Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Assignment 3061014
Caricato da
Krishnan MohanTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Assignment 3061014
Caricato da
Krishnan MohanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The University of Western Ontario
Faculty of Engineering
Assignment 3
CBE 2220a- Chemical Process Calculations
06-10- 2014 (DUE October 13, 2014 BY 5 PM)
Q. 1. Case Study: Extractive Distillation Process for Acetone
A mixture containing 50.0 wt% acetone and 50.0 wt% water is to be separated into two streams-
one enriched in acetone, the other in water. The separation process consists of extraction of the
acetone from the water into a solvent methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK), which dissolves acetone but is
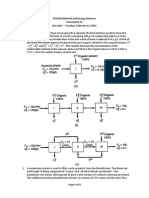
nearly immiscible with water. The process is shown below:
(water in this process) is referred to as the Raffinate and the phase rich in the solvent (MIBK) is
termed the Extract. The first mixer settler combination is the First Stage Extractor Unit for the
process. The raffinate then passes to a second mixer-settler combination or second extractor unit.
Here the raffinate is contacted with a second stream of pure MIBK which permits the transfer of
more acetone from the raffinate to the solvent. The phases separate in the settler of the second
extractor unit. The extracts from the two extraction steps are combined while raffinate 2 which is
very low in acetone is discarded. The combined extracts are fed to a distillation column where the
acetone and MIBK are separated. The overhead from the distillation column is rich in acetone and is
the required product. The bottom effluent from the distillation column is rich in MIBK. This could be
treated further and eventually recycled back to the process as pure MIBK.
In a pilot scale study, for every 100 Kg of acetone-water fed to the first extraction stage, 100 Kg of
MIBK is fed to the first extractor and 75 Kg to the second extractor. The extract from the first stage
is found to contain 27.5% (w/w) acetone, The second stage raffinate has a mass of 43.1 Kg and
contains 5.3% acetone, 1.6% MIBK and the rest water. The second stage extract contains 9.0%
acetone, 88.0% MIBK and 3.0% water. The overhead product from the distillation column contains
2.0% MIBK, 1.0% water and the rest acetone. Taking a basis of calculation of 100 Kg acetone-water
feed:
1. Show a simplified schematic by combining mixer settler into one (extractor) for the process?
2. Do a DF analysis around the 2 extractor subsystem.
3. Show a DF analysis for the OVERALL process.
4. Show a DF analysis for first extractor; second extractor; around the mixing point; and around the
distillation column.
5. Write mass balances around the 2 extractor unit and solve.
6. Write mass balances around the mxing point and solve.
7. Write mass balances around extractor 1 and etractor 2 and solve.
8 Why cannot we completely solve for the process?
Q 2. A reactor is fed an equi-molar mixture of three chemicals A,B, and C. The product D is
produced via the reaction below:
A + 2B + 1.5C 2D + E
The conversion in the reactor is 50% based on the limiting reactant.
(a) What is the limiting reactant?
(b) How many moles of D are produced per 100 moles of total feed to the reactor?
(b) How many moles of D are produced per 100 moles of total feed to the reactor?
The acetone (solute)-water (diluents) mixture is first contacted with the MIBK (solvent) in a mixer
that provides a good contact between the two liquid phases. A portion of the acetone in the feed
(water) transfers to the organic solvent (MIBK) phase in this step. The mixture passes into the
settling tank where the phases separate and are separately withdrawn. The phase rich in diluents
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- AZ-900T00 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals-01Documento21 pagineAZ-900T00 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals-01MgminLukaLayNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios.1-Varios Equipos, Multicomponentes, Sin RX PDFDocumento4 pagineEjercicios.1-Varios Equipos, Multicomponentes, Sin RX PDFMafee VelezNessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid Liquid Extraction ExperimentDocumento22 pagineLiquid Liquid Extraction ExperimentMohd Sharu Mamat67% (12)
- Liquid Liquid ExtractionDocumento40 pagineLiquid Liquid ExtractionMohsin Ehsan100% (1)
- Forensic Science From The Crime Scene To The Crime Lab 2nd Edition Richard Saferstein Test BankDocumento36 pagineForensic Science From The Crime Scene To The Crime Lab 2nd Edition Richard Saferstein Test Bankhilaryazariaqtoec4100% (25)
- INDUSTRIAL STOICHIOMETRY II: SEPARATION PROCESSESDocumento65 pagineINDUSTRIAL STOICHIOMETRY II: SEPARATION PROCESSESMeng KiatNessuna valutazione finora
- TK-315 CPI2 - 1 - NonReacting SystemsDocumento37 pagineTK-315 CPI2 - 1 - NonReacting SystemsIndahNessuna valutazione finora
- TK-315 CPI2 - 1 - NonReacting SystemsDocumento34 pagineTK-315 CPI2 - 1 - NonReacting SystemsMuhammad IkbalNessuna valutazione finora
- B48BA Tutorial 2 Mass Balance-1Documento2 pagineB48BA Tutorial 2 Mass Balance-1Mohamed AbdullaNessuna valutazione finora
- TK-315 CPI2 - 1 - NonReacting SystemsDocumento33 pagineTK-315 CPI2 - 1 - NonReacting SystemsBayu Purnama Ridjadi75% (4)
- Lista de ExerciciosDocumento30 pagineLista de ExerciciosFrancine MartinsNessuna valutazione finora
- A4 02-Aug-2016 Bit1008 EthDocumento34 pagineA4 02-Aug-2016 Bit1008 EthsantoshNessuna valutazione finora
- HW #2Documento4 pagineHW #2Rohit ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 4 Che422 Spring 2015Documento3 pagineTutorial 4 Che422 Spring 2015tarhuni100% (2)
- 4.material Balance For Mutiple UnitDocumento30 pagine4.material Balance For Mutiple UnitjamesdigolNessuna valutazione finora
- Material BalanceDocumento30 pagineMaterial BalanceJajejijojuNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems 2Documento32 pagineProblems 2Pritesh Bhakta50% (6)
- Inorganic Catalysts Bronze Problem 2Documento11 pagineInorganic Catalysts Bronze Problem 2joell2253h.01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 ExtractionDocumento11 pagineChapter 8 ExtractionPhuong CR100% (1)
- Revision - Mass BalanceDocumento3 pagineRevision - Mass BalancePorkkodi SugumaranNessuna valutazione finora
- 2K RPM A.V Radius / Sec S 60: St. Joseph's College of EngineeringDocumento16 pagine2K RPM A.V Radius / Sec S 60: St. Joseph's College of EngineeringPrincely ImmanuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cu2+ Extraction Using LIX984Documento10 pagineCu2+ Extraction Using LIX984Ben KalNessuna valutazione finora
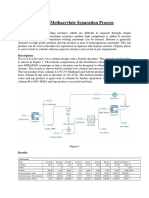
- 30,000 Metric Tonne Methacrolein ProductionDocumento13 pagine30,000 Metric Tonne Methacrolein ProductionTan Yong ChaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Methyl Methacrylate Separation Process: AbstractDocumento2 pagineMethyl Methacrylate Separation Process: Abstractgauri guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- UMP Faculty of Chemical & Natural Resources Engineering Material and Energy Balance Assignment 2Documento2 pagineUMP Faculty of Chemical & Natural Resources Engineering Material and Energy Balance Assignment 2Tuah Abadi RosmazamNessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid Liquid ExtractionDocumento40 pagineLiquid Liquid ExtractionApurba Sarker Apu93% (29)
- ChECal Probset 3Documento2 pagineChECal Probset 3Bea FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Separation ProcessesDocumento3 pagineSeparation ProcessesJoshua SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Liquid-Liquid Extraction Question 1 (Mar'14)Documento8 pagineChapter 4 Liquid-Liquid Extraction Question 1 (Mar'14)Nur Haslida AzmiNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Material Balances Multiple Unit ProcessesDocumento18 pagine4 Material Balances Multiple Unit ProcessesSnow Drop100% (3)
- Material and Energy Balance Process CalculationsDocumento18 pagineMaterial and Energy Balance Process CalculationsSiti Noranisa hidayahNessuna valutazione finora
- MethylbenzoateDocumento6 pagineMethylbenzoateLindelwa MthembuNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller Balance Sin RXN QCADocumento4 pagineTaller Balance Sin RXN QCAValentina BaldovinosNessuna valutazione finora
- Che F244 1183 C 2015 2Documento4 pagineChe F244 1183 C 2015 2shubhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 2 (2013)Documento7 pagineTutorial 2 (2013)Shah AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Separating gases with membranes and adsorptionDocumento4 pagineSeparating gases with membranes and adsorptionHanee Farzana HizaddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Separation Processes IDocumento3 pagineSeparation Processes IAmesh Chiyogami100% (1)
- Chapter 7.3 Liquid-Liquid ExtractionDocumento15 pagineChapter 7.3 Liquid-Liquid Extractionamira nabillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Extraction TechniquesDocumento40 pagineExtraction TechniquesAlexander Robert JennerNessuna valutazione finora
- Bridge To Ch. 5 - More On Recycle and PurgeDocumento17 pagineBridge To Ch. 5 - More On Recycle and PurgeMwanarusi MwatondoNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 09Documento19 pagineCH 09kentalNessuna valutazione finora
- ChE Cal LE 4 - 1sAY2223 - ANIESDocumento1 paginaChE Cal LE 4 - 1sAY2223 - ANIESRhean Rheign VergaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Problems Batch I (R.No. 102117001 To 102117011)Documento7 pagineAssignment Problems Batch I (R.No. 102117001 To 102117011)Nishanth ChandranNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 LLE-part 2 - 18nov2020Documento22 pagineChapter 2 LLE-part 2 - 18nov2020CaratsSVTNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 2 Part 1 QuestionDocumento2 pagineTutorial 2 Part 1 QuestionMuiz ZahuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp - 2 Bubble Cap Distillation ColumnDocumento13 pagineExp - 2 Bubble Cap Distillation ColumnAdawiyah Al-jufri100% (1)
- Liquid Liquid ExtractionDocumento9 pagineLiquid Liquid ExtractionHemant KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Plug Flow Reactor ExperimentDocumento16 paginePlug Flow Reactor ExperimentN Afiqah RazakNessuna valutazione finora
- Continuous Rectification Column Separates Binary MixtureDocumento6 pagineContinuous Rectification Column Separates Binary Mixtureanita_shar29Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4.liquid2 Extraction FullDocumento17 pagine4.liquid2 Extraction FullMuhammad Zaidi MisniNessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction OTKDocumento38 pagineLiquid-Liquid Extraction OTKJaffarudin Janu WahyudiNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp No.5 - LLE Phase DiagramDocumento4 pagineExp No.5 - LLE Phase DiagramPoonam ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 3 - Acetone Production Via The Dehydrogenation of IPADocumento7 pagineGroup 3 - Acetone Production Via The Dehydrogenation of IPAQuỳnh Như PhạmNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.7 - Liquid-Liquid Extractions - Chemistry LibreTextsDocumento8 pagine7.7 - Liquid-Liquid Extractions - Chemistry LibreTextsOmoshalewa AjayiNessuna valutazione finora
- PFR ReactorDocumento19 paginePFR Reactorkhairi100% (1)
- Lecture 9Documento23 pagineLecture 9amirmasoudNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM 230 Exam 1 Key AnalysisDocumento3 pagineCHEM 230 Exam 1 Key AnalysisMuhammad AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Biofilms in Bioelectrochemical Systems: From Laboratory Practice to Data InterpretationDa EverandBiofilms in Bioelectrochemical Systems: From Laboratory Practice to Data InterpretationNessuna valutazione finora
- Sustainable synthesis of ciclopentene derivatives through multicomponent reactions in continuous flow regimeDa EverandSustainable synthesis of ciclopentene derivatives through multicomponent reactions in continuous flow regimeNessuna valutazione finora
- Advances in Biofeedstocks and Biofuels, Volume 2: Production Technologies for BiofuelsDa EverandAdvances in Biofeedstocks and Biofuels, Volume 2: Production Technologies for BiofuelsLalit Kumar SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 3Documento49 pagineLec 3Krishnan MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Dates Calendar Oct-NovDocumento1 paginaImportant Dates Calendar Oct-NovKrishnan MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Joseph Murphy's Guide to Unlocking Your Subconscious PowerDocumento138 pagineJoseph Murphy's Guide to Unlocking Your Subconscious Poweralagu17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trapezoidal Rule - Equal SementsDocumento6 pagineTrapezoidal Rule - Equal SementsKrishnan MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab ManualDocumento76 pagineLab ManualKrishnan Mohan0% (1)
- Tutorial 1 SolutionsDocumento6 pagineTutorial 1 SolutionsKrishnan MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab+Manual+2014 Cbe 2207Documento63 pagineLab+Manual+2014 Cbe 2207Krishnan MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 - MATLAB FundamentalsDocumento31 pagineLecture 1 - MATLAB FundamentalsKrishnan MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Utah JazzDocumento1 paginaUtah JazzKrishnan MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Intro To ThermodynamicsDocumento42 pagineChapter 1 - Intro To ThermodynamicsKrishnan MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Supplementary NotesDocumento22 pagineSupplementary NotesKrishnan MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle Learning ManagementDocumento168 pagineOracle Learning ManagementAbhishek Singh TomarNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-1: Introduction: Question BankDocumento12 pagineUnit-1: Introduction: Question BankAmit BharadwajNessuna valutazione finora
- AATCC 100-2004 Assesment of Antibacterial Dinishes On Textile MaterialsDocumento3 pagineAATCC 100-2004 Assesment of Antibacterial Dinishes On Textile MaterialsAdrian CNessuna valutazione finora
- Log File Records Startup Sequence and Rendering CallsDocumento334 pagineLog File Records Startup Sequence and Rendering CallsKossay BelkhammarNessuna valutazione finora
- Wi FiDocumento22 pagineWi FiDaljeet Singh MottonNessuna valutazione finora
- Math5 Q4 Mod10 DescribingAndComparingPropertiesOfRegularAndIrregularPolygons v1Documento19 pagineMath5 Q4 Mod10 DescribingAndComparingPropertiesOfRegularAndIrregularPolygons v1ronaldNessuna valutazione finora
- Mtle - Hema 1Documento50 pagineMtle - Hema 1Leogene Earl FranciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maverick Brochure SMLDocumento16 pagineMaverick Brochure SMLmalaoui44Nessuna valutazione finora
- Inventory Control Review of LiteratureDocumento8 pagineInventory Control Review of Literatureaehupavkg100% (1)
- Progressive Myoclonic Epilepsies - Practical Neurology 2015. MalekDocumento8 pagineProgressive Myoclonic Epilepsies - Practical Neurology 2015. MalekchintanNessuna valutazione finora
- C6030 BrochureDocumento2 pagineC6030 Brochureibraheem aboyadakNessuna valutazione finora
- FX15Documento32 pagineFX15Jeferson MarceloNessuna valutazione finora
- Conv VersationDocumento4 pagineConv VersationCharmane Barte-MatalaNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.1 Interaction Diagrams: Interaction Diagrams Are Used To Model The Dynamic Aspects of A Software SystemDocumento13 pagine8.1 Interaction Diagrams: Interaction Diagrams Are Used To Model The Dynamic Aspects of A Software SystemSatish JadhaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Marine Engineering 1921Documento908 pagineMarine Engineering 1921Samuel Sneddon-Nelmes0% (1)
- Non Circumvention Non Disclosure Agreement (TERENCE) SGDocumento7 pagineNon Circumvention Non Disclosure Agreement (TERENCE) SGLin ChrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Thesis Report YacobDocumento114 pagineFinal Thesis Report YacobAddis GetahunNessuna valutazione finora
- Briana SmithDocumento3 pagineBriana SmithAbdul Rafay Ali KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- تاااتتاااDocumento14 pagineتاااتتاااMegdam Sameeh TarawnehNessuna valutazione finora
- Nama: Yetri Muliza Nim: 180101152 Bahasa Inggris V Reading Comprehension A. Read The Text Carefully and Answer The Questions! (40 Points)Documento3 pagineNama: Yetri Muliza Nim: 180101152 Bahasa Inggris V Reading Comprehension A. Read The Text Carefully and Answer The Questions! (40 Points)Yetri MulizaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Wheel ThunderDocumento9 pagine4 Wheel ThunderOlga Lucia Zapata SavaresseNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 1 1 124 9636 PDFDocumento11 pagine10 1 1 124 9636 PDFBrian FreemanNessuna valutazione finora
- Memo Roll Out Workplace and Monitoring Apps Monitoring Apps 1Documento6 pagineMemo Roll Out Workplace and Monitoring Apps Monitoring Apps 1MigaeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Udaan: Under The Guidance of Prof - Viswanathan Venkateswaran Submitted By, Benila PaulDocumento22 pagineUdaan: Under The Guidance of Prof - Viswanathan Venkateswaran Submitted By, Benila PaulBenila Paul100% (2)
- Water Jet CuttingDocumento15 pagineWater Jet CuttingDevendar YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Audit Acq Pay Cycle & InventoryDocumento39 pagineAudit Acq Pay Cycle & InventoryVianney Claire RabeNessuna valutazione finora
- JurnalDocumento9 pagineJurnalClarisa Noveria Erika PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- John Titor TIME MACHINEDocumento21 pagineJohn Titor TIME MACHINEKevin Carey100% (1)