Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Kimling Percobaan Penentuan CL
Caricato da
Rinda As EtaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Kimling Percobaan Penentuan CL
Caricato da
Rinda As EtaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
A.
B.
C.
TITTLE OF EXPERIMENT
DATE OF EXPERIMENT
AIM OF EXPERIMENT
: DETERMINE THE PERCENTAGE OF Cl: 15th OCTOBER 2014
: to determine the percentage of chloride in the
water sample
D.
BASIC THEORY
Wide - range of chemicals such as ozone (O3), chlorine (Cl2), Chlor dioxyde
(ClO2), and physical processes such as irradiation with UV, warming and others - others,
used for water disinfection. And wide - range of these substances, chlorine is a chemical
that is used.
Besides being able to eradicate bacteria and microorganisms such as amoebae,
algae and others - others, can oxidize chlorine ions - metal ions such as Fe2 + to Fe3 +,
Mn2 + to Mn4 +, and break down organic molecules such as color. During the process,
the chlorine itself becomes chloride (Cl), which does not have the power of disinfection.
Most chloride dissolves in water. But there are some chloride insoluble in water
such as mercury (I) chloride, Hg2Cl2, silver chloride, AgCl, lead chloride, PbCl2, copper
(I) chloride, CuCl, bismuth oxychloride, BiOCl, antimony oxychloride, SbOCl, etc.
Chloride (Cl) when reacted with a solution of silver nitrate (AgNO3) will produce a white
precipitate of silver chloride, AgCl, which is like curd. Insoluble in water and in dilute
nitric acid, but soluble in dilute ammonia solution and in solution - aqueous solution of
potassium cyanide and thiosulphate.
Cl- + Ag+ AgCl
AgCl + 2 NH3 [Ag(NH3)2]+ + Cl[Ag(NH3)2]+ + Cl- + 2 H+ AgCl
+ 2 NH4+
The formation of a chromate on the distillate showed the presence of a chloride
in solids, since chromil chloride is a volatile liquid (volatile) (mp 116.5 C) c
Cr2O72- + 4Cl- + 6 H+ 2CrO2Cl2
+ 3 H2O
CrO2Cl2 + 4OH- CrO42- + 2Cl- + 2 H2O
6 Cl- + Cr2O72- + 14 H+ 3 Cl2 + 2 Cr3+ + 7H2O
Bromide and iodide cause halogen-free, which resulted in a colorless solution
with sodium hydroxide solution. In an atmosphere of neutral or weak alkaline, chloride
ions into silver chloride precipitated. Excess silver nitrate reacts with potassium chromate
red brick Reactions involved are:
Cl- + AgNO3 AgCl + NO32AgCl + K2Cr2O7 Ag2Cr2O7 + 2KCl
Red brick precipitate
E.
TOOLS AND MATERIALS
-
F.
Buret 50 mL
Volumetric Pippte 25 mL
Volumetric Silinder
Statif and clame
Erlenmayer flask
Beakerglass
Water sample
K2Cr2O7
AgNO3
PROCEDUR
Water Sample
Take the sample using volumetric pippte 12,5
mL
Entered into Erlenmeyer flask 250 mL
Added with 10 drops of K2Cr2O7
Tittrated using basic solution of AgNO3 Until
the colour become red brick and you can see
Percentage of cl (mg/L)
at the last point of titration (A)
Water Blanko
Take the blanko using volumetric pippte 12,5
mL
Entered into erlenmeyer flask 250 mL
Added with 10 drops of K2Cr2O7
Tittrated using basic solution of AgNO3 Until
the colour become red brick and you can see
Percentage of cl (mg/L)
at the last point of titration (A)
G.
No
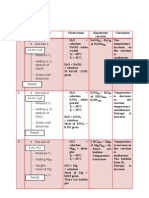
DATA OF EXPERIMENT
Procedur
Data
Before
Water Sample
Take the sample using
volumetric pippte 12,5 mL
Entered into erlenmeyer flask
250 mL
Added with 10 drops of
K2Cr2O7
Tittrated using basic solution of
AgNO3 Until the colour
become red brick and you can
the last point of titration
Percentage see
of clat(mg/L)
(A)
Dugaan Reaksi
Sample solution :
turbide, consist of
brown precipitate
V1 : 1,3 mL
V2 : 1,4 mL
V3 : 1,3 mL
K2Cr2O7
solution : yellow
solution
The sample
colour after
titration with
AgNO3 : the
colour bicome
orange turbide,
and there are
red brick
precipitate
AgNO3 solution :
colourless
Kesimpulan
After
AgNO3 + Cl- AgCl
+ NO3AgCl + K2Cr2O7
Ag2Cr2O7 + 2 KCl
Red brick
precipitate
Average of
blanco :
0,76 mL
V1 Cl : 1.531,44
mg/L
V1 C2 :
1.815,04 mg/L
V3 Cl : 1.531,44
mg/L
Blanco
blanko solution :
colourless
Take the Blanco using
volumetric pippte 12,5 mL
K2Cr2O7
solution : yellow
solution
Entered into Erlenmeyer flask
250 mL
AgNO3 solution :
colourless
Added with 10 drops of
K2Cr2O7
Tittrated using basic solution of
AgNO3 Until the colour
become redish brown and you
at the last point of
Percentage can
of clsee
(mg/L)
titration (A)
V1 : 0,7 mL
V2 : 0,8 mL
V3 : 0,8 mL
The sample
colour after
titration with
AgNO3 : the
colour bicome
orange turbide,
H.
ANALYSIS DATA
In our experiment the aim is to determin the percentage of chloride in the water
sample in the Porong . In this experiment we put 12.5 ml of water sampel and edded into
erlenmeyer flask 250 mL. And then we added with 10 drops of K 2Cr2O7 Solution and
than we tittrated with basic AgNO 3 Solution until the colour of solution become reddish
brown at the end point of tittrasion. Before the solution is tittrated the sample solution is
turbide and consist of brown precipitate. But, after added with 10 drops of K 2Cr2O7
solution, the solution is become yellow. Than we tittrated with AgNO3b until three
replications and the colour changes become dark and founded precipitate.
AgNO3 + Cl- AgCl + NO3AgCl + K2Cr2O7 Ag2Cr2O7 + 2 KCl
Red brick precipitate
From our experiment, we also determine the percentage of the chloride in our
water sample from porong. Becouse we do three replication of sample titration, so we got
three result, which is the average of percentage chloride in our sample is. 1.625,97 mg/L.
So its mean that in the sample that we use, is so many contain of chloride.
I.
CONCLUSION
The conclusion of our experiment is the percentage of the chloride in the water
sample in porong. We get the average percentage is 1.625,97 mg/L. Its mean that the
water sample contain so many of chloride. Because the standard percentage in the water
is 250 mg/L.
J.
DAFTAR PUSTAKA
:
Angelica, R.J.1969. Synthesis and Technique In Inorganic Chemistry.London :
W.B Saundary Company
Svehla, G.1979. Textbook Of Macro and Semimicro Qualitative Inorganic
Analysis.London : Longman Group Limited.
Tim. 2014. Petunjuk Praktikum Kimia Lingkungan.Surabaya : Unesa
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chemical Oxygen Demand (Cod) : TitleDocumento6 pagineChemical Oxygen Demand (Cod) : TitleWaleed KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Divya Ganeshwala 8. Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocumento11 pagineDivya Ganeshwala 8. Chemistry Investigatory ProjectChetan Suhas KamtheNessuna valutazione finora
- Argento Me TryDocumento5 pagineArgento Me TryGino GalanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsNessuna valutazione finora
- Reactions of Copper: Percent YieldDocumento20 pagineReactions of Copper: Percent Yieldwann711100% (1)
- Module 4 - Water Tech EssentialsDocumento8 pagineModule 4 - Water Tech EssentialsPrithviraj m PrithvimanickNessuna valutazione finora
- COD Test Procedure and ResultsDocumento4 pagineCOD Test Procedure and Resultsvk100Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical Chem - Post Lab NotesDocumento11 pagineAnalytical Chem - Post Lab NotesMare5Der5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Precipitation TitrationDocumento19 paginePrecipitation TitrationRoj Waleed BarwaryiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture5 - Chemical Oxygen Demand PDFDocumento40 pagineLecture5 - Chemical Oxygen Demand PDFgagileNessuna valutazione finora
- HCL Solution FinalDocumento12 pagineHCL Solution FinalGurjapsingh SandhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Env. Analysis Munawar HussainDocumento66 paginePractical Env. Analysis Munawar HussainMunawar HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 5 Sku3033Documento5 pagineExperiment 5 Sku3033Luw InNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM 421: Analytical Chemistry: Title: Solubility of Ionic Salts in SeawaterDocumento11 pagineCHM 421: Analytical Chemistry: Title: Solubility of Ionic Salts in Seawateriyla sallehNessuna valutazione finora
- Report Exp 9Documento10 pagineReport Exp 9KaVisha AShaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reactions of CopperDocumento20 pagineReactions of CopperChaimaaElborki100% (2)
- Chem ch31 9 33Documento2 pagineChem ch31 9 33Tang Hon Kit WilsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8Documento11 pagineChapter 8Tandra SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- s4 Chlorine and Its Compound TR MugumyaDocumento15 pagines4 Chlorine and Its Compound TR MugumyaLwin MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- ChlorideDocumento2 pagineChlorideMicrotesting labNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry - Unit3Documento6 pagineChemistry - Unit3123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical 1Documento11 pagineAnalytical 1Seyram DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Selina-Sol-Concise-Chem-Class-10-Ch-8 JGHHJKDocumento6 pagineSelina-Sol-Concise-Chem-Class-10-Ch-8 JGHHJKPROGRAMMING HUBNessuna valutazione finora
- ENVE 202 Week2Documento24 pagineENVE 202 Week2Halilcan ÖztürkNessuna valutazione finora
- Chloride Determination in Water by Mohr Method TitrationDocumento2 pagineChloride Determination in Water by Mohr Method TitrationDeep Dave100% (1)
- Assignment 4 SolutionsDocumento27 pagineAssignment 4 SolutionsMahimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis of Cobalt ComplexDocumento5 pagineSynthesis of Cobalt ComplexYang-hun Ban100% (2)
- Revision StoichiometryDocumento12 pagineRevision StoichiometryFangru CaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Flame test identification using metal ionsDocumento17 pagineFlame test identification using metal ionsTahir50% (4)
- Stoichiometry 2Documento7 pagineStoichiometry 2Raju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry ArihantDocumento31 pagineChemistry Arihantrahul100% (2)
- Experiment 9Documento9 pagineExperiment 9Oh Zi YiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 6. Precipitation TitrationDocumento21 pagineLecture 6. Precipitation TitrationMohamed Babiker SulimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt 7Documento6 pagineExpt 7Purnima NaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 7 Colloids ChemistryDocumento8 pagineExp 7 Colloids ChemistryNur Fadhilah100% (1)
- AP Chem Lab - Redox TitrationDocumento8 pagineAP Chem Lab - Redox TitrationTitus KoechNessuna valutazione finora
- Concise Chemistry Part II - Selina Solution for Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 8Documento10 pagineConcise Chemistry Part II - Selina Solution for Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 8ULTIMATE VEHICLENessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Discussion CL BR IDocumento8 pagineAnalysis and Discussion CL BR IanjanipanjalinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Calculations 2Documento6 pagineChemical Calculations 2Harshika Prasanganie Abeydeera100% (1)
- ArgentometryDocumento4 pagineArgentometryKeka DuariNessuna valutazione finora
- 1617 Level M Chemistry Brush-Up Make-Up Material PDFDocumento5 pagine1617 Level M Chemistry Brush-Up Make-Up Material PDFAndrewNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry IGCSE Edexcel RevisionDocumento5 pagineChemistry IGCSE Edexcel RevisionImran NooraddinNessuna valutazione finora
- AS-Level Chemistry Unit:3 NotesDocumento14 pagineAS-Level Chemistry Unit:3 NotesMehreenSaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical Separation by Ion-Exchange Chromatography - Lab ReportDocumento5 pagineAnalytical Separation by Ion-Exchange Chromatography - Lab ReportVu SonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chlorine and Its CompoundsDocumento19 pagineChlorine and Its Compoundskakembo hakimNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 CodDocumento4 pagine14 Codtfgrn7srtqNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment ReportDocumento16 pagineExperiment ReportichaNessuna valutazione finora
- Woah! So Practicool!Documento6 pagineWoah! So Practicool!fuzzy pillowNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemistryQB Topic6a MC eDocumento59 pagineChemistryQB Topic6a MC eNg Swee Loong StevenNessuna valutazione finora
- Reactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesDocumento44 pagineReactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesGlen Mangali100% (4)
- Quantitative Analytical Chemistry I ExperimentsDocumento7 pagineQuantitative Analytical Chemistry I ExperimentswimbotrionoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrolysis ExerciseDocumento4 pagineHydrolysis ExerciseetikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis of Cobalt Linkage IsomersDocumento7 pagineSynthesis of Cobalt Linkage IsomersKgasu MosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Soal Babak Penyisihan Olimpiade Kimia 2016Documento14 pagineSoal Babak Penyisihan Olimpiade Kimia 2016Muhaqqy50% (2)
- Cloruro de Hexamino Cobalto IIIDocumento5 pagineCloruro de Hexamino Cobalto IIIElizabeth Ayala BlancoNessuna valutazione finora
- Detect Carbon, Hydrogen & OxygenDocumento8 pagineDetect Carbon, Hydrogen & OxygenRhealyn Legaspi100% (2)
- Chemistry of ChlorineDocumento41 pagineChemistry of ChlorineKennedy ChitayiNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis GravimetriDocumento11 pagineAnalysis GravimetriRinda As EtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Picture of Precipitate TitrationDocumento2 paginePicture of Precipitate TitrationRinda As EtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental WorksheetDocumento3 pagineExperimental WorksheetRinda As EtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1: Test Tube 1Documento2 pagineExperiment 1: Test Tube 1Rinda As EtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Salt Hydrolysis Classification and ReactionsDocumento13 pagineSalt Hydrolysis Classification and ReactionsRinda As Eta0% (1)
- APC CoolingDocumento42 pagineAPC CoolingElson LinNessuna valutazione finora
- Remove Oil Grease Water 40Documento6 pagineRemove Oil Grease Water 40Sai PrasathNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review: Solar Water Heating Systems: Tadvi Sachin VinubhaiDocumento8 pagineA Review: Solar Water Heating Systems: Tadvi Sachin Vinubhaideebii dabalaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lorentz Ps2-100 Product BrochureDocumento3 pagineLorentz Ps2-100 Product BrochureSINES FranceNessuna valutazione finora
- 2013 Rubinos D.A. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Fractionation and Mobility of Metals in Bauxite Red Mud Journal Volume 1 16Documento17 pagine2013 Rubinos D.A. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Fractionation and Mobility of Metals in Bauxite Red Mud Journal Volume 1 16Ayashkant sahooNessuna valutazione finora
- Jensen Mixer Series 600 IOM 2010Documento24 pagineJensen Mixer Series 600 IOM 2010SergioNessuna valutazione finora
- Dissertation Antigoni-Maria VrochidouDocumento63 pagineDissertation Antigoni-Maria Vrochidouallaboutshipping100% (1)
- Ghadames BasinDocumento18 pagineGhadames Basinايمن مفتاحNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of AqueductDocumento5 pagineDesign of Aqueducthari_shresthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Smeg Manual GW1060Documento44 pagineSmeg Manual GW1060shtempelNessuna valutazione finora
- Enhancement of Energy Efficiency in Wastewater Treatment PlantsDocumento8 pagineEnhancement of Energy Efficiency in Wastewater Treatment PlantsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Dhaka's unhealthy air quality and calculating effects of ocean warmingDocumento4 pagineDhaka's unhealthy air quality and calculating effects of ocean warmingRose ]SwindellNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Tank Dewatering 1Documento4 pagineAutomatic Tank Dewatering 1JADNessuna valutazione finora
- Omori - EmotionDocumento18 pagineOmori - EmotionnatitvzandtNessuna valutazione finora
- Continents and OceansDocumento9 pagineContinents and Oceansapi-3718737100% (1)
- CE405-EE-I MOD.3 - ProblemsDocumento37 pagineCE405-EE-I MOD.3 - ProblemsShanihaKK100% (2)
- Becker Twisted FinDocumento4 pagineBecker Twisted FindecdeNessuna valutazione finora
- On Green SkillsDocumento9 pagineOn Green SkillsAbhinav SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Site Analysis of KanchipuramDocumento23 pagineSite Analysis of KanchipuramVivek Kumar0% (2)
- Roofing Code of PracticeDocumento379 pagineRoofing Code of Practicesepasepasepa100% (1)
- Assessment of Water Quality of Runoff From Sealed Asphalt SurfacesDocumento44 pagineAssessment of Water Quality of Runoff From Sealed Asphalt SurfacesTom EnnisNessuna valutazione finora
- Checklist For Technical Evaluation of Infrastructure Contracts Scope of Technical EvaluationDocumento1 paginaChecklist For Technical Evaluation of Infrastructure Contracts Scope of Technical EvaluationNadine DiamanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Mass Balance of Lakes and Wetlands (Formulas y Graficos)Documento9 pagineMass Balance of Lakes and Wetlands (Formulas y Graficos)Maria RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Rmas 20 e - Rad - Ing - Man - Inst - 0809B - Digitech PDFDocumento54 pagineRmas 20 e - Rad - Ing - Man - Inst - 0809B - Digitech PDFBotnaru AurelNessuna valutazione finora
- Breathable Soil WaterproofingDocumento2 pagineBreathable Soil WaterproofingANILNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning and Design of Sanitation System On Low Income People in Cox'S-BazarDocumento9 paginePlanning and Design of Sanitation System On Low Income People in Cox'S-BazarMd. Habibur Rahman Bejoy Khan ,155408Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Connection Involving PVC / Gi Pipes and Pipe FittingsDocumento5 pagineBasic Connection Involving PVC / Gi Pipes and Pipe FittingspsunmoorthyNessuna valutazione finora
- A Checklist of The Fish Species of The Mogol and Palala Rivers (Limpopo System) of The TransvaalDocumento6 pagineA Checklist of The Fish Species of The Mogol and Palala Rivers (Limpopo System) of The TransvaalJeyzack ÁlvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS) : SD Biolien Dengue Igg/Igm WBDocumento9 pagineSafety Data Sheet (SDS) : SD Biolien Dengue Igg/Igm WBAni HindayaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Asd Tug 3212 FactsheetDocumento1 paginaAsd Tug 3212 FactsheetRoda NiagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressDa EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsDa EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (146)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementDa EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeDa EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationDa EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (18)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (14)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsDa EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsDa EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksDa EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolDa EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Stuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials That Shape Our Man-Made WorldDa EverandStuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials That Shape Our Man-Made WorldValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (289)
- Process Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentDa EverandProcess Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilDa EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationDa EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNessuna valutazione finora
- Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryDa EverandNapoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (25)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (9)
- Meltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalDa EverandMeltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDa EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideDa EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Advanced Process Control: Beyond Single Loop ControlDa EverandAdvanced Process Control: Beyond Single Loop ControlNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsDa EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingDa EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisDa EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Introduction to Strategies for Organic SynthesisDa EverandIntroduction to Strategies for Organic SynthesisNessuna valutazione finora