Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Cement Plant Operations Handbook, Preview
Caricato da
emad sabriTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cement Plant Operations Handbook, Preview
Caricato da
emad sabriCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The Cement Plant
Operations Handbook
for Dry-Process Plants
Sixth Edition
January 2014
Philip A Alsop,
PhD
Tradeship
Publications Ltd
Cement Plant
Operations Handbook
Sixth Edition
Contents
Section A
Process summaries
1. Introduction
10
1. The basics of cement manufacture-2. History of cement manufacture-3. Portland cement in
today's world
2. Raw materials
14
milling
1. Raw
milling
2.
3. Raw
and
Blending
Crushing-5. Drying
6.
1. Raw materials-2. Raw mix-3. Reserves-4.
Pre-blending- 7. Storage and handling
blending
26
3. Kiln feed
Physics of combustion 4. Burner design 5. Cement kiln burners
8. Modelling
9. Fuel storage and firing systems in practice
10.
-
Alternative and waste fuels
and
cooling
60
and shutdown
12. Plant control
cooling
11.
bypass
Emergency
94
-
Storage of clinker and other components 2. Cement milling
storage-6. Cement dispatch 7. Distribution
7.
10. Kiln mechanical
systems
control -5. Cement
(classifiers) 4. Ball mill circuit
Quality assurance and customer service
3. Separators
-8.
Quality control
2. Chemical
114
Cement and Concrete
analysis 3. Particle size analysis 4. Thermal analysis 5. Microscopy 6. Virtual
Testing Laboratory (VCCTL) 7. Calorimetry 8. Burnability 9. Grindability 10. Physical
testing 11. Process control analysis 12. Chromate passivation 13. Cement quality 14. Setting time 15.
ASTM cement types and specifications
16. European EN 197 cement specification
17. Composite cements
(intergrinds) 18. Supersulphated cement 19. Calcium aluminate cement (CAC) 20. Shrinkage-compensating
21. ISO 9001:2000 Quality management system
22. Concrete problems
cements (SCC)
Sampling
1.
Kiln control -5. Volatiles in the kiln -6. Kiln
9. Clinker
milling
6. Cement
1.
burning-4.
8. Kiln refractories
power
startup
7. Kiln
Burning
1. Chemical reactions-2. Process variants-3. Kiln
-
3.
5.
-11.
2. Fuels
7. Pollutant formation
Insufflation
Chemistry of combustion
6. Heat transfer
34
1.
-
4. Flames and fuels
8.
Maintenance
144
1. Maintenance benefits and costs
2. Failure modes
3. Computerised Maintenance Management Systems
4. Reliability-Centred Maintenance (RCM)
5. Maintenance cost management
6. Maintenance
(CMMS)
organisation 7. Role, planning and control 8. Mobile equipment maintenance 9. People and indicators
-
1. Dust collection
2. Pollution control
9. Environment and pollution control
-
3. ISO 14000
4. Sustainable
154
development and climate change
Contents
Plant
-9. Plant
stage
4. Deceleration
stage
172
reporting 5. Miscellaneous reporting
Typical equipment downtime report
-
4. Downtime
process summary data
Typical
8.
7.
manning
Accounting
2. Investment
justification
3.
Capacity
increase
by
process
change
5. Financial statements
13. Technical and process audits
-
power consumption
5.
194
2. Kiln specific fuel consumption
3. Cement mill specific
Debottlenecking 6. Project audit 7. Risk assessment
Historical performance
4. Other systems
1.
capacity summary
20.
17. Process
18.
16. Maintenance
4.
13.
Quarry 5. Drying 6.
Quality control 14.
Materials analysis -19. Plant
12. Cement
11. Finish mill
15. Dust collectors
3. Communication with stakeholders
10. Clinker
Storage capacity
plant construction
15. Cement
1. New
9. Fuel
202
distribution
8. Kiln
Blending
-
7.
Administration and commercial
2.
milling
Packing and
Raw
14. Plant assessment list
1. General
management accounting
or
Project cost estimation
1. Cost
182
-
12.
3. Acceleration
3. Inventories ard feeders
Typical daily production report
2. List of reports
1. Definitions
stage
168
reporting
-
II.
4.
2. Induction or dormant
stage
I. Initial
6.
of Portland cement
Hydration
10.
plant construction
2.
Project management
and valuation
3. Cement
plant
212
investment costs
Project phases
4.
5. Plant valuation
Section B
Process calculations
and
MISCELLANEOUS DATA
Bl. Power
4. Motor power output
handling
5. Peak
3.
Impeller build-up 4. Gas properties 5. Plant air distribution 6. Pitots,
loading 9. Stack draught 10. Dewpoint of moist air at atmospheric
-
8. Dust
False air
233
7.
2. Fan mechanical
1. Fan laws
Three-phase power
B2. Fans and air
orifices and Venturis
3.
Specific power consumption 2. Power conservation
power tariffs 6. Power generation 7. Cogeneration
-
1.
231
pressure -11. Spray cooling of gas -12. Abrasion resistance
B3.
Conveying
238
1. Com parative power consumption for lift 2. Pneu matic conveyi ng 3. Bucket elevator power 4. Belt conveyor
power 5. Screw conveyor power-6. Airslide-7. Drag chain power-8. Tube belt conveyor-9. Air-supported belt
-
10. Sandwich conveyor
11. Modified belt conveyor
conveyor
12.
Capsule conveyor
13. Water pump power
Cement Plant
Circulating
load
3. Classifier recovery
Maximum ball size
B5. Kilns
Cement
parameters
required -11. Measurement of wear
and
4.
Tromp curve
8. Mill power
5. Mill
-
critical speed 6. Charge volume
10.
weight and surface area
9. Ball
2.
7. Grace factor and other ball mill
loading
241
-
1. Sieve sizes
1.
Sixth Edition
Milling
-
B4.
Operations Handbook
Effects of gypsum upon setting time
12.
burning
compounds and
247
ratios-2.
Theoretical heat of formation of clinker
-
Coating tendency-3. Burnability factor-4. Required burning temperature
6. Kiln gas velocities
7. Kiln heat balance
8. Kiln specific heat
loading (SHL) 9. Kiln retention time 10. Kiln volume loading 11. Kiln capacity vs diameter 12. Kiln drive
power 13. Cooler efficiency 14. Kiln exhaust gas (coal) -15. Circulation of volatile components -16. Estimation
5.
of kiln
bypass -17.
Other kiln types
B6. Fuels
1.
259
Typical data for solid fuels
B7.
2.
Typical data for liquid fuels
3.
Typical data for gaseous fuels
Materials
261
-
1. Bulk densities of materials for silo storage
2. Specific gravities and grindabilities
3. Solubilities of sulphates
4. Rates of dissolution of different forms of caicium sulphate at 20C
5. Influence of temperature on the
-
solubilities of various
sulphate forms
6. Chemical formula
weights
7. Coefficients of linear
expansion
B8. Statistics
264
B9. Miscellaneous data
269
Atmospheric pressure and density vs altitude (0C) 2. pH and normality 3. Laboratory reagents (aqueous
solutions) 4. Seawater composition 5. Abundance of elements in earth's crust 6. Hardness of materials
7. Earthquake scales 8. Beaufort wind scale
9. World cement production -10. Regional cement consumption
data -11. EU Environmental legislation -12. Ship and truck capacities -13. Patents
1.
3. Pressure
4.
Weight
5. Area
6.
Density
7.
Energy
8. Force
2. Volume
Length
275
-
1.
Conversion tables
-
BIO.
9. Miscellaneous
References
276
Index
287
Advertisers' index
290
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Thermos Design of Rotary Kiln For Reduction of Radiantion LossesDocumento20 pagineThermos Design of Rotary Kiln For Reduction of Radiantion LossesMadhav Krishna MNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotary KilnDocumento7 pagineRotary KilnhangarrodNessuna valutazione finora
- Cement Plant VIPDocumento51 pagineCement Plant VIPengr kazamNessuna valutazione finora
- Cement Plant Thermal EnergyDocumento7 pagineCement Plant Thermal Energytsrinivasan5083Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cement IndustryDocumento27 pagineCement IndustryAhmed Mahmoud100% (1)
- Bypass SystemsDocumento17 pagineBypass SystemsNael100% (1)
- Mod 4Documento58 pagineMod 4mkpqNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotary Kiln SimulatorDocumento10 pagineRotary Kiln SimulatorPassmore DubeNessuna valutazione finora
- AirslidesDocumento3 pagineAirslidesVisnu SankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Holcim Material Bulk Density PDFDocumento1 paginaHolcim Material Bulk Density PDFEdgar Raul RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Abccoolerinleta4 (Air Blast Controlled Cooler Inlet) .AshxDocumento4 pagineAbccoolerinleta4 (Air Blast Controlled Cooler Inlet) .Ashxabosede2013Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mean Residence Time and Hold-Up of Solids in Rotary KilnsDocumento6 pagineMean Residence Time and Hold-Up of Solids in Rotary KilnsAnonymous NxpnI6jCNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento5 pagine1Dee HsNessuna valutazione finora
- Loesche Grinding Plants For Coal GasificationDocumento45 pagineLoesche Grinding Plants For Coal GasificationMaxim Polevoy100% (1)
- CPB Brochure Diaphragms en 2Documento12 pagineCPB Brochure Diaphragms en 2ebrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization of Kiln Plants: Activities and Technical DetailsDocumento10 pagineOptimization of Kiln Plants: Activities and Technical DetailsPaulo VidasNessuna valutazione finora
- Ball Mill InspectionDocumento9 pagineBall Mill InspectionmahantmtechNessuna valutazione finora
- PG 1591-1634 Chap5-RawMealHomogenization TextDocumento44 paginePG 1591-1634 Chap5-RawMealHomogenization TextMKPashaPasha100% (3)
- Mechanical Training PreheatDocumento15 pagineMechanical Training Preheattricky777100% (1)
- Brochure 154 Loesche-Mills For Cement Raw Material EN PDFDocumento24 pagineBrochure 154 Loesche-Mills For Cement Raw Material EN PDFMohammed AbdoNessuna valutazione finora
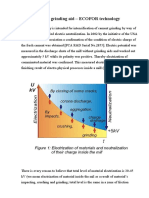
- New Hardware Grinding Aid - ECOFORDocumento5 pagineNew Hardware Grinding Aid - ECOFORlovjnxNessuna valutazione finora
- Boulder Formation in Cement Silos by Chettinad Cement CoDocumento11 pagineBoulder Formation in Cement Silos by Chettinad Cement CoWaka OngetiNessuna valutazione finora
- Maintenence in Cement Industry ProjectDocumento25 pagineMaintenence in Cement Industry ProjectSUMIT SHARMA95% (19)
- Cement Seminars and Courses 2016Documento68 pagineCement Seminars and Courses 2016Lucas Araújo100% (1)
- Cement ProcessingDocumento28 pagineCement ProcessingRish-ab KanwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Guide For Air Slide ConveyorDocumento4 pagineDesign Guide For Air Slide Conveyordoh16810% (1)
- Collaboration Cuts Costs and Increases Capacity by 35%: CASE: India Cements Limited, ChilamkurDocumento4 pagineCollaboration Cuts Costs and Increases Capacity by 35%: CASE: India Cements Limited, ChilamkurjmpbarrosNessuna valutazione finora
- Ikn Bee - Meet Ikni r12Documento28 pagineIkn Bee - Meet Ikni r12Junaid MazharNessuna valutazione finora
- KHD Pyroclon EnglDocumento4 pagineKHD Pyroclon Englkresimir.mikoc9765100% (1)
- CSI Guidelines For Co-Processing Fuels and Raw Materials in Cement Manufacturing - v2 PDFDocumento36 pagineCSI Guidelines For Co-Processing Fuels and Raw Materials in Cement Manufacturing - v2 PDFnaldsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Coolax CoolerDocumento19 pagineCoolax Cooleremad sabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Costing LafargeDocumento23 pagineProcess Costing LafargeGbrnr Ia AndrntNessuna valutazione finora
- Equip. Name:-RAW MILL Equip. TAG No. 300 RM-1Documento1 paginaEquip. Name:-RAW MILL Equip. TAG No. 300 RM-1vinodsnNessuna valutazione finora
- AFR Fact Sheet: Fly Ash AFR Co-Processed Volume ('000 T)Documento1 paginaAFR Fact Sheet: Fly Ash AFR Co-Processed Volume ('000 T)Safrin SangiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cement MagazineDocumento31 pagineCement Magazinedexter1850Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cyclone Separators: Learner GuideDocumento14 pagineCyclone Separators: Learner GuideRobson DE Freitas WerlingNessuna valutazione finora
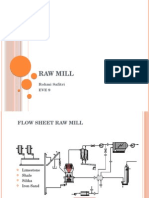
- Raw MillDocumento6 pagineRaw MillRohmi SafitriNessuna valutazione finora
- Burning The Mix 1Documento11 pagineBurning The Mix 1John GiannakopoulosNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion CalculationesDocumento3 pagineCombustion CalculationesSatish KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- By-Pass Calculation Method - DocbDocumento2 pagineBy-Pass Calculation Method - DocbElwathig BakhietNessuna valutazione finora
- Ball MillDocumento23 pagineBall MillSajjad Rasool ChaudhryNessuna valutazione finora
- 3500TPD Cement Plant Heat BalanceDocumento2 pagine3500TPD Cement Plant Heat BalanceIrshad HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Kiln Doctor FAQDocumento3 pagineKiln Doctor FAQgvrr1954Nessuna valutazione finora
- RIETVELD TC Champions Training Outline April 2006 V0 280206Documento6 pagineRIETVELD TC Champions Training Outline April 2006 V0 280206Tarek FennicheNessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Sidhee Cement Limited-SmitDocumento26 pagineGujarat Sidhee Cement Limited-SmitHimadri MahatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cement ProcessDocumento14 pagineCement ProcessChristian RuedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Raw MealDocumento48 pagineRaw Mealrashmiranjan1110Nessuna valutazione finora
- Simulation of Gas-Solid Flow & Design Modifications of Cement Plant CyclonesDocumento8 pagineSimulation of Gas-Solid Flow & Design Modifications of Cement Plant CyclonesNael100% (1)
- Click Here To Download Holcim, , Lafarge, Most Importnant Manuals, Most Important ExcelDocumento26 pagineClick Here To Download Holcim, , Lafarge, Most Importnant Manuals, Most Important ExcelhamedNessuna valutazione finora
- V6 EngineeringDocumento252 pagineV6 EngineeringRRHH100% (1)
- Rotary Kilns: Transport Phenomena and Transport ProcessesDa EverandRotary Kilns: Transport Phenomena and Transport ProcessesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- Preview-Cement Plant Operations HandbookDocumento4 paginePreview-Cement Plant Operations Handbookemad sabri0% (1)
- Cpoh6 ContentsDocumento3 pagineCpoh6 ContentsSTABNessuna valutazione finora
- 09-The Cement Plant Operations Handbook, 7th Edition PDFDocumento287 pagine09-The Cement Plant Operations Handbook, 7th Edition PDFNguyen Thanh100% (10)
- Seventh Edition Cement Hand BookDocumento6 pagineSeventh Edition Cement Hand Booksatfas50% (2)
- Cpoh6 Contents PDFDocumento3 pagineCpoh6 Contents PDFHazem DiabNessuna valutazione finora
- Cement Plant Operations Handbook, 5th Edition, PreviewDocumento3 pagineCement Plant Operations Handbook, 5th Edition, Previewemad sabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Cement PlantDocumento232 pagineCement PlantAnonymous iI88Lt100% (1)
- Year 4 Course Brief SPFDocumento4 pagineYear 4 Course Brief SPFMichel IsereNessuna valutazione finora
- Cement Plant Operation HandbookDocumento232 pagineCement Plant Operation HandbookFu_John91% (23)
- Glossary of Conveyor Belt TermsDocumento8 pagineGlossary of Conveyor Belt Termsemad sabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Effective MaintenanceDocumento19 pagineEffective Maintenanceemad sabri100% (1)
- Alternative Fuels in Cement IndustryDocumento25 pagineAlternative Fuels in Cement Industryemad sabri100% (1)
- Alternative Fuels in Cement IndustryDocumento25 pagineAlternative Fuels in Cement Industryemad sabri100% (1)
- 2013 Plant Info Summary Sample PDFDocumento38 pagine2013 Plant Info Summary Sample PDFemad sabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Maintenance Audit SampleDocumento4 pagineMaintenance Audit Sampleemad sabriNessuna valutazione finora
- CementDocumento24 pagineCementanshuldoc9100% (2)
- The Most Important Books of The Cement IndustryDocumento3 pagineThe Most Important Books of The Cement Industryemad sabriNessuna valutazione finora
- IEEE IASPCA 2012 Conference Plant Tours at TXI Hunter Cement PlantDocumento2 pagineIEEE IASPCA 2012 Conference Plant Tours at TXI Hunter Cement Plantemad sabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations: The PlantDocumento4 pagineOperations: The Plantemad sabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Alignment StandardsDocumento6 pagineAlignment StandardsFidelFornolles100% (2)
- Chapter 5 - The Role of Tribology in Engineering Materials: Friction, Lubrication and WearDocumento40 pagineChapter 5 - The Role of Tribology in Engineering Materials: Friction, Lubrication and Wearemad sabriNessuna valutazione finora
- The Role of Tribology in Engineering Materials: Friction, Lubrication and WearDocumento40 pagineThe Role of Tribology in Engineering Materials: Friction, Lubrication and Wearemad sabri100% (1)
- Lubrication, Friction and Wear PDFDocumento31 pagineLubrication, Friction and Wear PDFemad sabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Tribology (Surface Roughness and Measurements)Documento12 pagineTribology (Surface Roughness and Measurements)emad sabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Symptoms Causes Remedies: Rolling Bearing DamageDocumento1 paginaSymptoms Causes Remedies: Rolling Bearing Damageemad sabriNessuna valutazione finora
- The Economics of HardfacingDocumento6 pagineThe Economics of Hardfacingemad sabri100% (1)
- Shell InspectionDocumento23 pagineShell Inspectionemad sabri100% (1)
- Factors Affecting PerformanceDocumento33 pagineFactors Affecting Performanceemad sabri100% (1)
- ME-255 Principles of Tribology: Gamit Vipul M.E. (08214) Mechanical Engg - Dept. IiscDocumento14 pagineME-255 Principles of Tribology: Gamit Vipul M.E. (08214) Mechanical Engg - Dept. Iiscemad sabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Arguments and FallaciesDocumento18 pagineArguments and FallaciesSarah Mae Peñaflor Baldon-IlaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Good Parenting 1Documento6 pagineGood Parenting 1honey13Nessuna valutazione finora
- L-04 Analysis and Design of Two-Way Slab With Beams (Coloured)Documento63 pagineL-04 Analysis and Design of Two-Way Slab With Beams (Coloured)Hidayat Ullah100% (3)
- Reaction PaperDocumento2 pagineReaction PaperMisna Blasco Zurbano50% (2)
- Assignment On Training & Development Process of Uniliver BangladeshDocumento9 pagineAssignment On Training & Development Process of Uniliver BangladeshMohaiminul Islam50% (2)
- Segway v1 04 Eng Segway Atv Snarler Manual t3b L7eDocumento192 pagineSegway v1 04 Eng Segway Atv Snarler Manual t3b L7eMarouane LASRYNessuna valutazione finora
- MLA 7th Edition Formatting and Style GuideDocumento14 pagineMLA 7th Edition Formatting and Style Guideapi-301781586Nessuna valutazione finora
- How To Query Asham Tele Points (Telebirr)Documento13 pagineHow To Query Asham Tele Points (Telebirr)Fayisa ETNessuna valutazione finora
- Artikel Jurnal Siti Tsuwaibatul ADocumento11 pagineArtikel Jurnal Siti Tsuwaibatul Aaslamiyah1024Nessuna valutazione finora
- Transco Summary Gudinace For Work Method Statements R 0 300912Documento12 pagineTransco Summary Gudinace For Work Method Statements R 0 300912kla_alk100% (2)
- SP Post ListDocumento54 pagineSP Post ListJoel Eljo Enciso SaraviaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocumento2 pagineGujarat Technological UniversityShruti BiradarNessuna valutazione finora
- Banksy Responses Done With A Partner 655512Documento122 pagineBanksy Responses Done With A Partner 655512api-569248887Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reports On TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE PROVIDED by The Teachers To The Learners / Learning FacilitatorsDocumento2 pagineReports On TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE PROVIDED by The Teachers To The Learners / Learning FacilitatorsJerv AlferezNessuna valutazione finora
- 0404 eDocumento80 pagine0404 eFrancisco MisleNessuna valutazione finora
- Questionaire Abusive Supervision SurveyDocumento2 pagineQuestionaire Abusive Supervision SurveyAabee SyedNessuna valutazione finora
- 02.03.05.06.01 - Manage Sales Rebate AgreementDocumento11 pagine02.03.05.06.01 - Manage Sales Rebate AgreementVinoth100% (1)
- 2020-21 Series Test 1 QPDocumento1 pagina2020-21 Series Test 1 QPred18ggmuNessuna valutazione finora
- APTET 2014 Social Question Paper II With Solutions PDFDocumento47 pagineAPTET 2014 Social Question Paper II With Solutions PDFgayathriNessuna valutazione finora
- How To ComboDocumento15 pagineHow To Combosapabapjava2012Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction EthicsDocumento26 pagineIntroduction EthicsLawrence MarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Office Phone Number Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh (A.p.)Documento11 pagineCurrent Office Phone Number Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh (A.p.)Manoj Digi Loans100% (1)
- Tutorial Probability and Statistics: SolutionsDocumento3 pagineTutorial Probability and Statistics: SolutionsAdnanNessuna valutazione finora
- S&S PDFDocumento224 pagineS&S PDFMohammed MateenNessuna valutazione finora
- Hatton National Bank PLC: Instance Type and TransmissionDocumento2 pagineHatton National Bank PLC: Instance Type and TransmissiontaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagram 1 Shows An AbacusDocumento11 pagineDiagram 1 Shows An AbacusHema BalasubramaniamNessuna valutazione finora
- CasDocumento2 pagineCasJamesalbert KingNessuna valutazione finora
- Remembering Thanu Padmanabhan - The HinduDocumento3 pagineRemembering Thanu Padmanabhan - The HinduIucaa libraryNessuna valutazione finora
- Criteria For Use in Evaluation of Testing Laboratories and Organizations For Examination and Inspection of Steel, Stainless Steel, and Related AlloysDocumento5 pagineCriteria For Use in Evaluation of Testing Laboratories and Organizations For Examination and Inspection of Steel, Stainless Steel, and Related AlloysProduction DepartmentNessuna valutazione finora
- Control System Engineering: Topic Block Diagram RepresentationDocumento24 pagineControl System Engineering: Topic Block Diagram RepresentationWaqas AfzalNessuna valutazione finora