Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Tema2 Science
Caricato da
Inma JimenezTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Tema2 Science
Caricato da
Inma JimenezCopyright:
Formati disponibili
A
S
S
U
M
P
T
I
O
N
S
B
I
B
I
O
-
G
I
J
N
SCIENCE YEAR 5
UNIT 2-PLANTS
1. CHARACTERISTICS OF PLANTS
The living things in the plant kingdo have these !ha"a!te"isti!s#
o The$ a"e %ULTICELLULAR o"ganis&
o The$ CANN'T ove a"o(nd&
o The$ ake thei" o)n *ood&
o The$ have "oots+ a ste and leaves&
o Alost all plants live on land& Soe a"e a,(ati!
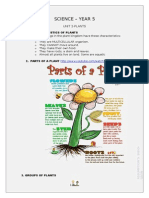
2. PARTS OF A PLANT http#--)))&$o(t(.e&!o-)at!h/v01(2a53'45iA
3. GROUPS OF PLANTS
6
A
S
S
U
M
P
T
I
O
N
S
B
I
B
I
O
-
G
I
J
N
Plants are classified into two groups: plants with flowers and plants
without flowers.
FLOWERING PLANTS a"e the la"gest g"o(p )ithin the plant
kingdo& App"o7iatel$ 289+999 spe!ies o* :o)e"ing plant have
.een naed so *a"& These plants "ep"od(!e )ith seeds&
;lo)e"ing plants !an .e GYMNOSPERMS o" ANGIOSPERMS&
NON-FLOWERING PLANTS a"e the sallest g"o(p o* plants&
%osses+ *e"ns+ and thei" "elatives a"e plants that do not p"od(!e
:o)e"s& The$ "ep"od(!e .$ eans o* SP'RES& %ost live in shad$ o"
dap ha.itats&
http#--)))&$o(t(.e&!o-)at!h/
*eat("e0pla$e"5e.edded<v0t=2Po,>I.9?t0@@
4. PLANT NUTRITION
http#--)))&$o(t(.e&!o-)at!h/
v0C65(eA5BC6o<list0PL(Bl;2IpR;!oY@vtU192C2>Dd1CY6thBE
Plants+ like all living things+ !a""$ o(t the p"o!ess o* n(t"ition&
The$ have three stages in n(t"ition#
2
o Gymnosperms: The term gymnosperm is derived from two Greek words:
gymnos, meaning naked, and sperma, meaning seed. The term refers to
plants, such as pine and spruce, in which seeds mature on the surface of
cone scales. When the cone falls, it breaks and releases seeds. The seeds are
blown by the wind, washed away by water, or moved by animals until they
reach a place where a new plant can grow.
Most gymnosperms are evergreens. Evergreens are trees that lose only a few
leaves at one time and constantly replace the leaves they have lost. So, they
look green all the time.
o Angiosperm is a seed plant that produces flowers. ruits, vegetables, grains,
and almost all nuts come from angiosperms. !ngiosperms are the most
abundant plants. There are more than "#$,%%% different kinds of
angiosperms.
A
S
S
U
M
P
T
I
O
N
S
B
I
B
I
O
-
G
I
J
N
Plants get the ntr!ents the$ need *"o the soil and ai"#
The" get #ar$%n &!'(!&e )r'* the a!r thr'gh the!r
lea+es,
The" get -.ter an& *!neral salts )r'* the s'!l thr'gh
the!r r''ts,
The$ ake thei" o)n *ood th"o(gh the p"o!ess o*
photos$nthesis#
Plants *a/e the!r '-n )''& $" *!(!ng #ar$%n &!'(!&e
an& the ("le* sa0, Th!s )''& !s #alle& 0h'le* sa0,
Plants nee& snl!ght )'r 0h't's"nthes!s, The Green
s$stan#e !n lea+es #at#hes the sns l!ght, Th!s
s$stan#e !s #hl'r'0h"ll,
1r!ng th!s 0r'#ess2 0lants 0r'&#e '("gen an& le! !t 't
!n the at*'s0here s' 'ther l!+!ng th!ngs #an $reathe,
Thei" *ood is t"anspo"ted th"o(gho(t the plant&
5. PLANT REPRODUCTION
@
A
S
S
U
M
P
T
I
O
N
S
B
I
B
I
O
-
G
I
J
N
I* $o( a"e an o"ganis+ $o( )ill need to re0r'&#e& 'the")ise+ the"e )ill
.e no o"e o* $o(" spe!ies and the spe!ies )ill die oE&
The ost advan!ed o* the plants have thei" o)n )a$ o* se7(all$
"ep"od(!ing& It is a ve"$ *an!$ and ve"$ !ople7 p"o!ess&
Plants that "el$ on 3'-ers *o" "ep"od(!tion a"e also ve"$ dependent on
o(tside help s(!h as inse!ts and anials& Bhile !oni*e"s have the t)o
st"(!t("es on one t"ee+ :o)e"ing plants )ent one step *("the" and p(t
the devi!es that ake and "e!eive pollen in the sae st"(!t("e&
Petals4 F"ightl$ !olo("ed& The$
a"e (sed to att"a!t inse!ts .$
thei" ."ight !olo(" and s!ent&
Se0als4 G"een leaves a"o(nd the
o(tside o* the :o)e"& Sepals a"e
(s(all$ salle" than the petals+&
Used to p"ote!t the :o)e" )hile it
is still in .(d&
Sta*ens4 This is )he"e pollen is
ade
It is the ale pa"t o* the :o)e"&
The staen has t)o pa"ts#
the 5la*ent Ha thin stalkI and
the anther)hi!h is
)he"e 0'llen is ade
6ar0el4 The !a"pel is the g"een
stalk in the iddle o* the :o)e"&
It is the *eale pa"t o* the :o)e"&
The !a"pel has th"ee pa"ts#
At the top is the st!g*a, This is
)he"e pollen has to land&
Felo) the stiga is the st"le and
then the '+ar" )hi!h is )he"e
seeds a"e *o"ed
Se7(al "ep"od(!tion in a :o)e"ing plant has ;'UR ain stages
=
Pollination: This is when pollen lands on a new flower
Fertilization: This is when the pollen and the seed meet
Seed dispersal: This is when the seed is spread around, away from the
plant that made it
Germination : This is when the seed, having reached the ground, starts to
grow into a new plant
Pollination: This is when pollen lands on a new flower
Fertilization: This is when the pollen and the seed meet
Seed dispersal: This is when the seed is spread around, away from the
plant that made it
Germination : This is when the seed, having reached the ground, starts to
grow into a new plant
A
S
S
U
M
P
T
I
O
N
S
B
I
B
I
O
-
G
I
J
N
Pollination http://www.youtue.com/watch!v"#tcm$%iomf&
' plant is pollinated when pollen from another flower reaches it.
Pollen is a yellow dust and it has to reach the stigma of the plant eing
pollinated.
The pollen has to e carried from the stamen of one flower to the stigma of
another.
&t is usually carried y ees (or other small animals) ut it can e carried y the
wind.
;e"tiliAation
'fter pollination fertilization ta*es place. This is when the pollen and the ovule
+oin together to ma*e a seed.
5
A
S
S
U
M
P
T
I
O
N
S
B
I
B
I
O
-
G
I
J
N
The seed also contains a food store, usually starch.
The part of the flower surrounding the seed is *nown as the fruit.
'fter fertilization the petals and stamens wither and die. The ovary (which forms
the fruit) swells up, sometimes consideraly. (ie as in the apple)
Seed dispe"sal
The +o of the fruit is to carry the seeds as far as possile from the parent plant
so the new plants have room to grow and do not compete for resources such as
light, water and nutrients in the soil.
This process is called seed dispersal.
http://www.bbc.co.uk/learningzone/clips/seed-dispersal/2258.html
A plant will dip!"! t#!i" !!d $%&" 'ain wa()
1. The fruit is eaten by animals such as birds but are not
digested. The seeds pass out the animal along with its
droppings eg cherry, blackberry. These fruits look and taste
nice.
2. The fruit splits open. sometimes this happens with a lot of
force and the seeds are shot out. eg beans. the pod is the
fruit and the beans are the seeds.
3. The fruits have little hooks. these hooks stick to the fur of
animals. eg burdock.
8
A
S
S
U
M
P
T
I
O
N
S
B
I
B
I
O
-
G
I
J
N
4. The fruits have wings or hairs and this lets them get
carried by the wind,. eg sycamore trees have winged fruits.
Ge"ination
Germination is the process y which the seed actually starts to grow.
Conditions needed for germination
The seed will not germinate untill it gets warm. 's well as warmth the seed also
needs o,ygen and water to grow.
-ithout all three (-ater, o,ygen and warmth) the seed will not grow.
The germination period is time etween planting and starting to germinate.
3
A
S
S
U
M
P
T
I
O
N
S
B
I
B
I
O
-
G
I
J
N
J
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- TERESA PERALES Biografia en InglesDocumento1 paginaTERESA PERALES Biografia en InglesInma JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Kids activities at the park spottedDocumento1 paginaKids activities at the park spottedInma JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Regular VerbsDocumento5 pagineList of Regular Verbssiiimpaaticaa79% (34)
- Vertebrates Classification GuideDocumento4 pagineVertebrates Classification GuideInma JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Refuerzo Curso12 13Documento55 pagineRefuerzo Curso12 13Inma JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Refuerzo Curso12 13Documento55 pagineRefuerzo Curso12 13Inma JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5 Scienceprehistory and AntiquityDocumento4 pagineUnit 5 Scienceprehistory and AntiquityInma JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Science 5º FichasDocumento64 pagineEssential Science 5º Fichasdanae_79% (38)
- The Economy Unit 6Documento6 pagineThe Economy Unit 6Inma JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Invertebrates Unit 4 TraduccionDocumento9 pagineInvertebrates Unit 4 TraduccionInma JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Tema2 ScienceDocumento8 pagineTema2 ScienceInma JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Pollination Project New 2Documento30 paginePollination Project New 2SagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of PlantsDocumento13 pagineClassification of PlantsCelCoracheaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tracheophyte Phylogeny Poster (TPP) - Vascular Plants: Systematics and Characteristics, 2016Documento2 pagineTracheophyte Phylogeny Poster (TPP) - Vascular Plants: Systematics and Characteristics, 2016Dayvson CostaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assertion and ReasonDocumento75 pagineAssertion and Reasondr.pujap935Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wood StructureDocumento6 pagineWood StructureikonopisNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Project: PollinationDocumento14 pagineBiology Project: PollinationArunkumar PNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Classification NotesDocumento9 paginePlant Classification NotesketakiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Diversity of Living Things: ObjectivesDocumento13 pagineThe Diversity of Living Things: ObjectivesTorzy TubeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 Diversity of PlantsDocumento13 pagineLesson 2 Diversity of PlantsCynna Faye CasaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 8:VASCULAR PLANTS: Non-Flowering Seed-Bearing Vascular Plants (Gymnosperms)Documento7 pagineLab 8:VASCULAR PLANTS: Non-Flowering Seed-Bearing Vascular Plants (Gymnosperms)Essay NationNessuna valutazione finora
- The Woody Plant Seed ManualDocumento1.236 pagineThe Woody Plant Seed ManualGregory BakasNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategy For Botany Optional in UPSC ExamsDocumento21 pagineStrategy For Botany Optional in UPSC ExamsRiVa SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Kingdom PlantaeDocumento34 pagineBiology Kingdom PlantaeRosanna LombresNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution of PlantsDocumento5 pagineEvolution of PlantsChristine ShellyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Evolution of Plant and Fungal Diversity: Chapter ObjectivesDocumento15 pagineThe Evolution of Plant and Fungal Diversity: Chapter Objectivesirene9tan9ailianNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Compressed Notes BioDDocumento23 pagine1 Compressed Notes BioDLIM ZHI SHUENNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Score Biodiversity Part IDocumento37 pagineBiology Score Biodiversity Part IPuvaan RaajNessuna valutazione finora
- Keanekaragaman TumbDocumento86 pagineKeanekaragaman TumbRinandar MusliminNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report Bio Exp 6Documento14 pagineLab Report Bio Exp 6SyamirConan50% (2)
- Plant Kingdom MCQDocumento17 paginePlant Kingdom MCQNawaraj RokayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 11 - Life Science - Revision Questions - PlantsDocumento10 pagineGrade 11 - Life Science - Revision Questions - PlantsJustinCase1991100% (2)
- The Non-Vascular to Vascular Plant KingdomDocumento7 pagineThe Non-Vascular to Vascular Plant KingdomGael Forbes RealNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution of Seed PlantsDocumento18 pagineEvolution of Seed PlantsMnqobi ZuluNessuna valutazione finora
- Thallophytes Proper NotesDocumento26 pagineThallophytes Proper NotesStarnley TemboNessuna valutazione finora
- Angiosperm Derived CharacteristicsDocumento7 pagineAngiosperm Derived CharacteristicsBreen DoteNessuna valutazione finora
- Plantae PDFDocumento20 paginePlantae PDFida nurpitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Kingdom Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento4 paginePlant Kingdom Multiple Choice QuestionsTharun SujithNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology document on plantae unit subjectsDocumento27 pagineBiology document on plantae unit subjectsjoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Gymnosperms: Naked SeedsDocumento14 pagineGymnosperms: Naked SeedsElijah Estes-BrinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- 05b5ad75b92540 - Ch-1 - Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry - SL Deore PDFDocumento17 pagine05b5ad75b92540 - Ch-1 - Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry - SL Deore PDFDhitendra KumarNessuna valutazione finora