Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Physics I Problems PDF
Caricato da
bosschellenDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Physics I Problems PDF
Caricato da
bosschellenCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Problems
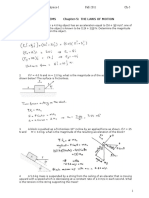
5.88 .. CP Losing Cargo. A 12.0-kg box rests on the at oor
of a truck. The coefcients of friction between the box and oor
are ms = 0.19 and mk = 0.15. The truck stops at a stop sign and
then starts to move with an acceleration of 2.20 m>s2. If the box is
1.80 m from the rear of the truck when the truck starts, how much
time elapses before the box falls off the truck? How far does the
truck travel in this time?
5.89 ... Block A in Fig. Figure P5.89
P5.89 weighs 1.90 N, and
A
block B weighs 4.20 N. The
S
coefcient of kinetic friction
B
F
between all surfaces is 0.30.
Find the magnitude
of the
S
horizontal force F necessary
to drag block B to the left at
constant speed if A and B
are connected by a light,
exible cord passing around a xed, frictionless pulley.
5.90 ... CP You are part of a design team for future exploration
of the planet Mars, where g = 3.7 m>s2. An explorer is to step out
of a survey vehicle traveling horizontally at 33 m>s when it is
1200 m above the surface and then fall freely for 20 s. At that time,
a portable advanced propulsion system (PAPS) is to exert a constant force that will decrease the explorers speed to zero at the
instant she touches the surface. The total mass (explorer, suit,
equipment, and PAPS) is 150 kg. Assume the change in mass of
the PAPS to be negligible. Find the horizontal and vertical components of the force the PAPS must exert, and for what interval of
time the PAPS must exert it. You can ignore air resistance.
5.91 .. Block A in Fig. P5.91 has a mass of 4.00 kg, and block B
has mass 12.0 kg. The coefcient of kinetic friction between block B
and the horizontal surface is 0.25. (a) What is the mass of block C
if block B is moving to the right and speeding up with an acceleration of 2.00 m>s2? (b) What is the tension in each cord when block
B has this acceleration?
Figure P5.91
B
C
A
5.92 .. Two blocks connected by a cord passing over a small,
frictionless pulley rest on frictionless planes (Fig. P5.92). (a) Which
way will the system move when the blocks are released from rest?
(b) What is the acceleration of the blocks? (c) What is the tension
in the cord?
Figure P5.92
100 kg
50 kg
30.0
53.1
171
5.93 .. In terms of m 1, Figure P5.93
m 2, and g, nd the acceleration of each block in
m1
Fig. P5.93. There is no
friction anywhere in the
system.
5.94 ... Block B, with
mass 5.00 kg, rests on
block A, with mass
8.00 kg, which in turn is
m2
on a horizontal tabletop
(Fig. P5.94). There is no
friction between block A and the tabletop, but the coefcient of
static friction between block A and block B is 0.750. A light string
attached to block A passes over a frictionless, massless pulley, and
block C is suspended from the other end of the string. What is the
largest mass that block C can have so that blocks A and B still slide
together when the system is released from rest?
Figure P5.94
B
A
5.95 ... Two objects with masses 5.00 kg and 2.00 kg hang
0.600 m above the oor from the ends of a cord 6.00 m long passing over a frictionless pulley. Both objects start from rest. Find the
maximum height reached by the 2.00-kg object.
5.96 .. Friction in an Elevator. You are riding in an elevator
on the way to the 18th oor of your dormitory. The elevator is
accelerating upward with a = 1.90 m>s2. Beside you is the box
containing your new computer; the box and its contents have a
total mass of 28.0 kg. While the elevator is accelerating upward,
you push horizontally on the box to slide it at constant speed
toward the elevator door. If the coefcient of kinetic friction
between the box and the elevator oor is mk = 0.32, what magnitude of force must you apply?
5.97 . A block is placed
Figure P5.97
against the vertical front
S
a
of a cart as shown in
Fig. P5.97. What acceleration must the cart
have so that block A
A
does not fall? The coefcient of static friction
between the block and
the cart is ms. How
would an observer on
the cart describe the Figure P5.98
behavior of the block?
8.00
kg
5.98 ... Two
blocks
with masses 4.00 kg and
4.00
8.00 kg are connected
kg
by a string and slide
down a 30.0 inclined
plane (Fig. P5.98). The
30
coefcient of kinetic
friction between the
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Physics 120 - 2 Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise ProblemsDocumento2 paginePhysics 120 - 2 Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise ProblemsJeford ManisanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 73 PS 2Documento15 paginePhysics 73 PS 2Marco ConopioNessuna valutazione finora
- Speed of SoundDocumento6 pagineSpeed of Soundmpho100% (2)
- Homework 3 PDFDocumento31 pagineHomework 3 PDFnaveena kumariNessuna valutazione finora
- Virtual Lab AnsweredDocumento6 pagineVirtual Lab Answeredrdixit2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment: Unit 1 Lesson 1 Important PointsDocumento3 pagineAssignment: Unit 1 Lesson 1 Important PointsHin Wa Leung100% (1)
- Unit 4 PacketDocumento13 pagineUnit 4 Packetbobno23Nessuna valutazione finora
- As Newtons Laws and Momentum QuestionsDocumento61 pagineAs Newtons Laws and Momentum Questionshasan_shahryar2008Nessuna valutazione finora
- DinmjgDocumento10 pagineDinmjghaker linkisNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Force and Newtons Laws of MotionDocumento23 pagineChapter 4 Force and Newtons Laws of MotionQassem MohaidatNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment: Unit 1 Lesson 2 Important PointsDocumento2 pagineAssignment: Unit 1 Lesson 2 Important PointsHin Wa LeungNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Momentum Practice TestDocumento11 pagineEnergy Momentum Practice TestMohamad SotoudehNessuna valutazione finora
- 5AL Pre-Lab 3 Submission Template - F23Documento6 pagine5AL Pre-Lab 3 Submission Template - F23kendygchenNessuna valutazione finora
- PC1431 Term Test 2014 PDFDocumento8 paginePC1431 Term Test 2014 PDFNg Pei Yao0% (1)
- hw08 Energy ConservationDocumento2 paginehw08 Energy Conservationapi-394084497Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 29 Tutorials Problems - With SolutionsDocumento5 pagineCH 29 Tutorials Problems - With Solutionsshihabsultan100% (1)
- Simple Harmonic Motion Pendulum and Spring-ProblemsDocumento2 pagineSimple Harmonic Motion Pendulum and Spring-ProblemsVedantNessuna valutazione finora
- VibDocumento12 pagineVibChristelle DomingoNessuna valutazione finora
- Last Name: - : University of Waterloo Final Examination Fall 2014Documento13 pagineLast Name: - : University of Waterloo Final Examination Fall 2014YuChenQianNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set #1 ME5655 Adv. Dynamic and VibDocumento2 pagineProblem Set #1 ME5655 Adv. Dynamic and VibMontoya UrquizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Lab ReportDocumento6 paginePhysics Lab ReportADITYANessuna valutazione finora
- WS XI PH Rotational Motion RollingDocumento11 pagineWS XI PH Rotational Motion Rollingkaushik247Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Set 1Documento4 pagineTutorial Set 1Yanto AjaNessuna valutazione finora
- ch19 Physics SolutionsDocumento30 paginech19 Physics Solutionsalkalkindin119284849Nessuna valutazione finora
- Isentropic Flow - Area VariationDocumento11 pagineIsentropic Flow - Area VariationMuhammad UsmanNessuna valutazione finora
- G12 Constrained Motion of Connected ParticlesDocumento14 pagineG12 Constrained Motion of Connected Particlesrahulnag10febNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank HTDocumento12 pagineQuestion Bank HTgreatrijuvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Written Problem SolutionsDocumento4 pagineChapter 7 Written Problem SolutionsdavparanNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Motion PracticalDocumento16 pagineLinear Motion PracticalAlastair TavernerNessuna valutazione finora
- DP Physics Chapter 2 Questions BDocumento5 pagineDP Physics Chapter 2 Questions BEnock KamugishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 15 Electric FieldsDocumento17 pagineChapter 15 Electric FieldsdrewNessuna valutazione finora
- Collision Lab - Conservation of Momentum (Newton's 3rd Law)Documento4 pagineCollision Lab - Conservation of Momentum (Newton's 3rd Law)Bahril Ilmiwan0% (1)
- Part 04 SET (251 - 252)Documento3 paginePart 04 SET (251 - 252)KartikNessuna valutazione finora
- Matter and Energy II WorkbookDocumento44 pagineMatter and Energy II WorkbookMaría Fernanda Morales ReyNessuna valutazione finora
- TB Chapter7 PDFDocumento24 pagineTB Chapter7 PDFAsmaa AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- UP HW CH 5 SDocumento5 pagineUP HW CH 5 SCarlo DomanaisNessuna valutazione finora
- 1402 Exam 1 ReviewDocumento16 pagine1402 Exam 1 ReviewMartin SeungWhan KimNessuna valutazione finora
- TB Chapter22Documento15 pagineTB Chapter22Mohammed AhemdNessuna valutazione finora
- Wolfson Eup3 ch09 Test BankDocumento15 pagineWolfson Eup3 ch09 Test Bank陳禹誌Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 30 TestDocumento27 pagineCH 30 TestEliceth MosqueraNessuna valutazione finora
- Phys 1011 Assignment IIDocumento3 paginePhys 1011 Assignment IIDanielNessuna valutazione finora
- Collision PracticeDocumento11 pagineCollision PracticeYohanes Ratnodiyanto100% (1)
- Phy 101 TutorialDocumento34 paginePhy 101 Tutorialcub.chiemekaNessuna valutazione finora
- Serway Physics II Example Questions Chapter 7Documento1 paginaSerway Physics II Example Questions Chapter 7AizuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set TorqueDocumento2 pagineProblem Set TorqueEndai DesuNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 04Documento135 pagineCH 04RODRIGO JAVIER BRIZUELA PADILLANessuna valutazione finora
- Additional Tutorial 1 Temperature Heat Part 1Documento6 pagineAdditional Tutorial 1 Temperature Heat Part 1TeeWenSengNessuna valutazione finora
- PC1431 MasteringPhysics Assignment 3Documento14 paginePC1431 MasteringPhysics Assignment 3stpmoment0% (2)
- Phys114 Ps 1Documento11 paginePhys114 Ps 1Reine Amabel JarudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Testbank Chapter15Documento11 pagineTestbank Chapter15AnaMendezNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Lab Information: Virtual Lab: Newton's Second LawDocumento8 paginePre-Lab Information: Virtual Lab: Newton's Second LawBrenda GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Single DOF System Excited Vibrations ProblemsDocumento3 pagineSingle DOF System Excited Vibrations ProblemsghulmNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 To 10Documento22 pagineChapter 3 To 10Angelica Ecal Migriño67% (3)
- The Laws of Motion: Multiple ChoiceDocumento42 pagineThe Laws of Motion: Multiple ChoiceCowdrey IlanNessuna valutazione finora
- Statics: SolutionDocumento32 pagineStatics: SolutionNecille Garcia SalinasNessuna valutazione finora
- 23-11 BioMechanics (BM)Documento2 pagine23-11 BioMechanics (BM)Manuel Christhoper Abayon DizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics For Scientists and EngineeringDocumento31 paginePhysics For Scientists and Engineeringjohnb2bNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellen0% (1)
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I ProblemsDocumento1 paginaPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNessuna valutazione finora
- Bharti Airtel Strategy FinalDocumento39 pagineBharti Airtel Strategy FinalniksforloveuNessuna valutazione finora
- Kallatam of Kallatar (In Tamil Script Tscii Format)Documento78 pagineKallatam of Kallatar (In Tamil Script Tscii Format)rprabhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Science of Materis ReportDocumento22 pagineLab Science of Materis ReportKarl ToddNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical & Ionic Equilibrium Question PaperDocumento7 pagineChemical & Ionic Equilibrium Question PapermisostudyNessuna valutazione finora
- Coke Drum Repair Welch Aquilex WSI DCU Calgary 2009Documento37 pagineCoke Drum Repair Welch Aquilex WSI DCU Calgary 2009Oscar DorantesNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Herd Health Management, Sanitation and HygieneDocumento28 pagineAdvanced Herd Health Management, Sanitation and Hygienejane entunaNessuna valutazione finora
- French Cuisine RecipeDocumento6 pagineFrench Cuisine RecipeJimmy AchasNessuna valutazione finora
- Ticket: Fare DetailDocumento1 paginaTicket: Fare DetailSajal NahaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 AMR Dashboard Funding Opportunity Announcement 11.18.2022Documento16 pagine2022 AMR Dashboard Funding Opportunity Announcement 11.18.2022Tuhin DeyNessuna valutazione finora
- LU 5.1 ElectrochemistryDocumento32 pagineLU 5.1 ElectrochemistryNurAkila Mohd YasirNessuna valutazione finora
- Fin Accounting IFRS 2e Ch13Documento62 pagineFin Accounting IFRS 2e Ch13Nguyễn Vinh QuangNessuna valutazione finora
- Dist - Propor.danfoss PVG32Documento136 pagineDist - Propor.danfoss PVG32Michal BujaraNessuna valutazione finora
- PCM Cables: What Is PCM Cable? Why PCM Cables? Application?Documento14 paginePCM Cables: What Is PCM Cable? Why PCM Cables? Application?sidd_mgrNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic Study of Parabolic Cylindrical Shell A Parametric StudyDocumento4 pagineDynamic Study of Parabolic Cylindrical Shell A Parametric StudyEditor IJTSRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Outlook of PonDocumento12 pagineOutlook of Ponty nguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 NSPC Proposed Changes Book PDFDocumento268 pagine2015 NSPC Proposed Changes Book PDFMichelle Pinohermoso JabatNessuna valutazione finora
- Previews 1633186 PreDocumento11 paginePreviews 1633186 PreDavid MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Parrot Mk6100 Userguide Zone1Documento100 pagineParrot Mk6100 Userguide Zone1Maria MartinNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 - TechDocs, Acft Gen, ATAs-05to12,20 - E190 - 202pgDocumento202 pagine01 - TechDocs, Acft Gen, ATAs-05to12,20 - E190 - 202pgေအာင္ ရွင္း သန္ ့Nessuna valutazione finora
- Art Integrated ProjectDocumento14 pagineArt Integrated ProjectSreeti GangulyNessuna valutazione finora
- Abas Drug Study Nicu PDFDocumento4 pagineAbas Drug Study Nicu PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Kortz Center GTA Wiki FandomDocumento1 paginaKortz Center GTA Wiki FandomsamNessuna valutazione finora
- Revenue Memorandum Circular No. 55-2016: For ExampleDocumento2 pagineRevenue Memorandum Circular No. 55-2016: For ExampleFedsNessuna valutazione finora
- JEE Mains Paper 1 (12 Apr 2019 Shift 2) EnglishDocumento131 pagineJEE Mains Paper 1 (12 Apr 2019 Shift 2) EnglishRudraksha KushwahaNessuna valutazione finora
- ManualDocumento50 pagineManualspacejung50% (2)
- Chronic Renal FailureDocumento54 pagineChronic Renal FailureAkia Cayasan BayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kootenay Lake Pennywise April 26, 2016Documento48 pagineKootenay Lake Pennywise April 26, 2016Pennywise PublishingNessuna valutazione finora
- Celula de CargaDocumento2 pagineCelula de CargaDavid PaezNessuna valutazione finora
- 1572 - Anantha Narayanan FFS CalculationDocumento1 pagina1572 - Anantha Narayanan FFS CalculationAnantha NarayananNessuna valutazione finora
- SL Generator Ultrasunete RincoDocumento2 pagineSL Generator Ultrasunete RincoDariaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDa EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (42)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDa EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (137)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlDa EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (58)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceDa EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (51)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDa EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (393)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (8)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDa EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceDa EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (517)
- Lessons for Survival: Mothering Against “the Apocalypse”Da EverandLessons for Survival: Mothering Against “the Apocalypse”Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessDa EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNessuna valutazione finora
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDa EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2193)
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonDa EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (103)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDa EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (51)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessDa Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (33)
- How Emotions Are Made: The Secret Life of the BrainDa EverandHow Emotions Are Made: The Secret Life of the BrainValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (440)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDa EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (69)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesDa EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (397)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyDa EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNessuna valutazione finora