Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chapter 7
Caricato da
manali_thakarCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 7
Caricato da
manali_thakarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 1
Strategic HR Planning
Lectures slides for Chapter 7
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 2
Objectives
Objectives of this lecture is to understand
meaning of strategic HR plan, its
difference from conventional HR plan and
what managerial actions required for
executing such plans in an organization.
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 3
What is HR planning?
Conventional meaning:
Estimation of demand for manpower in
various departments or divisions and
assessment of manpower available in both
internal and external markets.
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 4
Strategic HR Planning and its
goals
Strategic planning of human resources tries to
estimate demand for and availability of
competencies to create and maintain companys
long run competitive advantage.
Since sources of competitive advantage are
different for companies operating in different
industries, so the goals and actions for Strategic
HR planning are expected to be different for
organizations operating in different industries.
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 5
Classifications of Organization
Based on the goals of Strategic HR plans
are pursued, the industrial organizations
can be classified into four groups:
Regulatory compliance,
Strategy Implementation,
Strategy moderation
Strategy Integration
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 6
Strategic plan to achieve
regulatory compliance
In these industries, there is no occupational
entry barrier against employees moving from
one area to another. Naturally market supply is
plenty. In these industries HR are mainly to
ensure regulatory compliance e.g. minimum
wage law, equal remuneration acts, employment
reservation etc.
Example:
Agricultural employment, Govt. employment for low
level jobs.
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 7
Strategic plan to Implement
Market Driven Business Strategy
Source of competitive advantage :
Owner ship of tangible asset.
Business and HR plans are pursued comes for getting
maximum returns from investment in tangible assets.
These are physical assets driven businesses. Manpower
acquisition and deployment are more for making use of
these assets. Large scale manufacturing business e.g.
Motor cars, Tractors.
Example:
A tractor company having plants in South and North India. The
market for these two areas may be growing at different rates
which may require advance plan for manpower transfer from one
plant to another. Identifying employees who are willing to move
from their existing location is important part of the planning
activities.
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 8
Strategic HR Plan for Moderation
of Business Strategy
Industries where source of competitive advantage is still
ownership of tangible assets but importance of support
service areas is growing and the company needs lot
more employees in support areas who worked in primary
areas. Source of competitive advantage is fast moving
away from tangible assets to intangible assets areas of
employee skill and competencies.
Example:
Most big plant based manufacturing companies come under this
group. Due to product standardization, more jobs are emerging
in support service areas.
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 9
Strategic HR plan for Integration
Source of competitive advantage:
Employee skill and organizational competencies.
Investment in tangible assets are made to
enhance returns from the use of intangible
assets particularly the employee competencies
and commitments.
Example:
Highly skill driven service business e.g. Health care,
banking, insurance. Non-standard products.
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 10
What is an Integrated Strategic HR Plan?
It means deciding on the hr functional
requirements of recruitment and selection, off
the job and on the job training and
development, performance management,
compensation and reward system to ensure
availability of manpower both in terms of
number as well competency to maintain
company competitive advantage over its
competitors.
What does it imply in terms of skill and
expertise of an hr planner?
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 11
HR Plan and HR system: A
simple system
Business
Strategy
HR
Planning
Acquisition
T & D
Performance
evaluation
Selection
Incentive
Promotion
T & D
Union
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 12
Factors Affecting Integration
Environmental instability;
Structural Change in Industry due to
Diversification in forward or backward sides of
the industry;
Skill Shortage;
Changing Composition of Internal Work Force;
Merger & Acquisition;
Compensation;
Status of top HR managers.
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 13
Activities for HR planning
Understanding company business;
Understanding core and support functions;
Understanding company strategy;
Understanding current stock of competencies at
functional level;
Understanding employee career expectations;
Estimating the requirements of competencies at
functional levels;
Estimating the internal flow of competencies at different
levels;
Relating the internal flow with the company HR policies
and practices;
Understanding external availability of competencies and
their flow.
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 14
What does it mean in terms of
Managerial action?
It means getting
An estimate of manpower requirements both number
and competency in different departments at different
times in future years;
An estimate of availability of manpower in terms of
number and competency from internal market of the
company;
Suggest remedial action both in terms of internal
developmental and external acquisition activities for
closing the demand supply gap.
Suggest remedial actions in the areas of HR policies
to reduce demand supply gaps in future.
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 15
Estimating Demand for
Manpower at different times
Knowing the company manpower utilization in different departments
and divisions in recent past;
Knowing the skill set required for meeting the service demands of
different departments and divisions in recent past;
Knowing the company core and support functions for doing the
business;
Knowing company business strategy;
Knowing company Human resource strategy;
Converting business strategy and human resource strategy into
requirements of positions and skill set. As a first approximation you
may use company past practice as a starting point and then adjust
one variable at a time for the required change in business strategy
and human resource strategy.
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 16
Estimating Internal Availability of
manpower and competency
Internal demography: Education, work
experience and age distribution in different
departments;
Movement in internal hierarchy: eligibility
conditions and promotion rates;
Horizontal transfer policy across departments
and divisions;
External loss by way of turnover from different
departments and divisions;
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 17
Closing demand supply gap
Estimate demand supply gap at different critical
functions, departments and ranks;
Consider remedial steps by way of internal development
through ranks and through external developmental
activities;
Identify ranks with large demand-supply gaps and look
for cause in areas e.g. poor recruitment and selection
and placement system,lack of developmental
opportunity, poorly designed career management
system, poorly administered performance management
system, poorly designed reward system
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 18
Factors affecting external flow
Company Hr policies and practices;
Company image as an employer;
Popularity of local area as a place to live
and work for families;
External supply of human capital
development institutes.
Strategic HRM: Pulak Das 19
Key Learning
An integrated strategic hr plan is used to
support maintenance of company
competitive advantage. It not only
estimates manpower and competency
demands and their internal availabilities
but also evaluates other hr functions that
affect the availability of manpower and
competencies at different times.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Rudhiprayog Ane Kahevat Sangrah - GujaratiDocumento389 pagineRudhiprayog Ane Kahevat Sangrah - GujaratiHarshad Ashodiya Interior Designer57% (14)
- McCubbin, H. I., & Patterson, J. M. (1983) - The Family Stress Process. Marriage & Family Review, 6 (1-2), 7-37Documento33 pagineMcCubbin, H. I., & Patterson, J. M. (1983) - The Family Stress Process. Marriage & Family Review, 6 (1-2), 7-37Gimena MottaNessuna valutazione finora
- Build Size and Aesthetics with the 6-Week Hype Gains Hypertrophy ProgramDocumento21 pagineBuild Size and Aesthetics with the 6-Week Hype Gains Hypertrophy ProgramDanCurtis100% (1)
- Understanding Strategy and Strategic ManagementDocumento138 pagineUnderstanding Strategy and Strategic ManagementShivam JadhavNessuna valutazione finora
- Lines WorksheetDocumento3 pagineLines WorksheetJuzef StaljinNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Resource Management: Mcqs With AnswersDocumento25 pagineHuman Resource Management: Mcqs With AnswersOwais SamNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions 1 17 PDFDocumento326 pagineMultiple Choice Questions 1 17 PDFDedeepya MurathotiNessuna valutazione finora
- Management 101: Understanding Organizational Leadership: What's The Difference Between Leadership vs. Management?Documento9 pagineManagement 101: Understanding Organizational Leadership: What's The Difference Between Leadership vs. Management?kiran zahraNessuna valutazione finora
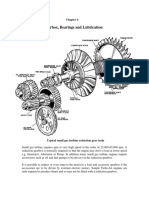
- Small Gas Turbines 4 LubricationDocumento19 pagineSmall Gas Turbines 4 LubricationValBMSNessuna valutazione finora
- RetrogradeJupiter ChangeofPlaceAndIncreaseinIncomeandStatusColorDocumento5 pagineRetrogradeJupiter ChangeofPlaceAndIncreaseinIncomeandStatusColormanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Short Answer Questions: Chapter 9 Ethics & StrategyDocumento5 pagineShort Answer Questions: Chapter 9 Ethics & Strategysiaw_ling_1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Human Resource Management Old QuestionsDocumento5 pagineHuman Resource Management Old QuestionsAbelNessuna valutazione finora
- 50 MCQs JOB ANALYSIS (Syed Muhit Hasan ID 202020234)Documento14 pagine50 MCQs JOB ANALYSIS (Syed Muhit Hasan ID 202020234)KaziTõmãl100% (1)
- Impact of Talent Management On Organisation CultureDocumento5 pagineImpact of Talent Management On Organisation CultureEvan OctviamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Outline Performance Mnagement and AppraisalDocumento4 pagineCourse Outline Performance Mnagement and AppraisalFazi Rajput100% (2)
- HRM Is Concerned With The - in The OrganisationDocumento6 pagineHRM Is Concerned With The - in The OrganisationPratiksha PatilNessuna valutazione finora
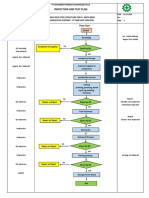
- Inspection and Test Plan: Flow Chart Start IncomingDocumento1 paginaInspection and Test Plan: Flow Chart Start IncomingSinden AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Training And Development A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDa EverandTraining And Development A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Terminal Tractors and Trailers 6.1Documento7 pagineTerminal Tractors and Trailers 6.1lephuongdongNessuna valutazione finora
- Egg Pasteurization Manual 1969Documento54 pagineEgg Pasteurization Manual 1969Tomas MuzzioNessuna valutazione finora
- Thetwelveyearcycleofanastrologicalsuperstition by KNRao BWDocumento8 pagineThetwelveyearcycleofanastrologicalsuperstition by KNRao BWPrasan NandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcqs On ModelsDocumento23 pagineMcqs On ModelsDarshitNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance DimensionsDocumento6 paginePerformance DimensionsSrinivas R. Khode0% (1)
- Managing Teams MCQSDocumento47 pagineManaging Teams MCQSABb0tTabAd Murshad kie batianNessuna valutazione finora
- 207 CFM MCQ 28 CFN MCQDocumento46 pagine207 CFM MCQ 28 CFN MCQSuyog RaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Organizational Structures and International HRM ChallengesDocumento27 pagineOrganizational Structures and International HRM Challengesarja2324Nessuna valutazione finora
- Course Name Prepare Don Course Code Credit Hours Course Prereq. Code Revised On Course Type Program Semester Instructor: Course DescriptionDocumento8 pagineCourse Name Prepare Don Course Code Credit Hours Course Prereq. Code Revised On Course Type Program Semester Instructor: Course DescriptionSaad OsmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- MBE PPT Unit IV Anna Universit Syllabus 2009 RegulationDocumento16 pagineMBE PPT Unit IV Anna Universit Syllabus 2009 RegulationstandalonembaNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality Practices & HRM LinkageDocumento64 pagineTotal Quality Practices & HRM Linkageharshada700Nessuna valutazione finora
- Personality, Leadership and Stress QuizDocumento9 paginePersonality, Leadership and Stress QuizTeena SaharanNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Human Resource Mgmt. CH 1 Pulak DasDocumento15 pagineStrategic Human Resource Mgmt. CH 1 Pulak DasPareen Joshi100% (2)
- BA 5019 SHRM 2 Marks Q & ADocumento22 pagineBA 5019 SHRM 2 Marks Q & AMathewNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are The Steps Involved in Manpower PlanningDocumento1 paginaWhat Are The Steps Involved in Manpower PlanningMeeka Singhal100% (2)
- Multiple Choice Questions 1 17 PDFDocumento326 pagineMultiple Choice Questions 1 17 PDFSuma Latha Naidu100% (1)
- TQM MCQs on Employee EmpowermentDocumento2 pagineTQM MCQs on Employee EmpowermentMuhammad Talha100% (1)
- Organizational Change: Perspectives On Theory and Practice: Chapter 1: IntroductionDocumento12 pagineOrganizational Change: Perspectives On Theory and Practice: Chapter 1: IntroductionAisha ShafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 4 Defining Performance and Choosing A Measurement ApproachDocumento2 pagineCHAPTER 4 Defining Performance and Choosing A Measurement ApproachDeviane CalabriaNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 2 HRP and HRDDocumento9 pagineMODULE 2 HRP and HRDTitus ClementNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Sharmistha Bhattacharjee 470 Research Article Oct 2011Documento18 pagine2 Sharmistha Bhattacharjee 470 Research Article Oct 2011Deepti PiplaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Sarhad University, Peshawar: (Distance Education)Documento18 pagineSarhad University, Peshawar: (Distance Education)Haris KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 03Documento47 pagineChapter 03HAMAD100% (1)
- Strategic Recruitment and Selection ProcessDocumento5 pagineStrategic Recruitment and Selection ProcessAli A. KhokhArNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Human Resource Management Review and Discussion Questions (General)Documento3 pagineFundamentals of Human Resource Management Review and Discussion Questions (General)alexander100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Strategy and Human Resources Planning: Multiple ChoiceDocumento19 pagineChapter 2 Strategy and Human Resources Planning: Multiple Choicedingdong ditch100% (1)
- Role Negotiation Yields Cooperation at Bokaro Steel PlantDocumento22 pagineRole Negotiation Yields Cooperation at Bokaro Steel PlantRaunak Kaushik0% (2)
- HRM AssignmentDocumento61 pagineHRM AssignmentSahanNivantha0% (1)
- TQMDocumento4 pagineTQMMatilda100% (1)
- IHRM Sec 2 - Organizational ContextDocumento24 pagineIHRM Sec 2 - Organizational ContextPrem Joseph0% (1)
- Que Paper of Strategic HRM (SYMMS) Sem IVDocumento3 pagineQue Paper of Strategic HRM (SYMMS) Sem IVDivyeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Questionnaire On Learning N DevelopmentDocumento4 pagineQuestionnaire On Learning N DevelopmentsptharunNessuna valutazione finora
- IMC Imp - QuestionsDocumento3 pagineIMC Imp - QuestionsShailendra SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Organizational Change: Perspectives On Theory and Practice: Chapter 2: Causes of ChangeDocumento16 pagineOrganizational Change: Perspectives On Theory and Practice: Chapter 2: Causes of ChangeAisha Shafiq100% (1)
- Chapter 1Documento6 pagineChapter 1Zeeshan Shaukat100% (2)
- HRM Assignment Questions (Human Resources Management)Documento21 pagineHRM Assignment Questions (Human Resources Management)kvvalencia2128valNessuna valutazione finora
- Labour Welfare OfficerDocumento7 pagineLabour Welfare OfficerashishNessuna valutazione finora
- Men Material Money MachineryDocumento34 pagineMen Material Money MachineryPRATIK MUKHERJEENessuna valutazione finora
- Assessing HRD NeedsDocumento11 pagineAssessing HRD NeedsMd.Shakhawat HossainNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Performance Management and Strategic PlanningDocumento3 pagineChapter 3 Performance Management and Strategic PlanningDeviane CalabriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Statistic and Mathametics in Business DecisionmakingDocumento5 pagineRole of Statistic and Mathametics in Business DecisionmakingPrajot Morajkar75% (4)
- Chapter 1-Human Resource Management in Organizations: Multiple ChoiceDocumento24 pagineChapter 1-Human Resource Management in Organizations: Multiple ChoiceEarl Joshua SampagaNessuna valutazione finora
- HRIS functions benefits organizationDocumento2 pagineHRIS functions benefits organizationCharmi PoraniyaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On Employee Welfare Measures in BhelDocumento19 pagineA Study On Employee Welfare Measures in BhelLovely ashwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Supervisory Support - HR Case StudyDocumento27 pagineSupervisory Support - HR Case StudyVijay MunirajNessuna valutazione finora
- Emerald List of JournalsDocumento10 pagineEmerald List of JournalsKuldeep Singh BidhuriNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 3 Stra IntentDocumento14 pagineCH 3 Stra IntentAnjali Angel ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Recruitment Selection Placement Induction ProcessDocumento28 pagineRecruitment Selection Placement Induction Processvidisha sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz No 1 (HRM)Documento2 pagineQuiz No 1 (HRM)Aiman KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 Foundations of Group Behavior: Organizational Behavior, 15e (Robbins/Judge)Documento21 pagineChapter 9 Foundations of Group Behavior: Organizational Behavior, 15e (Robbins/Judge)Nino Lomidzee100% (1)
- International Strategic Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandInternational Strategic Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Public Service Motivation A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDa EverandPublic Service Motivation A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Digital MarketingDocumento11 pagineFundamentals of Digital Marketingmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Digital MarketingDocumento11 pagineFundamentals of Digital Marketingmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Letter FormatDocumento1 paginaReference Letter Formatmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- PG DIPLOMA IN DIGITAL MARKETING: KEY BENEFITS OF PPCDocumento10 paginePG DIPLOMA IN DIGITAL MARKETING: KEY BENEFITS OF PPCmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- IELTS Task 1 Fundamentals Improve Your ScoreDocumento3 pagineIELTS Task 1 Fundamentals Improve Your Scoreabdul kuddus100% (1)
- AsdDocumento1 paginaAsdmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- DivisionDocumento1 paginaDivisionmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Sop2 PDFDocumento4 pagineSample Sop2 PDFDhrUv GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rangoli ColoursDocumento1 paginaRangoli Coloursmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Documents Married ApplicantDocumento7 pagineList of Documents Married Applicantmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- National Products Classification Code For Services in IndiaDocumento92 pagineNational Products Classification Code For Services in Indiakalanemi0% (2)
- Sports Safety: Related Kidshealth LinksDocumento10 pagineSports Safety: Related Kidshealth Linksmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Rangoli ColoursDocumento1 paginaRangoli Coloursmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocumento2 pagineNew Microsoft Office Word Documentmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocumento1 paginaNew Microsoft Office Word Documentmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocumento2 pagineNew Microsoft Office Word Documentmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- GPSC Class-1-2 Main 2002 Exam PaperDocumento11 pagineGPSC Class-1-2 Main 2002 Exam Papermanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Rangoli ColoursDocumento1 paginaRangoli Coloursmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento1 pagina1manali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento2 pagine1manali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocumento1 paginaNew Microsoft Office Word Documentmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- EE PracticesDocumento11 pagineEE Practicesmanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento1 pagina1manali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrigendum Result Gujarat Administrative Service Class 1 Gujarat Civil Service CL 1 2 Preliminary Advt 09 2014 15Documento1 paginaCorrigendum Result Gujarat Administrative Service Class 1 Gujarat Civil Service CL 1 2 Preliminary Advt 09 2014 15manali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Release NoteDocumento2 pagineRelease Notemanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Recent Banking Updates 2014 - Gr8AmbitionZDocumento75 pagineRecent Banking Updates 2014 - Gr8AmbitionZrajni165561Nessuna valutazione finora
- Advt 104 2011 12 Sample Paper English To GujaratiDocumento4 pagineAdvt 104 2011 12 Sample Paper English To Gujaratimanali_thakarNessuna valutazione finora
- G. Metals and NonmetalsDocumento26 pagineG. Metals and NonmetalsKyzer Calix LaguitNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario. Advanced Level.Documento68 pagineSolucionario. Advanced Level.Christian Delgado RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Programs Activities Timeframe Expected Output Child CareDocumento3 pagineHealth Programs Activities Timeframe Expected Output Child CareC SamNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9 P.EDocumento16 pagineGrade 9 P.EBrige SimeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Versidrain 150: Green RoofDocumento2 pagineVersidrain 150: Green RoofMichael Tiu TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- EMI InstructionsDocumento2 pagineEMI InstructionsAKSHAY ANANDNessuna valutazione finora
- Adolescent and Sexual HealthDocumento36 pagineAdolescent and Sexual Healthqwerty123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic and Molecular PhysicsDocumento28 pagineAtomic and Molecular PhysicsAvinash GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abnegation Faction:: Clothing Is Gray and Simple. The OnlyDocumento7 pagineAbnegation Faction:: Clothing Is Gray and Simple. The OnlylethaagathaNessuna valutazione finora
- PR Cuisine vs US CuisineDocumento2 paginePR Cuisine vs US CuisineJannette HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Accuracy of Real-Time Shear Wave Elastography in SDocumento10 pagineAccuracy of Real-Time Shear Wave Elastography in SApotik ApotekNessuna valutazione finora
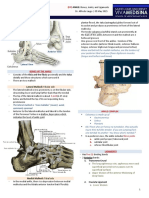
- (9F) Ankle - Bones, Joints, Tendons and LigamentsDocumento4 pagine(9F) Ankle - Bones, Joints, Tendons and LigamentsJeffrey RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Variable Displacement Engines: The Magic of Cylinder DeactivationDocumento3 pagineVariable Displacement Engines: The Magic of Cylinder DeactivationdinuNessuna valutazione finora
- PhilLife claims process ECQDocumento18 paginePhilLife claims process ECQNoel EboniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Arecaceae or Palmaceae (Palm Family) : Reported By: Kerlyn Kaye I. AsuncionDocumento23 pagineArecaceae or Palmaceae (Palm Family) : Reported By: Kerlyn Kaye I. AsuncionNamae BacalNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Anxiety Disorders and Abnormal PsychologyDocumento7 pagineUnderstanding Anxiety Disorders and Abnormal PsychologyLeonardo YsaiahNessuna valutazione finora
- Jaimin PatelDocumento3 pagineJaimin PatelSanjay SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Sentences and Service of PenaltyDocumento5 pagineMultiple Sentences and Service of PenaltyAngelNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluvial Erosion Processes ExplainedDocumento20 pagineFluvial Erosion Processes ExplainedPARAN, DIOSCURANessuna valutazione finora
- 3.SAFA AOCS 4th Ed Ce 2-66 1994Documento6 pagine3.SAFA AOCS 4th Ed Ce 2-66 1994Rofiyanti WibowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Persuasive Essay Eng 101nDocumento6 paginePersuasive Essay Eng 101napi-341545248Nessuna valutazione finora
- Almond Milk Case Study Executive SummaryDocumento19 pagineAlmond Milk Case Study Executive Summarygauthamsindia307Nessuna valutazione finora
- Undas Deployment PadsDocumento15 pagineUndas Deployment PadsVic NairaNessuna valutazione finora