Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
CELLULAR REPRODUCTION AND THE CELL CYCLE
Caricato da
Darwin Competente LagranDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CELLULAR REPRODUCTION AND THE CELL CYCLE
Caricato da
Darwin Competente LagranCopyright:
Formati disponibili
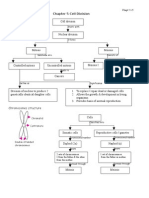
CHAPTER 5: CELLULAR REPRODUCTION
REPRODUCTION
-
It is the process by which an organism
produces offspring either sexually or
asexually. Its main purpose is for the
perpetuation of species
The Cell Cycle
-
CELL DIVISION
-
It is the process of cell reproduction
following several stages to produce two
daughter cells. It is often referred to as
CELLULAR REPRODUCTION.
Mitosis Promoting Factor (MPF)
-
Protein triggering agent for cell
division.
Interphase
-
a. MEMBRANE GROWTH
b. MITOSIS (eukaryotic cells)
c. MEIOSIS (eukaryotic cells)
Membrane Growth
The process wherein cells partition
their genetic material among
prokaryotic cell.
Mitosis
-
The process of nuclear division in
which duplicated chromosomes are
separated from one another,
producing nuclei, each with one copy
of each chromosomes.
Comes from the Greek word mitos,
meaning thread.
Mitosis is usually accompanied by
cytokinesis, resulting in two daughter
cells with genetic potential identical to
each other and the parent cell which
they arose.
This is a type of cell division that
occurs only in reproductive cells or
gametes.
Meiosis occurs only in diploid cells and
produces four daughter nuclei, each
containing haploid number of
chromosomes.
Two main steps
o Mitosis is a series of phases in
cell division during which the
nucleus of cell divides into two
nuclei with identical genetic
material.
o Cytokinesis is the process
during which the cytoplasm of
the cell divides into two new
cells, called daughter cells
Stages in Mitosis
-
Meiosis
-
The longest phase in the cell cycle of a
typical cell
M Phase
TYPES OF CELL DIVISION
The stages through which a cell
passes from one cell division to the
next.
Two main stages ( *Interphase * M
phase )
Interphase
o The period between cell
division. The genetic material is
in the form of chromatin.
o Centrosomes, a small oval
body, is found just outside the
nuclear membrane. This is true
in animal cell but not in plant
cell.
Prophase
o Chromatin shortens and
thickens.
o DNA in chromatins replicated.
o Chromatin now becomes
chromatid which is held
together at a single point by a
centromere
Metaphase
o Chromosomes move toward the
middle of the spindle fiber.
Anaphase
o Chromatids separate and begin
to travel away from each other
towards opposite poles.
Telophase
o In animal cells, centrosomes
reappear
Cytokinesis
o In animal cells, cytokinesis
results when a fiber ring
composed of a protein called
actin around the center of the
cell contracts pinching the cell
into two daughter cells, each
with one nucleus
CHAPTER 5: CELLULAR REPRODUCTION
Chromosome Number
In humans, each gamete contains 23
chromosomes.
All body cells contain two complete
sets of chromosomes, which in human
is 46 chromosomes.
Diploid
-
Sperm - Male gametes
Egg or Ova - Female gametes
one complete set of chromosomes
Asexual Reproduction
-
Tumor - abnormal growths of cells.
-
Benign Tumor
o cells remain together and
usually cause little harm.
Benign tumors can be often
removed by surgery.
Malignant Tumor
o cells do not remain together.
They break free from a tumor
and migrate to a new locations
in the body. The malignant cells
can start new tumors in new
locations.
Cancer
-
The spread of malignant cells to a new
location. Cancer cells can spread
freely because they lack the surface
proteins that bind the normal cells
together.
Asexual
o reproduce without the use of
gametes or sex cells. One
parent organism can reproduce
by itself.
Budding
o a parent organism produces
offspring by growing a tiny
replica of itself called a bud, on
some part of its body.
Fragmentation
o separated pieces of the parent
organism can develop into new
individuals
Vegetative Reproduction
o new plants grow from the
stems, roots, or leaves of an
existing plant
Fission
o splitting of organism body into 2
identical parts
Sporulation
o spore formation as in fern plant
and mushrooms.
Regeneration
-
Types of Reproduction
-
Sexual
o requires the union of male
and female gametes called
fertilization.
The cell with two complete sets of
chromosome
Haploid
-
The ability of some animals to grow
entire body parts lost through accident
or injury.
Pollination
-
the transfer of pollen grains from the
another of one flower to the stigma of
another flower
Self Pollination - the transfer of pollen
grains of one flower to the stigmata of the
same flower.
Cross Pollination - the transfer of pollen
grains of one flower to the stigmata of
another flower
Agents of Pollination
-
Wind Water Animals man
FERTILIZATION female gametes
The union of male gametes and
ZYGOTE -
The single cell that results from fertilization.
The zygote contains two complete sets of chromosomes and
therefore diploid
HOMOLOGOUS PAIRS chromosomes in a diploid cell.
CROSSING OVER -
The matching pairs of
It is the exchange of genes
between pairs of homologous chromosomes.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Handbook of The Worlds Conifers 2Documento1.154 pagineA Handbook of The Worlds Conifers 2ホセのアルフォンソ斗67% (3)
- Scientific Method Case StudiesDocumento1 paginaScientific Method Case Studiesapi-304326920Nessuna valutazione finora
- FLOWERDocumento3 pagineFLOWERhendrix obcianaNessuna valutazione finora
- GARDEN LORE OF ANCIENT ATHENSDocumento40 pagineGARDEN LORE OF ANCIENT ATHENSRo OrNessuna valutazione finora
- Botany Notes Part 3Documento13 pagineBotany Notes Part 3Rochenick MagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 5 Mitosis and MiosisDocumento11 pagineWeek 5 Mitosis and MiosisEarl RénzNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5, (Meiosis Mitosis) Biof4Documento94 pagineChapter 5, (Meiosis Mitosis) Biof4Rohana MatNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 Cell Cycle Chromosome and Mitosis 2018Documento42 pagineChapter 9 Cell Cycle Chromosome and Mitosis 2018Nehjoy GerangueNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis and MitosisDocumento6 pagineMeiosis and MitosisSummer LoveNessuna valutazione finora
- HeredityDocumento2 pagineHeredityAngelika TibayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 5Documento17 pagineBio 5Prince SanjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell DivisionDocumento94 pagineCell Divisionazfdin100% (2)
- Cell Cycle Stages and Phases ExplainedDocumento43 pagineCell Cycle Stages and Phases ExplainedMariam QaisNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Division - Key PointsDocumento10 pagineCell Division - Key PointssivarajeshwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology ICSE KeypointsDocumento94 pagineBiology ICSE Keypointsaklnew100% (1)
- Tri-Fold Template-1Documento2 pagineTri-Fold Template-1api-260947636Nessuna valutazione finora
- All About Stem CellsDocumento8 pagineAll About Stem CellsorangebackpackNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOLOGY Final Worksheet ImportantDocumento12 pagineBIOLOGY Final Worksheet ImportantGhadi غديNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocumento40 pagineMitosis Vs Meiosiscmillica1176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Examination-BiologyDocumento15 pagineFinal Examination-BiologyAlliah MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell DiversityDocumento10 pagineCell Diversitychristian lunaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cell Cycle: How Cells Divide and GrowDocumento6 pagineThe Cell Cycle: How Cells Divide and GrowbaneNessuna valutazione finora
- TB20003 Lab Manual GeneticsDocumento18 pagineTB20003 Lab Manual Geneticsluver_lynz903814Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Unit 2Documento7 pagineBio Unit 2Thathyana de SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 215 Notes Meiosis and MitosisDocumento17 pagineBio 215 Notes Meiosis and MitosisPrecious ObhasedoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 001 Cell DivisionDocumento8 pagineBio 001 Cell DivisionKnick KnackNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Cell Division: Chapt 5:1/5Documento5 pagineChapter 5 Cell Division: Chapt 5:1/5ctazimaNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Biology Lab 3 QuestionsDocumento3 pagineAP Biology Lab 3 Questionsedwarddame100% (1)
- Group 5 Gametes and FertilizationDocumento74 pagineGroup 5 Gametes and FertilizationLira PagaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 3xasanDocumento12 pagineBiology 3xasanAbdulkadir IbraahimNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO 103 Lecture 11Documento27 pagineBIO 103 Lecture 11EnmuskNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Science 2 RPK - Chap 5 Cell Division (Part 1)Documento58 pagine4 Science 2 RPK - Chap 5 Cell Division (Part 1)zanayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis vs Meiosis: Cell Division Processes ExplainedDocumento7 pagineMitosis vs Meiosis: Cell Division Processes ExplainedJD DX100% (1)
- Unit 1: The World of Cell Chapter 1: Introduction To Cell Biology Cell Theory - The Cell Theory Is The Universal For All Living Things, No Matter HowDocumento22 pagineUnit 1: The World of Cell Chapter 1: Introduction To Cell Biology Cell Theory - The Cell Theory Is The Universal For All Living Things, No Matter HowCamille BonsayNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Division LessonDocumento9 pagineCell Division LessonGerry100% (1)
- BHS Biology SS1Documento8 pagineBHS Biology SS1Oluwatosin Peter AtandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Division and Reproduction GuideDocumento6 pagineCell Division and Reproduction GuideA C100% (1)
- Biology ReviewerDocumento6 pagineBiology Reviewerleleidy19emanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Cycle Stages and Phases ExplainedDocumento3 pagineCell Cycle Stages and Phases ExplainedXiasamaNessuna valutazione finora
- CELL DIVISION-MitosisDocumento28 pagineCELL DIVISION-MitosisAVINASH VARMANessuna valutazione finora
- 4.2 Cell As A Unit of LifeDocumento7 pagine4.2 Cell As A Unit of Lifehola adiosNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure and DivisionDocumento70 pagineCell Structure and DivisionAMALIA INDAH ALLIZA ALLIZANessuna valutazione finora
- SCIENCE (Key To Correction & References)Documento6 pagineSCIENCE (Key To Correction & References)Patricia Anne GregorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Module-2-Meiosis-and-MitosisDocumento88 pagineModule-2-Meiosis-and-MitosisSevdred CadelinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Division: Dr. P. Pokorski University of Michigan - Dearborn Department of BiologyDocumento52 pagineCell Division: Dr. P. Pokorski University of Michigan - Dearborn Department of BiologyZuha HarithNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 4Documento8 pagineLesson 4Marie Antonette BaligodNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Ten:: Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocumento12 pagineChapter Ten:: Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionShivani Shree SundaramoorthyNessuna valutazione finora
- BIODocumento7 pagineBIOREYES, Kyla Marie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Unit 2 Revision Topic 3Documento6 pagineBiology Unit 2 Revision Topic 3YasinKureemanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cell Cycle: A Concise Guide to Cell DivisionDocumento27 pagineThe Cell Cycle: A Concise Guide to Cell DivisionAnindita MishiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis and Meiosis: TranscriptDocumento2 pagineMitosis and Meiosis: TranscriptKareem AghaNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 3 Revision: Structure of A Eukaryotic CellDocumento10 pagineTopic 3 Revision: Structure of A Eukaryotic CellCam J BaileyNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction and Sexual Cycle in Flowering PlantsDocumento34 pagineReproduction and Sexual Cycle in Flowering PlantsNarveer SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 2 and 3 - Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento63 pagineDay 2 and 3 - Mitosis and MeiosisDarlene Joyce ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis: Four Haploid CellsDocumento10 pagineSexual Reproduction and Meiosis: Four Haploid CellsJohnieer Bassem MoferdNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis & MeiosisDocumento28 pagineMitosis & MeiosisEma ColleteNessuna valutazione finora
- mitosis-WPS OfficeDocumento5 paginemitosis-WPS OfficeSheila Mae AramanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Cell The Cell Cycle: (Before) NucleusDocumento2 pagineCell Cell The Cell Cycle: (Before) NucleusRyan ForteNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 15 NotesDocumento5 pagineCH 15 NotesCJNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.introduction To EmbryologyDocumento63 pagine8.introduction To EmbryologyAhmed OrabyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5Documento14 pagineChapter 5ingridvirginia2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis MeiosisDocumento8 pagineMitosis MeiosisJascha Isaac PangandianNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Topic 3 Student RoomDocumento10 pagineBio Topic 3 Student RoomFaizan SanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6tb SchedDocumento40 pagine6tb SchedDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 240 480 1 SM PDFDocumento7 pagine240 480 1 SM PDFDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch10 PurchaseCycleDocumento18 pagineCh10 PurchaseCycleDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- Information Technology I PDFDocumento40 pagineInformation Technology I PDFDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- Appointment Slip for SC Demo InterviewDocumento1 paginaAppointment Slip for SC Demo InterviewDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 33 8708903 9 PDFDocumento1 pagina33 8708903 9 PDFDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- Appointment Slip: 2 X 2 ID PictureDocumento1 paginaAppointment Slip: 2 X 2 ID PictureDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- Jzanzig - Auditing CH 10 LectureDocumento35 pagineJzanzig - Auditing CH 10 LectureTrish CalumaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6tb Sched 1Documento43 pagine6tb Sched 1Darwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 33 8708903 9 PDFDocumento1 pagina33 8708903 9 PDFDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 6tb Sched 1Documento48 pagine6tb Sched 1Darwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 34 3584935 4 PDFDocumento1 pagina34 3584935 4 PDFDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 6tb Sched 1Documento48 pagine6tb Sched 1Darwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 7Documento1 pagina7Darwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 8Documento1 pagina8Darwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- Appointment Slip: 2 X 2 ID PictureDocumento1 paginaAppointment Slip: 2 X 2 ID PictureDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 240 480 1 SM PDFDocumento7 pagine240 480 1 SM PDFDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- Appointment Slip: 2 X 2 ID PictureDocumento1 paginaAppointment Slip: 2 X 2 ID PictureDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 6130.september - Not UpdatedDocumento63 pagine6130.september - Not UpdatedDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 34 5062057 4 PDFDocumento1 pagina34 5062057 4 PDFDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 34 5062057 4 PDFDocumento1 pagina34 5062057 4 PDFDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- Appointment Slip: 2 X 2 ID PictureDocumento1 paginaAppointment Slip: 2 X 2 ID PictureDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 34 5062057 4 PDFDocumento1 pagina34 5062057 4 PDFDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 A-1 Class Notes PDFDocumento3 pagine2009 A-1 Class Notes PDFCzarina CasallaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 A-2 Class NotesDocumento5 pagine2009 A-2 Class Notescome2sayNessuna valutazione finora
- 6130.september - Not UpdatedDocumento63 pagine6130.september - Not UpdatedDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- Auditing 3 Class Notes I. Auditing 3: © 2009 Devry/Becker Educational Development Corp. All Rights ReservedDocumento7 pagineAuditing 3 Class Notes I. Auditing 3: © 2009 Devry/Becker Educational Development Corp. All Rights ReservedDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 A-5 Class Notes PDFDocumento8 pagine2009 A-5 Class Notes PDFDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 Assurance Class NotesDocumento6 pagine2009 Assurance Class NotesAgayatak Sa ManenNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 SOAR PK and Selling Performance - SeptemberDocumento16 pagine2016 SOAR PK and Selling Performance - SeptemberDarwin Competente LagranNessuna valutazione finora
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in BiologyDocumento2 pagineSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in BiologyRJ CC67% (6)
- Leptadinia ReticulataDocumento8 pagineLeptadinia ReticulatavijendrakumarsahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Raven Biology of Plants: Eighth EditionDocumento32 pagineRaven Biology of Plants: Eighth EditionMoath EnnabNessuna valutazione finora
- Komyiama Et Al. (2008) - Allometry, Biomass, and Productivity of Mangrove Forests - A Review PDFDocumento10 pagineKomyiama Et Al. (2008) - Allometry, Biomass, and Productivity of Mangrove Forests - A Review PDFcarlitos254Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bougainvillea - WikipediaDocumento5 pagineBougainvillea - WikipediaShukri RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Name Changes in PlantsDocumento27 pagineWhy Name Changes in PlantsPhani Bhusan SahooNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepare Riccia SlideDocumento2 paginePrepare Riccia SlideAishwarya MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction 3 - Flowering and Non-FloweringDocumento27 pagineReproduction 3 - Flowering and Non-Floweringrenato.minaNessuna valutazione finora
- Eugene MunroeDocumento3 pagineEugene MunroeAndrew ZaikinNessuna valutazione finora
- September 2017: Trichocereus Growers Worldwide Instagram: Trichocereus PageDocumento83 pagineSeptember 2017: Trichocereus Growers Worldwide Instagram: Trichocereus PageAgustina LongoNessuna valutazione finora
- Q2e LS2 U02 AudioScriptDocumento6 pagineQ2e LS2 U02 AudioScriptyen523459Nessuna valutazione finora
- Beginner PackageDocumento30 pagineBeginner Packagespsubash4409100% (1)
- IEO Class 8 Paper 2015 Set A Part 1Documento3 pagineIEO Class 8 Paper 2015 Set A Part 1sangdeep waldeNessuna valutazione finora
- Endemic Flora of Bosilegrad RegionDocumento10 pagineEndemic Flora of Bosilegrad RegionbrankomitovNessuna valutazione finora
- Killling On A Tree Quetion AnswarsDocumento3 pagineKillling On A Tree Quetion AnswarsAnjan BasakNessuna valutazione finora
- Moringa Presentation For Cattle FoodDocumento27 pagineMoringa Presentation For Cattle FoodStefan KatzNessuna valutazione finora
- Master Mind Quiz For Gr-5Documento3 pagineMaster Mind Quiz For Gr-5sasi202906437Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rhode Island Coastal Buffer Zone Planting Guide - University of Rhode IslandDocumento14 pagineRhode Island Coastal Buffer Zone Planting Guide - University of Rhode IslandFree Rain Garden Manuals and MoreNessuna valutazione finora
- NSA34 The Taking of Chelsea 426 David LlewellynDocumento257 pagineNSA34 The Taking of Chelsea 426 David LlewellynRachelle McDonald100% (1)
- LTC Vaidyah (Set 1) NEET Part Test - 2 (26-Feb-24) Question PaperDocumento41 pagineLTC Vaidyah (Set 1) NEET Part Test - 2 (26-Feb-24) Question Papersai982005Nessuna valutazione finora
- List of Autumn Bulbs South of Africa.Documento8 pagineList of Autumn Bulbs South of Africa.Renato Cajaleon SuarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Activi Learning Outcomes: Week Topic Ties I-Think/ Teaching AidsDocumento35 pagineActivi Learning Outcomes: Week Topic Ties I-Think/ Teaching AidsSang 90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Distribution, Identification and Genetic Diversity Among Bamboo Species: A Phenomic ApproachDocumento8 pagineDistribution, Identification and Genetic Diversity Among Bamboo Species: A Phenomic ApproachAMALIA RIZQI ROSANINGDYAHNessuna valutazione finora
- Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation in CucumberDocumento4 pagineAgrobacterium-Mediated Transformation in CucumberAPOTEK DE DUA JAYA FARMANessuna valutazione finora
- Coal Petrology PDFDocumento16 pagineCoal Petrology PDFMeiliza Fitri100% (1)
- Biology Formal Lab Auxins 2Documento14 pagineBiology Formal Lab Auxins 2Ryan Holinshead100% (1)