Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Pre-Lab 3
Caricato da
adnanTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pre-Lab 3
Caricato da
adnanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pre Lab #3
Objective
Measure the High Level Voltage, Current using Instrument Transformers.
Basic Technical Information and Application
The name instrument transformer is a general classification applied to
current and voltage devices used to change currents and voltages from one
magnitude to another or to perform an isolating function, that is, to isolate
the utilization current or voltage from the supply voltage for safety to both
the operator and the end device in use
Basic information
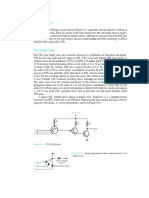
Current transformers are used to measure high values of current and are
used as input to the relay as detecting signal. The primary winding of CT is
connected in series with the power lines while it is not the case with PT. CT
therefore must withstand the network short-circuit current.
A VT is an open-circuited transformer whose primary winding is
connected across the main electrical system where voltage is being
monitored. The most voltage produced by VTs is 100-120V (as per local
country standards).
Practical information
Wound Primary type CT is used for smaller currents and it can only be
applied on low fault level installations due to thermal limitations and
magnetic forces on this type of structure. For current greater than 100A, the
bar type CT is used. Protection CTs are most frequently used of the bar
primary type, toroidal core with evenly distributed secondary winding type
construction.
The accuracy of VT is more relevant for metering purposes, while the
margin of accuracy is comparatively less for protection purposes. Permissible
errors vary depending on the burden and purpose of use and typical values
as per IEC 186. The accuracy is not a major cost-deciding factor for a VT and
it is common to select VTs based on the loads.
Pre-Labs of Electrical Power Distribution & Utilization (EE-357)
Department of Electrical
Engineering
Construction-wise:
Pre-Study Question
1. What is the difference between current transformer and normal
transformer?
2. What is the impact on ratio of current transformer when burden is
increased on secondary?
3. Why secondary winding of CT cannot be left open? Also which part of
CT is damaged in this case?
4. What is basic difference between metering and protective CT?
5. What is the difference between construction of voltage transformer
and normal transformer?
6. Why do we couple capacitor with a VT?
7. What is the standard voltage on secondary of VT?
Pre-Labs of Electrical Power Distribution & Utilization (EE-357)
Department of Electrical
Engineering
8. What are the different designs available for construction of potential
transformer?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Power System Fault AnalysisDocumento26 paginePower System Fault AnalysisadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Generator ReactancesDocumento3 pagineGenerator ReactancesLora BishopNessuna valutazione finora
- 16-Hydraulic Turbines (Compatibility Mode)Documento70 pagine16-Hydraulic Turbines (Compatibility Mode)Rachit ParikhNessuna valutazione finora
- 16-Hydraulic Turbines (Compatibility Mode)Documento70 pagine16-Hydraulic Turbines (Compatibility Mode)Rachit ParikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Make This 1KVA (1000 Watts) Pure Sine Wave Inverter CircuitDocumento1 paginaMake This 1KVA (1000 Watts) Pure Sine Wave Inverter CircuitStefan CorneaNessuna valutazione finora
- BRBCL Vocational Training Report.Documento63 pagineBRBCL Vocational Training Report.Rashmirathi Pathak67% (3)
- Lecture Notes 04 PDFDocumento17 pagineLecture Notes 04 PDFGABRIEL MORENONessuna valutazione finora
- Article1380787061 - Yilmaz and Yanikoglu PDFDocumento8 pagineArticle1380787061 - Yilmaz and Yanikoglu PDFadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Annual Report 2016-2017 PDFDocumento106 pagineAnnual Report 2016-2017 PDFadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- EEGJulyrevisedFINAL1 2003 030 0548 2Documento30 pagineEEGJulyrevisedFINAL1 2003 030 0548 2adnanNessuna valutazione finora
- ECT Aa ProceedingsDocumento5 pagineECT Aa ProceedingsadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Preliminary Design Hydroelectric Station Problem Without Prime UnitsDocumento13 paginePreliminary Design Hydroelectric Station Problem Without Prime UnitsadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- 15-Hydraulic Turbines-New031211 (Compatibility Mode) PDFDocumento86 pagine15-Hydraulic Turbines-New031211 (Compatibility Mode) PDFSultan IbibNessuna valutazione finora
- Research PaperDocumento8 pagineResearch PaperadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- EBC Annex 53 Appendix Volume 5Documento248 pagineEBC Annex 53 Appendix Volume 5adnanNessuna valutazione finora
- RAP Lazar TeachingDuckToFly 2014 JANDocumento28 pagineRAP Lazar TeachingDuckToFly 2014 JANadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics Fundamentals For Energy Conversion Systems Sunum 60 PagesDocumento60 pagineThermodynamics Fundamentals For Energy Conversion Systems Sunum 60 Pageskalite123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transformer MaintenanceDocumento88 pagineTransformer MaintenanceadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- 37 Report PDFDocumento39 pagine37 Report PDFadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tlines 1Documento19 pagineTlines 1sathi420Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Machines II Course Notes on Synchronous Generator Operation and CharacteristicsDocumento12 pagineElectrical Machines II Course Notes on Synchronous Generator Operation and CharacteristicsNWALLLNessuna valutazione finora
- Slideshare Iscombinedheatandpowerrightforyoursitev2 140805042654 Phpapp01Documento14 pagineSlideshare Iscombinedheatandpowerrightforyoursitev2 140805042654 Phpapp01adnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cogeneration 140526230456 Phpapp02Documento11 pagineCogeneration 140526230456 Phpapp02adnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydro Low Head Power Plant PDFDocumento16 pagineHydro Low Head Power Plant PDFDO CAT DAONessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Biogas Cogeneration CHP Technologies We Provide Value and Economical BenefitsDocumento35 pagineAdvanced Biogas Cogeneration CHP Technologies We Provide Value and Economical BenefitsadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bagliharhydroelectricpowerplant 140504084709 Phpapp01Documento69 pagineBagliharhydroelectricpowerplant 140504084709 Phpapp01Rickson Viahul Rayan CNessuna valutazione finora
- Shayan Khan Ee-153Documento1 paginaShayan Khan Ee-153adnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Motor NameplatesDocumento7 pagineMotor NameplatesaguilafedeNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Text 01Documento86 pagineFull Text 01adnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Aaboexhibitjawilliams Oh Vs Ug PaperDocumento10 pagineAaboexhibitjawilliams Oh Vs Ug PaperadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 2 - HVDC PaperDocumento8 pagineGroup 2 - HVDC PaperadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- HVDCDocumento36 pagineHVDCadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Sheet RSTDocumento4 pagineData Sheet RSTIndra Hans AditiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Investigatory Project-1Documento30 paginePhysics Investigatory Project-1Horrible WorldNessuna valutazione finora
- PGC 1 Powder Gun Control: Operating Instructions and Spare Parts ListDocumento28 paginePGC 1 Powder Gun Control: Operating Instructions and Spare Parts ListRizwan AdeelNessuna valutazione finora
- VLSI Lab Viva Questio Ns and Answers PDF - Sushanth KJ - Academia - Edu PDFDocumento7 pagineVLSI Lab Viva Questio Ns and Answers PDF - Sushanth KJ - Academia - Edu PDFVishnuNessuna valutazione finora
- Datasheet - TPC8116-H ToshibaSemiconductorDocumento7 pagineDatasheet - TPC8116-H ToshibaSemiconductorOscar AredeNessuna valutazione finora
- SheetDocumento9 pagineSheetLasin Chottu SureshNessuna valutazione finora
- United States Patent (19) : WeberDocumento12 pagineUnited States Patent (19) : Weberaless2056Nessuna valutazione finora
- TTL Nand Gate: Digital CircuitsDocumento10 pagineTTL Nand Gate: Digital CircuitsKurt CargoNessuna valutazione finora
- Belt Conveyor Pull Rope Switch Safety SystemDocumento4 pagineBelt Conveyor Pull Rope Switch Safety SystemOussema ElloumiNessuna valutazione finora
- Stiker PBRDocumento1 paginaStiker PBRKejar TayangNessuna valutazione finora
- SL Series IEC Vacuum Contactors TD en 6 2012Documento22 pagineSL Series IEC Vacuum Contactors TD en 6 2012rprojetos001tiNessuna valutazione finora
- SC-BRICs Manual LRDocumento60 pagineSC-BRICs Manual LRabattzNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Drive and Control SystemsDocumento18 pagineElectrical Drive and Control SystemsNasreddine SiaghNessuna valutazione finora
- Recessed: Arioso LED 2x4Documento4 pagineRecessed: Arioso LED 2x4Alexandra Castro ValenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ InsulatorDocumento2 pagineMCQ InsulatorMd. Mostafizur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- En 5 AppendixDocumento32 pagineEn 5 AppendixTURKI69Nessuna valutazione finora
- Greenbook ManualDocumento402 pagineGreenbook Manuallacey forrestNessuna valutazione finora
- MOS Capacitor - StructureDocumento22 pagineMOS Capacitor - Structurerounak aliNessuna valutazione finora
- CI 555 Datasheet - RevA3Documento8 pagineCI 555 Datasheet - RevA3marceNessuna valutazione finora
- Main Panel - 1setDocumento1 paginaMain Panel - 1setHytech Pvt. Ltd.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mercedes SEAS instructionsDocumento5 pagineMercedes SEAS instructionsMuhamedomar Jojo JojoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bosch Isp Brochure BSWDocumento5 pagineBosch Isp Brochure BSWAlexanderNessuna valutazione finora
- Uso de Analizador de Video Sencore TVA92 - 2Documento2 pagineUso de Analizador de Video Sencore TVA92 - 2Antonio ChavezNessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductor KIA393P/S/F/FK: Technical DataDocumento4 pagineSemiconductor KIA393P/S/F/FK: Technical DataAdam SchwemleinNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Test A SolenoidDocumento3 pagineHow To Test A SolenoidVyas SrinivasanNessuna valutazione finora
- cd772 771 770catalog eDocumento2 paginecd772 771 770catalog eDiego ÁlvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Datasheet MultiGrid 3000VA enDocumento2 pagineDatasheet MultiGrid 3000VA enJason CarrNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Sheet 5SL4232-7CC: ModelDocumento3 pagineData Sheet 5SL4232-7CC: ModelAtiqah Putri SariNessuna valutazione finora