Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Sex Linked Traits Worksheet 2015
Caricato da
Jeffrey EllsTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Sex Linked Traits Worksheet 2015
Caricato da
Jeffrey EllsCopyright:
Formati disponibili
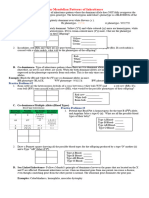
Sex-Linked Traits Worksheet
Background Information:
Sex-linked traits are those whose genes are found on the X
chromosome but not on the Y chromosome. In humans the X chromosomes
are much larger than the Y chromosome and contains thousands of more
genes than the Y chromosome. For each of the genes that are exclusively on
the X chromosomes, females, who are XX, would obviously have two alleles.
Males, who are XY, would have only one allele. Thus females with one
recessive allele and one dominant allele, for a gene that is unique to the X
chromosome, will always display the dominant phenotype. However, a male
with a recessive allele for a gene unique to the X chromosome will always
exhibit that recessive trait because there is no other corresponding allele on
the Y chromosome.
In humans, each of two different sex-linked genes has a defective
recessive allele that causes a disease. The diseases are hemophilia and
colorblindness. In hemophilia, the defective allele prevents the synthesis of a
factor needed for blood clotting. In colorblindness, the defective allele
prevents a person from seeing certain colors.
Use the information below to answer the following questions.
XH- X chromosome with normal dominant allele (no hemophilia)
Xh - X chromosome with recessive hemophilia allele
Y - Y chromosome (does not contain comparable gene)
XB - X chromosome with normal dominant allele (not colorblind)
Xb - X chromosome with recessive colorblind allele
Y -Y chromosome (does not contain comparable gene)
1. Write the genotypes for the following phenotypes of red-green
colorblindness.
a. normal male ____________________
b. normal female carrying no colorblind alleles (Homozygous)
______________
c. colorblind male _________________________
d. normal female carrying the colorblind allele (Heterozygous)
______________
e. colorblind female ______________
2. PUNNETT SQUARE EXAMPLE:
X B XB x
a. What proportion/percent of the male children
are colorblind? ___________
b. What proportion/percent of the female children
are colorblind?___________
3. XBXb x
XB
XbY
X
Y
XB
XBXb
XBXb
XBY
XBY
XBY
a. What proportion of the male children are
colorblind? _____________
b. What proportion of the female children are
colorblind?_______________
4. What is the probability that a colorblind woman who marries a man with normal
vision will have a colorblind child? ______________
5. A normal-sighted woman (whose father was colorblind)
marries a colorblind man.
a. What is the probability that they will have a son
who is colorblind? _____________
b. What is the probability that they will have a
colorblind daughter? _________________
For the following Sex-Linked Punnett Squares:
H= normal blood clotting
h=hemophilia
6. XHXh x
XHY
a. What is the probability that any of their offspring
will have hemophilia? ______________
7. A woman who is a carrier for hemophilia marries a hemophiliac man.
a. What proportion of the male children are
hemophiliacs?_____________
b. What proportion of the female children are
hemophiliacs?____________
8. A phenotypically normal man marries a homozygous normal woman.
a. What is the probability that any of their children
will be hemophiliacs?___________________
9. A phenotypically normal woman has phenotypically normal parents. However, she
has a hemophiliac brother.
(Mom is carrier)
(Dad)
Brother
a. What are her chances of being a carrier for
Hemophilia?______________
ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS USING YOUR KNOWLEDGE OF SEXLINKED TRAITS, THE BACKGROUND INFORMATION AND YOUR NOTES.
10. What is a sex-linked trait?
11. Why must males inherit colorblindness or hemophilia from their mothers?
12. Why is colorblindness or hemophilia more common in males than in
females?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Pedigree Worksheet 2Documento1 paginaPedigree Worksheet 2Rey PinedaNessuna valutazione finora
- X Linked Traits WorksheetDocumento4 pagineX Linked Traits WorksheetKathelyn Ruiz-SumandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sex Linked WorksheetDocumento4 pagineSex Linked WorksheetKathelyn Ruiz-Sumando100% (1)
- Sex-Linked Traits Practice ProblemsDocumento2 pagineSex-Linked Traits Practice ProblemsLaila MahmudahNessuna valutazione finora
- When N 2, 2n + 1 5 Each Phenotypic Category Can Have 4, 3, 2, 1, or 0 Additive Alleles and So OnDocumento5 pagineWhen N 2, 2n + 1 5 Each Phenotypic Category Can Have 4, 3, 2, 1, or 0 Additive Alleles and So OnEaron Van JaboliNessuna valutazione finora
- Abo Blood Type Worksheet 0Documento2 pagineAbo Blood Type Worksheet 0api-233187566Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Punnett Square Packet 2012Documento13 pagineBiology Punnett Square Packet 2012api-241528754Nessuna valutazione finora
- Video Recap of Dihybrid Cross by Amoeba SistersDocumento1 paginaVideo Recap of Dihybrid Cross by Amoeba Sistersapi-2331875660% (2)
- Incomplete and Codominance Review Worksheet 2012Documento3 pagineIncomplete and Codominance Review Worksheet 2012Brasa Y. de Almira0% (1)
- Simple Genetics Practice ProblemsDocumento3 pagineSimple Genetics Practice Problemsapi-265883279Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mendels Peas WorksheetDocumento4 pagineMendels Peas WorksheetLouis Fetilo FabunanNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood-Type GeneticsDocumento2 pagineBlood-Type Geneticsapi-305436791Nessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Allele WorksheetDocumento2 pagineMultiple Allele WorksheetTim SooNessuna valutazione finora
- Build An Atom Worksheet-AnswersDocumento3 pagineBuild An Atom Worksheet-AnswersBilly JoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mendelian Genetics Worksheet PDFDocumento4 pagineMendelian Genetics Worksheet PDFgilNessuna valutazione finora
- Sex Chromosomes, Sex-Linked Genes and DNADocumento4 pagineSex Chromosomes, Sex-Linked Genes and DNAAlyn Mondrano AlonzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Incomplete Codominance Multiple Alleles WorksheetDocumento2 pagineIncomplete Codominance Multiple Alleles WorksheetBeverly Carballo - MoguelNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionic Packet For Lab Chem 2010 2011Documento16 pagineIonic Packet For Lab Chem 2010 2011Victor BritoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pedigree Intro WorksheetDocumento5 paginePedigree Intro WorksheetRONNELNessuna valutazione finora
- Characteristics of PopulationsDocumento6 pagineCharacteristics of PopulationsAnn Marilette100% (2)
- Week 5 Genetics WorksheetDocumento2 pagineWeek 5 Genetics WorksheetTerri A RidallNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet in BloodDocumento12 pagineWorksheet in BloodBryan Mae H. DegorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Pedigree AnalysisDocumento12 paginePedigree AnalysisNeha PathaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Incomplete-and-Codominance-Worksheet AnswersDocumento2 pagineIncomplete-and-Codominance-Worksheet Answersreielleceana0779% (19)
- Pedigree Charts WorksheetDocumento3 paginePedigree Charts Worksheetapi-518315180Nessuna valutazione finora
- AP Biology - Worksheet - Pedigrees 2 PDFDocumento3 pagineAP Biology - Worksheet - Pedigrees 2 PDFVictoria LowmanNessuna valutazione finora
- 27-28 LP MltplallelesDocumento3 pagine27-28 LP MltplallelesCharlesNessuna valutazione finora
- Mixed Genetics Practice Problems KeyDocumento4 pagineMixed Genetics Practice Problems KeynareshyadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Mutations Worksheet PDFDocumento2 pagineMutations Worksheet PDFNouradin Ibrahim OmerNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulatory WksDocumento6 pagineCirculatory WksPak RisNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Science Workbook - HeredityDocumento27 pagine7 Science Workbook - HeredityJorge SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- ABO Blood Type WorksheetDocumento4 pagineABO Blood Type WorksheetJed MarceloNessuna valutazione finora
- Alien Translation ActivityDocumento12 pagineAlien Translation Activityapi-382372564Nessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide A: Key ConceptDocumento17 pagineStudy Guide A: Key ConceptKarla MaríaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sex-Linked Traits Worksheet: Background InformationDocumento4 pagineSex-Linked Traits Worksheet: Background InformationWilson RobertsNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 13 Practice ProblemsDocumento4 pagineChapter 13 Practice ProblemsChachi CNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12 - Chromosomal Basis of InheritanceDocumento7 pagineChapter 12 - Chromosomal Basis of InheritanceKasieSnowNessuna valutazione finora
- Unlock SGCh24Documento7 pagineUnlock SGCh24SilaxNessuna valutazione finora
- Incomplete Multiple AllelesDocumento8 pagineIncomplete Multiple AllelesMarc RusselNessuna valutazione finora
- Non Mendelian PrinciplesDocumento38 pagineNon Mendelian PrinciplesEzra Denise Lubong RamelNessuna valutazione finora
- Sex LinkedDocumento2 pagineSex LinkedsNessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 Sex Linked & Pedigree Notes-2Documento5 pagine2015 Sex Linked & Pedigree Notes-2api-264255406100% (1)
- Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocumento3 pagineNon-Mendelian GeneticsMarlon EllamilNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Long Quiz ScienceDocumento3 pagine2nd Long Quiz ScienceRosel IndolosNessuna valutazione finora
- When Gender MattersDocumento30 pagineWhen Gender MattersJeck Sison100% (2)
- Long Test No.2 Sex Linked TraitsDocumento2 pagineLong Test No.2 Sex Linked TraitsBercia Halikul100% (1)
- q1 Week 5 6 Sex Linked TraitsDocumento25 pagineq1 Week 5 6 Sex Linked Traitskyn chiNessuna valutazione finora
- Non Mendalian Patterns of InheritanceDocumento33 pagineNon Mendalian Patterns of InheritanceTentenNessuna valutazione finora
- Sex Linked Practice Problems TCDocumento17 pagineSex Linked Practice Problems TCanon_11091143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics PacketDocumento6 pagineGenetics Packetjohnny tinambacanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unlock SGCh23Documento8 pagineUnlock SGCh23Silax100% (1)
- Sex-Linked Inheritance & PedigreesDocumento7 pagineSex-Linked Inheritance & PedigreesDaniel BerryNessuna valutazione finora
- Science - G9 - Week 4 (Lessons 11-13)Documento28 pagineScience - G9 - Week 4 (Lessons 11-13)Rhyan Zero-four BaluyutNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5. B. Extensions of Mendelian GeneticsDocumento25 pagineChapter 5. B. Extensions of Mendelian GeneticsXilca JamaimahNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics Review Questions - KeyDocumento6 pagineGenetics Review Questions - KeyAxle JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Sex Determination and Sex LinkedpptxDocumento47 pagineSex Determination and Sex LinkedpptxJanloydNessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocumento39 pagineNon-Mendelian GeneticsKing TagabuenNessuna valutazione finora
- Rinhs Science 9 1st Activity 2 Non Mendelian GeneticsDocumento2 pagineRinhs Science 9 1st Activity 2 Non Mendelian GeneticsRyan BersaminNessuna valutazione finora
- Non Mendelian WorksheetsDocumento2 pagineNon Mendelian WorksheetsAcel PeñalozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sex Linkage and Sex DeterminationDocumento8 pagineSex Linkage and Sex DeterminationBrian MachachaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomes DocumentDocumento37 pagineBiomes DocumentJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading-Habitat & NicheDocumento2 pagineReading-Habitat & NicheJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Biome InvestigationDocumento4 pagineBiome InvestigationJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology-Lecture WKSH 1Documento2 pagineEcology-Lecture WKSH 1Jeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- AOTW Polar Bear MediumDocumento6 pagineAOTW Polar Bear MediumJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology LectureDocumento93 pagineEcology LectureJeffrey Ells0% (1)
- AOTW Shark MigrationDocumento7 pagineAOTW Shark MigrationJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Monohybrid Cross Practice 2-10-15 PDFDocumento5 pagineMonohybrid Cross Practice 2-10-15 PDFJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- A Probable Situation-Lab WorksheetDocumento4 pagineA Probable Situation-Lab WorksheetJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- AOTW Mummy MediumDocumento7 pagineAOTW Mummy MediumJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Non Mendelian Genetics-Sex Linked Lecture NotesDocumento3 pagineNon Mendelian Genetics-Sex Linked Lecture NotesJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Alleles Trait Lecture NotesDocumento2 pagineMultiple Alleles Trait Lecture NotesJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Types WorksheetDocumento2 pagineBlood Types WorksheetJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- AOTW-Rip Current - MDocumento6 pagineAOTW-Rip Current - MJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pure Gold WKSHDocumento1 paginaPure Gold WKSHJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Vocab Worksheet Starter ScaffoldedDocumento2 pagineVocab Worksheet Starter ScaffoldedJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- AOTW-Measles Outbreak PDFDocumento5 pagineAOTW-Measles Outbreak PDFJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Article of The WeekDocumento2 pagineArticle of The WeekJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics Lecture NotesDocumento58 pagineGenetics Lecture NotesJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Charactistics of Life Unit With VocabDocumento16 pagineCharactistics of Life Unit With VocabJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- AOTW-Genetics and AncesteryDocumento3 pagineAOTW-Genetics and AncesteryJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Traits Lab-2015Documento7 pagineHuman Traits Lab-2015Jeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- A Probable Situation-LabDocumento5 pagineA Probable Situation-LabJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Food Label-Cell UnitDocumento5 pagineFood Label-Cell UnitJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Make A CO2 Sandwich-Student DataDocumento1 paginaHow To Make A CO2 Sandwich-Student DataJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- VOCAB-Characteristics of LifeDocumento5 pagineVOCAB-Characteristics of LifeJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- VOCAB-Characteristics of LifeDocumento5 pagineVOCAB-Characteristics of LifeJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Should I Be Concerned-E Coli ExperimentDocumento1 paginaShould I Be Concerned-E Coli ExperimentJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Graphing Exercise Food Label-Cell Unit-Muskegon HeightsDocumento2 pagineGraphing Exercise Food Label-Cell Unit-Muskegon HeightsJeffrey EllsNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Picture On EvolutionDocumento16 pagineBig Picture On EvolutionWellcome Trust100% (1)
- Benzopyrene Exposure Disrupts DNA Methylation and Growth DynamicsDocumento11 pagineBenzopyrene Exposure Disrupts DNA Methylation and Growth DynamicsLorena IntriagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. M. A. Mazid Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Dhaka, Dhaka-1000Documento66 pagineDr. M. A. Mazid Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Dhaka, Dhaka-100053-Deepankar SutradharNessuna valutazione finora
- NobuoDocumento5 pagineNobuosolarnageNessuna valutazione finora
- Edwards Syndrome NotesDocumento2 pagineEdwards Syndrome Notesapi-386407615Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 2-12 SecAss 11-3Documento1 paginaBiology 2-12 SecAss 11-3Edward Egan100% (1)
- Anthropology SyllabusDocumento8 pagineAnthropology Syllabusvijaya senthilNessuna valutazione finora
- Mendel ExtDocumento28 pagineMendel Extapi-27589736Nessuna valutazione finora
- RetrotranscriptasaDocumento59 pagineRetrotranscriptasaulises delgadilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Associate Degree Program/ Ba-Bsc/Part Ii Examination2020 Subject: Genetics Ii, Paper ADocumento5 pagineAssociate Degree Program/ Ba-Bsc/Part Ii Examination2020 Subject: Genetics Ii, Paper AMuhammadQasimNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Biology of The Gene: Figures 10.1 - 10.5Documento75 pagineMolecular Biology of The Gene: Figures 10.1 - 10.5Arif MulyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Trevor Nong Final ProjectDocumento7 pagineTrevor Nong Final Projectapi-375199340Nessuna valutazione finora
- AP Biology - 7.9 - PhylogenyDocumento27 pagineAP Biology - 7.9 - PhylogenyVictoria LowmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Histone Family PDFDocumento17 pagineHistone Family PDFDelos NourseiNessuna valutazione finora
- FBI Quality Assurance Standards For DNA Testing 2009Documento28 pagineFBI Quality Assurance Standards For DNA Testing 2009jac_blakeNessuna valutazione finora
- 9th - Mar 31stDocumento5 pagine9th - Mar 31stLiên NghiêmNessuna valutazione finora
- 32 New Seminar Topics On Future Technology - 2019-2055Documento51 pagine32 New Seminar Topics On Future Technology - 2019-2055Anurav KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- The Science of LongevityDocumento5 pagineThe Science of LongevityTogrul MusabeyliNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 3rd Edition Starr Test BankDocumento12 pagineBiology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 3rd Edition Starr Test Bankjoanneesparzagwjxmyqont100% (28)
- Topic 1.6: Stages of Mitosis: Stage Diagram Key EventsDocumento1 paginaTopic 1.6: Stages of Mitosis: Stage Diagram Key EventsKaleab GebreegizabiherNessuna valutazione finora
- The Truth Behind The Polio VaccineDocumento28 pagineThe Truth Behind The Polio VaccineFreedomFighter32100% (2)
- BioMEMS Introduction PDFDocumento11 pagineBioMEMS Introduction PDFDravvy Sahayam100% (1)
- Assign 01 (8610) Wajahat Ali Ghulam BU607455 B.ed 1.5 YearsDocumento9 pagineAssign 01 (8610) Wajahat Ali Ghulam BU607455 B.ed 1.5 YearsAima Kha KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- A-Level Biology Question and Answers 20 20/2021Documento76 pagineA-Level Biology Question and Answers 20 20/2021FireFrostNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading The World Now 3 Answer Key 2Documento60 pagineReading The World Now 3 Answer Key 2Kanyapat WichienNessuna valutazione finora
- 1603LEADERACHIEVERMLABCDEMAZA MAJOR TEST 65760 TEST PDF Fv16Si8njhDocumento64 pagine1603LEADERACHIEVERMLABCDEMAZA MAJOR TEST 65760 TEST PDF Fv16Si8njhGjgcdNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacterial TransductionDocumento22 pagineBacterial TransductionBatool AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Selection Lab-Phet Simulation Astrid 10DDocumento8 pagineNatural Selection Lab-Phet Simulation Astrid 10DMary Fatima LlanesNessuna valutazione finora
- 15589627941404895685Documento38 pagine15589627941404895685Sher Singh MathurNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3.3Documento21 pagineLesson 3.3Claude Nathan AlidoNessuna valutazione finora