates a new
NH and again tries this procedure until it receives a valid RRP.
If source receives a Fail packet within time 2TTL, it estimates a new NH and
again tries this procedure until it receives an RRP that does not exceed the maximum number of hops for that environment.
If the source does not receive any response and the waiting time exceeds 2TTL,
the source estimates a new NH and again tries the above procedure until it receives an
RRP. The source repeats this procedure as long as the NH of its packet is smaller than the
maximum number of hops for that environment.
Forwarders or Destinations Working Procedure: On receiving an RRQ, a forwarder
checks whether it is the destination or not.
If it is the destination, then it generates an RRP and sends this RRP on the reverse
path.
If it is not the destination, then it forwards the RRQ and waits for time 2TTL1.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Programming Logic and Design, 9th Edition. Chapter 1Documento19 pagineProgramming Logic and Design, 9th Edition. Chapter 1John0% (3)
- Arduino Bluetooth Controlled Car Project ReportDocumento9 pagineArduino Bluetooth Controlled Car Project ReportSyed Adil Javed100% (1)
- CNT 5106C HW 3Documento9 pagineCNT 5106C HW 3Dhanush PakanatiNessuna valutazione finora
- 5440 - 1 - NASSCOM Perspective 2025 - Shaping The Digital RevolutionDocumento13 pagine5440 - 1 - NASSCOM Perspective 2025 - Shaping The Digital Revolutionprayukth100% (1)
- Week 5 TCP and SSLDocumento63 pagineWeek 5 TCP and SSLManmeetSinghDuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5Documento26 pagineUnit 5ashwani tyagiNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE RACH ProcedureDocumento29 pagineLTE RACH Procedurekalyanvarmak5887Nessuna valutazione finora
- End To End Issues:: TH THDocumento9 pagineEnd To End Issues:: TH THMathew ManojNessuna valutazione finora
- TCP Retransmission Timers and Karn's AlgorithmDocumento2 pagineTCP Retransmission Timers and Karn's AlgorithmFakhar AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.3.1-Problems On Stop and Wait Flow ControlDocumento19 pagine3.3.1-Problems On Stop and Wait Flow ControltheonlygodNessuna valutazione finora
- Sliding Window PptsDocumento26 pagineSliding Window PptsNeelima SaxenaNessuna valutazione finora
- TCP and Its Algorithms (Slow-Start, Congestion Avoidance, Fast Retransmit and Fast Recovery)Documento4 pagineTCP and Its Algorithms (Slow-Start, Congestion Avoidance, Fast Retransmit and Fast Recovery)Afzal BhattiNessuna valutazione finora
- StnproDocumento4 pagineStnproSairam GamidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport Layer Protocols: Simple ProtocolDocumento8 pagineTransport Layer Protocols: Simple ProtocolMohmed AwadNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks NotesDocumento421 pagineComputer Networks NotestrevorNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow Control and Error ControlDocumento5 pagineFlow Control and Error ControlThaddeus MooreNessuna valutazione finora
- Vtc05ir CoopDocumento5 pagineVtc05ir CoopMao BourichaNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport Layer ResponsibilitiesDocumento3 pagineTransport Layer ResponsibilitiesRafia ShoukatNessuna valutazione finora
- Multicasting With Quality of Service GuaranteesDocumento22 pagineMulticasting With Quality of Service GuaranteeskrithigaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Transport LayerDocumento57 pagineIntroduction To Transport LayerkjhofboaNessuna valutazione finora
- ARQDocumento6 pagineARQamukhopadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Access Control Update in NetworkingDocumento39 pagineAccess Control Update in NetworkingThe MatrixNessuna valutazione finora
- TCP Flags Explained in 40 CharactersDocumento3 pagineTCP Flags Explained in 40 CharactersMohit Saini100% (1)
- 3.5 TCP-Transport LayerDocumento3 pagine3.5 TCP-Transport Layerkaushik surikuchiNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Link Layer-IIDocumento12 pagineData Link Layer-IIimtiyaz beighNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Link ControlDocumento21 pagineData Link ControlJonald BualNessuna valutazione finora
- Congestion Control and Packet Reordering For Multipath Transmission Control ProtocolDocumento56 pagineCongestion Control and Packet Reordering For Multipath Transmission Control ProtocolEng Ali HussienNessuna valutazione finora
- NW Lec 6Documento28 pagineNW Lec 6omarnader16Nessuna valutazione finora
- CN R19 Unit-3Documento25 pagineCN R19 Unit-3Perla Dayana Sri VarshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 5Documento35 pagineWeek 5AKANKSHA RAJNessuna valutazione finora
- Petrinet ReportDocumento27 paginePetrinet ReportEsha KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Queues and Delay AnalysisDocumento9 paginePacket Queues and Delay AnalysisSaagar AshaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Delays in Computer NetworksDocumento60 pagineDelays in Computer NetworksSakshi ChidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Idresss sir#10OKDocumento12 pagineIdresss sir#10OKDil NawazNessuna valutazione finora
- Idresss Sir#9 OKDocumento14 pagineIdresss Sir#9 OKDil NawazNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Data Link LayerFlow ControlDocumento56 pagine10 Data Link LayerFlow Controlanushka aroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport Layer Challenges By: Talha Mudassar 015 Fahad Nabi 63 Rashid Mehmood 96Documento6 pagineTransport Layer Challenges By: Talha Mudassar 015 Fahad Nabi 63 Rashid Mehmood 96Noman AliNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is NQADocumento5 pagineWhat Is NQAion marianNessuna valutazione finora
- TCP Error Control Mechanisms ExplainedDocumento21 pagineTCP Error Control Mechanisms ExplainedPrakhyat GoelNessuna valutazione finora
- AODV Routing Protocol OverviewDocumento31 pagineAODV Routing Protocol Overviewdeath_readerNessuna valutazione finora
- RCDA - Reliable Data TransferDocumento31 pagineRCDA - Reliable Data TransferLaura Cathalina RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow Control (Data) : Stop-And-WaitDocumento7 pagineFlow Control (Data) : Stop-And-Waitpy thonNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile TCP: Optimizing TCP for Wireless NetworksDocumento27 pagineMobile TCP: Optimizing TCP for Wireless NetworksMfleh MflehNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow Control & ARQsDocumento34 pagineFlow Control & ARQsamitsaharulzNessuna valutazione finora
- Protocal Functioning:: Neighbor SensingDocumento5 pagineProtocal Functioning:: Neighbor SensingShah Zeb YousafzaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 6Documento6 pagineLecture 6Rylan2911Nessuna valutazione finora
- Data Link Layer FunctionDocumento35 pagineData Link Layer Functionsyanikuri33Nessuna valutazione finora
- Flow Control ProtocolsDocumento4 pagineFlow Control ProtocolsSandeep shahNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Unit-2 Congestion, SCTP, QosDocumento40 pagineCN Unit-2 Congestion, SCTP, QosKowsalya GNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12: Media Access Control (MAC)Documento21 pagineChapter 12: Media Access Control (MAC)Selvakrishnan SekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Medium AccessDocumento85 pagineMedium AccessSandeep VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee132b Homework 2Documento3 pagineEe132b Homework 2YouRong YangNessuna valutazione finora
- Data LinkDocumento3 pagineData Linksairajdash189Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Overall Architecture of The Proposed System Is Shown in Fig. 3.1Documento13 pagineThe Overall Architecture of The Proposed System Is Shown in Fig. 3.1Sameera AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Error Detection Is The Ability To Detect The Presence ofDocumento16 pagineError Detection Is The Ability To Detect The Presence ofgirijesh2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Flow and Error Control: Bore Gowda S.B Associate Professor E and C Engg. Dept. MIT, ManipalDocumento41 pagineFlow and Error Control: Bore Gowda S.B Associate Professor E and C Engg. Dept. MIT, ManipalDhaval DoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) : Reliable Connection-Oriented Point-To-Point Full-Duplex Streams, Not MessagesDocumento25 pagineTransmission Control Protocol (TCP) : Reliable Connection-Oriented Point-To-Point Full-Duplex Streams, Not Messagesarunnair2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- HARQ ProcessDocumento6 pagineHARQ Processteam DinnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework Solution 4 - TCP Congestion Control AnalysisDocumento4 pagineHomework Solution 4 - TCP Congestion Control AnalysisAhmad ANessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Reliable Data TransferDocumento54 paginePrinciples of Reliable Data Transfersumi kannaNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Unit-2 Imp QA'sDocumento22 pagineCN Unit-2 Imp QA'shajirasabuhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Arq 1Documento19 pagineArq 1pratyaysarkar.csNessuna valutazione finora
- IP MULTICAST ROUTING Part -3: Use of multicast routing.Da EverandIP MULTICAST ROUTING Part -3: Use of multicast routing.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 88Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 88JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 74Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 74JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 90Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 90JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 89Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 89JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 73Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 73JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 80Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 80JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 84Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 84JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 87Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 87JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 85Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 85JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 79Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 79JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 82Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 82JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 72Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 72JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 83Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 83JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 81Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 81JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 77Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 77JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 76Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 76JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 68Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 68JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 75Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 75JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 66Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 66JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 67Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 67JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 70Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 70JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 71Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 71JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 69Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 69JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 65Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 65JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 63Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 63JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 64Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 64JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 62Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 62JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 60Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 60JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 61Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 61JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 59Documento1 paginaFinancial Risk Management A Prket and Credit Risk - 2 Edition 59JasmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Modus 2 - 2001Documento36 pagineModus 2 - 2001BroCactusNessuna valutazione finora
- Ccure-9000-V2 0-Webclient-Guide Ra0 LT enDocumento120 pagineCcure-9000-V2 0-Webclient-Guide Ra0 LT enhuiryk goncalvesNessuna valutazione finora
- Voice Processing ToolDocumento51 pagineVoice Processing Toolhamza salihNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic For The Class: Ethernet Physical Layer, Ethernet Mac Sub Layer Protocol. Date & Time: 19/01/2022Documento20 pagineTopic For The Class: Ethernet Physical Layer, Ethernet Mac Sub Layer Protocol. Date & Time: 19/01/2022LkdisisosoNessuna valutazione finora
- LaptopDocumento17 pagineLaptopViswanath ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Process MemoryDocumento39 pagineUnderstanding Process MemorynicolasvNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Wise Java Important Questions1Documento3 pagineUnit Wise Java Important Questions1honaday945100% (5)
- 355 Computer Science Engg PDFDocumento118 pagine355 Computer Science Engg PDFjyoti raniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chatgpt SlidesDocumento112 pagineChatgpt SlidesmkranthikumarmcaNessuna valutazione finora
- CAREER AT MNC WITH WALK-IN INTERVIEWDocumento2 pagineCAREER AT MNC WITH WALK-IN INTERVIEWJames KarthickNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.1 - Introduction To MultimediaDocumento57 pagine5.1 - Introduction To Multimediamansor100% (1)
- CPS3Documento159 pagineCPS3wrosman@gmail.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Blue Eyes Technology IEEE+FORMATDocumento18 pagineBlue Eyes Technology IEEE+FORMATBalaji King100% (2)
- Educational InnovationDocumento31 pagineEducational InnovationChristian BehilNessuna valutazione finora
- TMF635 Usage Management API REST Specification R14.5.1Documento51 pagineTMF635 Usage Management API REST Specification R14.5.1DuyHung DangNessuna valutazione finora
- Internet Threats To ChildrenDocumento23 pagineInternet Threats To ChildrenDr Tushar DashoraNessuna valutazione finora
- 8051 Timer and CounterDocumento11 pagine8051 Timer and CountermahavishnuNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis Docu - Group 3Documento163 pagineThesis Docu - Group 3Charles Ramos KabilingNessuna valutazione finora
- 4G Technology: Past SimpleDocumento4 pagine4G Technology: Past SimpleDamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Weekly MeetingDocumento2 pagineWeekly MeetingSenior Software Engineer Emil RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- WaltographDocumento3 pagineWaltographapi-26866651Nessuna valutazione finora
- Msi MS-7152 - Rev 0aDocumento32 pagineMsi MS-7152 - Rev 0aMauro CamiloNessuna valutazione finora
- Proyecto ICARO TestCaseDocumento20 pagineProyecto ICARO TestCasePol MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Smoke Test Mind Map PDFDocumento1 paginaSmoke Test Mind Map PDFmeet kajanaNessuna valutazione finora
- SC18 - Support UpdateDocumento9 pagineSC18 - Support Updatedaniel_vp21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Week 5 Lecture MaterialDocumento97 pagineWeek 5 Lecture MaterialSmita Chavan KhairnarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - SelectionsDocumento52 pagineChapter 3 - Selectionsnaqibullah2022faryabNessuna valutazione finora