Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Standard Costing 2010 Insights From Companies
Caricato da
rabi_kungleCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Standard Costing 2010 Insights From Companies
Caricato da
rabi_kungleCopyright:
Formati disponibili
FI NANCI AL MANAGEMENT
Standardcosting
Insightsfromleadingcompanies
February2010
ADVI SORY
ExecutiveSummary
Thecurrenteconomiccrisishascreatedsignicantcost
pressuresonbusinesses.Thiscoupledwithforeignexchange,
rawmaterialandcommoditypricevolatilityhasincreased
thefocusontheappropriateness,applicationanduseof
standardcosts.
Historicallymanycompanieshave
tendedtocalculatestandardcosts
annuallybasedonunderlyingcosts
atthetimeofbudgetpreparation.
Intimesofeconomicstabilitythese
standardcostshaveprovidedagood
measureagainstwhichtomanage
thebusinessthroughthefollowing
nancialyear.However,recentvolatility
hasoftenresultedinsignicant
managementtimebeinginvestedin
understandingvariancesagainst
standardcostthataredrivenlargely
bynon-controllablemacro-economic
factorsratherthanthemoreusefuland
value-addactivitiesofunderstanding
andaddressingmanufacturing
efciencyandeffectiveness.
Inthelightofthecurrentclimate
KPMGintheUKhasundertakensome
globalresearchdesignedtohighlight
thecurrenttrendsandissuesaround
standardcosting.Thisdocumentsets
outasummaryofthekeyndingsof
thatresearch.
Allcompaniessurveyedusestandard
costsandvariancestovalue
inventoryforstatutorypurposes,for
managementreportingpurposesand
forperformancemeasurementand
management. Despiteitsprevalence
norespondentsarendingiteasyto
obtaintheinformationandinsight
requiredtosatisfyallthreeof
theseareas.
Keyinsightsandthemesfromthe
surveyinclude:
1. Standardcostingissometimes
over-usedasadecisionmakingtool:
Wherestandardcostingisusedits
limitationsarenotalwaysfully
understoodwithusersoftentreating
itasascienceratherthananart.
Manycompaniesaremovingaway
fromusingstandardcostingastheir
primarytoolforpricingorglobalsupply
chainsourcingdecisions.
2. Comparabilityofstandardcosts
andvariancescanbecompromised
byinconsistentlocalapplicationof
globalmethodologies:
Manygroupshaveoneglobalapproach
butonlyafewcanclaimglobally
consistentapplication.
3.Thebestgroupsinvestin
governanceandorganisation
structurestomaintaintheright
balancebetweenefciencyand
insight:
Centralisedandfocussedvariance
calculationfreesuplocalresources
tofocusonanalysis,interpretation
andaction.
4.Understandingthekey
componentsofastandardproduct
costisvital:
Attimesusinganextractofthe
standardcostcardmaybemore
appropriatetosupportcertainbusiness
decisions,forexampleusingdirect
costsonlytosupportmarginal
productiondecisions.Thebest
companieshadmorethanonecost
perSKUsohadthefunctionalityto
identifyjustdirectcosts,bestever
standard,assetoptimisedstandard,
localcountrystandardandglobal
standardforeachSKU.
5. Increasedeconomicvolatilityis
leadingtomorefrequentstandard
costupdates:
Ingeneralcompaniesareupdating
standardcostsonanannualbasis
howeverthetrendistowardsallowing
morefrequentupdatesinparticular
wheresignicantunderlyingcost
changeshavebeenseen.
6. Policiesandpracticesaround
absorptionofoverheadsinstandard
costsvary:
Recenttrendstowardscentralisation
ofsupportfunctionshaveoftenled
toinclusionofwhatarenowcentral
overheadsinstandardsdespitethelack
ofcontrolovertheseatafactorylevel.
7. Standardcostscanbeusedas
aspirationalperformancetargetsbut
careshouldbetakentoensurethey
donotbakeininefciency:
Inclusionofwastage,scraporunder
utilisationofassetsinstandardscan
leadtoinefciencyontheshopoor
andhencevalueleakage.
8. Effectiveperformance
managementfocuseson
controllablecosts:
Costingeffort,varianceanalysisand
remediationactivityshouldfocuson
thecontrollableelementsof
performance.
9. Levelsofautomationvarybut
spreadsheetsremainrife:
Norespondentsarendingstandard
costingeasyoreffortless,thisisa
resourceintensiveprocess.Leading
groupsarestrugglingtofullyautomate
standardcostinggloballywithinERPs
andstillrelyinpartonspreadsheets.
2010KPMGLLP,aUKlimitedliabilitypartnership,isasubsidiaryofKPMGEuropeLLPandamemberrmoftheKPMGnetworkofindependentmember
rmsafliatedwithKPMGInternationalCooperative,aSwissentity.Allrightsreserved.
Abouttheresearch
KPMGintheUKconductedbothtelephoneandfacetoface
interviewscovering12largelyFortune500manufacturinggroups
duringsummer/autumn2009acrossthefollowingsectors:
Pharmaceuticals
Consumergoods
Industrials
Weconductedaseriesofinterviewsaimedatunderstandingtheoverall
methodologyincludingthepoliciesandprocessesbywhichanumberofglobal
groupsarecalculatingtheirstandardcostsaswellashowthosegroupsareusing
theirstandardcostinginformationeitherasacontrolorotherwise.
Allgroupsinterviewedhadaglobalsupplychain.
Intervieweescomprisedgroupnancedirectors,groupnancialcontrollers,
divisionalnancedirectors,divisionalnancecontrollers,supplychainnance
directorsandtheirdirectreports,andfactorycontrollers.Theinterviewswere
conductedusingastandardstructuredquestionnaire.
Thisdocumentsummarisesthemainndingsagainsteachofninekey
themesidentied.
Background
Standardcostingwhatdowemean?
CIMA,theUKsCharteredInstituteofManagementAccountants
denesstandardcostingasacontroltechniquethatreports
variancesbycomparingactualcoststopre-setstandardsso
facilitatingactionthroughmanagementbyexception.Itgoes
ontofurthersetoutthatastandardcostisacarefully
predeterminedunitcostwhichispreparedforeachcostunit.
Itcontainsdetailsofthestandardamountandpriceofeach
resourcethatwillbeutilisedinprovidingtheserviceor
manufacturingtheproduct.
Costsincludedwithinstandardscomprisedirectmaterialcosts,directlabourcosts
togetherwithindirectoroverheadcosts.Forthepurposesofthispaperwehave
assumedthefollowingdenitions:
1. Costallocationtheprocessofcollectingtogethercertaintypesofoverhead
costrelatedtoproduction,andplannedtobeincludedwithinstandardcosts,
suchthatitcanthenbeeitherdirectlyattributedtoaproductcostorincluded
withinaproductcostsbymeansofanabsorptiontechnique.
2. Costabsorptiontheprocessofapportioningcostsincludingthoseidentied
abovetoindividualstockkeepingunits(SKUs)orproductsonthebasisof
productionactivity.
2010KPMGLLP,aUKlimitedliabilitypartnership,isasubsidiaryofKPMGEuropeLLPandamemberrmoftheKPMGnetworkofindependentmember
rmsafliatedwithKPMGInternationalCooperative,aSwissentity.Allrightsreserved.
Thereisagrowingrecognitionfromall
intervieweesthatmoresophistication
isrequiredaroundtheircosting
methodology.Leadingcompaniesare
usingextractsofthestandardcostcard
mostrelevanttoaparticularbusiness
decisionorcalculatingmorethanone
standardcostcardtodrivedifferent
behaviours,forexample:
1. Useonlydirectcostsformarginal
productiondecisions
2. Buildanalternativecostcard
basedonanassumptionoffull
assetutilisation
3. Buildanalternativecostcard
basedonbesteverachievedcost
FurtherresearchbyCambridge
University,commissionedbyKPMG,
indicatesthatasmuch50percent
ofmanagementdonottrustthe
informationpresentedtothem.
Thisisdueinlargeparttotheuse
madeoftheinformationaswellasthe
governancemodelsdeployedaround
it. Inmanyorganisationsthereis
inconsistentownershipandapplication
ofdenitionsandstandards.Many
globalcompaniesarendingthat
communicationregardingstandards
ismisinterpreted,whichmakes
like-for-likecomparisondifcult,ifnot
impossible.Furtherchallengesare
thattheinformationisnotproduced
throughatrustedchannelandmuch
manipulationofdataisrequired.
Organisationsthathavesolved
thisproblemareabletosignicantly
reducethecostofinformationdelivery,
speedofproductionandimprovethe
usability(referenceKPMGreport
2009:Does your business intelligence
tell you the whole story?).
CIMAcommentary
ThisresearchbyKPMGintostandard
costingillustratestheimportanceof
ensuringtherightinformationisboth
madeavailableandusedeffectively.
Thisprovisionofthemostrelevant
managementinformationandits
properuseispartofamuchwider
issueofsignicancetobusiness
leadersandmanagement
accountants.
TheWalkerReviewwhichscrutinised
corporategovernanceintheUK
nancialsectorhighlightedtheneed
fornonexecutivedirectorstobe
betterinformedandmoreengaged.
Butnonexecutivedirectorscannever
becloseenoughtothebusinessto
becertainoftheirpreciseinformation
needs,nortoinuencemanagements
decisionmakingatanoperational
level.Thisisbecausegood
governanceatboardlevelisa
necessarybutnotasufcient
conditiontoensuregoodperformance
andriskmanagement.
Itisdifcultforthedecisionmakersin
anyorganisationtomaintainakeen
understandingofitscompetitive
position,driversofvalue,potential
risksorevenitsfundamental
economics;itsrevenuesandcosts.
Managementaccountantshave
avitalroletoplayinlteringthe
nancialandothermanagement
information,includingleading
indicatorsandanalysis,aboutposition,
costs,performance,risksand
opportunitiesthatisprovidedto
decisionmakers. Theycanalsohelpto
implementstrategyandcascade
performanceandriskmanagement
throughoutthebusiness. This
percolatoreffectisessentialto
ensuringnotonlygoodgovernance
butalsothepropermanagementof
therminthelongterminterestsof
shareholdersandotherstakeholders.
Theshortcomingsincosting
informationfoundinthisKPMG
surveyillustratewhythispercolator
effect,withinformationlteredupand
inuencecascadeddown,iscrucial.
Inmyopinionitstimetowakeup
andsmellthecoffee.
Leadingorganisationsarealready
transformingtheirnancefunctionsto
bemoreefcientandprovidebetter
informationtoenableevidencebased
decisionmaking. Theyarealso
developinganddeployingmanagement
accountantswhocaninuence
performanceandriskmanagementin
thelongterminterestsofstakeholders.
Organisationsnottransformingtheir
nancefunctioninthiswaycouldbe
puttingtheircompetitivepositionat
risk.
Charles Tilley
Chief Executive CIMA
Keythemesidentiedthrough
ourresearch
1. Standard costing is sometimes
over-used as a decision making tool:
Leadingcompanieshadveryclearly
denedwherestandardcosting
shouldbeusedastheprimarydecision
supporttool,andindeedwhereit
shouldnotbeused.However,a
numberofparticipantswereless
structuredintheirapproachandhad
notformallydenedwhetherstandard
costingshouldbeusedasanindicator
ormeasureforanyorallofinventory
valuation,performancemanagement,
factoryefciency,productsourcing
(bothshortterm/oneoffandlong
term),oneoffcontractpricingdecisions
andoverallpricingdecisions.
Someofthesurveyparticipants
hadmovedawayfromtheuseof
standardcostingasakeymeasure
ofoperationaleffectivenessandlong
termsourcingdecisionspreferring
insteadtouseotheroperationalor
nancialmeasuresandinternaland
externalbenchmarking.
Severalofthesurveyparticipantshad
investedinenhancingthebusiness-
wideunderstandingofthestrengthsof,
limitationsofandalternativesto
standardcostingthroughtrainingand
communications.
KPMGpointofview:
Standardcostingremainsanimportant
partofanydecisionmakingtoolkitbut
itshouldnotbethewholeanswer.
Companiesthatadoptindustrybest
practiceformallydenewherestandard
costingshouldbeusedasaprimary
measureorindicatorfordecision
making,whereitwouldbeappropriate
tousestandardcostsasasecondary
orsupportingmeasureandwhere
standardcostsshouldnotbeused.
2010KPMGLLP,aUKlimitedliabilitypartnership,isasubsidiaryofKPMGEuropeLLPandamemberrmoftheKPMGnetworkofindependentmember
rmsafliatedwithKPMGInternationalCooperative,aSwissentity.Allrightsreserved.
2. Comparabilityofstandardcosts
andvariancescanbecompromised
byinconsistentlocalapplicationofa
globalmethodology:
Oneofthemostefcientapproaches
callsforoneglobalmethodologyand
onegroup-widestandardcostcard
togetherwithalimitednumberof
focussedextractstosupportspecic
deneddecisions.
Thelevelatwhichparticipantsdene
theirstandardcostmethodologyvaries,
withsomegroupssimplysettingan
overallgroup-widepolicytosay,fully
absorbfactoryoverheads,others
deningspecicallyonalinebyline
basisthecoststobeincludedwithin
standardsandthemethodbywhich
toincludethem.
Anumberofgroupsdenedone
overheadallocationorabsorption
methodhoweverothersleftthe
decisionastothemethodusedtothe
localfactorycontrollersdiscretion.
KPMGpointofview:
Consistentdenitionsarenotenough
inthemselves.Todelivervaluable
informationtheyshouldbeapplied
consistentlyatalocallevel.
Organisationsshouldseektoclearly
denetheitemstobeincludedin
standardcostandtheallocationand
absorptionmethodstobeusedfor
overheadsandthenputinplace
governancestructurestoensure
dataintegrityismaintained.
3.Thebestgroupsinvestin
governanceandorganisation
structurestomaintaintheright
balancebetweenefciency
andinsight:
Oneparticipanthadformedaglobal
costingcounciltosetpolicy,ensure
consistencyandopineonitemsthat
shouldorshouldnotbeincluded
withinstandards.
Oneofthegroupssurveyedhadmoved
thebackofceanalysisactivityrelated
tostandardcostsandvarianceanalysis
intohighervaluesharedservice
centresleavingonlythevalueadding
analysis,interpretationandresponse
activityatthefactory.
KPMGpointofview:
Centralisedgovernanceand
centresofexcellencefocussedon
calculatingvariancescanhelpreduce
inconsistenciesandfreeuplocal
factorybasedstafftounderstandand
addresstheissueshighlightedatthe
factorylevel.
4. Understandingthekey
componentsofastandardproduct
costisvital:
Halfofthepopulationsurveyedhad
denedmorethanonetypeofcostfor
certainSKUsorproducts.Asmall
numberoftheparticipantshaddened
theseadditionalcostsasasliceor
carveoutsfromtheirstandardcost
cards;thesedenedslicesofcostare
usedtosupportmarginalproduction
decisions,measureperformanceand
assistwithlongandshortterm
sourcingdecisions.
KPMGpointofview:
Flexibilityisakeyelementhelping
toensuretherightinformationis
usedtosupporttherightdecisions.
Themosteffectiveorganisations
stratifytheirbusiness,productsor
decisionsanddeterminewhereit
wouldbevaluablefordecisionmaking
purposestohavemorethanonecost
typeperSKU.
5. Increasedeconomicvolatilityis
leadingtomorefrequentstandard
costupdates:
Manygroupsupdatestandardcostson
anannualbasis;increasinglygroupsare
providingtheoptionformorefrequent
updateswhennecessary.
Onlyoneofthesurveyparticipants
updatedstandardcostsmore
frequentlythanannually,inthiscase
quarterly.Onegrouphadchosennotto
updatestandardsfortwoyearsgiven
thetimeandresourcerequirementsof
theupdateprocess.
Inthecurrenteconomicclimateseveral
groupswerendingthatanin-year
updatehadbeenorwasexpectedto
benecessaryreectingcommodity
rawmaterialpricechanges,foreign
exchangemovementsand/orpartial
orfullfactoryclosures.In-yearupdates
couldbedealtwithonagroup-wideor
factoryspecicbasis.
KPMGpointofview:
Standardcostsshouldbeupdatedat
leastannuallyandmorefrequentlyin
timesofeconomicturbulence.
2010KPMGLLP,aUKlimitedliabilitypartnership,isasubsidiaryofKPMGEuropeLLPandamemberrmoftheKPMGnetworkofindependentmember
rmsafliatedwithKPMGInternationalCooperative,aSwissentity.Allrightsreserved.
Inthecurrenteconomicclimate
provisionshouldbemadeforin-year
updates,inparticularwherethereare
signicantcommoditypriceandforeign
exchangemovementsorchangesto
theshapeofthebusiness.Timeboxing
theupdateprocessprovidesameans
oflimitingthedrainonresources
encouragingan80/20approach
focussingactivityonmaterialitems.
6. Policiesandpracticesaround
absorptionofoverheadsinstandard
costsvary.Whatcostsshouldyou
includeinstandardsandhowfully
absorbedshouldyoube?
Anumberofparticipantsallowed
orrequiredtheinclusionofcertain
centraloverheadssuchasshared
servicecentrecosts.Manyspecied
thatonlyfactoryleveloverheadscould
beabsorbedintostandardshoweveron
furtherenquiryexceptionstothisrule
wereoftenfound.
Twoparticipantschosenottoabsorb
overheadsduringtheyearbutinstead
toincludesuchcostsininventory
valuationbywayofayearend
adjustment.
Allgroupschosetoadoptanassetlife
ratherthanproductlifeapproachtothe
inclusionofdepreciationinstandards.
Whilepuredevelopmentcostswere
excludedfromstandardcostbyall
participantsanumberdidincludethe
costsofcertainproductdevelopment
activity.
Therewasnocleartrendinthe
treatmentoffreightcostswhen
calculatingstandardcostfactory
specicbasis.
KPMGpointofview:
Thelevelofabsorptioninstandard
costsisdrivenbyacompanysculture
andbehavioursaroundcost
management.
Someformofallocationandabsorption
ofoverheadattheSKU,productor
factorylevelispreferableintermsof
thedaytodaymanagementofyour
overallinventorylevels.Howeverwe
supporttheexclusionofcertaincosts
indenedsituationsaspartofthe
slicinganddicingofyourstandard
costcard.Thekeyishaveclear
denitionsandconsistentapplication
acrosstheorganisationtodeliver
valuableinformation.Wherecostsare
notfullyabsorbeditisveryimportant
thatnancecommunicatewith
thosemakingdecisionssotheycan
understandwhatthestandardcost
includesandexcludes.
7. Arestandardcostsaspirational
performancetargetsordotheybake
ininefciency?e.g.theinclusionof
wastage,scraporunderutilisation
ofassetsinstandardscanleadto
inefciencyontheshopoorand
hencevalueleakage:
Anumberofparticipantsusetheir
standardcostingtodriveperformance
improvement,choosingtoset
standardsatatargetbestever
achievedorassetoptimisedlevel.
Oneparticipantfoundthatinusing
standardcostsasatargettheywereat
timesdrivingthewrongbehaviourson
theshopoor.Insteadofstrivingfor
continuouscostreduction,oncea
targethadbeenachievedworkers
continuedtoaimtomeetthattarget
ratherthanexceed.
KPMG point of view:
Signicantshareholdervaluecanleak
throughunderutilisedassetsand
oracceptingnormalwastagelevels.
Overperiodsoftimeinsetting
standardsthesecoreassumptions
shouldbechallenged.Whereused
correctlyhavingmorethanonecostper
SKUorusingbesteverstandardcan
drivebehaviourstoimproveefciency.
8. Effectiveperformance
managementfocusesoncontrollable
costs:
Anumberoftheparticipantsmake
bonusorperformanceadjustments
toremovethenon-controllable
elementsincludedwithinstandard
costsandvarianceanalysiswhen
assessingindividual,factoryor
regionalresults.
Adjustmentsareoftenmanualand
madeonanadhocorone-offbasis
makingperformancecomparisons
acrosspeople,productsandsitesless
meaningfulandaddingcomplexityto
theperformancemanagementprocess.
KPMG point of view:
Focusingcostingeffort,variance
analysisandremediationactivityonthe
controllableelementsofperformance
isvital,thisenablesmanagement
focustoshiftvarianceanalysisto
understandingandactingratherthan
calculationandanalysis.
9. Levelsofautomationvarybut
spreadsheetsremainrife:
Whilemanyofthegroupsincluded
intheresearchhadgroup-wideor
regionalERPsystemsveryfew
benettedfromsignicantautomation
ofstandardcostingandvariance
analysis.Themajorityofgroups
continuetorelyonasignicantnumber
ofspreadsheetstosupportthisactivity.
KPMG point of view:
Automationoftheendtoendstandard
costingandvarianceanalysisprocessis
noteasyandthisisusuallyaresource
intensiveprocess.Effective,value
adduseofresourcesandappropriate
governanceandcontrolofoff-system
calculationsisimportantinderiving
valueformoneyfromyourstandard
costingprocess
2010KPMGLLP,aUKlimitedliabilitypartnership,isasubsidiaryofKPMGEuropeLLPandamemberrmoftheKPMGnetworkofindependentmember
rmsafliatedwithKPMGInternationalCooperative,aSwissentity.Allrightsreserved.
KPMGs Business Intelligence framework
KPMG Framework Leading Practice
Business Strategy
Alignment
Align information requirements to strategic objectives
Provide clarity of the role of standard costs in decision making
Governance Dene rigid process with clear guidelines via global
costing council
Develop one standard policy that is applied consistently
across all global divisions
Use shared services and centres of excellence to produce
standard reports and variance analysis
Performance
Management Process &
Reporting
Automate data collection
Concentrate on understanding and corrective action rather
than collection and analysis
Integrated Information
Management
Gain clarity and agreement on data denitions globally
Remove data duplication
Ensure there is dimensional protability matching revenue
with costs
Business Intelligence
Platform
Consolidate tools and ensure application ability is maximised
Exploit software as a service
Infrastructure Standardise
Summary
Standardcostingisanimportant
nancialtoolthatoftenisusedto
determinedimensionalprotability
e.g.theprotbycustomer,byproduct
andbychannel.
Standardcostingneedstobe
consideredinawiderframework
ofbusinessintelligencewhere
companiesareseekingtoimprove
performanceandcompetitiveness.
Ensuringthattherightinformationis
deliveredtotherightpeopleattheright
timeandfocussingonhowstrategies
andoperationsareconnectedcan
improvestrategiccompetitveness.
KPMGrmshavedevelopeda
sixlayeredbusinessintelligence
framework.Ourprofessionalshave
foundthatsomecompanieshave
failedtoapplysufcientresource
andinvestmenttoeachlayerona
sustainablebasis.
Researchhasdemonstratedthatasmuchas50percentofmanagement
donottrusttheinformationpresentedtothem.Addressingtherelevance,
timelinessandconsistencyofyourstandardcostinformationisarststep
onthepathwaytoenhancingyourbusinessintelligence.
Special thanks
Wearegratefultothesurveyparticipantsfortheirvaluabletimeandinsights
wewouldalsoliketothankthefollowingKPMGcontributors:SimonOsmer,
RachelWoodsandJeremyThomas
2010KPMGLLP,aUKlimitedliabilitypartnership,isasubsidiaryofKPMGEuropeLLPandamemberrmoftheKPMGnetworkofindependentmember
rmsafliatedwithKPMGInternationalCooperative,aSwissentity.Allrightsreserved.
kpmg.co.uk
Formoreinformation
pleasecontact:
Simon Osmer
Partner, KPMG in the UK
+44(0)7711473241
simon.osmer@kpmg.co.uk
Herman Heyns
Partner, KPMG in the UK
+44(0)2073114478
herman.heyns@kpmg.co.uk
Jeremy Thomas
Director, KPMG in the UK
+44(0)2073118237
jeremy.thomas@kpmg.co.uk
Rachel Woods
Principal advisor, KPMG in the UK
+44(0)2073114276
rachel.woods@kpmg.co.uk
Theinformationcontainedhereinisofageneralnatureandisnotintendedtoaddressthecircumstancesofany
particularindividualorentity.Althoughweendeavortoprovideaccurateandtimelyinformation,therecanbeno
guaranteethatsuchinformationisaccurateasofthedateitisreceivedorthatitwillcontinuetobeaccurateinthe
future.Nooneshouldactonsuchinformationwithoutappropriateprofessionaladviceafterathoroughexamination
theparticularsituation.
of
2010KPMGLLP,aUKlimitedliabilitypartnership,is
asubsidiaryofKPMGEuropeLLPandamemberrm
oftheKPMGnetworkofindependentmemberrms
afliatedwithKPMGInternationalCooperative,
aSwissentity.Allrightsreserved.Printedinthe
UnitedKingdom.
KPMGandtheKPMGlogoareregisteredtrademarks
ofKPMGInternationalCooperative,aSwissentity.
DesignedandproducedbyKPMGLLP(UK)s
DesignServices
Publicationname:Standardcosting
Publicationnumber:RRD-176583
Publicationdate:February2010
Printedonrecycledmaterial.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- 005-012 Fuel Injection Pumps, In-Line: InstallDocumento14 pagine005-012 Fuel Injection Pumps, In-Line: InstallMuhammad Ishfaq100% (3)
- MF 5460Documento586 pagineMF 5460Maximiliano Hitschfeld100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Stress Relief PrescriptionDocumento8 pagineThe Stress Relief PrescriptionRajesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Scor Overview v2 0Documento62 pagineScor Overview v2 0Grace Jane Sinaga100% (1)
- Curtis E50 Pump Parts ListDocumento8 pagineCurtis E50 Pump Parts ListrobertNessuna valutazione finora
- HydrodynamicsDocumento122 pagineHydrodynamicsIustin Cristian100% (2)
- Ventilation Plan For Confined Space EntryDocumento9 pagineVentilation Plan For Confined Space EntryMohamad Nazmi Mohamad Rafian100% (1)
- Working Capital Management Finance Project MbaDocumento67 pagineWorking Capital Management Finance Project Mbaimran shaikh67% (3)
- Cash Management ProjectDocumento74 pagineCash Management ProjectDinesh Kumar Karur77% (78)
- Cash Management ProjectDocumento74 pagineCash Management ProjectDinesh Kumar Karur77% (78)
- Cash Management ProjectDocumento74 pagineCash Management ProjectDinesh Kumar Karur77% (78)
- Project On Demat Account FinalDocumento74 pagineProject On Demat Account Finalgoyalraju073% (48)
- Project Report On Child Labour in India 2Documento44 pagineProject Report On Child Labour in India 2Manza DeshmukhNessuna valutazione finora
- IfrsDocumento1 paginaIfrsrabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- YouTube/Scholarszilla Reduced Syllabus of OCMDocumento2 pagineYouTube/Scholarszilla Reduced Syllabus of OCMRahul SinghNessuna valutazione finora
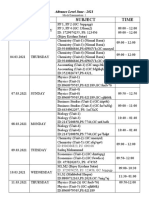
- STD: 12 Subject: OCM Marks: 80 Time: 3 HrsDocumento2 pagineSTD: 12 Subject: OCM Marks: 80 Time: 3 Hrsrabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Insurance?Documento1 paginaWhat Is Insurance?rabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- K. M. E. S. English Medium High School & Jr. College.: Subject Class byDocumento12 pagineK. M. E. S. English Medium High School & Jr. College.: Subject Class byrabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- ResearchFile 3579-13-6Documento10 pagineResearchFile 3579-13-6rabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- Zara Terms and Conditions en - IN 20190115 PDFDocumento12 pagineZara Terms and Conditions en - IN 20190115 PDFNancygirdherNessuna valutazione finora
- .Documento24 pagine.rabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- ResearchFile 3579-13-6Documento10 pagineResearchFile 3579-13-6rabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- Public DepositDocumento1 paginaPublic Depositrabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- AuditingDocumento86 pagineAuditingrabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study 2Documento2 pagineCase Study 2rabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Integrated vs Non-Integrated Accounting SystemsDocumento20 pagineUnderstanding Integrated vs Non-Integrated Accounting Systemsrabi_kungle0% (2)
- Introduction On Service Tax-Negative List, Levy of Service Tax, ExemptionDocumento4 pagineIntroduction On Service Tax-Negative List, Levy of Service Tax, Exemptionrabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- Semester - Iv Project Report On "Sources of Finance" Subject: Advanced Financial Management SubmittedtoDocumento5 pagineSemester - Iv Project Report On "Sources of Finance" Subject: Advanced Financial Management Submittedtorabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Strategy of PepsiDocumento1 paginaMarketing Strategy of Pepsirabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- Fati FM Main 17Documento20 pagineFati FM Main 17rabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- Semester - Iii Project Report On "Cost of Capital" Subject: Advanced Financial Management Submitted ToDocumento6 pagineSemester - Iii Project Report On "Cost of Capital" Subject: Advanced Financial Management Submitted Torabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- Index: SR - No Particulars Pag. NODocumento4 pagineIndex: SR - No Particulars Pag. NOrabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- H DIL AuditDocumento55 pagineH DIL Auditrabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- Gfey RiyDocumento1 paginaGfey Riyrabi_kungleNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Strategy of WIPRO by SrinivasDocumento19 pagineMarketing Strategy of WIPRO by Srinivashisri6350100% (5)
- Corporategovernanceproject 110201062752 Phpapp01Documento26 pagineCorporategovernanceproject 110201062752 Phpapp01Vikranth CmNessuna valutazione finora
- Retail ProjectDocumento33 pagineRetail Projectshah faisal0% (1)
- Anagrams in Enhancing The Learner's Vocabolary in Filipino Language Using WordwallDocumento19 pagineAnagrams in Enhancing The Learner's Vocabolary in Filipino Language Using WordwallJARYL PILLAZARNessuna valutazione finora
- Cahyadi J Malia Tugas MID TPODocumento9 pagineCahyadi J Malia Tugas MID TPOCahyadi J MaliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Prof BlankoDocumento11 pagineDesign Prof BlankoAousten AAtenNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper Velocity String SPE-30197-PADocumento4 paginePaper Velocity String SPE-30197-PAPablo RaffinNessuna valutazione finora
- Curios AllianceDocumento32 pagineCurios AllianceyesterowNessuna valutazione finora
- Power and Energy Meters: Model No. Remarks Sl. WH WH W Va Var 1. ET3021 ET4021Documento1 paginaPower and Energy Meters: Model No. Remarks Sl. WH WH W Va Var 1. ET3021 ET4021Ram KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- English Test 03Documento6 pagineEnglish Test 03smkyapkesbi bjbNessuna valutazione finora
- UAE Branch AGM 2018/19 ElectionsDocumento6 pagineUAE Branch AGM 2018/19 ElectionsDavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Mock Examination Routine A 2021 NewDocumento2 pagineMock Examination Routine A 2021 Newmufrad muhtasibNessuna valutazione finora
- Sae Technical Paper Series 2015-36-0353: Static and Dynamic Analysis of A Chassis of A Prototype CarDocumento12 pagineSae Technical Paper Series 2015-36-0353: Static and Dynamic Analysis of A Chassis of A Prototype CarGanesh KCNessuna valutazione finora
- Series Portable Oscilloscopes: Keysight DSO1000A/BDocumento15 pagineSeries Portable Oscilloscopes: Keysight DSO1000A/BNestor CardenasNessuna valutazione finora
- Toms2003 A Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of The Periodontal Ligament Under Orthodontic Tooth LoadingDocumento9 pagineToms2003 A Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of The Periodontal Ligament Under Orthodontic Tooth LoadingPuttnaree NiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Snel White Paper 2020Documento18 pagineSnel White Paper 2020Zgodan NezgodanNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Overview PsasDocumento19 pagine5 Overview Psasعلي صالحNessuna valutazione finora
- OAF Hello Word Page PDFDocumento20 pagineOAF Hello Word Page PDFNaveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 NEC Table of ContentsDocumento124 pagine2017 NEC Table of ContentsFaheem PP13Nessuna valutazione finora
- ZF 4hp14 - 2Documento9 pagineZF 4hp14 - 2Miguel BentoNessuna valutazione finora
- Components of GlobalizationDocumento26 pagineComponents of GlobalizationGiyan KhasandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Chapter 2 Original TestDocumento6 paginePhysics Chapter 2 Original TestJanina OrmitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Project 4 FinalDocumento2 pagineProject 4 Finalapi-307253935Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5: Attention and PerformanceDocumento10 pagineChapter 5: Attention and Performancerebela29Nessuna valutazione finora
- Duplichecker Plagiarism Report 3Documento3 pagineDuplichecker Plagiarism Report 3Mushfiqur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam - Movie Analysis of Respeto - Sec90 - K. Dela CruzDocumento9 pagineFinal Exam - Movie Analysis of Respeto - Sec90 - K. Dela CruzKylie Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora