Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Opportunistic Infections-Micro
Caricato da
ninja-2001Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Opportunistic Infections-Micro
Caricato da
ninja-2001Copyright:
Formati disponibili
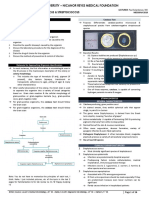
OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS: NECROTIZING PNEUMONIAS
G POS STAPH AUREUS
GENERAL:
Imp Staph: aureus, epidermidis, saprophyticus
G Pos cocci form clumps/ clusters
VIRULENCE:
Many cell surface PRO; multifactorial
disease
Staph Aureus 1:10 infxns
Cell-Associated Virulence:
o 1. capsule
o 2. PRO A: (bind Fc empnt lgG); stop phagocytosis &
complement activation
o 3. Clumping Factor: binds fibrinogen fibrin bacterial
aggregation Extracellular Enzymes:
o 1. coagulase: prothrombin staphylothrombin fibrin
formation = clotting! o
2. hyaluronidase/nucleases/lipases
o 3. catalase: stops MPO system; inhibit phagocytosis
o 4. staphylokinase: dissolves fibrin clots o 5. PCNases: when
inappropriate therapy Toxins:
o Exfoliative/TSST-1 /Enterotoxins = release of cytokines
o Cytotoxins lyse many cells
o Panton-Valentine Leukocidin (PVL): leuko destruction/tissue
necrosis
Severe necrotic hemorrhagic pneumonia
(immuno-comp, kids)
Previously healthy lungs + predisposing viral
infxn
Community acquired!
EPIDEMIOLOGY of STAPH AUREUS:
Nml flora: anterior nares/perineum/skin (shed from here)
Trans: close contact/ ingested in food/fomites
Asympomatic carriers
PATHOLOGY/DISEASE of STAPH AUREUS:
Lots of ways to enter = ultimate opportunist
Affects any body site (skin, deep tissues, wounds, etc)
RESPIRATORY INFXNS due to STAPH AUREUS:
Inhalation Pneumonia
o Community acquired after influenza (varied severity )
Aspiration Pneumonia:
o Hospital-acquired after intubation
Hematogenous Pneumonia:
o From thrombus or vegetation
o Empyema, pulmonary infxn (common cause)
PREDISPOSING FACTORS:
Chemotaxis, opsonization, staphylocida! (DM decompensation) defects,
presence of foreign body
DX:
Clinical: (nothing unique or radiologic!!!)
o Helpful!: Predisposing factors, poor response pnemococcal
pneumo, rapid cavitation bronchopneumonia, lots of
pulmonary consolidation, empyema
Lab: G stain, direct specimen, need colonies (blood), catalase?,
coagulase?, beta-hemolytic on BAP, facultative halophile MSA yellow
TX:
Hospital strains resistant to AB! Need antimicrobial suscep testing
o MRSA (methiciliin resis); hospital & community w/PVL o VISA
(vanco intermediate resistant) o VRSA (vanco resistant: van A
operon)
PREVENTION:
Candidate
Vaccines:
o
1. NABI Pharm (failed clinical trials)
o
2. Inhibitex (veronate. aurexis)
Non-immunc based:
Good hygiene, prophylaxis for surg. hand washing
G NEG PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA
GENERAL:
G Neg aerobic bacillus
Used in bioremediation of petrochem waste materials
Degrades materials w'ith C, H, O, N (or combo)
Pyoverdin (green pigmnt) & pyocyanin (blue pigmnt)
VIRULENCE:
I. pyocyanin: ROS production
2. exotoxin A. A-B toxin, same mech diphtheria toxin, ciliastasis,
immunosuppressor
3. elastases (LasA/LasB): elastolytic
4. alginate: slime layer/biofllm, inhibit muco escalator, glycocalyx
5. pili: attachment
6. LPS: endotoxin activity
EPIDEMIOLOGY of PSEUDOMONAS AEROGINOSA:
widespread in environment
carried on skin/feces
nml flora & opportunistic flora in hospital
Trans: sinks, fomites, plants, fruits, hands, etc
PATHOLOGY/DISEASE of PSEUDOMONAS AEROGINOSA:
Not super virulent
Needs significant break in host defense
Compromised hosts only
INFXNS (non-pneumonia):
UTI. pneumonia, eye, ear, skin
2nd leading cause infection in bum patients
common cause of death in CF
RESPIRATORY INFXNS due to PSEUDOMONAS AEROGINOSA:
Primary
o Inhalation therapy with nebulization
Secondary
o Immunosuppression/ host compromise o
Associated with bacteremia (IV drug use)
Clinically:
o Nml Pts: toxicity, cyanosis, empyema o CF: chronic/recurrent.
confined to respiratory tract, bilateral w/residual damage
DX:
Need to isolate & ID in lab!
Grow in lots of different media
Blue-green water soluble pigment highly characteristic
IX:
MDR common; need susceptibility tests!
Hard to clear, relapse common
Systemic inxn needs combos for synergism
NO broad spectrum Ab (suppress nml flora)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Behavioral QuizDocumento56 pagineBehavioral Quizninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Behavioral QuizDocumento56 pagineBehavioral Quizninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Peroxi ERDocumento32 pagine07 Peroxi ERninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- 06 NucleusDocumento26 pagine06 Nucleusninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Golgi DiseasesDocumento1 paginaGolgi Diseasesninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Med BiochemistryDocumento51 pagine01 Med Biochemistryninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cy To SkeletonDocumento6 pagineCy To Skeletonninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz Behavioral ScienceDocumento91 pagineQuiz Behavioral ScienceMedShare92% (12)
- Peroxisomes ERDocumento4 paginePeroxisomes ERninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- 07 MitoDocumento36 pagine07 Mitoninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Catalase Uses The H2O2 H2O2 + R'H2 - R' + 2H2ODocumento2 pagineCatalase Uses The H2O2 H2O2 + R'H2 - R' + 2H2Oninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- 08 Vessicular TraffDocumento84 pagine08 Vessicular Traffninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Med BiochemistryDocumento81 pagine03 Med Biochemistryninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- 04 Ph-IntroDocumento31 pagine04 Ph-IntroAnonymous t5TDwdNessuna valutazione finora
- Istology: Lymphatic SystemDocumento48 pagineIstology: Lymphatic Systemninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Med BiochemistryDocumento51 pagine01 Med Biochemistryninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular System-IIDocumento39 pagineCardiovascular System-IIninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Med BiochemistryDocumento41 pagine02 Med Biochemistryninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Week 7 PPTDocumento90 pagineWeek 7 PPTKevinMathewNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Exercises For EpidemiologyDocumento8 paginePractice Exercises For Epidemiologyninja-2001100% (2)
- Usmle Study Tip 4Documento10 pagineUsmle Study Tip 4ninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quick Immunology ReviewDocumento9 pagineQuick Immunology Reviewninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathoma NotesDocumento28 paginePathoma NotesHarun Rashid100% (4)
- Inflammation Phagocytosis Chemical MediatorsDocumento53 pagineInflammation Phagocytosis Chemical Mediatorsninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Behavioral Science Practice QuestionsDocumento52 pagineBehavioral Science Practice QuestionsUsman KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Opportunistic Infections-MicroDocumento1 paginaOpportunistic Infections-Microninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4 ImmunopathDocumento136 pagine4 Immunopathninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Immunology High Yield For STEP 1Documento13 pagineImmunology High Yield For STEP 1Lucykesh100% (6)
- Opportunistic InfectionsDocumento1 paginaOpportunistic Infectionsninja-2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- (Microbio) Staphyloccocus and Streptococcus-Dr. Salandanan (BHND)Documento16 pagine(Microbio) Staphyloccocus and Streptococcus-Dr. Salandanan (BHND)Lee Delos Santos100% (1)
- 5 - Antibiotics 2018Documento11 pagine5 - Antibiotics 2018nae100% (3)
- MRSA Training For Student, Families and School Staff PPTDocumento30 pagineMRSA Training For Student, Families and School Staff PPTSam TullyNessuna valutazione finora
- La Consolacion University Philippines Catmon, City of Malolos, BulacanDocumento11 pagineLa Consolacion University Philippines Catmon, City of Malolos, BulacanRoven Angelo GalloNessuna valutazione finora
- Microbio Lec 5 - StaphylococcusDocumento6 pagineMicrobio Lec 5 - Staphylococcusapi-3743217100% (2)
- Week 8 - Bacteriology LectureDocumento7 pagineWeek 8 - Bacteriology LectureReangg SerranoNessuna valutazione finora
- RVM Mediastinitis y Factores de RiesgoDocumento8 pagineRVM Mediastinitis y Factores de RiesgoMartha CeciliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Metallic Oxide Antibacterial EvaluationDocumento6 pagineMetallic Oxide Antibacterial EvaluationRodolfo Angulo OlaisNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Products From Polar OrganismsDocumento20 pagineNatural Products From Polar OrganismsRDVVNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulation Stabilisation and Encapsulation of Bacteriophage For Phage TherapyDocumento34 pagineFormulation Stabilisation and Encapsulation of Bacteriophage For Phage TherapyGerman GodiNessuna valutazione finora
- Medication For Staph InfectionDocumento7 pagineMedication For Staph InfectiondelmontlabsNessuna valutazione finora
- Appl - Environ.microbiol. 2015 Gutirrez 3336 48Documento14 pagineAppl - Environ.microbiol. 2015 Gutirrez 3336 48ANA MARIA HERNANDEZ ARTEAGANessuna valutazione finora
- SSTi Diabetic PETRI 2019Documento36 pagineSSTi Diabetic PETRI 2019intermoska soloNessuna valutazione finora
- MRSA Brochure Simple EnglishDocumento2 pagineMRSA Brochure Simple EnglishYS NateNessuna valutazione finora
- Antimicrobial StewardshipDocumento7 pagineAntimicrobial StewardshipMehwish MughalNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundations in Microbiology: TalaroDocumento71 pagineFoundations in Microbiology: Talaromertx013Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bacte Midterm Di TaposDocumento9 pagineBacte Midterm Di TaposAL-HUSSEIN NAWABNessuna valutazione finora
- DrugsDocumento56 pagineDrugssheela100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/41Documento20 pagineCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/41Kaew ThanidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hipochlorous Acid Anjing Kucing 2-5 Mikro L LDocumento10 pagineHipochlorous Acid Anjing Kucing 2-5 Mikro L LyulianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neonatal Sepsis: A Study of The Risk FactorsDocumento42 pagineNeonatal Sepsis: A Study of The Risk FactorsNithin100% (3)
- Joint InfectionsDocumento10 pagineJoint InfectionsJPNessuna valutazione finora
- Approach To Pediatric Periorbital EdemaDocumento10 pagineApproach To Pediatric Periorbital EdemaismailtaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- BBA Timetable V17Documento11 pagineBBA Timetable V17Alisa Sharen AssyfaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quizlet MicroParaDocumento9 pagineQuizlet MicroParaKat JornadalNessuna valutazione finora
- Prevention of Surgical Site Infections: Surgical Patient Care SeriesDocumento11 paginePrevention of Surgical Site Infections: Surgical Patient Care Seriestien duongNessuna valutazione finora
- Arch Dis Child 1998 Ladhani 85 8Documento5 pagineArch Dis Child 1998 Ladhani 85 8Dian Ayu Permata SandiNessuna valutazione finora
- Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) Evolution: The Multiple Facets of An Old PathogenDocumento8 pagineMethicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) Evolution: The Multiple Facets of An Old PathogenAmar SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- MSS Lab 2022-2023Documento19 pagineMSS Lab 2022-2023zaina.bookshopNessuna valutazione finora
- Supertable HLDocumento82 pagineSupertable HLCyden YapNessuna valutazione finora