Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
What Is Process Safety Engineering
Caricato da
CLPWCDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
What Is Process Safety Engineering
Caricato da
CLPWCCopyright:
Formati disponibili
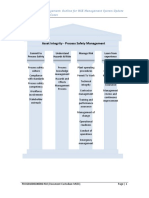
What is Process Safety Engineering?
Implementing into everyday engineering procedures, a broad-based understanding of the
complex interaction of chemical process technology, mechanical and process design, process
control, and Process Safety Management Systems (PSMS) and by virtue of knowledge and
experience, evaluate an integrated petrochemical process and:
Identify hazards:
• overpressure/underpressure hazards
• thermal expansion and brittle fracture hazards
• fire and explosion hazards
• dust explosion hazards
• static electricity hazards
• human factors hazards
• chemical and reactive chemistry hazards
• toxic exposure
Evaluate the risk from those hazards, both qualitatively and quantitatively:
• knowledge of previous incidents that have occurred in the company and industry
• failure mechanisms that could lead to risks being realized
• risk scenarios that should be evaluated
• sufficient and effective hazard controls in place or needed
• analyze the consequences and probabilities of those risk scenarios
• assess the significance of risk posed by those scenarios
Assist in the identification of and evaluation of cost-effective engineering solutions to reduce or
mitigate those risks:
• remove or reduce the hazard through inherently safer solutions
o simplify the process
o substitute less hazardous materials for more hazardous materials
o operate at less hazardous operating conditions
o reduce inventories
• reduce the likelihood of risks by providing more or better layers of protection
• reduce the consequence of risks by employing mitigating systems
• apply Human Factors principles to reduce the error potential at the interfaces of people with
equipment and instrumentation
To successfully perform these functions by being knowledgeable in the following areas:
Knowledge:
• Engineering Standards and Practices:
o Legislation and regulations
o Company engineering practices
o Industry Standards (API, etc.)
o Consensus Standards and Codes (ASME, ASTM, NFPA, ANSI, ISA, EN, etc.)
o Recognized and Generally Accepted Good Enginering Practices (CCPS, etc.)
o Process Safety Management Systems
• Human Factors:
o Human-machine concepts
o Principles of human error reduction
• Process Safety Information:
o Process Flow Diagrams (PFDs)
o Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&IDs)
o Mechanical Drawings and plot plans
o Instrumentation and Electrical Diagrams
o Electrical Area Classification
o Facility Siting and Equipment Spacing
o Relief System Design and Design Basis
o Material and Energy Balance
o Materials Envelope Statement/Safe Operating Envelope
o Properties and Hazards of Materials, including incompatibilities
o Safety Instrumented Function SIL Target and relevance to installation, inspection and
maintenance
o Buildings blast resistance design basis
o Fire fighting and associated facilities such as Sewer Design Basis
• Process Hazards Analysis Methodologies:
o Hazard and Operability study (HAZOP)
o What-If Analysis
o Preliminary Hazards Analysis
o Checklist Analysis
o Inherent Safety Analysis
o Critical Task Analysis (CTA)
o Human Factors Review
o Pre-Startup Safety Review
o Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
• Technical Systems Analysis Methodologies:
o Safety Relief Valve and Flare Header analysis
o Fire Protection System analysis
o Safety Instrumented System quantitative analysis
• Risk Analysis and Assessment Methodologies:
o Fault Tree Analysis
o Event Tree Analysis
o Release and Dispersion Analysis
o Consequence Analysis
o Qualitative, scenario-based risk assessments
o Quantitative risk assessments (QRA)
o Root-cause Incident Investigation techniques
• Decision Analysis Methodologies:
o Benefit/Cost Analysis
o Semi-quantitative Risk and Decision Analysis
o Quantitative Risk and Decision Analysis
o Evaluating options in the context of ALARP
Typical work activities in Process Safety Engineering include:
Site Level
• Audit key elements of process safety to ensure processes are being followed and are working as
intended
• Ensure proper application of MOC and appropriate hazard analysis and risk assessments are
performed on changes
• Confirm proper resolution and closure of recommendations from process safety studies, audits,
and incident investigations
• Coordinate and ensure effective execution of hazard and risk assessment studies
• Ensure site personnel are trained and recognize their role in process safety
• Communicate and work with management to ensure leadership and proper emphasis on
process safety, including employee participation
• Help prioritize actions to eliminate/mitigate process safety risks
• Ensure that projects fully address process safety in-design and satisfy process safety requirements
Company/Central Engineering Services Level
• Provide specialist consulting service in safety and fire protection in the design, engineering,
construction and operation of chemical plants and refineries
• Provide on-call advice and recommendations on applicability and interpretation of both
internal and external guidelines and standards
• Develop new criteria and guidelines
• Monitor additions and changes to codes and standards applicable to company operations
• Actively participate to influence and remain current with new developments and positions taken
on updates to existing standards
• Assist in the implementation and improvement of Process Safety Management Systems
• Develop and deliver training and other presentations on Process Safety Management and
related subjects
• Develop or assist in the development of new and updated tools for process safety applications
and reviews
• Participate in or lead process hazards and other process safety analysis at existing sites and for
new projects
• Participate in or lead formal Risk Assessments of existing operations
• Represent the Company in outside professional process safety organizations (CCPS, EPSC, IPSG,
etc.), research consortia (MKOPSC, Wharton, etc.), and process safety committees of trade
organizations (API, ACC, TCC, SOCMA, etc.)
• Develop and maintain contacts with other companies to remain abreast of Industry Best
Practices
• Provide Process Safety advice related to ongoing site risk management
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Skincare Routine Order Cheat SheetDocumento10 pagineSkincare Routine Order Cheat SheetYel Salenga100% (3)
- The Working of KarmaDocumento74 pagineThe Working of KarmaSuhas KulhalliNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Safety AuditDocumento21 pagineProcess Safety AuditKailash Pandey100% (2)
- Process Safety InformationDocumento7 pagineProcess Safety InformationMohammed Zubair100% (1)
- Process Safety Management PDFDocumento31 pagineProcess Safety Management PDFMuhammad Husnul Khuluq100% (4)
- Pre Startup Safety Review-PSSRDocumento19 paginePre Startup Safety Review-PSSRPrem Shanker Rawat100% (2)
- Updated Technical SafetyDocumento122 pagineUpdated Technical SafetyElla Agbettor100% (2)
- Kimi No Na Wa LibropdfDocumento150 pagineKimi No Na Wa LibropdfSarangapani BorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Inherently Safer DesignDocumento64 pagineInherently Safer Designchetan_7927Nessuna valutazione finora
- Stopping by Woods On A Snowy EveningDocumento9 pagineStopping by Woods On A Snowy EveningJulia Garces100% (2)
- Guide For Process Safety in DesignDocumento35 pagineGuide For Process Safety in DesignpoundingNessuna valutazione finora
- EXCEL For Pump DesignDocumento2 pagineEXCEL For Pump Designkad-7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Process Safety Management TrainingDocumento232 pagineProcess Safety Management TrainingTallal Joiya92% (25)
- 0 Egpc-Aud-001-Aprc Bowtie Voume 5Documento111 pagine0 Egpc-Aud-001-Aprc Bowtie Voume 5mohamed ashor100% (1)
- QRA PresentationDocumento34 pagineQRA PresentationAmol LakareNessuna valutazione finora
- KppProcess Safety AuditDocumento26 pagineKppProcess Safety Auditkirandevi1981Nessuna valutazione finora
- HSE GuidelineDocumento59 pagineHSE GuidelineDia Putranto HarmayNessuna valutazione finora
- ProcessSafetyManagement AuditApproachDocumento8 pagineProcessSafetyManagement AuditApproachismailayarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Process Hazard AnalysisDocumento41 pagine2 Process Hazard AnalysisSHANZAY21111111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Process Safety Performance IndicatorsDocumento30 pagineProcess Safety Performance Indicatorskanakarao1100% (2)
- Guidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsDa EverandGuidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsNessuna valutazione finora
- Osha Study Material: Project Sound EstDocumento43 pagineOsha Study Material: Project Sound EstMohammed Anati100% (1)
- Process Safety ManagementDocumento23 pagineProcess Safety ManagementMuhammad AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- DNV Process Vs Occupational SafetyDocumento17 pagineDNV Process Vs Occupational Safetymarsulex100% (1)
- Progress On Process Safety IndicatorsDocumento23 pagineProgress On Process Safety IndicatorsDuNessuna valutazione finora
- HAZID PresentationDocumento11 pagineHAZID PresentationAlvian FachrurroziNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To PSM at UI-WCP Oct 2019 (Workshop)Documento60 pagineIntro To PSM at UI-WCP Oct 2019 (Workshop)Aditya SetiadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsDa EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Guidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyDa EverandGuidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyNessuna valutazione finora
- Blank PSM & RMP Audit FormDocumento298 pagineBlank PSM & RMP Audit Formclashu2Nessuna valutazione finora
- 09 1HAZOPStudyTrainingCourseDocumento55 pagine09 1HAZOPStudyTrainingCoursehelton_bsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Process and Plant Safety HazardsDocumento71 pagineProcess and Plant Safety Hazardsapi-2614241788% (17)
- Guidelines for Fire Protection in Chemical, Petrochemical, and Hydrocarbon Processing FacilitiesDa EverandGuidelines for Fire Protection in Chemical, Petrochemical, and Hydrocarbon Processing FacilitiesNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Safety Master Class I Sreejith Pillai 2018Documento22 pagineProcess Safety Master Class I Sreejith Pillai 2018Pillai Sreejith100% (1)
- Types of Loads Considered For Design of BridgeDocumento45 pagineTypes of Loads Considered For Design of BridgeAbhishek100% (1)
- Guidelines for Developing Quantitative Safety Risk CriteriaDa EverandGuidelines for Developing Quantitative Safety Risk CriteriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Based Process Safety DesignDocumento13 pagineRisk Based Process Safety DesignVan SotNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre Startup Safety ReviewDocumento29 paginePre Startup Safety ReviewAhsan100% (1)
- FebvreDocumento449 pagineFebvreIan Pereira AlvesNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Safety Management OutlineDocumento24 pagineProcess Safety Management Outlineismailines100% (1)
- PSSR FormDocumento16 paginePSSR Formmythee100% (5)
- 14 Elements of PSM - Industry ResourcesDocumento5 pagine14 Elements of PSM - Industry ResourcesSaad Ghouri100% (2)
- SWP Bypassing Critical Protections GuidelinesDocumento10 pagineSWP Bypassing Critical Protections Guidelinesesakkiraj1590100% (1)
- QRA PresentationDocumento34 pagineQRA PresentationAmol LakareNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsDa EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNessuna valutazione finora
- Is All Safety-Critical Equipment Critical To SafetyDocumento6 pagineIs All Safety-Critical Equipment Critical To SafetyLi QiNessuna valutazione finora
- CCPS Monograph Reflections From Global Process Safety LeadersDocumento29 pagineCCPS Monograph Reflections From Global Process Safety LeadersKiranNessuna valutazione finora
- (III) PSSR Procedure (Rev00)Documento19 pagine(III) PSSR Procedure (Rev00)ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Quartile1 PDFDocumento2 pagineQuartile1 PDFHanifah Edres DalumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Health, Safety & Environment: Understanding Oil and Gas BusinessDocumento34 pagineHealth, Safety & Environment: Understanding Oil and Gas BusinessMadhur ChopraNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Safety StudyDocumento33 pagineProcess Safety Studyadilmomin45100% (3)
- Rachel Joyce - A Snow Garden and Other Stories PDFDocumento118 pagineRachel Joyce - A Snow Garden and Other Stories PDFИгорь ЯковлевNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Safety Conference Presentation - Benoy JosephDocumento16 pagineProcess Safety Conference Presentation - Benoy JosephBenoy Johnson JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- WWW - Hse.gov - Uk Comah Buncefield Bstgfinalreport PDFDocumento118 pagineWWW - Hse.gov - Uk Comah Buncefield Bstgfinalreport PDFhulmanNessuna valutazione finora
- KPI Process SafetyDocumento6 pagineKPI Process SafetyKrishnan RajappanNessuna valutazione finora
- Iec60227-3 (Ed2.1) en DDocumento6 pagineIec60227-3 (Ed2.1) en Duntuk donlod aaaNessuna valutazione finora
- COMAH and Safety Case RegulationsDocumento16 pagineCOMAH and Safety Case RegulationsAdeel RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecological Quality RatioDocumento24 pagineEcological Quality RatiofoocheehungNessuna valutazione finora
- Colour FastnessDocumento37 pagineColour FastnessSivakumar K100% (1)
- Process Safety Management Guidelines For ComplianceDocumento16 pagineProcess Safety Management Guidelines For CompliancewinarnobNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 43 - Process Hazard Analysis Protocol PDFDocumento5 pagineSection 43 - Process Hazard Analysis Protocol PDFzironelNessuna valutazione finora
- Iodide and Bromide Ions in Brackish Water, Seawater, and Brines D 3869 - 04Documento12 pagineIodide and Bromide Ions in Brackish Water, Seawater, and Brines D 3869 - 04stevgonNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsDa EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Isolation of Process Equipment Procedure Rev 0Documento39 pagineIsolation of Process Equipment Procedure Rev 0eulalio_méndezNessuna valutazione finora
- Asset Integrity Process Safety Management Improvements PDODocumento15 pagineAsset Integrity Process Safety Management Improvements PDOMash Harthy100% (2)
- PSM Best Practices Workshop - Pre-Startup Safety Review PresentationDocumento15 paginePSM Best Practices Workshop - Pre-Startup Safety Review PresentationRod Lafrades100% (1)
- Bow Ties and Offshore Safety StudiesDocumento3 pagineBow Ties and Offshore Safety StudiesPillai Sreejith100% (7)
- Job Description For Hse AdvisorDocumento2 pagineJob Description For Hse AdvisorSam JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Safety Day Presentations 2014pptxDocumento16 pagineProcess Safety Day Presentations 2014pptximafishNessuna valutazione finora
- 331-10 331 Operators Manual enDocumento12 pagine331-10 331 Operators Manual enYahir VidalNessuna valutazione finora
- YoungMan EN131 GUIDEDocumento16 pagineYoungMan EN131 GUIDErcpawar100% (1)
- Esterification Oil of WintergreenDocumento8 pagineEsterification Oil of WintergreenMaria MahusayNessuna valutazione finora
- SR No Service CodeDocumento30 pagineSR No Service CodeShiva KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE199R-C12 Final Document OJTDocumento48 pagineECE199R-C12 Final Document OJTRigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- GB GW01 14 04 02Documento2 pagineGB GW01 14 04 02Muhammad LukmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Scattering of Gold NanosphereDocumento24 pagineOptical Scattering of Gold NanosphereParas KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Carrefour-SA Shopping Center TurkeyDocumento2 pagineCarrefour-SA Shopping Center TurkeyVineet JogalekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Coding DecodingDocumento21 pagineCoding DecodingAditya VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Minimalist KWL Graphic OrganizerDocumento2 pagineMinimalist KWL Graphic OrganizerIrish Nicole AlanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Model Detailed Project Report: Animal Feed Making UnitDocumento19 pagineModel Detailed Project Report: Animal Feed Making UnitShashi ShekharNessuna valutazione finora
- Tips For A Healthy PregnancyDocumento2 pagineTips For A Healthy PregnancyLizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Designing and Building A Computer TableDocumento9 pagineDesigning and Building A Computer Tablemaster_codersNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Circuit TheoryDocumento34 pagine1 Circuit TheoryLove StrikeNessuna valutazione finora
- Test7 PointersDocumento16 pagineTest7 PointersPratibha DwivediNessuna valutazione finora
- Maintenance Páginas-509-580Documento72 pagineMaintenance Páginas-509-580Alexandra Gabriela Pacheco PrietoNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Ticket Receipt, January 27 For MS NESHA SIVA SHANMUGAMDocumento2 pagineElectronic Ticket Receipt, January 27 For MS NESHA SIVA SHANMUGAMNesha Siva Shanmugam ShavannahNessuna valutazione finora