Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Ch3 WS1
Caricato da
FerminTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Ch3 WS1
Caricato da
FerminCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Worksheet3.
1
Ionisationenergyandatomicorbitals
Ionisationenergy
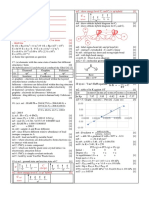
1 a Definethefollowingterms:
i 1stionisationenergy
ii 3rdionisationenergy.
b Writeequationswhichdescribe:
i the 1stionisationofmagnesium
ii the 3rdionisationofmagnesium.
c Whichionisationenergyisrepresentedbyeachequationbelow?
i Mg3+(g)Mg4+(g)+e
Hint: Thenumberoftheionisationenergyisthe
ii Al5+(g)Al6+(g)+e
chargeontheionproducedbytheionisation.
2 a Thetablebelowshowsthefirstfiveionisationenergiesforfiveelements(AtoE).
Statewhichgroupeachoftheseelementsbelongsto.
Element
[3]
[3]
[2]
[2]
[1]
[1]
[5]
Ionisationenergy/kJmol1
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
5th
786
1580
3230
4360
16090
418
3070
4600
5860
7975
1090
2350
4610
6220
37830
548
1060
4120
5440
6908
577
1980
2960
6190
8200
b ExplainthereasoningbehindyouranswerforelementC.
[2]
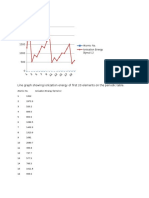
c Drawasketchgraphtoshowhowlog10 ionisationenergyforchlorine(atomicnumber17)
varieswhenplottedagainstthenumberofelectronsremoved.
[7]
Atomicorbitals
3 Whatismeantbythetermatomicorbital?
[2]
4 Drawtheshapesandtherelativedirectionsinspaceofalltheatomicorbitalsatenergy
level n=2.
[4]
5 Statethemaximumnumberofelectronsthateachofthefollowingorbitalscanhold.
a A4sorbital.
b Alltheorbitalsatthethirdenergyleveltogether.
c A4dorbital.
[1]
[1]
[1]
6 Whatisthemeaningoftheterm degenerateorbitals?
[2]
7 Whyaredegenerateorbitalssinglyoccupiedatfirst?
[4]
CambridgeInternationalASandALevelChemistry
OriginalmaterialCambridgeUniversityPress2011
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Da EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Valutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (4)
- Electron Structure, Ionisation Energy WorksheetDocumento1 paginaElectron Structure, Ionisation Energy Worksheetyathinp822Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electron Arrangement Successive Ionisation Energies For PotassiumDocumento1 paginaElectron Arrangement Successive Ionisation Energies For PotassiumMahfuz A. AzimNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment-2B-Periodic TableDocumento1 paginaAssignment-2B-Periodic Tableindra1_2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sem1 Unit4 Periodic TableDocumento10 pagineSem1 Unit4 Periodic Tableshehdilanun0% (1)
- CHE 123 - Worksheet - Atomic Structure - IonizationDocumento6 pagineCHE 123 - Worksheet - Atomic Structure - IonizationJanet UsherNessuna valutazione finora
- 12.1 L7 All QuestionbankDocumento13 pagine12.1 L7 All Questionbankadham fadelNessuna valutazione finora
- Solving Problem: Objective QuestionsDocumento4 pagineSolving Problem: Objective QuestionsLily MardyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electron Arrangement Ionisation Energies in Group I and Period 2Documento1 paginaElectron Arrangement Ionisation Energies in Group I and Period 2Mahfuz A. AzimNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.0 Modul Set BDocumento5 pagine3.0 Modul Set BhernaniabdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure and Periodic TrendsDocumento5 pagineAtomic Structure and Periodic TrendsJithesh ParambathNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure Answers 15 09 2021 at 9 AmDocumento61 pagineAtomic Structure Answers 15 09 2021 at 9 AmPevin De silvaNessuna valutazione finora
- S6 Chemistry: Duration: 2 Hour 30 MinutesDocumento11 pagineS6 Chemistry: Duration: 2 Hour 30 MinutesAine VisionNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 H1 Chemistry Dec Revision Book - Question - FinalDocumento42 pagine2022 H1 Chemistry Dec Revision Book - Question - Final2022 BALAKRISHNAN ADHITHINessuna valutazione finora
- Modul 4Documento7 pagineModul 4zuliana1Nessuna valutazione finora
- CHEMISTRY-19-11 - 11th (J-Batch) SpaceDocumento21 pagineCHEMISTRY-19-11 - 11th (J-Batch) SpaceRaju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionisation EnergyDocumento4 pagineIonisation EnergyKhadija PrescottNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Atomic Structure Multiple ChoiceDocumento13 pagine1.1 Atomic Structure Multiple ChoiceAmmaarah PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Families QDocumento2 pagineChemical Families QleoamenyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure Consolidation Ex (Answers)Documento5 pagineAtomic Structure Consolidation Ex (Answers)Terence Sze Zheng YangNessuna valutazione finora
- Kolej Matrikulasi Selangor: Name: Practicum: Lecturer'S Name: Date SubmittedDocumento4 pagineKolej Matrikulasi Selangor: Name: Practicum: Lecturer'S Name: Date SubmittedLeevandraaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12: Nuclear Reaction: Sf026: Past Year PSPM QuestionsDocumento3 pagineChapter 12: Nuclear Reaction: Sf026: Past Year PSPM QuestionsIain Choong WKNessuna valutazione finora
- AA Chem CW (2nd Term) (9) 2nd - InddDocumento3 pagineAA Chem CW (2nd Term) (9) 2nd - InddTing TCNessuna valutazione finora
- Kahawa West Tuition CoverDocumento3 pagineKahawa West Tuition CoverJOHN MURIGINessuna valutazione finora
- Set IIDocumento4 pagineSet IIChew Gee LanNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.0 Module Q&ADocumento13 pagine3.0 Module Q&AhernaniabdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic TableDocumento23 paginePeriodic Tabled anjilappaNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic DPP 2Documento4 paginePeriodic DPP 2Varsha YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 6 A I Ionic Bonding 1Documento59 pagine1 6 A I Ionic Bonding 1zainabNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Table - Practice Sheet - Varun JEE Advanced 2024Documento3 paginePeriodic Table - Practice Sheet - Varun JEE Advanced 2024aryasushama2611Nessuna valutazione finora
- Example Test (110 Marks) : MarkschemeDocumento42 pagineExample Test (110 Marks) : MarkschemeSONIA VIVIANA BELTRAN CATAMANessuna valutazione finora
- 05 - Ans To Bonding Supplemtary QN - 2012Documento2 pagine05 - Ans To Bonding Supplemtary QN - 2012caspersoongNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 3 SPM 2011 Mastery PracticesDocumento30 paginePaper 3 SPM 2011 Mastery Practicesaganbasm100% (1)
- Test 1 202101Documento5 pagineTest 1 202101许敬霖Nessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 3 SPM 2011 Mastery PracticesDocumento30 paginePaper 3 SPM 2011 Mastery PracticesaganbasmNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercises Part 1Documento5 pagineExercises Part 1Le Thai SonNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure HL Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento3 pagineAtomic Structure HL Multiple Choice QuestionsMalak AlqaidoomNessuna valutazione finora
- Metal Reaction, Chemical BondingDocumento3 pagineMetal Reaction, Chemical BondingDuong Anh HoàngNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.111 Exam 1 Practice PDFDocumento9 pagine5.111 Exam 1 Practice PDF15klaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Summary Worksheet: Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocumento1 paginaChapter Summary Worksheet: Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableAdnan ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation Chemistry I - CHM 092 July - Nov 2020 Tutorial 4 (Topic 2)Documento3 pagineFoundation Chemistry I - CHM 092 July - Nov 2020 Tutorial 4 (Topic 2)MUHAMMAD LUQMAN HAKIMI MOHD ZAMRINessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 3/13 Practice IB Chem TestDocumento12 pagineTopic 3/13 Practice IB Chem TestKeyerria HowardNessuna valutazione finora
- s2 Form 5 Chap 5 Carbon CompoundDocumento23 pagines2 Form 5 Chap 5 Carbon CompoundCaiyan LiewNessuna valutazione finora
- Üsküdar American Academy Grade 9 Chemistry Worksheet # 1 Subject: Periodic Trends Name: Number: ClassDocumento2 pagineÜsküdar American Academy Grade 9 Chemistry Worksheet # 1 Subject: Periodic Trends Name: Number: ClassMustafa Ayhan DuduNessuna valutazione finora
- Electron Configuration 2Documento6 pagineElectron Configuration 2268953Nessuna valutazione finora
- Answers 10 NSA3 ChemistryDocumento4 pagineAnswers 10 NSA3 ChemistryshamooNessuna valutazione finora
- STPM 2004 p2 AnswerDocumento20 pagineSTPM 2004 p2 AnswersuhailieliasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry s4 Theory and Pract.Documento26 pagineChemistry s4 Theory and Pract.kubwimanajeandamour359Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure HL Multiple Choice Questions AnswersDocumento3 pagineAtomic Structure HL Multiple Choice Questions AnswersMalak AlqaidoomNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure (AP MC)Documento4 pagineAtomic Structure (AP MC)Habiba AbdeenNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3.0: Periodic TableDocumento3 pagineChapter 3.0: Periodic TablehernaniabdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Form Two QuestionsDocumento22 pagineChemistry Form Two QuestionsDAVID NAMASAKANessuna valutazione finora
- S-C-5-3 - Periodic Trends Worksheet and KEYDocumento6 pagineS-C-5-3 - Periodic Trends Worksheet and KEYSanim Choudhury40% (5)
- Marks: Parent's Signature: Name: Class: Date:: Science Year 5 Sim Education GroupDocumento9 pagineMarks: Parent's Signature: Name: Class: Date:: Science Year 5 Sim Education GroupSANTOSHANDIAPPA THANEERMALAI A/L KANESAN MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ans Gerak Gempue Sem 1 2023Documento2 pagineAns Gerak Gempue Sem 1 2023revathy varatharajahNessuna valutazione finora
- C Hemistry 1: Fac 0015 Tutorial 4 (Chapters 7-9)Documento2 pagineC Hemistry 1: Fac 0015 Tutorial 4 (Chapters 7-9)Sin YeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Al-based Energetic Nano Materials: Design, Manufacturing, Properties and ApplicationsDa EverandAl-based Energetic Nano Materials: Design, Manufacturing, Properties and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Plasma Chemistry: International Symposium on Plasma ChemistryDa EverandPlasma Chemistry: International Symposium on Plasma ChemistryD. E. JensenNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch15 WS2Documento1 paginaCh15 WS2FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch5 WS2Documento1 paginaCh5 WS2FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Titration Laboratory Sodium Hydroxide and Hydrochloric AcidDocumento7 pagineTitration Laboratory Sodium Hydroxide and Hydrochloric AcidFermin100% (1)
- Molar Calculation WorksheetDocumento3 pagineMolar Calculation WorksheetFerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch5 WS1Documento1 paginaCh5 WS1FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch15 WS1Documento1 paginaCh15 WS1FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- N, L, ML, MsDocumento7 pagineN, L, ML, MsclassicalcatNessuna valutazione finora
- CHP 5 Supplementary Notes (Acids Bases and Salts)Documento12 pagineCHP 5 Supplementary Notes (Acids Bases and Salts)FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry I - Practice Exercise: Alkene Reactions and MechanismsDocumento9 pagineOrganic Chemistry I - Practice Exercise: Alkene Reactions and MechanismsElliot JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- AS Edexcel Chemistry Unit 1 Revision NotesDocumento5 pagineAS Edexcel Chemistry Unit 1 Revision NotesTheMagicCarpetNessuna valutazione finora
- Markov Niko VsDocumento9 pagineMarkov Niko VsPipit Aditia ListiyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Bonding and Structure Revision NotesDocumento23 pagineBonding and Structure Revision NotesFerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry I - Practice Exercise: Alkene Reactions and MechanismsDocumento9 pagineOrganic Chemistry I - Practice Exercise: Alkene Reactions and MechanismsElliot JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch4 WS5Documento1 paginaCh4 WS5FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 4.1: Electrical Properties of Ionic SolutionsDocumento2 paginePractical 4.1: Electrical Properties of Ionic SolutionsFerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch4 WS4Documento1 paginaCh4 WS4FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch4 WS2 PDFDocumento1 paginaCh4 WS2 PDFFerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch4 WS1Documento1 paginaCh4 WS1FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- 09 Stereo NotesDocumento15 pagine09 Stereo NotesDebarati Das GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch4 WS3Documento1 paginaCh4 WS3FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch4 Pract3Documento2 pagineCh4 Pract3FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Notebook Policy and FromatDocumento3 pagineLab Notebook Policy and FromatFermin100% (1)
- Ch4 Pract2Documento3 pagineCh4 Pract2FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Stereochemistry Practce PDFDocumento6 pagineStereochemistry Practce PDFFerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch14 WS1Documento1 paginaCh14 WS1FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch13 WS1Documento1 paginaCh13 WS1FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch14 WS2Documento1 paginaCh14 WS2FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch14 WS3Documento1 paginaCh14 WS3FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch13 WS2Documento1 paginaCh13 WS2FerminNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 13.1: Isomerism, Naming and Drawing StructuresDocumento1 paginaActivity 13.1: Isomerism, Naming and Drawing StructuresFerminNessuna valutazione finora