Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Physics I Problems
Caricato da
bosschellen0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
1K visualizzazioni1 paginaA figure skater's outstretched hands and arms can be considered a slender rod. His hands and arms span 1. M; when wrapped, they form a cylinder of radius 25 cm. A diver comes off a board with arms straight up and legs straight down.
Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Physics I Problems (104)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoA figure skater's outstretched hands and arms can be considered a slender rod. His hands and arms span 1. M; when wrapped, they form a cylinder of radius 25 cm. A diver comes off a board with arms straight up and legs straight down.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
1K visualizzazioni1 paginaPhysics I Problems
Caricato da
bosschellenA figure skater's outstretched hands and arms can be considered a slender rod. His hands and arms span 1. M; when wrapped, they form a cylinder of radius 25 cm. A diver comes off a board with arms straight up and legs straight down.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
Exercises
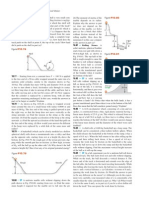
10.43 .. The Spinning Figure Figure E10.43
Skater. The outstretched hands
and arms of a gure skater
preparing for a spin can be considered a slender rod pivoting
about an axis through its center
(Fig. E10.43). When the skaters
hands and arms are brought in
and wrapped around his body to
execute the spin, the hands and
arms can be considered a thinwalled, hollow cylinder. His hands and arms have a combined mass of
8.0 kg. When outstretched, they span 1.8 m; when wrapped, they form
a cylinder of radius 25 cm. The moment of inertia about the rotation
axis of the remainder of his body is constant and equal to 0.40 kg # m2.
If his original angular speed is 0.40 rev>s, what is his nal angular
speed?
10.44 .. A diver comes off a board with arms straight up and legs
straight down, giving her a moment of inertia about her rotation
axis of 18 kg # m2. She then tucks into a small ball, decreasing this
moment of inertia to 3.6 kg # m2. While tucked, she makes two
complete revolutions in 1.0 s. If she hadnt tucked at all, how many
revolutions would she have made in the 1.5 s from board to water?
10.45 .. A large wooden turntable in the shape of a at uniform
disk has a radius of 2.00 m and a total mass of 120 kg. The
turntable is initially rotating at 3.00 rad>s about a vertical axis
through its center. Suddenly, a 70.0-kg parachutist makes a soft
landing on the turntable at a point near the outer edge. (a) Find the
angular speed of the turntable after the parachutist lands. (Assume
that you can treat the parachutist as a particle.) (b) Compute the
kinetic energy of the system before and after the parachutist lands.
Why are these kinetic energies not equal?
10.46 .. A solid wood door 1.00 m wide and 2.00 m high is
hinged along one side and has a total mass of 40.0 kg. Initially open
and at rest, the door is struck at its center by a handful of sticky mud
with mass 0.500 kg, traveling perpendicular to the door at 12.0 m>s
just before impact. Find the nal angular speed of the door. Does
the mud make a signicant contribution to the moment of inertia?
10.47 .. A small 10.0-g bug stands at one end of a thin uniform
bar that is initially at rest on a smooth horizontal table. The other
end of the bar pivots about a nail driven into the table and can rotate
freely, without friction. The bar has mass 50.0 g and is 100 cm in
length. The bug jumps off in the horizontal direction, perpendicular
to the bar, with a speed of 20.0 cm>s relative to the table. (a) What
is the angular speed of the bar just after the frisky insect leaps? (b)
What is the total kinetic energy of the system just after the bug
leaps? (c) Where does this energy come from?
10.48 .. Asteroid Collision! Suppose that an asteroid traveling
straight toward the center of the earth were to collide with our planet
at the equator and bury itself just below the surface. What would
have to be the mass of this asteroid, in terms of the earths mass M,
for the day to become 25.0% longer than it presently is as a result of
the collision? Assume that the asteroid is very small compared to the
earth and that the earth is uniform throughout.
10.49 .. A thin, uniform metal bar, 2.00 m long and weighing
90.0 N, is hanging vertically from the ceiling by a frictionless
pivot. Suddenly it is struck 1.50 m below the ceiling by a small
3.00-kg ball, initially traveling horizontally at 10.0 m>s. The ball
rebounds in the opposite direction with a speed of 6.00 m>s.
(a) Find the angular speed of the bar just after the collision.
(b) During the collision, why is the angular momentum conserved
but not the linear momentum?
337
10.50 .. A thin uniform rod has a length of 0.500 m and is rotating
in a circle on a frictionless table. The axis of rotation is perpendicular
to the length of the rod at one end and is stationary. The rod has an
angular velocity of 0.400 rad>s and a moment of inertia about the
axis of 3.00 * 10 -3 kg # m2. A bug initially standing on the rod at
the axis of rotation decides to crawl out to the other end of the rod.
When the bug has reached the end of the rod and sits there, its tangential speed is 0.160 m>s. The bug can be treated as a point mass.
(a) What is the mass of the rod? (b) What is the mass of the bug?
10.51 .. A uniform, 4.5-kg, square, solid wooden gate 1.5 m on
each side hangs vertically from a frictionless pivot at the center of
its upper edge. A 1.1-kg raven ying horizontally at 5.0 m>s ies
into this door at its center and bounces back at 2.0 m>s in the opposite direction. (a) What is the angular speed of the gate just after it
is struck by the unfortunate raven? (b) During the collision, why is
the angular momentum conserved, but not the linear momentum?
10.52 .. Sedna. In November 2003, the now-most-distant-known
object in the solar system was discovered by observation with a telescope on Mt. Palomar. This object, known as Sedna, is approximately
1700 km in diameter, takes about 10,500 years to orbit our sun, and
reaches a maximum speed of 4.64 km>s. Calculations of its complete
path, based on several measurements of its position, indicate that its
orbit is highly elliptical, varying from 76 AU to 942 AU in its distance
from the sun, where AU is the astronomical unit, which is the average
distance of the earth from the sun (1.50 * 10 8 km). (a) What is
Sednas minimum speed? (b) At what points in its orbit do its maximum and minimum speeds occur? (c) What is the ratio of Sednas
maximum kinetic energy to its minimum kinetic energy?
Section 10.7 Gyroscopes and Precession
10.53 .. The rotor (ywheel) of a toy gyroscope has mass 0.140
kg. Its moment of inertia about its axis is 1.20 * 10 -4 kg # m2. The
mass of the frame is 0.0250 kg. The gyroscope is supported on a
single pivot (Fig. E10.53) with its center of mass a horizontal distance of 4.00 cm from the pivot. The gyroscope is precessing in a
horizontal plane at the rate of one revolution in 2.20 s. (a) Find the
upward force exerted by the pivot. (b) Find the angular speed with
which the rotor is spinning about its axis, expressed in rev>min.
(c) Copy the diagram and draw vectors to show the angular
momentum of the rotor and the torque acting on it.
Figure E10.53
Rotor
4.00 cm
10.54 . A Gyroscope on the Moon. A certain gyroscope precesses at a rate of 0.50 rad>s when used on earth. If it were taken
to a lunar base, where the acceleration due to gravity is 0.165g,
what would be its precession rate?
10.55 . A gyroscope is precessing about a vertical axis. Describe
what happens to the precession angular speed if the following
changes in the variables are made, with all other variables remaining
the same: (a) the angular speed of the spinning ywheel is doubled;
(b) the total weight is doubled; (c) the moment of inertia about the
axis of the spinning ywheel is doubled; (d) the distance from the
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersDa EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- PHY11 Problem SetDocumento24 paginePHY11 Problem SetAlyssa AtienzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oscillation and Rotation Review QuestionsDocumento2 pagineOscillation and Rotation Review QuestionsJasdeep singh0% (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Da EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculations for Science Fiction Writers/Circular OrbitsDa EverandCalculations for Science Fiction Writers/Circular OrbitsNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Spinning Stuff Answers Part 1Documento7 pagineCourse Spinning Stuff Answers Part 1Sandeep BadigantiNessuna valutazione finora
- PH600 CH 9 Problems PDFDocumento3 paginePH600 CH 9 Problems PDFMike GaoNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 AngularMomentumDocumento31 pagine11 AngularMomentumaliswheeler12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics PaperDocumento17 paginePhysics PaperharshanauocNessuna valutazione finora
- Phys Exam 3 ReviewDocumento4 paginePhys Exam 3 Reviewsydneyrawls7Nessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Vibratory MotionDocumento2 pagine11 Vibratory MotionJerico LlovidoNessuna valutazione finora
- HW (Rotary Motion)Documento4 pagineHW (Rotary Motion)naikin_1031Nessuna valutazione finora
- PH600 CH 10 Problems PDFDocumento5 paginePH600 CH 10 Problems PDFMike GaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6 ExercisesDocumento4 pagineUnit 6 Exercises张书Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH-7 Rotational Motion Worksheet-1Documento2 pagineCH-7 Rotational Motion Worksheet-1negishreshth1985Nessuna valutazione finora
- QuestionsDocumento25 pagineQuestionsSkye JabaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10Documento11 pagineChapter 10kiaunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Question MoreDocumento12 pagineRevision Question MoreFiedDinieNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz - Board Work DynamicsDocumento1 paginaQuiz - Board Work DynamicsNathanielle AlvaradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz - Board Work DynamicsDocumento1 paginaQuiz - Board Work DynamicsNathanielle AlvaradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam Review ProblemsDocumento8 pagineFinal Exam Review ProblemsIrina StefaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotation Review Questions AnswersDocumento2 pagineRotation Review Questions AnswersPffflyers KurnawanNessuna valutazione finora
- I.E - Circular Motion and RotationDocumento91 pagineI.E - Circular Motion and RotationAnonymous xspOY8ycnNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamics Extra Study Questions: Short AnswerDocumento109 pagineDynamics Extra Study Questions: Short Answeramitdeo99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Phy ProblemsDocumento6 paginePhy Problemsheropaldo447Nessuna valutazione finora
- AnswersDocumento15 pagineAnswersjrence33% (3)
- Quiz 2Documento4 pagineQuiz 2Bhong T. LucenecioNessuna valutazione finora
- Rec ch10Documento5 pagineRec ch10tivakholisNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics ReviewerDocumento4 pagineMechanics Reviewerrmgc1003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Motion Questions?Documento29 pagineCircular Motion Questions?Muhammad RafayNessuna valutazione finora
- Phys10 Chap10 DynamicsOfRotationalMotionDocumento6 paginePhys10 Chap10 DynamicsOfRotationalMotionEngelbert Bicoy AntodNessuna valutazione finora
- CH-7 Rotational Motion Worksheet-3Documento2 pagineCH-7 Rotational Motion Worksheet-3negishreshth1985Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Exercise For Grade 11Documento2 paginePhysics Exercise For Grade 11Daniel GtsadkanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 6Documento6 pagineAssignment 6CapsanneNessuna valutazione finora
- General Physics I - Finals Practice TestDocumento2 pagineGeneral Physics I - Finals Practice TestGD GriclosNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotation Motion - ExDocumento45 pagineRotation Motion - ExAratrik MondalNessuna valutazione finora
- SHM WSDocumento3 pagineSHM WSTrishnee MunusamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Motion and Energy Review QuestionsDocumento6 pagineCircular Motion and Energy Review QuestionsUnzal FatehullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Sheet On Circular Motion: Physics For Preparatory Year Students Fall 2021 - 2022Documento2 pagineTutorial Sheet On Circular Motion: Physics For Preparatory Year Students Fall 2021 - 2022MousTafa NaGuibNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment On Rigid Body DynamicsDocumento9 pagineAssignment On Rigid Body DynamicsKaveesh KulkarniNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Test2 ps150Documento3 paginePractice Test2 ps150Antoine S. NdiayeNessuna valutazione finora
- 10308634Documento10 pagine10308634dsfsdfsdfNessuna valutazione finora
- Centripetal Acceleration WorksheetDocumento4 pagineCentripetal Acceleration WorksheetKevin KroytNessuna valutazione finora
- Examples Chapter10Documento28 pagineExamples Chapter10Mario GlezNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 ExercisesDocumento4 pagineUnit 4 Exercises张书Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics RequirementDocumento14 paginePhysics RequirementVinky SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular MotionDocumento15 pagineCircular Motionpraveen alwisNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 6 Problem SolvingDocumento24 pagineTutorial 6 Problem Solvingzieko AminNessuna valutazione finora
- UP HW CH 10 SDocumento6 pagineUP HW CH 10 SLester MarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 Rotation of Rigid BodiesDocumento3 pagine06 Rotation of Rigid BodiesJerico LlovidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment # 2Documento3 pagineAssignment # 2Spyro5557Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics 1Documento4 pagineMechanics 1Carl VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Mechanics of Rigid BodiesDocumento8 pagineChapter 3 - Mechanics of Rigid BodiesPhúc Lộc NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellen0% (1)
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- LHC Project Report 374Documento9 pagineLHC Project Report 374Binay Prasanna JenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetic Waves: JEE-PhysicsDocumento10 pagineElectromagnetic Waves: JEE-PhysicsManas kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Experiment 1 VectorDocumento6 paginePhysics Experiment 1 Vectorbookdotcom7221Nessuna valutazione finora
- AStudyontheOverheatingofthePowerCableTray IeeeDocumento7 pagineAStudyontheOverheatingofthePowerCableTray IeeebitshitassNessuna valutazione finora
- OATBooster Formula Sheet (July 2022) PDocumento11 pagineOATBooster Formula Sheet (July 2022) PzainabNessuna valutazione finora
- IEE STD C95-3-2002Documento133 pagineIEE STD C95-3-2002Ejder Yildiz100% (1)
- Literature Review + ANSYS ReportDocumento13 pagineLiterature Review + ANSYS ReportTahseen JuttNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report of ExperimentDocumento20 pagineLab Report of ExperimentFitri YusofNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol Prism 1Documento2 pagineVol Prism 1Moneyball7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet On Atomic Structure, STD 8thDocumento3 pagineWorksheet On Atomic Structure, STD 8thArshad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Magick Reconfiguring The Field, A Powerful Companion To Mind Magic Methods (The Mind Magic System Book 2) (Merlin Starlight) (Z-Library)Documento225 pagineQuantum Magick Reconfiguring The Field, A Powerful Companion To Mind Magic Methods (The Mind Magic System Book 2) (Merlin Starlight) (Z-Library)Raynald Sumampouw100% (1)
- Lame ConstantsDocumento2 pagineLame ConstantsAldi NurseptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Som QB PDFDocumento32 pagineSom QB PDFvasanthmech092664Nessuna valutazione finora
- Day 3Documento5 pagineDay 3John Cyril0% (1)
- Extra Problem Phys 4 CH 1Documento48 pagineExtra Problem Phys 4 CH 1Kha MaNessuna valutazione finora
- Https App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 550sap 2Documento9 pagineHttps App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 550sap 2sumany7052Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formula Sheet Class 12Documento5 pagineFormula Sheet Class 12shikhary167100% (1)
- Science 2004Documento5 pagineScience 2004yilongwei.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Discovery of New ElementsDocumento5 pagineDiscovery of New ElementsTyler DickinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Physics-Formula SheetDocumento2 pagineIGCSE Physics-Formula SheetPraveen PeterNessuna valutazione finora
- Still Water BM and SFDocumento5 pagineStill Water BM and SFpothirajkalyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Arschs KK PDFDocumento312 pagineArschs KK PDFilgarNessuna valutazione finora
- Three Phase Transformer TrainerDocumento20 pagineThree Phase Transformer TrainerHaroon AsadNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Chemistry: Electronic Structure MethodsDocumento8 pagineQuantum Chemistry: Electronic Structure MethodsNikhil Sharma RayaproluNessuna valutazione finora
- The Evolution of Lifter TechnologyDocumento8 pagineThe Evolution of Lifter TechnologyCristian ViolaNessuna valutazione finora
- FSI Manuscript Rev05Documento9 pagineFSI Manuscript Rev05ADITYA SINGH PATELNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Unit 2 Fluid Kinematics & DynamicsDocumento20 pagineFluid Mechanics and Machinery Unit 2 Fluid Kinematics & DynamicsPalaniVelRajanNessuna valutazione finora
- P 62Documento25 pagineP 62JohnnardBelenNessuna valutazione finora
- PosDocumento3 paginePosAndre De VillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Meherwan P Boyce - Gas Turbine Engineering Handbook-Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann (2012) 27Documento5 pagineMeherwan P Boyce - Gas Turbine Engineering Handbook-Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann (2012) 27amir moniriNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDa EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDa EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2193)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDa EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDa EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (69)
- When the Earth Had Two Moons: Cannibal Planets, Icy Giants, Dirty Comets, Dreadful Orbits, and the Origins of the Night SkyDa EverandWhen the Earth Had Two Moons: Cannibal Planets, Icy Giants, Dirty Comets, Dreadful Orbits, and the Origins of the Night SkyValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (7)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldDa EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (64)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDa EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (51)
- When the Heavens Went on Sale: The Misfits and Geniuses Racing to Put Space Within ReachDa EverandWhen the Heavens Went on Sale: The Misfits and Geniuses Racing to Put Space Within ReachValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (27)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyDa EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNessuna valutazione finora
- Under Alien Skies: A Sightseer's Guide to the UniverseDa EverandUnder Alien Skies: A Sightseer's Guide to the UniverseValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (16)
- Cosmos and Psyche: Intimations of a New World ViewDa EverandCosmos and Psyche: Intimations of a New World ViewValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (7)
- The Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityDa EverandThe Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityNessuna valutazione finora
- The Creator and the Cosmos: How the Latest Scientific Discoveries Reveal GodDa EverandThe Creator and the Cosmos: How the Latest Scientific Discoveries Reveal GodValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDa EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1395)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismDa EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (500)
- Believing Is Seeing: A Physicist Explains How Science Shattered His Atheism and Revealed the Necessity of FaithDa EverandBelieving Is Seeing: A Physicist Explains How Science Shattered His Atheism and Revealed the Necessity of FaithValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (32)
- Fire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterDa EverandFire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterNessuna valutazione finora
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDa EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (410)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectDa EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (20)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsDa EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (94)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1108)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldDa EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (8)