Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chapter-16: Logistics and Supply Chain Management What Is Logistics?
Caricato da
KaziRafiDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter-16: Logistics and Supply Chain Management What Is Logistics?
Caricato da
KaziRafiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
5/24/2013
What is Logistics?
Chapter-16: Logistics and Supply
Chain Management
Logistics is the management of the flow of physical materials.
In the context of marketing channels Logistics is a process of
systemizing information to facilitate the efficient and cost-
Lecture-12
Course: Marketing Channels
(MKT 450)
effective flows of goods & services to produce customer
satisfaction.
-
Faculty: Abdullah Al Faruq (AFq)
Logistics in marketing channels involves the processing and
tracking of factory goods during warehousing, inventory
control, transport, customs documentation and delivery to
customers.
North South University (NSU)
-
In sum logistics creates the rights of passage in marketing
channels.
The Building Blocks of Logistics
Right Place
Right Cost
The building blocks of logistics are:
a. Inventory.
b. Order fulfillment and transportation.
Right Product
c. The documentation.
Inventory
Right Time
Inventory is the stocks of goods or the components of goods
that will be used for the production or successful delivery of a
Right condition
service.
Figure: The logistics Rights of Passage
There four good reasons for holding inventory they are:
a. Demand surge management.
b. Economies of scale in production.
5/24/2013
Inventory (Cont.)
-
There four good reasons for holding inventory they are (Cont.):
c. Reduce the transportation loss time.
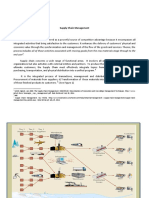
Order Fulfillment and Transportation (Cont.)
-
The concept of cross-docking came into implementation.
The cross-docking is an effective and efficient process of order
The steps of cross-docking are:
d. To meet uncertainty.
fulfillment and transportation of a goods for end-users.
Order Fulfillment and Transportation
-
Orders product
The implementation of logistics ensures orders are receive quickly
Retailer
from a customer and dispatch as early as possible.
-
Packs the product
and transfer to
delivery unit
Manufacturer
Factory
F t
Transportation is another important element in marketing channel
Delivery
Unit
U it
Ships the product
which has been made manageable by the implementation of
logistics.
-
Transportation in marketing channel does not only involve the
product being transported to the shops/end-users but also the point
process efficient and effective.
where the raw-materials are acquired and brought to the factory.
Documentation
-
The final blocks of logistics is removal of documentation i.e. filling up
order form, invoices, receipts etc are heavily minimized with the
What is Supply Chain Management?
-
chain as efficiently as possible.
The main player here has been the utilization of computers and
third-party computer software that has remove filling up bundles of
Supply chain management (SCM) is the process of planning,
implementing and controlling the operations of the supply
utilization of logistical concept.
-
Nowadays, even third-party logistics provider is used to make the
Supply Chain Management spans all movement and storage of
raw materials, work-in-process inventory, and finished goods
papers and substituted it with click and drag.
from point-of-origin to point-of-consumption.
-
The concept of SCM goes all the way back to the point where
the manufacturers acquires the materials to be used for
production of a product, how it reaches the factory, how it
leaves the factory to reach to the doors of the
wholesalers/retailers to be consumed by the end-user.
5/24/2013
Approaches to Supply Chain Management (SCM)
i. Efficient Consumer Response (ECR)
-
Efficient Consumer Response (ECR) is a joint trade and industry
body working towards making the grocery sector as a whole
more responsive to consumer demand and promote the removal
of unnecessary costs from the supply chain.
Th principle
The
i i l off ECR was to
t find
fi d outt a way to
t better
b tt serve the
th
customers supplying only what was required.
There are four areas of ECR:
a. Continuous Replenishment Program (CRP)
-
The practice of replacing stock based on speedy knowledge of
consumer sales.
Which SCM Approach to choose?
ii. Quick Response (QR)/Rapid Response
-
Quick Response (QR) was developed in the early 1980s and it comes from the
Both the approaches has benefits but however, which approach to choose is a
The answer lies in the product/service itself i.e. certain products are
critical question that needs to be answered by the manufacturer.
fashion industry. The basic idea of QR is to let clients tell the whole channel what to
make and what to distribute and then do it fast. QR contains keeping production
categorized as functional products/brands i.e. these are products whose
flexibility as to what to do and how many to do
demands are predictable, serves basic stable need, people buy in many outlets
The Areas of QR
and long life cycles. For example, toothpaste, bread, tools etc.
a. Unstable Market Nature
-
Initially designed to face the unstable and changing demand of the market with
are unpredictable, does not serve stable and basic need, products are highly
ease.
b.
Manufacturing oriented
QR is more manufacture based and thinks less of promotion and pricing thus they
differentiated. For example, cars, dresses etc.
-
are heavy users of flexible manufacturing techniques.
c.
Transportation
QR is about shipping the product as quickly as possible and if required pay premium
pricing for transportation
On the other hand, innovative products/brands has less age life cycle, demands
Functional products require holding down cost, fast delivery and as demand
are predictable decision taking are easy so ECR fits the profile i.e. physically
efficient production.
Innovative products needs to be market responsive i.e. product designs needs
to equip to change or postponement any time, performance are less cost
driven so QR fits the profile here.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Supply Chain Management and It's Role in Success of Mcdonalds in India and Walmarts.Documento54 pagineSupply Chain Management and It's Role in Success of Mcdonalds in India and Walmarts.Aditya Gupta100% (4)
- Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementDocumento55 pagineLogistics and Supply Chain ManagementminucNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Business Analysis-Reporting-Text-3Documento6 pagineStrategic Business Analysis-Reporting-Text-3Christine Marie GazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics ManagementDocumento7 pagineLogistics ManagementAdnan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1: Introduction To Supply Chain and Processes: SCM AdvantagesDocumento8 pagineModule 1: Introduction To Supply Chain and Processes: SCM AdvantagesAaron Jolo AlcantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Supply Chain Hand-Outs 1Documento8 pagineSupply Chain Hand-Outs 1MarkmarilynNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementDocumento8 pagineLogistics and Supply Chain ManagementAkhiNessuna valutazione finora
- E-Business Topic 2 PDFDocumento51 pagineE-Business Topic 2 PDFMariela GDNessuna valutazione finora
- University Institute of Information Technology Himachal Pradesh UniversityDocumento52 pagineUniversity Institute of Information Technology Himachal Pradesh UniversityacademyNessuna valutazione finora
- C2X Chain To Excellence: KonseputoDocumento26 pagineC2X Chain To Excellence: KonseputoRishabh AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- 13.0 Chapter - 13 - Integrated Logistics ManagementDocumento9 pagine13.0 Chapter - 13 - Integrated Logistics ManagementNor NaimahNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide Module 1Documento3 pagineStudy Guide Module 1José Carlos Cardoso GamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Definition of LogisticsDocumento31 pagineDefinition of LogisticsArun Narayanan100% (1)
- 7 Areas of Supply ChainDocumento4 pagine7 Areas of Supply ChainSharath BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Supply ChainDocumento16 pagineSupply ChainbridaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Supply Chain Management Pankaj and RamaneetDocumento13 pagineIntroduction To Supply Chain Management Pankaj and RamaneetRamneet ParmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction & Importance of Supply Chain ManagementDocumento8 pagineIntroduction & Importance of Supply Chain ManagementRiddhi ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Supply Chain and Logistics in Marketing - CDocumento20 pagineSupply Chain and Logistics in Marketing - CvibuNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.fundamental of Logistics (Week9) - 2566Documento41 pagine9.fundamental of Logistics (Week9) - 2566nattapon nnNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment On:: Supply Chain Management (SCM)Documento9 pagineAssignment On:: Supply Chain Management (SCM)Kumardeep Singha100% (1)
- SCM Unit-2Documento22 pagineSCM Unit-2Aashish Singh IINessuna valutazione finora
- Production - Inventory - Location - Transportation - InformationDocumento7 pagineProduction - Inventory - Location - Transportation - InformationKushal BagadiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sourcing - Logistics - LEC01 04102023 064133pmDocumento31 pagineSourcing - Logistics - LEC01 04102023 064133pm7drkn2vtybNessuna valutazione finora
- Supply Chain Management FinalDocumento12 pagineSupply Chain Management FinalManJyot SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Production Supply Chain AssignmentDocumento11 pagineProduction Supply Chain AssignmentAyman JiwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec2.1-OP & SCM - Logistics MGTDocumento19 pagineLec2.1-OP & SCM - Logistics MGTAbhishek JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Term Paper OF Operation Management (O.M) : TopicDocumento15 pagineTerm Paper OF Operation Management (O.M) : TopicreyazmbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary Logistics Chapter 1 5 7-8-10 en 14.docx FDocumento21 pagineSummary Logistics Chapter 1 5 7-8-10 en 14.docx FasdfasfasdfasdfasdfsdafNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations Module-5Documento19 pagineOperations Module-5Jeleetta MathewNessuna valutazione finora
- Advertising and Sales Promotion Study Guide Module 5Documento6 pagineAdvertising and Sales Promotion Study Guide Module 5Anthony CreationNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 - NotesDocumento8 pagineUnit 1 - NotesAnas K MakNessuna valutazione finora
- Into To Supply Graduation ProjectDocumento27 pagineInto To Supply Graduation ProjectMahmoud AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- International Logistics ManagementDocumento205 pagineInternational Logistics ManagementAnand JherwerNessuna valutazione finora
- Final SCM2Documento10 pagineFinal SCM2xylasugNessuna valutazione finora
- POB Logistics and Supply ChainDocumento59 paginePOB Logistics and Supply Chainmalindabissoon312Nessuna valutazione finora
- Procedure and Documentation in Supply Chain Management: Business strategy books, #1Da EverandProcedure and Documentation in Supply Chain Management: Business strategy books, #1Nessuna valutazione finora
- LSCM Chap 1 NotesDocumento32 pagineLSCM Chap 1 Notesprasanna murthyNessuna valutazione finora
- TSCM Eq SolutionDocumento104 pagineTSCM Eq Solutionch0c018Nessuna valutazione finora
- Production and OperationsDocumento7 pagineProduction and OperationsVarun KukrejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 21Documento19 pagineChapter 21Fire BoltNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics ManagementDocumento27 pagineLogistics Managementapi-375001183% (12)
- Unit - IDocumento100 pagineUnit - Irajeeeva100% (1)
- Introduction To Supply ChainDocumento6 pagineIntroduction To Supply ChainAlexisNessuna valutazione finora
- Supply Chain ReviewerDocumento7 pagineSupply Chain ReviewerAlexisNessuna valutazione finora
- W Hy Logistics ? History of Logistics:: Type of Logistics: How To Improve Your Logistics Network FlowDocumento10 pagineW Hy Logistics ? History of Logistics:: Type of Logistics: How To Improve Your Logistics Network FlowAnas BouchikhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Importance of Reverse Logistics in Supply Chain ManagementDocumento27 pagineImportance of Reverse Logistics in Supply Chain ManagementRenjith SdNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment For Product and Brand ManagementDocumento9 pagineAssignment For Product and Brand Managementravijat53080Nessuna valutazione finora
- History & Evolution of Supply Chain ManagemantDocumento41 pagineHistory & Evolution of Supply Chain ManagemantGreeshma100% (7)
- Handout 03 04Documento71 pagineHandout 03 04Tommba TommyNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz Chapter 1 CJRODocumento7 pagineQuiz Chapter 1 CJROPamela ValdesNessuna valutazione finora
- Supply Chain Management - TQMDocumento11 pagineSupply Chain Management - TQMsuriya kishoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To Logis - Quynh Tram - Sem1-2014Documento40 pagineIntro To Logis - Quynh Tram - Sem1-2014Chip choiNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic I - Introduction To SCMDocumento9 pagineTopic I - Introduction To SCMHobiNessuna valutazione finora
- NIket Operations Ka BadshahDocumento37 pagineNIket Operations Ka BadshahParthNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: Muhammad Taha Anwar Section: 2a ID: 1839132 Course: Supply Chain Operations Instructor Name: Sir Muhammad Zuhair MohsinDocumento4 pagineName: Muhammad Taha Anwar Section: 2a ID: 1839132 Course: Supply Chain Operations Instructor Name: Sir Muhammad Zuhair Mohsintaha anwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Project.Documento105 pagineFinal Project.lakshmanlakhsNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics in Manufacturing, Supply Chain, and DistributionDa EverandLogistics in Manufacturing, Supply Chain, and DistributionNessuna valutazione finora
- Technology Trends in Materials Management: A Systematic Review of the Use of Technology in Materials Management to Achieve Competitive AdvantagesDa EverandTechnology Trends in Materials Management: A Systematic Review of the Use of Technology in Materials Management to Achieve Competitive AdvantagesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Capital Equipment Purchasing: Optimizing the Total Cost of CapEx SourcingDa EverandCapital Equipment Purchasing: Optimizing the Total Cost of CapEx SourcingNessuna valutazione finora
- MKT 470 RajuDocumento66 pagineMKT 470 RajuKaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Conjugation in SpirogyraDocumento3 pagineConjugation in SpirogyraKaziRafi100% (1)
- HR NSU - ContentsDocumento1 paginaHR NSU - ContentsKaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3: The Changing Environment of Management: MGT 210 Section17&18Documento24 pagineChapter 3: The Changing Environment of Management: MGT 210 Section17&18KaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2: The Evolution of Management ThoughtDocumento16 pagineChapter 2: The Evolution of Management ThoughtKaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Top Tips: Access Cavities and Canal LocationDocumento8 pagine10 Top Tips: Access Cavities and Canal LocationKaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Children Preventive & Community DentistryDocumento2 pagineChildren Preventive & Community DentistryKaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Inch 2 Column Front / Back PageDocumento1 pagina4 Inch 2 Column Front / Back PageKaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Capital Structure and LeverageDocumento16 pagineCapital Structure and LeverageKaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bus173 Chap03Documento42 pagineBus173 Chap03KaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- ECO 104 Faculty: Asif Chowdhury: The Influence of Monetary & Fiscal Policy On Aggregate Demand (Part 1) (Ch:21 P.O.M.E)Documento9 pagineECO 104 Faculty: Asif Chowdhury: The Influence of Monetary & Fiscal Policy On Aggregate Demand (Part 1) (Ch:21 P.O.M.E)KaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- ECO 104 Faculty: Asif Chowdhury: Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply (Part 1) (Ch:20 P.O.M.E)Documento16 pagineECO 104 Faculty: Asif Chowdhury: Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply (Part 1) (Ch:20 P.O.M.E)KaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cost of Capital: Sources of Capital Component Costs Wacc Adjusting For RiskDocumento22 pagineThe Cost of Capital: Sources of Capital Component Costs Wacc Adjusting For RiskKaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Financial StatementsDocumento30 pagineAnalysis of Financial StatementsKaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Money Growth & Inflation (Ch:17 P.O.M.E) : ECO 104 Faculty: Asif ChowdhuryDocumento18 pagineMoney Growth & Inflation (Ch:17 P.O.M.E) : ECO 104 Faculty: Asif ChowdhuryKaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- ECO 104 Faculty: Asif Chowdhury: Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply (Part 2) (Ch:20 P.O.M.E)Documento9 pagineECO 104 Faculty: Asif Chowdhury: Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply (Part 2) (Ch:20 P.O.M.E)KaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Monetary System (Ch:16 P.O.M.E) : ECO 104 Faculty: Asif ChowdhuryDocumento13 pagineThe Monetary System (Ch:16 P.O.M.E) : ECO 104 Faculty: Asif ChowdhuryKaziRafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Coursera Qs-Ans For Financial AidDocumento2 pagineCoursera Qs-Ans For Financial AidMarno03Nessuna valutazione finora
- 9702 s02 QP 1Documento20 pagine9702 s02 QP 1Yani AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- ShakespeareDocumento12 pagineShakespeareapi-510189551Nessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Market Making Agreement 31.03Documento13 pagineRevised Market Making Agreement 31.03Bhavin SagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Trust Is The Coin of The Realm by George P. ShultzDocumento13 pagineTrust Is The Coin of The Realm by George P. ShultzHoover Institution100% (2)
- HDLSS Numerical Assignments - DOC FormatDocumento3 pagineHDLSS Numerical Assignments - DOC FormatNikhil UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Precision Nutrition. Nutrient TimingDocumento21 paginePrecision Nutrition. Nutrient TimingPaolo AltoéNessuna valutazione finora
- (2016) The Role of Requirements in The Success or Failure of Software Projects-DikonversiDocumento11 pagine(2016) The Role of Requirements in The Success or Failure of Software Projects-DikonversiFajar HatmalNessuna valutazione finora
- 17373.selected Works in Bioinformatics by Xuhua Xia PDFDocumento190 pagine17373.selected Works in Bioinformatics by Xuhua Xia PDFJesus M. RuizNessuna valutazione finora
- The Utopia of The Zero-OptionDocumento25 pagineThe Utopia of The Zero-Optiontamarapro50% (2)
- NyirabahireS Chapter5 PDFDocumento7 pagineNyirabahireS Chapter5 PDFAndrew AsimNessuna valutazione finora
- Democracy in SomalilandDocumento118 pagineDemocracy in SomalilandAbdirahman IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution of Corporate Social Responsibility in IndiaDocumento12 pagineEvolution of Corporate Social Responsibility in IndiaVinay VinuNessuna valutazione finora
- Creativity and AestheticDocumento17 pagineCreativity and AestheticSyahirah Erahzs100% (1)
- Followup Centres May12Documento14 pagineFollowup Centres May12Suresh NagpalNessuna valutazione finora
- Brenda Alderman v. The Philadelphia Housing Authority, 496 F.2d 164, 3rd Cir. (1974)Documento16 pagineBrenda Alderman v. The Philadelphia Housing Authority, 496 F.2d 164, 3rd Cir. (1974)Scribd Government DocsNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Live A Healthy LifestyleDocumento2 pagineHow To Live A Healthy LifestyleJocelynNessuna valutazione finora
- SCHEEL, Bernd - Egyptian Metalworking and ToolsDocumento36 pagineSCHEEL, Bernd - Egyptian Metalworking and ToolsSamara Dyva86% (7)
- Dnyanadeep's IAS: UPSC Essay Series - 7Documento2 pagineDnyanadeep's IAS: UPSC Essay Series - 7Rahul SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Prof Chase B. Wrenn - The True and The Good - A Strong Virtue Theory of The Value of Truth-Oxford University Press (2024)Documento196 pagineProf Chase B. Wrenn - The True and The Good - A Strong Virtue Theory of The Value of Truth-Oxford University Press (2024)Mihaela DodiNessuna valutazione finora
- Constitutional Law Sem 5Documento5 pagineConstitutional Law Sem 5Ichchhit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Στέργος Νεκτάριος-Μικκιος-CVDocumento4 pagineΣτέργος Νεκτάριος-Μικκιος-CVNektarios MikkiosNessuna valutazione finora
- ABS Parametric RollDocumento2 pagineABS Parametric RollAdvan Zuidplas100% (1)
- Letter From MomDocumento3 pagineLetter From MomSonia Beron-Mosot Guias75% (20)
- FASUPDocumento60 pagineFASUPPranjal KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Gayatri Mantram SPDocumento17 pagineGayatri Mantram SPvaidyanathan100% (1)
- Current Technique in The Audiologic Evaluation of Infants: Todd B. Sauter, M.A., CCC-ADocumento35 pagineCurrent Technique in The Audiologic Evaluation of Infants: Todd B. Sauter, M.A., CCC-AGoesti YudistiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Pustaka 7689Documento20 pagineDaftar Pustaka 7689Rivani KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sand Casting Lit ReDocumento77 pagineSand Casting Lit ReIxora MyNessuna valutazione finora
- Culture and Creative Industries in TanzaniaDocumento70 pagineCulture and Creative Industries in TanzaniaYana ArsyadiNessuna valutazione finora