Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
CPTP - Epilepsy
Caricato da
AinahMahaniTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CPTP - Epilepsy
Caricato da
AinahMahaniCopyright:
Formati disponibili
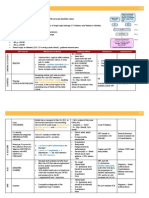
EPILEPSY
MODE OF ACTION
INDICATION
1.
CARBAMAZEPINE
Prolongation of Na+
channel inactivation
PHENYTOIN
Prolongation of Na+
channel inactivation
SODIUM
VALPROATE
Block voltage-gated
inward positive
+
currentsNa or
++
Ca
Highly Pleiotrophic
2.
3.
4.
5.
Simple/Complex Partial
seizures
Tonic-clonic seizures
Trigeminal Neuralgia
MDP
Diabetic Neuropathy
Tonic/clonic & Partial seizures,
Status epilepticus, Trigeminal
Neuralgia(rare)
1.
2.
3.
First line myoclonus
All forms of Epilepsy
Tonic / Clonic, myoclonic,
Atonic, Absence seizures
Acute mania
1.
Lamotrigine
DIAZEPAM
LORAZEPAM
Prolongation of Na+
channel inactivation
Bind to GABA
inhibitory receptors
to reduce firing rate.
Primary / secondary
generalized Tonic-Clonic
2. Prevention of relapse in
BPD
3. Trigeminal Neuralgia
Given PR in initial status
epilepticus
Initial management in status
epilepticus. Given IV
CI/INTERACTION
Auto-inducer; i.e
increase their
own metabolism.
Interact w/
warfarin lamotrigine
Fetal hydantoin
syndrome
Auto-inducer
Causes liver
toxicity
Neural tube
defects
inhibits CYP450
enzymes
ADVERSE EFFECTS
Leucopenia
Diplopia, Blurring of vision
SIADH
Drowsiness
Ataxia
Generalized rash
Risk of Steven Johnson syndrome(HLA-B 1502 PM)
Ataxia and Nystagmus
Cognitive impairment
Hirsutism
Gingival hyperplasia
Coarsening of facial features
Dose-dependent zero order kinetics.
Apetite / Weight gain
Liver failure
Pancreatitis
Reversible hair loss
Oedema
Ataxia
Tremor / Thrombocytopenia
Encephalopathy
Steven Johnson syndrome - rash
Diplopia, Blurring of vision
Photosensitivity
Agitation
Tremor
Simple partial (focal) seizures
First line treatment for focal seizures:
o Carbamazepine or lamotrigine
First-line treatment if above contra-indicated:
o Levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine or sodium valproate
Second-line treatment
o Alternative from above
Adjunctive treatment (1)
o As above, also clobazam, topiramate, gabapentin
Adjunctive treatment (2)
o Eslicarbazepine, lacosamide, phenytoin, phenobarbital, pregabalin, tiagabine, zonisamide, vigabatrin
Generalised epileptic seizure
ABCDE
Oxygen
Safe environment
Keep patient supported during seizure protecting from injury. As soon as movements cease put into recovery
position and ensure she is watched until she has recovered consciousness
Counselling for people with epilepsy
Nature and causes of epilepsy
Pregnancy and teratogenicity
Precipitating factors
Interactions of AEDs esp with OCP
Need for regular medication
Adverse effects of medication
Employment/education
Driving
Free prescriptions
Dangerous situations
Psychological issues
(NB also emergency contraception)
Status epilepticus
More than 30 minutes of continuous seizure activity
Two or more sequential seizures spanning this period without full recovery between seizures
Medical emergency
Management
>5mins medical intervention advised
IV lorazepam, PR diazepam, Buccal midazolam
20 mins : Alert anaesthetist
30mins : Emergency investigations
ABG, glucose, U+E, LFTs, Ca, Mg, FBC, clotting screen, Anticonvulsant blood level
Blood + urine sample for future analysis (tox screen)
Glucose +- IV thiamine
60/90mins : ICU
Continuous ECG monitoring +- intracranial pressure monitoring if appropriate
Myoclonus
First-line treatment:
Sodium valproate
Consider levetiracetam or topiramate if sodium valproate unsuitable or not tolerated
Adjunctive treatment:
Sodium valproate, levetiracetam or topiramate
Clobazam, clonazepam, piracetam or zonisamide (after discussion with tertiary centre)
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome
Clinical features
1. Delirium tremens
a. hyperadrenergic state, disorientation, tremors, diaphoresis, impaired attention/consciousness
2. Hallucinations (auditory, visual, or olfactory)
3. Seizures
a. Generalised tonic-clonic seizures
Symptoms occur after 8 hours, peaking on day 2, recovering by day 5.
Treatment
ABC assessment
Treat any hypoglycaemia
Sedation with benzodiazepines
Barbiturates/ITU may also be necessary in those refractory to benzodiazepine
Screening for Wernicke's encephalopathy or Korsakoff , and treatment 2x 500 mg thiamine should be given IV three times daily for three days. Continued OD for 5 more days if
the patient is responsive to the treatment
Benzodiazepines
Fixed-dose regimens
e.g chlordiazepoxide (long acting)
20mg qds on day 1, then reduced by 10 mg a day
Symptom triggered regimen
50 mg chloridiazepoxide as required based on a symptom score scale e.g CIWA score
Note risks of respiratory depression and can precipitate hepatic encephalopathy in patients with ALD
EPILEPSY
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- CSIM2.26 - Pituitary FunctionDocumento3 pagineCSIM2.26 - Pituitary FunctionAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Csim2.26 - Pituitary F (X) Unusual DiabetesDocumento2 pagineCsim2.26 - Pituitary F (X) Unusual DiabetesAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Csim2.25 - Electrolyte Imbalance Iron Metabolism & StorageDocumento1 paginaCsim2.25 - Electrolyte Imbalance Iron Metabolism & StorageAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Csim2.25 - Iron Metabolism & StorageDocumento4 pagineCsim2.25 - Iron Metabolism & StorageAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Csim2.26 - Pituitary F (X)Documento1 paginaCsim2.26 - Pituitary F (X)AinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary IncontinenceDocumento1 paginaUrinary IncontinenceAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Csim2.25 - Electrolyte ImbalanceDocumento4 pagineCsim2.25 - Electrolyte ImbalanceAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Csim2.25 - Electrolyte Imbalance Calcium and BoneDocumento7 pagineCsim2.25 - Electrolyte Imbalance Calcium and BoneAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Csim2.94 - Interstitial Lung DiseaseDocumento3 pagineCsim2.94 - Interstitial Lung DiseaseAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CSIM2.91 - COPD and Pulmonary HypertensionDocumento2 pagineCSIM2.91 - COPD and Pulmonary HypertensionAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CSIM2.24 - Signal TransductionDocumento6 pagineCSIM2.24 - Signal TransductionAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Csim2.92 - HypoventilationDocumento1 paginaCsim2.92 - HypoventilationAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Csim2.71 - The Patient With Proteinuria and HaematuriaDocumento11 pagineCsim2.71 - The Patient With Proteinuria and HaematuriaAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Penilaian Bahan TamhidiDocumento3 paginePenilaian Bahan TamhidiAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CPTP - PainDocumento3 pagineCPTP - PainAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CSIM2.90 - Occupational AsthmaDocumento1 paginaCSIM2.90 - Occupational AsthmaAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CPTP - Pud + Altered Bowel HabitDocumento3 pagineCPTP - Pud + Altered Bowel HabitAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CPTP - Pregnancy & LactatingDocumento1 paginaCPTP - Pregnancy & LactatingAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CPTP - HPT & HFDocumento4 pagineCPTP - HPT & HFAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Penilaian Bahan MUAYYIDDocumento3 paginePenilaian Bahan MUAYYIDAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CPTP - Poisonig MH Misuse of DrugsDocumento5 pagineCPTP - Poisonig MH Misuse of DrugsAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CPTP - Infection and Antibiotics 2Documento3 pagineCPTP - Infection and Antibiotics 2AinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CPTP - Parkinson & MVMT DisordersDocumento2 pagineCPTP - Parkinson & MVMT DisordersAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Infection and AntibioticsDocumento4 pagineInfection and AntibioticsAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CPTP - Af & Anti CoagulationDocumento4 pagineCPTP - Af & Anti CoagulationAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Themed Week 7 - LIVERDocumento24 pagineThemed Week 7 - LIVERAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CPTP - Asthma & CopdDocumento5 pagineCPTP - Asthma & CopdAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CPTP - Diabetes and Lipid Lowering DrugsDocumento4 pagineCPTP - Diabetes and Lipid Lowering DrugsAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Infection and AntibioticsDocumento4 pagineInfection and AntibioticsAinahMahaniNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Pamaran Vs MejiaDocumento7 paginePamaran Vs MejiaRuab PlosNessuna valutazione finora
- Mid Term Assignment On PartnershipDocumento37 pagineMid Term Assignment On PartnershipManjare Hassin RaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Trust, Partnership & Agency: Aejay V. BariasDocumento22 pagineTrust, Partnership & Agency: Aejay V. BariasAejay Villaruz BariasNessuna valutazione finora
- FM17-37 Air Cavalry Squadron 1969Documento163 pagineFM17-37 Air Cavalry Squadron 1969dieudecafeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ravi - Flight Ticket - HYD - PNQ - 19 FebDocumento2 pagineRavi - Flight Ticket - HYD - PNQ - 19 FebMahesh NerkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sabello Vs DECSDocumento5 pagineSabello Vs DECSFelora MangawangNessuna valutazione finora
- Doctrine of Legitimate Expectation: The Emerging Trends in Indian JudiciaryDocumento8 pagineDoctrine of Legitimate Expectation: The Emerging Trends in Indian JudiciarySpackRoxNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentación Departamento de ValleDocumento13 paginePresentación Departamento de ValleMelissa MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- FM NumbersDocumento14 pagineFM Numberstashmore1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Skin-to-Skin Contact CaseDocumento1 paginaSkin-to-Skin Contact Caseadvyamini bishtNessuna valutazione finora
- Associated Gun Clubs of Baltimore Candidate 2010 Election RecommendationsDocumento1 paginaAssociated Gun Clubs of Baltimore Candidate 2010 Election RecommendationsAmmoLand Shooting Sports NewsNessuna valutazione finora
- DTM RULES Final Version 1Documento8 pagineDTM RULES Final Version 1MaxCarMXNessuna valutazione finora
- Hacking Web ServersDocumento4 pagineHacking Web ServersDeandryn RussellNessuna valutazione finora
- Mint 10.04.2024?Documento18 pagineMint 10.04.2024?yashh1708Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar Bank Answers Pre Intermediate PDFDocumento9 pagineGrammar Bank Answers Pre Intermediate PDFb100% (2)
- Anoja WeerasingheDocumento10 pagineAnoja WeerasinghePrasanna RameswaranNessuna valutazione finora
- T01C03 People V Prieto 80 Phil 138Documento3 pagineT01C03 People V Prieto 80 Phil 138CJ MillenaNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Universe Animated Original MoviesDocumento24 pagineDC Universe Animated Original MoviesHarry TsionasNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Law Assignment 1Documento13 pagineFamily Law Assignment 1Rishab ChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Rising Action: Write The Second Part of The Plot To Your Short StoryDocumento1 paginaRising Action: Write The Second Part of The Plot To Your Short StoryDr MundoNessuna valutazione finora
- List of MoviesDocumento7 pagineList of Moviesmanoj batraNessuna valutazione finora
- Thus at Least Presuppose, and Should Perhaps Make Explicit, A Normative AccountDocumento5 pagineThus at Least Presuppose, and Should Perhaps Make Explicit, A Normative AccountPio Guieb AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Wayne's World / Austin Powers CrossoverDocumento7 pagineWayne's World / Austin Powers CrossoverTom Ryan RyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Danh Động Từ Và Bài Tập: Choose the best answer for each of the following sentencesDocumento3 pagineDanh Động Từ Và Bài Tập: Choose the best answer for each of the following sentencesBonbon NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- People Vs AlboferaDocumento2 paginePeople Vs Alboferaraffy tanNessuna valutazione finora
- BODYCOMBAT 65 Choreography Booklet - Print ReadyDocumento12 pagineBODYCOMBAT 65 Choreography Booklet - Print ReadyKazNessuna valutazione finora
- Ppt-Hukum Ham - AsminDocumento55 paginePpt-Hukum Ham - AsminKusuma WijajaNessuna valutazione finora
- WordbuilderDocumento9 pagineWordbuilderPHAT PHAM KIMNessuna valutazione finora
- Brief of CasesDocumento3 pagineBrief of CasesDeepanshita SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5: Sec.3 - Bar of LimitationDocumento23 pagineUnit 5: Sec.3 - Bar of Limitationindrajit royNessuna valutazione finora