Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Ci - B13 (LS)
Caricato da
Kimber ManiulitTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Ci - B13 (LS)
Caricato da
Kimber ManiulitCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MANIULIT, Marian Kimberly Claire B.
2009-11763
University of the Philippines Manila
The Health Sciences Center
COLLEGE OF NURSING
Sotejo Hall, Pedro Gil Street, Ermita, City of Manila
WARD: CI
BED NO: 13
DATE OF ADMISSION: January 19, 2012
NAME OF PATIENT: AMA, Editha
SEX: Female
AGE: 48 y/o
C.STATUS:Single EDUC.ATTAIN: BS Commerce
DIAGNOSIS: Squamous cell carcinoma skin/breast, St IV
LABORATORY STUDY
NAME OF
TEST/ DATE
DONE
01/05/12
Blood-typing
01/09/12
Radiologic
Report
(Chest Bucky)
INDICATION FOR THE
TEST
Other than the need for
this test to be routine
information collected
about the patient, this
was done to identify the
types of blood that are
compatible with the
patient esp after a
hemorrhage when BT is
absolutely indicated.
This test was done to
determine the extent of
the tumor and to identify
whether or not there is
already an involvement
of the skeletal system, if
the cancer has already
damaged any bones;
consequently be
considered in planning
NORMAL VALUES/FINDINGS
ACTUAL RESULTS/FINDINGS
+
SIGNIFICANCE OF THE RESULTS/FINDINGS
A, B, O
The test result indicates that the patient can
receive blood from donors with blood type A and O
only. This is important to know because if the
patient was transfused with the wrong type of
blood, adverse reactions may occur which may
cause death.
Negative findings/Normal
anatomical findings
The cortical outlines are
intact, no osseus or joint
space abnormalities
The findings indicate that the there are no
abnormalities in the skeletal system of the chest,
that there is no damage or involvement of any
bone in the current state of the patients
skin/breast cancer
Ignatavicius, Workman. Medical-Surgical Nursing: Patient-Centered Collaborative Care (with Media), 6th Edition. W.B. Saunders Company, 022009, NANDA - Doenges,
Moorhouse, Murr, 2010, Pathophysiology, Concepts of Altered States Porth, 2007, Nursing Care Plans Gulanick, Myers, 2007, Carpenito-Moyet, L. J. (2008). Handbook of
Nursing Diagnosis. Quezon City: C&E Publishing Bulechek, G. et.al. Nursing Interventions Classification (NIC) 5th ed. Moorhead, S. et al. Nursing Outcomes Classification
(NOC) 4th ed., Oncology Nursing
MANIULIT, Marian Kimberly Claire B.
2009-11763
and implementing the
treatment for the patient
which is in this case,
radiotherapy.
01/18/12
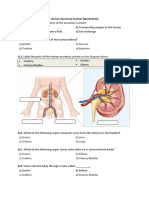
Kidney,
Ureter,
Bladder
Study
Also, this test was done
as a pre-treatment
documentation of the
patients chest cavity
state as a basis for
evaluation during and
after radiotherapy to
be able to monitor
changes to body
structures.
This test was done to
determine the etiology of
the patients distended
abdomen and its steady
increase in size; to check
if there is some kind of
intestina bstruction, to
evaluate the presence of
renal, ureter, or other
organ calculi, to evaluate
the size, shape, and
position of the liver,
kidneys, and spleen,
evaluate suspected
abnormal fluid, air, or
obstruction in the
abdomen.
Normal size and shape of
kidneys
Normal bladder, absence of
masses and
renal calculi, and no abnormal
accumulation
of air or fluid
Fatty liver changes
Cholecystolithiasis
Gallbladder polyps VS
Encrusted stones*
The pts risk fx r/t to these are:
- Gender (F)
- Multiple pregnancies (2)
- Freq changes in W and rapid W loss (since
devt of cancer)
- Estrogen intake (contraceptive used for at
least 2 years)
Significant S/Sx r/t are:
- Mild GI sx
- Epigastric distress: fullness
- Abd distention (beginning ascites
- Jaundice (usu occurs with obstruction of
common bile duct)
- Mild DOB and activity intolerance (mainly
mobility)
According to the NHH, the pt does not drink
alcohol but prior to hospitalization had poor
nutritional habits (preference of oily, fatty foods
and soft drinks). The patient has been found to
have fatty liver changes which is not alcoholinduced but could instead be associated to her
Ignatavicius, Workman. Medical-Surgical Nursing: Patient-Centered Collaborative Care (with Media), 6th Edition. W.B. Saunders Company, 022009, NANDA - Doenges,
Moorhouse, Murr, 2010, Pathophysiology, Concepts of Altered States Porth, 2007, Nursing Care Plans Gulanick, Myers, 2007, Carpenito-Moyet, L. J. (2008). Handbook of
Nursing Diagnosis. Quezon City: C&E Publishing Bulechek, G. et.al. Nursing Interventions Classification (NIC) 5th ed. Moorhead, S. et al. Nursing Outcomes Classification
(NOC) 4th ed., Oncology Nursing
MANIULIT, Marian Kimberly Claire B.
2009-11763
poor diet then: the excess fat present in the foods
she ate were probably too much at one time and
had accumulated to an amount enough to cause
significant physiologic changes in the liver. It
synthesizes proteins (something that could be
associated with her current ascites) and clotting
factors (very significant esp in relation to her
tumors frequent bleeding which leads to low
RBCs etc). If the pt develops any problem with the
formation of clotting factors or any hema condition
for that matter, she becomes at high risk for
excessive blood loss/hemorrhage which can
ultimately be lethal. In its capacity for metabolizing
drugs and hormones, the liver serves as an
excretory organ. In this respect, the bile, which
carries the end products of substances metabolized
by the liver, is much like the urine, which carries
the body wastes filtered by the kidneys. Thus,
preventing progression of fatty changes and
maintaining optimal physiologic functioning is
important for the patient because of the many
medications that she has been taking (which are
taxing both on the liver and the kidneys).
Similarly, any possible sources of obstruction of
the urinary system are very significant esp. in
excreting the wastes of the body. If the patient will
be subjected to chemotherapy to go with her RT,
her body must be able to filter all these substances
properly such that no residue is left in the
bloodstream and the pt does not suffer from any
kind of toxicity or complication that might
eventually lead to kidney failure, further impairing
her hematologic system.
*Common duct stones also can obstruct the
outflow of the pancreatic duct, causing a secondary
pancreatitis.
Ignatavicius, Workman. Medical-Surgical Nursing: Patient-Centered Collaborative Care (with Media), 6th Edition. W.B. Saunders Company, 022009, NANDA - Doenges,
Moorhouse, Murr, 2010, Pathophysiology, Concepts of Altered States Porth, 2007, Nursing Care Plans Gulanick, Myers, 2007, Carpenito-Moyet, L. J. (2008). Handbook of
Nursing Diagnosis. Quezon City: C&E Publishing Bulechek, G. et.al. Nursing Interventions Classification (NIC) 5th ed. Moorhead, S. et al. Nursing Outcomes Classification
(NOC) 4th ed., Oncology Nursing
MANIULIT, Marian Kimberly Claire B.
2009-11763
Overall, any possible causes for obstruction of
paths of blood flow and flow of other fluids in the
body should be determined and appropriate
medical-surgical interventions must be done such
that the pt does not develop any complications
that will hinder her body from fighting her cancer
and recovering from it.
01/17/12
Culture and
Sensitivity
Test
01/30/12
Blood
Chemistry
To determine the
presence of an infection
and to know if the
pharmacologic
interventions are working
This test is used for
electrolyte screening in
acute and critical
illnesses, to assess fluid
and electrolyte imbalance
and for evaluation of
drug therapy.
No growth
Crea
AST
ALT
Tot Bilirubin
Dir Bilirubin
Ind Bilirubin
Albumin
Mg
Na
K
01/30
62
47
24
H
22.8
H
11.0
H
11.8
13
L
0.77
133 L
3.4
L
Pseudomonas x
Protum Vulgaris
Light MRSA (sample from
wound)
01/21
01/20
62
44.4
20.4
24.0
H
H
H
The patient had an infection. This must be resolved
with antibiotics such as Clindamycin, Ciprofloxacin.
***Careful in administering drugs. Check
compatibilities and incompatibities first.
The alanine aminotransferase (ALT) value is
markedly high. This is can be associated with pts
liver disease which can be supported further by the
values of Bilirubin in the blood which can be
increased d/t the ff:
-Hemolytic anemia
-Biliary Obsruction Disease
- Hepatocellular damage
This is probably d/t
Insufficient intake:
Malabsorption
Malnutrition
Decreased synthesis by the liver:
d/t possible non-alcoholic liver disease
Inflammation and chronic diseases
Bacterial infections
Neoplasm
Conventional SI Units (Conventional
Ignatavicius, Workman. Medical-Surgical Nursing: Patient-Centered Collaborative Care (with Media), 6th Edition. W.B. Saunders Company, 022009, NANDA - Doenges,
Moorhouse, Murr, 2010, Pathophysiology, Concepts of Altered States Porth, 2007, Nursing Care Plans Gulanick, Myers, 2007, Carpenito-Moyet, L. J. (2008). Handbook of
Nursing Diagnosis. Quezon City: C&E Publishing Bulechek, G. et.al. Nursing Interventions Classification (NIC) 5th ed. Moorhead, S. et al. Nursing Outcomes Classification
(NOC) 4th ed., Oncology Nursing
MANIULIT, Marian Kimberly Claire B.
2009-11763
Age Units Units _ 10)
Newborn4 d 2.84.4 g/dL 2844 g/L
5 d14 y 3.85.4 g/dL 3854 g/L
1518 y 3.24.5 g/dL 3245 g/L
1960 y 3.44.8 g/dL 3448 g/L
6190 y 3.24.6 g/dL 3246 g/L
Greater than 90 y 2.94.5 g/dL 2945 g/L
DESCRIPTION & RATIONALE: Most
of the bodys total protein is a combination
of albumin and globulins.
Albumin, the protein present in
the highest concentrations, is the
main transport protein in the body.
Albumin also maintains plasma
oncotic pressure. Serum albumin
values are affected by the process of
synthesis, distribution, and degradation.
Low levels may be the result of
either inadequate production or excessive
loss. Albumin levels are more useful
as an indicator of chronic
deficiency than of short-term deficiency.
Albumin levels are affected by posture.
Results from specimens collected
in an upright posture are higher than
results from specimens collected in a
supine position.
The A/G ratio is useful in the evaluation
of liver and kidney disease. The
ratio is calculated using the following
formula:
albumin/(total protein albumin)
where globulin is the difference
between the total protein value and
the albumin value. For example, with
a total protein of 7 g/dL and albumin
of 4 g/dL, the A/G ratio is calculated
Ignatavicius, Workman. Medical-Surgical Nursing: Patient-Centered Collaborative Care (with Media), 6th Edition. W.B. Saunders Company, 022009, NANDA - Doenges,
Moorhouse, Murr, 2010, Pathophysiology, Concepts of Altered States Porth, 2007, Nursing Care Plans Gulanick, Myers, 2007, Carpenito-Moyet, L. J. (2008). Handbook of
Nursing Diagnosis. Quezon City: C&E Publishing Bulechek, G. et.al. Nursing Interventions Classification (NIC) 5th ed. Moorhead, S. et al. Nursing Outcomes Classification
(NOC) 4th ed., Oncology Nursing
MANIULIT, Marian Kimberly Claire B.
2009-11763
as 4/(7 4) or 4/3 _ 1.33. A reversal
in the ratio, where globulin exceeds
albumin (i.e., ratio less than 1.0), is
clinically significant.
Peptic ulcer
Prolonged immobilization
Rheumatic diseases
Severe skin disease
Increased loss over body surface:
Burns
Enteropathies related to sensitivity
to ingested substances (e.g.,
gluten sensitivity, Crohns
disease, ulcerative colitis)
Fistula (gastrointestinal or
lymphatic)
Hemorrhage
Kidney disease
Rapid hydration or overhydration
Repeated thoracentesis or
paracentesis
Trauma and crush injuries
Increased catabolism:
Fever
Cushings disease
Pre-eclampsia
Thyroid dysfunction
Increased blood volume (hypervolemia):
Congestive heart failure
Monoclonal gammopathies
(Waldenstrms disease,
myeloma)
01/17/12
Active Partial
Thrombin
This was done to
monitor the bloods
ability to clot and
stabilize bleedings.
Pt ref :14. 0 secs
Pt actual value: 17.8
% activity 0.64
INR 1.32
Ignatavicius, Workman. Medical-Surgical Nursing: Patient-Centered Collaborative Care (with Media), 6th Edition. W.B. Saunders Company, 022009, NANDA - Doenges,
Moorhouse, Murr, 2010, Pathophysiology, Concepts of Altered States Porth, 2007, Nursing Care Plans Gulanick, Myers, 2007, Carpenito-Moyet, L. J. (2008). Handbook of
Nursing Diagnosis. Quezon City: C&E Publishing Bulechek, G. et.al. Nursing Interventions Classification (NIC) 5th ed. Moorhead, S. et al. Nursing Outcomes Classification
(NOC) 4th ed., Oncology Nursing
MANIULIT, Marian Kimberly Claire B.
Time
02/04/12
Complete
Blood Count
This test of the peripheral
blood provides a
tremendous amount of
information about the
hematologic system. It is
used as a preoperative
test to ensure both
adequate oxygen
carrying capacity and
hemostasis.
This can also confirm
findings related to
infection and help in
determining the bodys
response to it. It was
also done to monitor
bleeding tendencies,
monitor treatment for
anemia and other blood
diseases and to
determine the effects of
chemotherapy and
radiation therapy on
blood cell production
(indication for future
CBCs of the pt esp bec
she will be starting her
RT already and will be
prescribed chemo drugs
to go with it).
2009-11763
APTT ref 30.6
Pts 29
NORMAL VALUES
5.0-10.0
WBC x10^9/L
01/29/12
02/04/12
42.50
41.00
55.50
RBC
4.0-6.0
x10^12/L
3.18
3.27
2.34
Hgb
120-170
g/L
91
94
71
Hct
0.380.48
0.282
0.278
0.204
MCV
80.0100.0 fL
88.6
85.1
87.2
MCH
27.031.0 pg
28.7
28.8
30.2
MCHC
320-360
g/L
324
338
346
RDW
10.016.0 %
18.4
16.0
15.9
150-450
x10^9/L
383
431
591
0.924
0.898
0.894
0.047
0.054
0.054
Plt
Diff Count
Neut
Also, this test is used to
monitor the effect of
01/24/12
Lymph
0.500.75
0.200.50
The WBC count is very high in value because of her
infection (P. Aeru), because she is anemic has a
form of inflammation (L breast) and a very large
malignancy, a foreign body which is the L breast
tumor. The RBC, Hgb and Hct are low d/t her
previous (and whenever CDW is done) and
frequent/prolonged hemorrhage. Although the
pts MCV, MCH and MCHC are still within range,
they are remarkably borderline minumun, which
means that the pt is at risk for various types of
anemia which will only worsen her dyspnea d/t
decr RBC for O2 distribution. In relation to this, the
pt is prescribed drugs that support hemostasis such
as FeSO4, Folic Acid and Tranexamic Acid. All of the
compnenets of the diff. count are elevated. The
Neut of the pt is high bec of her infection and
because of her malignanacy. Her Lymph are
decreaed because of her immunodeficiency state
in cancer.
Her Eosin is increased because of the stress she has
been through ever since she was diagnosed with
cancer. The Baso are high probably because of the
stress she has undergone as well.
***
-Observe venipuncture site for bleeding
or hematoma formation. Apply
paper tape or other adhesive to
hold pressure bandage in place, or
replace with a plastic bandage.
-Nutritional considerations: Instruct
patients to consume a variety of
Ignatavicius, Workman. Medical-Surgical Nursing: Patient-Centered Collaborative Care (with Media), 6th Edition. W.B. Saunders Company, 022009, NANDA - Doenges,
Moorhouse, Murr, 2010, Pathophysiology, Concepts of Altered States Porth, 2007, Nursing Care Plans Gulanick, Myers, 2007, Carpenito-Moyet, L. J. (2008). Handbook of
Nursing Diagnosis. Quezon City: C&E Publishing Bulechek, G. et.al. Nursing Interventions Classification (NIC) 5th ed. Moorhead, S. et al. Nursing Outcomes Classification
(NOC) 4th ed., Oncology Nursing
MANIULIT, Marian Kimberly Claire B.
blood transfusion on the
body whether or not it
was able to raised the
amt of RBCs present in
the bld for example.
2009-11763
Mono
Eosin
Baso
Stab
0.020.09
0.010.04
0-0.01
0.020.05
0.025
0.044
0.044
0.002
0.003
0.005
0.001
0.001
0.004
foods within the basic food groups,
maintain a healthy weight, be physically
active, limit salt intake, limit
alcohol intake, and be a nonsmoker.
Ignatavicius, Workman. Medical-Surgical Nursing: Patient-Centered Collaborative Care (with Media), 6th Edition. W.B. Saunders Company, 022009, NANDA - Doenges,
Moorhouse, Murr, 2010, Pathophysiology, Concepts of Altered States Porth, 2007, Nursing Care Plans Gulanick, Myers, 2007, Carpenito-Moyet, L. J. (2008). Handbook of
Nursing Diagnosis. Quezon City: C&E Publishing Bulechek, G. et.al. Nursing Interventions Classification (NIC) 5th ed. Moorhead, S. et al. Nursing Outcomes Classification
(NOC) 4th ed., Oncology Nursing
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Sdks LSDKNVLKDDocumento1 paginaSdks LSDKNVLKDKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Praise Be To GodDocumento1 paginaPraise Be To GodKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 NSD MagnoDocumento1 pagina1 NSD MagnoKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- XKS, MDocumento1 paginaXKS, MKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio EnergeticsDocumento18 pagineBio EnergeticsKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Purines Pyrimidines: de Novo Pyrimidine and Purine SynthesisDocumento44 paginePurines Pyrimidines: de Novo Pyrimidine and Purine SynthesisKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Electron Transport ChainDocumento15 pagineElectron Transport ChainKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Nmat Identification Form: Quezon City, Metro Manila (NCR) 1116 PhilippinesDocumento1 paginaNmat Identification Form: Quezon City, Metro Manila (NCR) 1116 PhilippinesKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Some Other Trans Guidelines (Roles)Documento3 pagineSome Other Trans Guidelines (Roles)Kimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Copyright LicenseDocumento1 paginaCopyright LicenseKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Mededportal® Publication: Neuro-Logic: The Principles of Lesion Localization in Patients With Neurological SymptomsDocumento1 paginaMededportal® Publication: Neuro-Logic: The Principles of Lesion Localization in Patients With Neurological SymptomsKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Wallenberg's Syndrome?Documento1 paginaWhat Is Wallenberg's Syndrome?Kimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Laryngeal CancerDocumento3 paginePathophysiology Laryngeal CancerKimber Maniulit67% (6)
- Trans by Samantha Isabel CarmellaDocumento4 pagineTrans by Samantha Isabel CarmellaKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Pray For Good Men and Women ForDocumento1 paginaPray For Good Men and Women ForKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- GAG v16 WebversionDocumento49 pagineGAG v16 WebversionKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Phenylketonuria: Katrice Shorter, Steven Williams, Rodrigo Hallais, April Mcclendon "The Juice"Documento24 paginePhenylketonuria: Katrice Shorter, Steven Williams, Rodrigo Hallais, April Mcclendon "The Juice"Kimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Male Circumcision PXDocumento28 pagineMale Circumcision PXKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Edited Edited QuestionnaireDocumento2 pagineEdited Edited QuestionnaireKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Making An Epidemic Curve (Epicurve) : Preben AavitslandDocumento11 pagineMaking An Epidemic Curve (Epicurve) : Preben AavitslandKimber ManiulitNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- مذكرة علوم للصف الخامس الابتدائي الترم الثاني لغات science for primary second term 2015Documento37 pagineمذكرة علوم للصف الخامس الابتدائي الترم الثاني لغات science for primary second term 2015rabei87% (23)
- Case Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento101 pagineCase Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseZNEROL100% (6)
- Organ System and FunctionDocumento17 pagineOrgan System and FunctionLajilaNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 5 THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM DefDocumento3 pagineUNIT 5 THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM DefShalini Hotwani NathaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Parasitology PDFDocumento33 pagineMedical Parasitology PDFRohan100% (1)
- Grade 6 Human System NotesDocumento12 pagineGrade 6 Human System Notestharun pranav100% (2)
- Bio270 Chapter 1 TutorialDocumento5 pagineBio270 Chapter 1 TutorialNamNessuna valutazione finora
- The Excretory System in The HumanDocumento48 pagineThe Excretory System in The Humanapi-266618926Nessuna valutazione finora
- HUMAN EXCRETORY AND Reproductive SystemDocumento35 pagineHUMAN EXCRETORY AND Reproductive SystemShilpa Born To LoveNessuna valutazione finora
- Summative Assessment 1 Class X 2014-15Documento6 pagineSummative Assessment 1 Class X 2014-15Apex InstituteNessuna valutazione finora
- Excretion and Osmoregulation - ModuleDocumento10 pagineExcretion and Osmoregulation - ModuleDarelle GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- THE GRASSHOPPERclassDocumento37 pagineTHE GRASSHOPPERclassSafiqa Tasfia100% (1)
- Assignment # 1Documento4 pagineAssignment # 1Abrar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQSDocumento3 pagineMCQSShahzad RasoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Organs of The BodyDocumento2 pagineDifferent Organs of The BodyVon Ramwel NicolasNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Excretion System IGCSE 9th GradeDocumento33 pagineHuman Excretion System IGCSE 9th GradebenunosNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcqs On Excretory SystemDocumento3 pagineMcqs On Excretory SystemIshfaq LoneNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Quest 8 AC 3E c04 PDFDocumento94 pagineScience Quest 8 AC 3E c04 PDFmaxx100% (1)
- Respiration and Excretion: Name DateDocumento7 pagineRespiration and Excretion: Name DateCristina TorrenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hodder Science-Stage-6-answersDocumento11 pagineHodder Science-Stage-6-answersjean wongNessuna valutazione finora
- Science f3 Yearly Lesson Plan 2018Documento21 pagineScience f3 Yearly Lesson Plan 2018shu kadirNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge Checkpoint Notes ExcretionDocumento3 pagineCambridge Checkpoint Notes Excretionanimemaster2kNessuna valutazione finora
- A) Hormone Production B) Transporting Oxygen To The Tissues C) Removal of Waste and Extra Fluid D) Gas ExchangeDocumento2 pagineA) Hormone Production B) Transporting Oxygen To The Tissues C) Removal of Waste and Extra Fluid D) Gas ExchangepancadewisNessuna valutazione finora
- Excretion in Humans: Question Paper 1Documento10 pagineExcretion in Humans: Question Paper 1Annmary AbrahamNessuna valutazione finora
- The Urinary SystemDocumento2 pagineThe Urinary SystemArl PasolNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Material - 2Documento5 pagineStudy Material - 2rohitsonkarrohit15Nessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Structural Organisation in Animals PPT - Part 5Documento22 pagine7 Structural Organisation in Animals PPT - Part 5Jeevan RaajNessuna valutazione finora
- The Excretory System: by Group 1Documento35 pagineThe Excretory System: by Group 1Gresia FalentinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Excretory SystemDocumento3 pagineBiology Excretory Systemias100% (1)
- Biology SPM Quick RevisionDocumento37 pagineBiology SPM Quick RevisionAsyraf GhaniNessuna valutazione finora