Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Hydrocarbons
Caricato da
KatMVCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Hydrocarbons
Caricato da
KatMVCopyright:
Formati disponibili
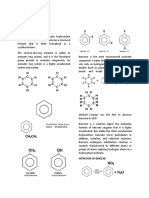
HYDROCARBONS
In bromine tests, bromine does not react with saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes)
because alkanes contain only C-C bonds which cannot add bromine. Where in the
cycloalkanes solution, the color of the bromine solution was only diluted to orange
to light orange unless added with UV light where it resulted in Bromine slowly
disappearing over time. Bromine readily reacts with unsaturated hydrocarbons due
to the C=C bonds that can be broken through addition reaction. Where adding the
bromine solution to Cyclohexene will result in the disappearance of color of the
bromine solution after each drop and agitation. Aromatic Hydrocarbons are
unreactive with bromine without a catalyst and may result in the dilution of the
color of bromine to orange to yellow. In adding KMnO4 to cyclohexane, the KMnO4
was only diluted indicated that it is unreactive to alkanes. In adding KMnO4 to
cyclohexene, it resulted in forming a purple precipitate. Aromatic Hydrocarbons just
like with alkanes are unreactive to potassium permanganate.
12. Conclusion Hydrocarbons can be known and be differentiated by their physical
properties and chemical reactivity. According to their solubility, these hydrocarbons
are insoluble; immiscible to water as they are nonpolar substances as opposed to
the high polarity of water. The densities are the same for each with the exception
chlorobenzene due to the hydrogen bonds that have to be broken, the dispersion
forces that are acting upon the molecule as opposed to making new bonds in
reacting water with chlorobenzene. These hydrocarbons also react with a conc.
H2SO4 solution although insoluble forming hydrogen bonds to the hydrocarbons.
Even Aromatic compounds also react with conc. Sulfuric acid as it undergoes a
substitution reaction. Alkanes are unreactive to bromine unless under special
condition or catalyst like being exposed to UV light also alkanes are unreactive to
potassium permanganate. Alkenes are readily reactive to bromine since its double
bounds can be broken easily through addition reaction also is relatively similar if
alkenes are added with KMnO4. Aromatic Compounds are unreactive because they
are usually stable and can only be reacted if given a catalyst.
toluene + KMnO4 ===> benzoic acid
cyclohexene + KMnO4 ===> 1,2-cyclohexadiol
hexane + KMnO4 ===> no reaction
Addition of Bromine (Br2)
As mentioned above, saturated hydrocarbons will only react with bromine under free radical conditions,
meaning you have to add UV light. So simply adding some bromine to cyclohexane wont cause a reaction
to occur. Aromatic hydrocarbons can react with bromine only in the presence of a strong Lewis acid
catalyst such as FeBr3- youll learn about this next semester (Carey CH 12.5). So simply adding some
bromine to toluene wont cause a reaction to occur. Cyclohexene will readily react with bromine (see
Carey CH 6.15 and 6.16).
Reaction with Potassium
Permanganate (KMnO4)
Potassium permanganate reacts with anything
unsaturated. KMnO4 reacts with alkenes to
form vicinal diols (similar mechanism as with OsO 4, Carey CH 15.5). KMnO4 will also react with alkyl
benzenes, such as toluene, to form benzoic acids (Carey CH 11.13). Although I dont think any reaction will
take place without adding heat. Alkanes wont react with KMnO 4.
Reaction with Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4)
Sulfuric acid reacts with both alkenes and aromatic
hydrocarbons, although in different ways. Sulfuric acid adds to
cyclohexene via an acid catalyzed addition (Carey CH 6.9).
Sulfuric acid adds to toluene via electrophilic aromatic
substitution- once again, something youll learn about next
semester (Carey CH 12.4). Sulfuric acid wont react with
cyclohexane.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Exp 1 Properties of HydrocarbonDocumento4 pagineExp 1 Properties of HydrocarbonNigel LoewNessuna valutazione finora
- Discussion Exp 1Documento6 pagineDiscussion Exp 1Dhirah Yuhans67% (3)
- Properties of HydrocarbonDocumento9 pagineProperties of Hydrocarbon刘象100% (1)
- Hydrocarbon PDFDocumento19 pagineHydrocarbon PDFPrincess Lou CarpenteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Some Reactions of HydrocarbonsDocumento15 pagineSome Reactions of HydrocarbonsValli SankaranarayananNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment Properties of AlkenesDocumento3 pagineExperiment Properties of AlkenesMei Hui100% (8)
- Eastern Nazarene College - Organic Chemistry I Lab - CH321LDocumento6 pagineEastern Nazarene College - Organic Chemistry I Lab - CH321LSreejithNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment Properties of AlkenesDocumento3 pagineExperiment Properties of AlkenesCalvin ChinNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic MaterialDocumento15 pagineOrganic MaterialAditya GathwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrocarbons Lab RepDocumento2 pagineHydrocarbons Lab Repyeji kimNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkanes and Alkenes NotesDocumento4 pagineAlkanes and Alkenes Notessohaila ibrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Benedict's Reagent/Test: OxidationDocumento15 pagineBenedict's Reagent/Test: OxidationToby LeNessuna valutazione finora
- La Salle University - Dasmariñas College of Science and Computer Studies Physical Science DepartmentDocumento15 pagineLa Salle University - Dasmariñas College of Science and Computer Studies Physical Science DepartmentmaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrocarbons: The First Family: Exercise 6Documento8 pagineHydrocarbons: The First Family: Exercise 6Gagay Villamor CañeteNessuna valutazione finora
- Discussion Exp 1 CHM 301 Alcohol TestDocumento4 pagineDiscussion Exp 1 CHM 301 Alcohol TestCik Mira YusoffNessuna valutazione finora
- Postlab 3Documento20 paginePostlab 3Lyra Ane IlaganNessuna valutazione finora
- of HydrocarbonsDocumento45 pagineof HydrocarbonsSneha KediaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHE143 Organic Chemistry Lab Report CompDocumento8 pagineCHE143 Organic Chemistry Lab Report CompSN2-0618 Nur Anith Aqilah Binti Mohd RaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic ChemistryDocumento4 pagineOrganic ChemistryChan Jiun Haur83% (6)
- Sion Orgchemlab4 PDFDocumento6 pagineSion Orgchemlab4 PDFshellNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 4 CHM207Documento7 pagineExperiment 4 CHM207Nur Syakirah Abd NasirNessuna valutazione finora
- Carboxylic Acid - NotesDocumento16 pagineCarboxylic Acid - NotesVANSHIKA GOELNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction of HydrocarbonsDocumento6 pagineReaction of HydrocarbonsSALIFU88% (8)
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Question Bank (Subjective)Documento16 pagineAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Question Bank (Subjective)helixvector45411Nessuna valutazione finora
- Saturated and Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocumento4 pagineSaturated and Unsaturated HydrocarbonsgefegNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Notes PDFDocumento8 pagineChem Notes PDFAliHassanMushtaqNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 HydrocarbonsDocumento10 pagine1 HydrocarbonsJuan Miguel Sebasian OrilleNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification Tests For Hydrocarbons Formal-ReportDocumento5 pagineClassification Tests For Hydrocarbons Formal-ReportKristineAnneMabansagNessuna valutazione finora
- Carboxylic AcidDocumento2 pagineCarboxylic AciddemNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Carbon To Carbon Double BondDocumento2 pagineChemistry Carbon To Carbon Double BondJAYLEN TRACEYNessuna valutazione finora
- HYDROCARBONSDocumento7 pagineHYDROCARBONSHarsh vardhan SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- CONSCHEMDocumento3 pagineCONSCHEM-09876543123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II4Documento7 pagineChapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II4wimal nayanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 12Documento74 pagineVollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 12superfr3shmNessuna valutazione finora
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocumento28 pagineHaloalkanes and HaloarenesDevansh TiwaryNessuna valutazione finora
- H 0 CCL Naoh H So Cyclohexane (Clear Liquid)Documento5 pagineH 0 CCL Naoh H So Cyclohexane (Clear Liquid)Mark GirasolNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 12Documento7 pagineExperiment 12Hugo Andrei Zambrano IglesiasNessuna valutazione finora
- EXPE222Documento6 pagineEXPE222K-yanVehraaYomomaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes NotesDocumento17 pagineElectrophilic Addition of Alkenes NotesAnanda Vijayasarathy100% (1)
- Experiment 2 Gen Chem 2 LabDocumento4 pagineExperiment 2 Gen Chem 2 LabSam BenjaminNessuna valutazione finora
- 13.HYDROCARBONS Full Chapter 2021Documento14 pagine13.HYDROCARBONS Full Chapter 2021raziabegum03761Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anims and UreaDocumento25 pagineAnims and UreaShivam GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry (Hydrocarbon)Documento3 pagineOrganic Chemistry (Hydrocarbon)azzatul amiraNessuna valutazione finora
- 22.4: Alpha Bromination of Carboxylic Acids: ObjectivesDocumento3 pagine22.4: Alpha Bromination of Carboxylic Acids: ObjectivesTinotenda ZisengweNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehydes Ketone Carboxylic AcidsDocumento4 pagineAldehydes Ketone Carboxylic AcidspoornaNessuna valutazione finora
- Carboxylic Acids PrepaRAtionDocumento5 pagineCarboxylic Acids PrepaRAtionJyoti Gaba -ChemistryNessuna valutazione finora
- Elimination: A. MaterialsDocumento5 pagineElimination: A. MaterialsLevy Medina TrayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohols: N n+1 N 2n+2Documento18 pagineAlcohols: N n+1 N 2n+2PrakharNessuna valutazione finora
- Anic Ep 3.Documento8 pagineAnic Ep 3.Ummu Umar Wa AisyahNessuna valutazione finora
- AromaticsDocumento53 pagineAromaticsIbsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment in Org ChemDocumento25 pagineAssignment in Org ChemFrancine MaramagNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry Named Reaction InDetail by MeritnationDocumento9 pagineOrganic Chemistry Named Reaction InDetail by MeritnationAtif AteeqNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Booklet CHEMISTRY BOOK II 2021 ColouredDocumento42 pagineRevision Booklet CHEMISTRY BOOK II 2021 ColouredChitransh MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and CarboxylDocumento26 pagineNotes Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and CarboxyltcbrihzllmkmkvxfovNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 11 Expt12Documento8 pagineChem 11 Expt12Leeann LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- A Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidDa EverandA Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidNessuna valutazione finora
- An Introduction to the Chemistry of Benzenoid CompoundsDa EverandAn Introduction to the Chemistry of Benzenoid CompoundsNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNessuna valutazione finora
- EcologyDocumento2 pagineEcologyKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertension Action Guide For Health Care ProvidersDocumento35 pagineHypertension Action Guide For Health Care ProvidersKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- MendelDocumento1 paginaMendelKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- MendelDocumento1 paginaMendelKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- MendelDocumento1 paginaMendelKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Chok - 1st Shift - Co-EnzymesDocumento2 pagineChok - 1st Shift - Co-EnzymesKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Physioex Activties 1-3 Cell TransportDocumento5 paginePhysioex Activties 1-3 Cell TransportKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- MendelDocumento1 paginaMendelKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- EcologyDocumento2 pagineEcologyKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Physioex Activties 1-3 Cell TransportDocumento5 paginePhysioex Activties 1-3 Cell TransportKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- EcologyDocumento2 pagineEcologyKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- HydrocarbonsDocumento2 pagineHydrocarbonsKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- EcologyDocumento2 pagineEcologyKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- MethodologyDocumento2 pagineMethodologyKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 1Documento3 paginePart 1KatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt. 7 Velocity of SoundDocumento23 pagineExpt. 7 Velocity of SoundKatMV100% (1)
- MendelDocumento1 paginaMendelKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- ConservationDocumento1 paginaConservationKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Allium Cepa-Iodine Solution For Nucleus Staining TetrahymenaDocumento1 paginaAllium Cepa-Iodine Solution For Nucleus Staining TetrahymenaKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Allium Cepa-Iodine Solution For Nucleus Staining TetrahymenaDocumento1 paginaAllium Cepa-Iodine Solution For Nucleus Staining TetrahymenaKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Even The Most Enthusiastic Home Computer Owners Have Little Idea of The Link Their Machines Represent in The Historical Chain of Computer TechnologyDocumento7 pagineEven The Most Enthusiastic Home Computer Owners Have Little Idea of The Link Their Machines Represent in The Historical Chain of Computer TechnologyKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- 100Documento1 pagina100KatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Usb 3Documento1 paginaUsb 3KatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Allium Cepa-Iodine Solution For Nucleus Staining TetrahymenaDocumento1 paginaAllium Cepa-Iodine Solution For Nucleus Staining TetrahymenaKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- CPMA Official Entry Form - Final 03-01-2013Documento1 paginaCPMA Official Entry Form - Final 03-01-2013honeymylovesosweetNessuna valutazione finora
- Literature: Away May Refer To:gh7tbyr7tbhfjuykihrstdvftihdtudybgrseb6hrbr6tDocumento1 paginaLiterature: Away May Refer To:gh7tbyr7tbhfjuykihrstdvftihdtudybgrseb6hrbr6tKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Literature: Away May Refer To:gh7tbyr7tbhfjuykihrstdvftihdtudybgrseb6hrbr6tDocumento1 paginaLiterature: Away May Refer To:gh7tbyr7tbhfjuykihrstdvftihdtudybgrseb6hrbr6tKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Literature: Away May Refer To:gh7tbyr7tbhfjuykiDocumento1 paginaLiterature: Away May Refer To:gh7tbyr7tbhfjuykiKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Literature: Away May Refer To:gh7tbyr7tbhfjuykihrstdvftihdtudDocumento1 paginaLiterature: Away May Refer To:gh7tbyr7tbhfjuykihrstdvftihdtudKatMVNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Sensors PDFDocumento211 pagineIntroduction To Sensors PDFVũ Mạnh Cường100% (2)
- Stereoisomerization and Homolytic Decomposition of Cis and Trans Bridgehead Diazenes1 2Documento10 pagineStereoisomerization and Homolytic Decomposition of Cis and Trans Bridgehead Diazenes1 2Nabil KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Fighting Foam Principles and Ethanol-Blended FuelDocumento38 pagineFire Fighting Foam Principles and Ethanol-Blended FuelFrancois HamiauxNessuna valutazione finora
- Offshore Oil & GasDocumento27 pagineOffshore Oil & GasArash HamidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiitjee PDT Courseware FTRE - 8th Moving To 9th-PHY-ColourDocumento10 pagineFiitjee PDT Courseware FTRE - 8th Moving To 9th-PHY-ColourYASHNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Arc Welding - GMAW and GTAW Gas Arc Welding - GMAW and GTAWDocumento3 pagineGas Arc Welding - GMAW and GTAW Gas Arc Welding - GMAW and GTAWJulioNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract of ASTM A574M 1997Documento7 pagineAbstract of ASTM A574M 1997Jesse ChenNessuna valutazione finora
- Refrigerant Selection CriteriaDocumento7 pagineRefrigerant Selection CriteriazetseatNessuna valutazione finora
- Focuse Ion BeamDocumento34 pagineFocuse Ion BeamAhsan SaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- 206 ManualDocumento16 pagine206 ManualNikshit RafaliyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiitjee: Solutions To JEE (Main) - 2020Documento36 pagineFiitjee: Solutions To JEE (Main) - 2020srijan jhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stockmann 2016Documento12 pagineStockmann 2016Barbara SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- DatabaseDocumento112 pagineDatabaseamirulamirNessuna valutazione finora
- Tunneling Brochure English 04Documento7 pagineTunneling Brochure English 04xcvNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Physics Notes Ch05 Magnetism and MatterDocumento8 pagine12 Physics Notes Ch05 Magnetism and MatterAmrit KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Omnirad 819 - EN PDS 2Documento3 pagineOmnirad 819 - EN PDS 2brausenpaulNessuna valutazione finora
- DSR Unit 1Documento69 pagineDSR Unit 1hujefaNessuna valutazione finora
- Suncroma: Organic and Inorganic PigmentsDocumento12 pagineSuncroma: Organic and Inorganic PigmentsKetav Patel100% (1)
- Microbiology of Waste Water TreatmentDocumento22 pagineMicrobiology of Waste Water TreatmentDevendra SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Auto 4sem MSEMDocumento214 pagineAuto 4sem MSEMkhairnarsayali257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Encapsulation State of Messenger RNA Inside Lipid NanoparticlesDocumento5 pagineEncapsulation State of Messenger RNA Inside Lipid NanoparticlesPencari IlmuNessuna valutazione finora
- Copper (II) Sulfate - Reagent - Anhydrous 98 - Acros OrganicsDocumento5 pagineCopper (II) Sulfate - Reagent - Anhydrous 98 - Acros OrganicsGaryoNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 4th Edition Rizzo Test BankDocumento14 pagineFundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 4th Edition Rizzo Test BankGeorgeCobbjgbcs100% (16)
- Fire Shield LFST - 42E: Premium Performance Industry Applications Product AvailabilityDocumento1 paginaFire Shield LFST - 42E: Premium Performance Industry Applications Product Availabilityray9699Nessuna valutazione finora
- CHM-101 Chapter 1Documento23 pagineCHM-101 Chapter 1razan136Nessuna valutazione finora
- DOC316.53.01122 11ed PDFDocumento6 pagineDOC316.53.01122 11ed PDFJean Carlos ArangoNessuna valutazione finora
- Asme Sec V A-15-2006Documento4 pagineAsme Sec V A-15-2006Muhammed Abo-FandoodNessuna valutazione finora
- MohitDocumento3 pagineMohitVivek kumar0% (1)
- A Study of Copper (II) Complexes With Different LigandsDocumento3 pagineA Study of Copper (II) Complexes With Different LigandsZul Nazrie50% (6)
- Physics Today: Quantum CriticalityDocumento8 paginePhysics Today: Quantum CriticalityAndré RojasNessuna valutazione finora