Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Demographics
Caricato da
cbellsnlCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Demographics
Caricato da
cbellsnlCopyright:
Formati disponibili
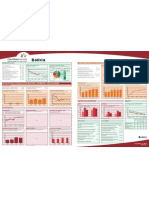
Indonesia
DEMOGRAPHICS MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH
Total population (000) 228,864 (2006) Under-five mortality rate Causes of under-five deaths Causes of maternal deaths Coverage along the continuum of care
Deaths per 1000 live births Globally more than one third of child deaths are attributable to Regional estimates for Asia, 1997-2002
Total under-five population (000) 21,720 (2006) undernutrition
Unmet need for family planning (%) 9 (2002-2003) Abortion
Births (000) 4,427 (2006) Measles Injuries Malaria Causes of neonatal
Contraceptive
3% 1% deaths Obstructed labor 6% 57
100 91 5% Diarrhoea 1% Antenatal visits for woman (4 or more visits, %) 81 (2002-2003) prevalence rate Pre-pregnancy
Birth registration (%) 55 (2006) Pneumonia HIV/AIDS Tetanus 1% 9%
Congenital 6% Antenatal visit
Under-five mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 34 (2006) 80 14% 0% (1 or more) 92 Pregnancy
Other 8% Intermittent preventive treatment for malaria (%) --- Hypertensive Haemorrhage
Sepsis/ Skilled attendant
Infant mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 26 (2006) disorders 31% 72 Birth
60 Pneumonia 20% C-section rate (total, urban, rural; %) 9%
at birth
Neonatal mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 18 (2000) Neonatal (Minimum target is 5% and maximum target is 15%) 4,7,2 (2002-2003)
34 *Postnatal care Neonatal period
Total under-five deaths (000) 151 (2006) 40 30 38% Asphyxia 28%
Sepsis/Infections,
Early initiation of breastfeeding (within 1 hr of birth, %) 39 (2002-2003) including AIDS
Exclusive
40 Infancy
Maternal mortality ratio (per 100,000 live births) 420 (2005) 20 Diarrhoea breastfeeding
MDG Target 12%
97 (2005)
18% Postnatal visit for baby (within 2 days for home births, %) --- Other causes Measles
Lifetime risk of maternal death (1 in N) Preterm 36% Anaemia 72
0 Other
13% 21%
Total maternal deaths 19,000 (2005) 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 22%
Source: Lawn JE, Cousens SN for
0 20 40 60 80 100
Source: UNICEF, 2006 Source: WHO, 2006 CHERG (Nov 2006) Source: Khan, Khalid S., et al, Lancet 2006:367:1066-74 Source: DHS, MICS, Other NS
*See Annex for indicator definition
Antenatal care Skilled attendant at delivery Neonatal tetanus protection
INTERVENTION COVERAGE FOR MOTHERS, NEWBORNS AND CHILDREN Percent women aged 15-49 years attended at least once by a Percent live births attended by skilled health personnel Percent of newborns protected against tetanus
NUTRITION skilled health provider during pregnancy
Stunting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) --- Complementary feeding rate (6-9 months, %) 75 (2002-2003) 100 92 100 100
89 83
82
Wasting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) --- Low birthweight incidence (%) 9 (2002-2003) 80 76 80 80
67 64 68 66 72
Underweight prevalence Exclusive breastfeeding Vitamin A supplementation 60 60 50
56 56 60
Percent
Percent
Percent
Percent children < 5 years underweight for age* Percent infants < 6 months exclusively breastfed Percent children 6-59 months receiving vitamin A doses 41 43
40 40 36 37 40
32
At least one dose Two doses
100 100 100 20 20 20
82
76
80 80 80 71 73 0 0
64 61 62 1987 1999 1991 1994 1995 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 02-03 2004
1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2006
76 1991 1994 1997 2002-2003 Other NS Other NS DHS DHS Other NS DHS Other NS Other NS Other NS Other NS Other NS DHS DHS
60 60 60 73
68 63
DHS DHS DHS DHS
Percent
Percent
Percent
Source: WHO/UNICEF
45 62
42 40 57
40 40 37 40
27
23
20 20 20 WATER AND SANITATION EQUITY
0
0 0 0
1995 2003 1991 1994 1997 2002-2003 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Water Sanitation Coverage gap by wealth quintile
Other NS Other NS DHS DHS DHS DHS
Source: UNICEF
Percent population using improved drinking water sources Percent population using improved sanitation facilities
*Based on 2006 WHO reference population Rural Urban Total Rural Urban Total
100 92 100 100
CHILD HEALTH 87
77
80 72 80 73 80
69 65
63
Immunization Malaria prevention Prevention of mother to child 60 60 55 60
Percent
Percent
Percent
Percent of children immunised against measles 46
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses DPT
Percent children < 5 years sleeping under ITNs* transmission of HIV 37 40
Percent HIV+ pregnant women receiving ARVs for PMTCT
40 40 40
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses Hib
20 20 20
100 100 10
0 0 0
80 72 80 8 1990 2004 1990 2004 Poorest 2nd 3rd 4th Wealthiest
Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006 Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006
60 70 60 6 1997 2003
Percent
Percent
Percent
DHS DHS
40 40 4 POLICIES SYSTEMS
2
20 20 2
0.8 Coverage gap (%) 30 27
0.1 0.2 International Code of Marketing of Breastmilk Financial Flows and Human Resources
0 0 0 Substitutes Partial Ratio
1990 1995 2000 2005 2006 2000 2004 2005 2006 Per capita total expenditure on health (US$) 118 (2007) poorest/wealthiest 2.7 2.4
Source: WHO/UNICEF MICS Other NS Other NS Other NS
New ORS formula and zinc for management of Difference
*Sub-national risk of malaria transmission General government expenditure on health as
diarrhoea Yes poorest-wealthiest (%) 27 22
% of total government expenditure (%) 5 (2007)
Diarrhoeal disease treatment Malaria treatment Pneumonia treatment
Percent children < 5 years with diarrhoea receiving oral rehydration Percent febrile children < 5 years using antimalarials* Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia taken to Community treatment of pneumonia with antibiotics No Out-of-pocket expenditure as % of total
therapy or increased fluids, with continued feeding appropriate health provider
Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia receiving expenditure on health (%) 49 (2007)
IMCI adapted to cover newborns 0-1 week of age Yes
antibiotics
Density of health workers (per 1000 population) 1.0 (2003)
100 100 100 Costed implementation plan(s) for maternal,
newborn and child health available No Official Development Assistance to child health
80 80 80 per child (US$) 1 (2005)
64 69 Midwives be authorised to administer a core set of
Indonesia
61 63 61
60 56 60 60 life saving interventions Partial Official Development Assistance to maternal and
Percent
Percent
Percent
neonatal health per live birth (US$) 3 (2005)
40 37 37 40 40 Maternity protection in accordance with ILO
Convention 183 No National availability of Emergency Obstetric Care
20 20 20 services (% of recommended minimum) ---
4 1 Specific notification of maternal deaths No
0 0 0
1994
DHS
1997
DHS
2000
MICS
2002-2003
DHS
2000
MICS
2002-2003
DHS
1991
DHS
1994
DHS
1997
DHS
2002-2003
DHS
Countdown to 2015
*Sub-national risk of malaria transmission 2008 Report
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- An Go LaDocumento1 paginaAn Go LacbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Guinea BissauDocumento1 paginaGuinea BissaucbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Ye MenDocumento1 paginaYe MencbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Ben inDocumento1 paginaBen incbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Burkina FasoDocumento1 paginaBurkina FasocbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Liberia: Country ProfileDocumento4 pagineLiberia: Country Profilegeorgeloto12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Country Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child SurvivalDocumento4 pagineCountry Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child Survivalpaperpin27Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal CZEDocumento4 pagineMaternal CZEYajie LuoNessuna valutazione finora
- On Epidemological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthDocumento30 pagineOn Epidemological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthBisma Maqbool67% (3)
- Nutrition IDN PDFDocumento2 pagineNutrition IDN PDFdini mutia KhairunnisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Materi Sesi 1 - Pembicara 1 - Dr. Asri C. Adisasmita, MPH, PH.D (Seminar Kesehatan Nasional Universitas Indonesia Tahun 2017 FKM)Documento33 pagineMateri Sesi 1 - Pembicara 1 - Dr. Asri C. Adisasmita, MPH, PH.D (Seminar Kesehatan Nasional Universitas Indonesia Tahun 2017 FKM)Niluh Putu DikaNessuna valutazione finora
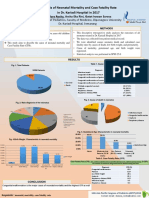
- CAH Causes Death U5 Neonates 2008Documento1 paginaCAH Causes Death U5 Neonates 2008raissa leeNessuna valutazione finora
- Poster CFRDocumento1 paginaPoster CFRIka Rara RositaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Open Ophthalmology JournalDocumento5 pagineThe Open Ophthalmology JournalFenny Duma SariNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition PHL PDFDocumento2 pagineNutrition PHL PDFJaiy HingcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Child Health Programme: 4.2.2 Causes of Child Mortality in IndiaDocumento24 pagineChild Health Programme: 4.2.2 Causes of Child Mortality in IndiaSolomon JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Newborn Care: From Evidence To Practice: Maria Asuncion Silvestre, MD, FPSNBM, FaapDocumento84 pagineEssential Newborn Care: From Evidence To Practice: Maria Asuncion Silvestre, MD, FPSNBM, FaapShane Lim GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- G Minaccia Parto PretDocumento64 pagineG Minaccia Parto PretEleonora Francesco Consalvo DonzelliNessuna valutazione finora
- KMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016Documento63 pagineKMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016mimimomopipiNessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal Health: Family Revolves Around MotherDocumento16 pagineMaternal Health: Family Revolves Around MotherFatima IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Reporting On Reproductive Health in Africa (Ayorinde Ajayi)Documento35 pagineReporting On Reproductive Health in Africa (Ayorinde Ajayi)National Press FoundationNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition LCADocumento2 pagineNutrition LCAShernia EliboxNessuna valutazione finora
- 1malnutrition As Health ProblemDocumento37 pagine1malnutrition As Health ProblemIntan Sahara BachsinNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 The High Risk MotherDocumento161 pagine1 The High Risk MotherRaquel M. MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- MOR Health System Profiles 2018Documento2 pagineMOR Health System Profiles 2018Chaymae SahraouiNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Newborn CareDocumento54 pagineEssential Newborn CareBrigitte CovarrubiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Globo Can Ecuador 2020Documento2 pagineGlobo Can Ecuador 2020Park Triple S Kim HyungNessuna valutazione finora
- Stakeholder Meeting - Revitalizing IudDocumento52 pagineStakeholder Meeting - Revitalizing Iudkarun009640Nessuna valutazione finora
- Situation Analysis (1) FinalDocumento5 pagineSituation Analysis (1) Finalsitikantha sahooNessuna valutazione finora
- Serbia: 2016 TOTAL POPULATION: 8 820 000 2016 TOTAL DEATHS: 107 000Documento1 paginaSerbia: 2016 TOTAL POPULATION: 8 820 000 2016 TOTAL DEATHS: 107 000Dejan ŽujovićNessuna valutazione finora
- WHO CancerReport 2020 MEXDocumento2 pagineWHO CancerReport 2020 MEXAldo Leonardo De Jesus GarduzaNessuna valutazione finora
- WHO CancerReport 2020 CUBDocumento2 pagineWHO CancerReport 2020 CUBaxelNessuna valutazione finora
- A Practical Approach To Preventing Child Deaths: What The Pediatrician Can DoDocumento44 pagineA Practical Approach To Preventing Child Deaths: What The Pediatrician Can DoSophia Loraine Dorone JesuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Epidemiological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthDocumento30 pagineEpidemiological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthNitin Sharma100% (1)
- 2022 March of Dimes Report Card-ArkansasDocumento2 pagine2022 March of Dimes Report Card-ArkansasCurtisNessuna valutazione finora
- Infertility Among Productive AgeDocumento18 pagineInfertility Among Productive Ageari gunawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer Sudan 2020 Country ProfileDocumento2 pagineCancer Sudan 2020 Country ProfilemohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- High Rate of Uterine Rupture in A Conflict Setting of Hajjah, YemenDocumento3 pagineHigh Rate of Uterine Rupture in A Conflict Setting of Hajjah, YemenShofi Dhia AiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal Mortality in OmanDocumento2 pagineMaternal Mortality in OmanmRta03100% (1)
- Jamaica: Country ProfileDocumento4 pagineJamaica: Country ProfileZineil BlackwoodNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 March of Dimes Report Card For LouisianaDocumento2 pagine2022 March of Dimes Report Card For LouisianaCurtisNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Ye MenDocumento1 paginaYe MencbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Ye MenDocumento1 paginaYe MencbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Tanzania, United Republic ofDocumento1 paginaTanzania, United Republic ofcbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Ben inDocumento1 paginaBen incbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Burkina FasoDocumento1 paginaBurkina FasocbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- The GambiaDocumento1 paginaThe GambiacbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Ben inDocumento1 paginaBen incbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Sierra LeoneDocumento1 paginaSierra LeonecbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Ben inDocumento1 paginaBen incbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Ben inDocumento1 paginaBen incbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Ben inDocumento1 paginaBen incbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- DemographicsDocumento1 paginaDemographicscbellsnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Script 1 EnglishDocumento6 pagineSample Script 1 EnglishKelhei GabrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- The Corona Panic Is A PlayDocumento28 pagineThe Corona Panic Is A PlayABU NASHRAHNessuna valutazione finora
- A Family Physician's Perspective On Vaccine Hesitancy: Margot Savoy, MD, MPH, FaafpDocumento6 pagineA Family Physician's Perspective On Vaccine Hesitancy: Margot Savoy, MD, MPH, FaafpNational Press FoundationNessuna valutazione finora
- SBO#06 - Anti-Rabies OrdinanceDocumento6 pagineSBO#06 - Anti-Rabies OrdinanceLeonardo Miranda BayotasNessuna valutazione finora
- ImmunisationDocumento58 pagineImmunisationBharatBGNessuna valutazione finora
- (E) Hostel Form-DPSB - A4Documento4 pagine(E) Hostel Form-DPSB - A4ghjegjwNessuna valutazione finora
- Krizia Joy Borromeo-Galve, MD: Bulacan Medical Center, Department of PediatricsDocumento84 pagineKrizia Joy Borromeo-Galve, MD: Bulacan Medical Center, Department of PediatricsTara Oliveros Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Bissonette, Andrew H. - Chanmugam, Arjun S. - Desai, Sanjay v. - Putman, Shannon B - Infectious Diseases Emergencies (2017, Oxford University Press)Documento441 pagineBissonette, Andrew H. - Chanmugam, Arjun S. - Desai, Sanjay v. - Putman, Shannon B - Infectious Diseases Emergencies (2017, Oxford University Press)Bagus Wahyu M.100% (1)
- Biology Chapter 5 Form 5Documento15 pagineBiology Chapter 5 Form 5Nadiah BorhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Imunisasi HajiDocumento89 pagineImunisasi HajiFakikha AditamiNessuna valutazione finora
- FINAL Benefits, Rights & Privileges of SC & PWD 2019Documento26 pagineFINAL Benefits, Rights & Privileges of SC & PWD 2019Hazelle BondocNessuna valutazione finora
- Biographical DataDocumento29 pagineBiographical DataJai - HoNessuna valutazione finora
- Soal MCQ 3 Nov 2014Documento17 pagineSoal MCQ 3 Nov 2014Funnie AdeliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Covid CertificateDocumento1 paginaCovid CertificateTamer BadranNessuna valutazione finora
- July 2012 Nle Tips-Chn and CDDocumento7 pagineJuly 2012 Nle Tips-Chn and CDJerome Asuncion67% (3)
- Ef Ficacy, Immunogenicity and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocumento11 pagineEf Ficacy, Immunogenicity and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisCRS1973Nessuna valutazione finora
- MMRDocumento6 pagineMMRleeperlhan2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Winsted Journal 12-25-15 PDFDocumento22 pagineThe Winsted Journal 12-25-15 PDFLakeville JournalNessuna valutazione finora
- Covid-19 Vaccination: Knowledge, Attitude & Challenges Among Medical and Nursing Students-A Web Based SurveyDocumento8 pagineCovid-19 Vaccination: Knowledge, Attitude & Challenges Among Medical and Nursing Students-A Web Based SurveyIJAR JOURNALNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes MellitusDocumento28 paginePathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes MellitusJuan Diego Fernández MurielNessuna valutazione finora
- Diseases of Dairy CowsDocumento15 pagineDiseases of Dairy CowsShahbaz AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Certificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsDocumento1 paginaCertificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsMs DhoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Norovirus Fact SheetDocumento1 paginaNorovirus Fact SheetovwebmasterNessuna valutazione finora
- Jibachha's Textbook of Equine, Rabbit & Pet Animals-By Dr. Jibachha SahDocumento16 pagineJibachha's Textbook of Equine, Rabbit & Pet Animals-By Dr. Jibachha SahJibachha Shah100% (1)
- Clements High School Feb. 4, 2014Documento29 pagineClements High School Feb. 4, 2014clementsrangersNessuna valutazione finora
- General CM CatalogueDocumento56 pagineGeneral CM CatalogueJonathan ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- We Get Results!: Labor Day Weekend!Documento39 pagineWe Get Results!: Labor Day Weekend!The WorldNessuna valutazione finora
- E-PrepTalk Aug 2009Documento73 pagineE-PrepTalk Aug 2009tharkibudhauNessuna valutazione finora
- Listening Jahshan OET CollectionDocumento214 pagineListening Jahshan OET Collectionsplendid_ira68% (19)
- Bordetella Pertussis: Dr. M. NoofeliDocumento50 pagineBordetella Pertussis: Dr. M. NoofeliJlizi MalekNessuna valutazione finora