Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Community Health Nursing Lecture
Caricato da
EzraManzanoTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Community Health Nursing Lecture
Caricato da
EzraManzanoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Community Health
Nursing
Lectured by: Z. Famorca, PhD, RN
DOTS
-
Under the office of the president
Many are from Mindanao
Hospice home care
Parish Community Nursing
Faith community nursing
Treatment partner follows up medication
Public health is supposed to be given for free FALSE
PHN appoints a treatment partner
Financing of health services
Another health worker that is accessible
- Out of pocket
BHW
- Health maintenance organization (Phil Health)
3. Population/aggregatefocused
- Free at the point of care
- The greater good of the majority
GovernmentTaxes are paid
- Community Diagnosis
Test taking technique
Vital Statistics
- When choosing numbers choose the middle
ground
Demography
- Do not choose the extreme numbers
- Magnitude (prevalence) of a problem
CHN: Definition
A criterion for priority setting
1. Developmental Services
4. Promotive and preventive
- Development of health capability of Individual,
- Preventive treatment, e.g. DOTS
Family, Group, Community
- Health Education
Groups with common susceptibility
Same working group
5. Pre-paid service
- Enabling service self- reliance
- Taxation (public and school health)
- Health educationdone for health promotion
- Passed on to consumer (occupational)
Patient EducationDone when person
is sick
Transfer of Technology
6. Generalist Practice
- Community organizing
Labor Code: Health, Safety and Welfare Benefits
2. Community-based
- Book 4: Health, safety and welfare benefits
- Catchment
Number of workers
OH services
- Natural environment of people
10-50
Graduate first aider who may be
one of the workers
Home PHN
50-200
Non-hazardous: full-time first
School SHN
aider
Workplace OHN
Hazardous workplace: OHN
3 fields of CHN Practice
- Case-finding of CHN practice
Direct Sputum Smear Microscopy (TB)
Weighing Scale or tape measure for
mid-upper arm circumference
(Malnourishment)
2 types of community:
- Geo political community
Barangay
City
Province
- Phenomenological
GIDA- Geographically Isolated and Deprived Areas
- Cooperative Development Authority
200-300
>300
OHN, Part-time physician and
dentist (at least 2hrs a day),
emergency clinic (1 bed: 100
workers) or hospital within 5 km
Full time DMD and MD
RA 124mandates all schools to have a school clinic for
the treatment of minor ailments and attendance to
emergency cases (1947)
- School health physician reports to the board of
health (DOH)
Functions of OHN and SHN
1. Health care provider
- Promotive and preventive services
Health advocacy
Health education and counseling
Immunization, prenatal care
Margadi
BSN 2013
Treatment of common ailments and emergency
nursing care
CD control
- Screening for health problems:
School health and nutrition survey
done on the 1st visit by the nurse and
every 3 years thereafter
Random/rapid classroom inspection
Annual individual health inspection
o Interview
o Height and weight
measurement
Head to foot examination for
cleanliness, skin disease and other
obvious abnormalities
Visual acuity test: a child with visual
acuity of 20/40 or poorer to be referred
Ear exam and hearing acuity test:
otoscopy, whisper test, ballpen click
test or with the use of tuning fork
(ototoxicity for Streptomycin)
2. Environmental Manager
- Monitoring environmental conditions
- Recognizing and reporting accident and health
hazards in workplace/school
- Healthful school living
- Application of ergonomic principles (physical
environment)
3. Health coordinator
- Making referrals to other agencies and health
personnel
- Coordination with public health nurse, e.g. for
immunization of school children
- Private sector
Philosophy of public health nursing (Margaret Shetland)
- PHN is based on the worth and dignity of man
Contribute to the integrity of the
Individual, Family and Community
- The family is the basic unit of service in PHN
- Physical and emotional health are inseparable
Consider physical and emotional
aspects of the needs of all the members
of the family
Public Health Nursing (WHO expert committee on
nursing)
- PHN is a special field of nursing that combines
the skills of:
Public health
Nursing
Some phases of social assistance
feeding program
4Ps Pantawid pamilyang Pilipino Program
(CCT- conditional cash transfer)
- Poverty alleviation
MDG1: Eliminate hunger and poverty
th
- 5 Quintile and instrument to identify True
Poor
Benefits:
1. P500/month
2. For every qualified child (max of 4 up to 15yrs)
- P300/month for 10 mos.
Conditions:
1. 85% of class days, students should be present
2. Immunization up to the age of 4
3. Children will be in the garantisadong pambata
program
-
Public Health (C.E.Winslow)
Philosophy of public heatlh
- Health and longevity as birth rights
- Premature death (*untimely death)
Objectives of public health
- To prevent disease
- To prolong life
- To promote health and efficiency
Organized community efforts
- People
Primary Health Care
RHU
PHN functions as part of a total public health
program
Health team
1 municipal health plan
- Objectives of PHN
Promotion of health
Improvement of conditions in the
physical and social environment
Rehabilitation
Prevention of illness and disability
Basic competencies of the Public Health Nurse
- Patient care competencies
Margadi
BSN 2013
CHN process
Nursing procedures during clinic and
home visits
Surveillance
- Health promotion and education
- Communication
- Collaboration: community organizing
- Empowering competencies
Legal responsibility
Ethico-moral responsibilities
Personal and professional development
- Enabling competencies
Management of resources and
environment
Record management
- Enhancing competencies
Research
Quality improvement
Level of Prevention
- Target population:
Beneficiaries (For whom?)
Purpose of the nursing action: aspect of
prevention (for what?)
Primary level
- Target population: well individuals, families,
groups and communities
- Aspects of prevention
General health promotion
Specific disease prevention
o Prevent from a single person
Specific protection
o Groups of people
o ASIN Law- An Act for Salt
Iodization Nationwide
Secondary Level
- Target Population: Early sick + subclinical cases
(asymptomatic)
- Aspects of prevention
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment
Prevention of complications
Tertiary Level
- Target population: Late sick: convalescent,
disabled, complicated case, terminal ill
Natural hx of disease
PrePathogenesis
Pathogenesis
Interaction
Millennium Summit: September 6-8, 2000
1. Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
2. Achieve universal primary education
3. Promote gender equality and empower women
4. Reduce by2/3 the under 5 mortality rate
(1990:80/1000 live births 2015: 26.7/1000)
5. Reduce by the maternal mortality rate (1990:
2.09/1000 live births 2015: 52/1000 live
births)
6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other disease
1993: eradication of
1. Polio
2. Neonatal Tetanus
3. Measles
4. Rabies
7. Ensure environmental sustainability
8. Develop a global partnership for development
World Health Organization (MDG4-6)
The Department of Health
Vision- Mission
Vision
To staunch advocate, model and leader of health for all
in the Philippines
A global leader for attaining better health
outcomes, competitive and responsive health
care system, and equitable health financing.
Mission
To guarantee equitable, sustainable and quality health
for all Filipinos, especially the poor, and to lead the
quest for excellence in health.
Roles and functions of the DOH
1. Leader
a. Planner and policy-maker
b. Regulator of health services
c. Advocate in the adoption of health policies,
plans and programs
Margadi
BSN 2013
2. Enabler and capacity builder
a. Develop new strategies in health
b. Initiate public discussion on health issues
and disseminate info on research outputs
c. Ensure standards of health promotion,
protection and care (training)
3. Administrator of specific services
a. Manage selected national health facilities
b. Administer direct services for emergent
health concerns that require new
complicated technologies
c. Administer health emergency responses
Universal Health Care
(2010-2016)
FOURmula One for
Health (2005-2010)
Health Sector Reform
Agenda (1999-2004)
Goals
Better Health
outcomes
Responsive
health system
Equitable health
financing
Health care delivery system of the Philippines
Primary Level
- Promotion and prevention
- Management of prevalent conditions
- Out-patient services
Secondary
- Hospitalization
Tertiary
- Specialized care
Specially trained personnel
Highly departmentalized
Sophisticated equipment
National hospitals/DOH national office/ medical
centers/ university hospitals/ special hospitals
Center for health development
Provincial hospital (PHO)
Priority Health Policy Directions of the Aquino
Administration
Prove Health Board
Chair: Governor
Vice-chair: IPHO
District hospital (DHO)
RHU/CHC/CHO
Financial Risk
Protection
BHS
Municipal/city Health Board
Chair: Mayor
Vice-chair: Municipal Health Officer
RA 7160devolution code
Achieving
MDGmax
Health
facilities
enhancement
Universal Health Care
Strategies
1
2
Health Financing Service Delivery
6
Health Human
Resource
5
Health
information
3
Policy and
regulation
4
Governance for
Health
Inter Local Health System
- To ensure quality of health care service at the
local level integrate hospital and public
health services holistic health care
- Inter Local Health Zone (ILHZ)
Clustered municipalities (defined
population within a defined area)
Primary level facilities (RHUs and
BHSs)
Central referral hospital
Margadi
BSN 2013
Components of the ILHZ
- Peoplemay vary, according to WHO, between
100, 000 to 500, 000
- Boundariesto determine accountability of
health service providers
- Health facilities- secondary level hospital
(district of provincial), RHUs BHSs and other
health facilities
- Health workersboth government and nongovernment
Two-way referral system
- Communication among facilities
The RHU team
Margadi
BSN 2013
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Community Health NursingDocumento43 pagineCommunity Health Nursingstellie2593% (69)
- Classroom Observation Form 2019Documento5 pagineClassroom Observation Form 2019Luzviminda Britanico100% (2)
- Community Health NursingDocumento7 pagineCommunity Health NursingFreeNursingNotes87% (47)
- Community Health Nursing PDFDocumento25 pagineCommunity Health Nursing PDFCharles J B. Visaya80% (5)
- Pediatric Nursing ReviewDocumento45 paginePediatric Nursing Reviewɹǝʍdןnos98% (87)
- Community Health Nursing Notes SummaryDocumento9 pagineCommunity Health Nursing Notes Summarysorryandreosayanisalreadytaken100% (28)
- Aklan State University Community Health Nursing ModuleDocumento28 pagineAklan State University Community Health Nursing ModulemysterioushumaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health Nursing Philippines PDFDocumento2 pagineCommunity Health Nursing Philippines PDFHeidi13% (8)
- Comparative Education in Developing CountriesDocumento16 pagineComparative Education in Developing CountriesPoppi HSNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 C H N: A O: What Is A Community ?Documento43 pagineUnit 1 C H N: A O: What Is A Community ?Marcus, RN96% (49)
- Community Health Nursing ProcessDocumento69 pagineCommunity Health Nursing ProcessDharylle CariñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Community-Health-Nursing-By-Maglaya-Pdf 3 PDFDocumento2 pagineCommunity-Health-Nursing-By-Maglaya-Pdf 3 PDFCarissa May De Borja-Laraño0% (1)
- Module 6 CHN Family Nursing Process (Formulating and ImplementingDocumento22 pagineModule 6 CHN Family Nursing Process (Formulating and ImplementingAirah Fajardo100% (5)
- Community Health Nursing: I - Definition of TermsDocumento25 pagineCommunity Health Nursing: I - Definition of TermsRichard Ines Valino97% (29)
- CHN Complete NotesDocumento237 pagineCHN Complete NotesMelody B. Miguel100% (1)
- Primary Health CareDocumento35 paginePrimary Health CarenchlrysNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health Nursing 1: (Individual and Family As Clients)Documento63 pagineCommunity Health Nursing 1: (Individual and Family As Clients)Wilma Nierva Beralde100% (4)
- Community Health Nursing LectureDocumento5 pagineCommunity Health Nursing LectureEzraManzano33% (3)
- A Lion To Guard Us Lesson PlanDocumento6 pagineA Lion To Guard Us Lesson PlanMeritSoftware100% (3)
- Community Health NursingDocumento237 pagineCommunity Health Nursingjhing_apdan100% (2)
- Overall CHN Handout 1Documento54 pagineOverall CHN Handout 1Tifanny Shaine Tomas86% (7)
- COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING: AN OVERVIEWDocumento111 pagineCOMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING: AN OVERVIEWRhodora Mae Battung Mathis100% (6)
- Community Health Nursing Board ExamDocumento15 pagineCommunity Health Nursing Board Examrhenier_ilado86% (14)
- Community Health NursingDocumento22 pagineCommunity Health NursingBunzay Geline100% (9)
- Community Health Nursing Review (Edited)Documento407 pagineCommunity Health Nursing Review (Edited)api-2658787991% (35)
- Community Health Nursing - HandoutDocumento27 pagineCommunity Health Nursing - Handoutisaac_dre100% (8)
- Community Health NursingDocumento8 pagineCommunity Health NursingFirenze Fil93% (30)
- CHNDocumento11 pagineCHNR-Chian Jose Germanp100% (2)
- IMCIDocumento3 pagineIMCIwordlife360Nessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health Nursing PRELIMS OverviewDocumento40 pagineCommunity Health Nursing PRELIMS OverviewSherlyn PedidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health Nursing ReviewDocumento80 pagineCommunity Health Nursing ReviewJan Patrick ArrietaNessuna valutazione finora
- PHC Community HealthDocumento6 paginePHC Community HealthRoshin Tejero100% (1)
- Community Health Nursing 3 (Ansari Notes)Documento41 pagineCommunity Health Nursing 3 (Ansari Notes)Mrs Rehan80% (5)
- Community Health Nursing Topical Exam ReviewDocumento21 pagineCommunity Health Nursing Topical Exam ReviewExemplar ReviewNessuna valutazione finora
- COPAR ReviewerDocumento6 pagineCOPAR ReviewerRichard Ines Valino94% (16)
- EPI Vaccines HandoutsDocumento14 pagineEPI Vaccines HandoutsBurhan uddin100% (11)
- Community Health NursingDocumento60 pagineCommunity Health NursingDthird Mendoza Claudio100% (2)
- Community Health Nursing ProcessDocumento6 pagineCommunity Health Nursing ProcessAmiel Francisco ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Concepts of Community Health NursingDocumento22 pagineBasic Concepts of Community Health NursingkirbsNessuna valutazione finora
- CHN 100 ItemsDocumento7 pagineCHN 100 ItemsYaj CruzadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health NursingDocumento55 pagineCommunity Health NursingCes Aria100% (3)
- COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSE: Passbooks Study GuideDa EverandCOMMUNITY HEALTH NURSE: Passbooks Study GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Primary Health Care: Prepared By: Ezra Angeli C. Joaquin, RNDocumento18 paginePrimary Health Care: Prepared By: Ezra Angeli C. Joaquin, RNRaRe TV0% (1)
- Primary Health Care As An Approach To HealthDocumento31 paginePrimary Health Care As An Approach To HealthRea Andrea CuaresmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health Nursing: Gracyespino@uc-Bcf - Edu.phDocumento43 pagineCommunity Health Nursing: Gracyespino@uc-Bcf - Edu.phGrape Juice100% (1)
- Module 1 Community Health NursingDocumento12 pagineModule 1 Community Health NursingZanesville Lymont L. SubidoNessuna valutazione finora
- CHN Notes - Kleyr1Documento24 pagineCHN Notes - Kleyr1Gia VillamorelNessuna valutazione finora
- The ROLE OF The Public Health Nurse-AnnievadneDocumento39 pagineThe ROLE OF The Public Health Nurse-AnnievadneDolores BeeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Health Care Delivery SystemDocumento12 pagineThe Health Care Delivery SystemBrigitte CovarrubiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Public Health Nursing: An OverviewDocumento27 paginePublic Health Nursing: An OverviewKristel AnneNessuna valutazione finora
- Department F Health Plans, Programs, Projects NotesDocumento26 pagineDepartment F Health Plans, Programs, Projects NotesEdgar DumagpiNessuna valutazione finora
- CHN Lecture 082217Documento43 pagineCHN Lecture 082217Florabel Tolentino Sera JosefNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Concept of Health and Primary Health CareDocumento213 pagineModern Concept of Health and Primary Health CareMatt AndreyNessuna valutazione finora
- CHN OverviewDocumento5 pagineCHN OverviewJune Dumdumaya100% (1)
- Health Care Delivery System 1Documento21 pagineHealth Care Delivery System 1Carson BirthNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health NursingDocumento39 pagineCommunity Health NursingMark Villarmea Alforque100% (1)
- HCDS KK (2023)Documento123 pagineHCDS KK (2023)hrithiksankarNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 103Documento48 pagineNCM 103Cheenapot BerberNessuna valutazione finora
- Primary Health CareDocumento28 paginePrimary Health CareJHONESSA LAYOSNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab CPHDocumento73 pagineLab CPHYam100% (1)
- Community Health Nursing: Arby James Abonalla, RN, MSN, PHDN (C)Documento237 pagineCommunity Health Nursing: Arby James Abonalla, RN, MSN, PHDN (C)Roshie Kaye AbalorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health Nursing: An OverviewDocumento11 pagineCommunity Health Nursing: An OverviewAngelica Kaye BuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health Nursing ReviewerDocumento28 pagineCommunity Health Nursing ReviewerJenie Munar RosarioNessuna valutazione finora
- CHN NotesDocumento17 pagineCHN NotesJohnny Yao JrNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health NursingDocumento96 pagineCommunity Health NursingEric PromentilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Schizoid Personality Disorder: Social Withdrawal and Lack of EmotionDocumento3 pagineSchizoid Personality Disorder: Social Withdrawal and Lack of EmotionEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- CHF Case Study (Documento35 pagineCHF Case Study (EzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Fetal Monitoring: Premature LaborDocumento5 pagineElectronic Fetal Monitoring: Premature LaborEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs in HyperthyroidismDocumento4 pagineDrugs in HyperthyroidismEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Adams Bryan I. Lopez BSN 4BDocumento2 pagineAdams Bryan I. Lopez BSN 4BEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Xpeptic UlcerDocumento62 pagineXpeptic UlcerEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Head Nursing!Documento3 pagineHead Nursing!EzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- 137 140 (Rationale)Documento2 pagine137 140 (Rationale)EzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Strength Weakness Oppurtunities TreathDocumento3 pagineStrength Weakness Oppurtunities TreathEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Aetiology, Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Dengue Infection: DR Lee Oi Wah Peg. Perubatan Ud54Documento40 pagineAetiology, Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Dengue Infection: DR Lee Oi Wah Peg. Perubatan Ud54EzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Ecg: Internal Medicine Cardiology Critical Care SpecialistDocumento128 pagineBasic Ecg: Internal Medicine Cardiology Critical Care SpecialistEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- WeekDocumento2 pagineWeekEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Thyroid DiseaseDocumento133 pagineBenign Thyroid DiseaseEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- CHF Case Studty (Draft)Documento33 pagineCHF Case Studty (Draft)EzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- EmphysemaDocumento24 pagineEmphysemaEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 2 JenellaDocumento3 pagineCHAPTER 2 JenellaEzraManzano85% (20)
- Community (Case Study)Documento21 pagineCommunity (Case Study)EzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Community (Case Study)Documento21 pagineCommunity (Case Study)EzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- BULLYINGDocumento23 pagineBULLYINGEzraManzano57% (7)
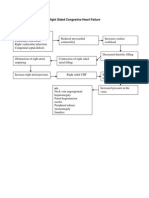
- Right Sided Congestive Heart FailureDocumento1 paginaRight Sided Congestive Heart FailureEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- BULLYINGDocumento23 pagineBULLYINGEzraManzano57% (7)
- BullyingDocumento7 pagineBullyingEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- CHF Case Studty (Draft)Documento34 pagineCHF Case Studty (Draft)EzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- CHF-drug StudyDocumento8 pagineCHF-drug StudyEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pedia AbnormalDocumento34 paginePedia AbnormalEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dengue Case Study1Documento75 pagineDengue Case Study1EzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Communicable DiseasesDocumento8 pagineCommunicable DiseasesKarla Fralala100% (1)
- Using IDEA to Create Lesson ExemplarsDocumento2 pagineUsing IDEA to Create Lesson ExemplarsMay Ann AlcantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Reasoning Strategy Guide - by Veera KarthikDocumento52 pagineCritical Reasoning Strategy Guide - by Veera KarthikVeera karthik100% (2)
- Math 8 ADocumento4 pagineMath 8 Aapi-280517032Nessuna valutazione finora
- Research Paper / Thesis: The Title of YourDocumento25 pagineResearch Paper / Thesis: The Title of Yourmarivic amorNessuna valutazione finora
- Bartolazo - MST 101d Learning Task 2 - Space ManagementDocumento2 pagineBartolazo - MST 101d Learning Task 2 - Space ManagementRonan Byron BartolazoNessuna valutazione finora
- SDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing AspirationsDocumento6 pagineSDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing AspirationsSalve SerranoNessuna valutazione finora
- SWECOM Public ReviewDocumento110 pagineSWECOM Public Reviewsaif1270% (1)
- Anatomy Syllabus 2013-BarronDocumento3 pagineAnatomy Syllabus 2013-Barronapi-233497584Nessuna valutazione finora
- B L GuptaDocumento13 pagineB L GuptaJuan JacksonNessuna valutazione finora
- Background of Curriculum DevelopmentDocumento44 pagineBackground of Curriculum DevelopmentKL PablicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Valenzuela City Polytechnic CollegeDocumento4 pagineValenzuela City Polytechnic CollegeJhoerey D Villegas100% (1)
- IBM Cognos TM1 Developer's Certification Guide: Chapter No. 7 "Virtual and Lookup Cubes"Documento31 pagineIBM Cognos TM1 Developer's Certification Guide: Chapter No. 7 "Virtual and Lookup Cubes"jagdevs7234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aiims Mbbs 2013 Question Paper AnsDocumento20 pagineAiims Mbbs 2013 Question Paper AnsRahim AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Operational Guidelines PRBCEDocumento7 pagineFinal Operational Guidelines PRBCEbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Guitar PraticeDocumento3 pagineHome Guitar PraticekondamudisagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Holdman 2day Pbi Lesson-2Documento44 pagineHoldman 2day Pbi Lesson-2api-210118947Nessuna valutazione finora
- CLOSE PROTECTION APPLICATIONDocumento4 pagineCLOSE PROTECTION APPLICATIONAnonymous pOggsIhOMNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Data Gathering Instrument For TraineeDocumento3 pagineSample Data Gathering Instrument For TraineeReginaMapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Medkart Interview Evaluation Form: Rating Key - NS: Not Satisfactory S: Satisfactory VS: Very Satisfactory NaDocumento2 pagineMedkart Interview Evaluation Form: Rating Key - NS: Not Satisfactory S: Satisfactory VS: Very Satisfactory NaanirudhNessuna valutazione finora
- ENVS 546 EIA 172 SyllabusDocumento2 pagineENVS 546 EIA 172 SyllabusAbu Muhsin Al Ngapaky100% (1)
- Instructional Planning for Triangle CongruenceDocumento4 pagineInstructional Planning for Triangle CongruencePablo JimeneaNessuna valutazione finora
- Religion Lesson Plan 3Documento4 pagineReligion Lesson Plan 3api-229687706Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Tips On Passing The Licensure Exam For TeachersDocumento2 pagine10 Tips On Passing The Licensure Exam For TeachersMacario Manubag Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Systematic Review SampleDocumento5 pagineSystematic Review SampleRubeenyKrishnaMoorthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Kampala Kindergarten Begins New TermDocumento3 pagineKampala Kindergarten Begins New TermNALULE JULIETNessuna valutazione finora
- Fourth Quarter SmeaDocumento18 pagineFourth Quarter SmeaRenge TañaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading and Writing q1 w3 Mod3Documento12 pagineReading and Writing q1 w3 Mod3Renz Ian T. Dacoron100% (1)