Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Combustion Engine Emissions
Caricato da
Sanjay Gomasta0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
50 visualizzazioni1 paginacombustion engine
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentocombustion engine
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
50 visualizzazioni1 paginaCombustion Engine Emissions
Caricato da
Sanjay Gomastacombustion engine
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
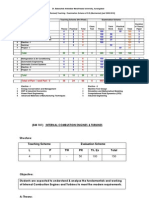
COMBUSTION ENGINE EMISSIONS
Course Code: BTM 709 Credit Units: 03
Course Objective:
The main objective of this course is to introduce students the fundamentals, Operations and performance of internal combustion engines
and their different types; to provide them with the theoretical and experimental ability to operate, analyze and design internal combustion
engines; to assess the relation between engine power output to the required power for vehicle propulsion; to make them understand the
fuel metering systems and assembling and dismantling internal combustion engines.
Course Contents:
Module I: Engine Fundamentals
Cycle analysis, fuels, and types of hydrocarbons, gasoline specifications, effect of engine parameters on performance, carburetion,
engine vehicle road performance, road performance and fuel economy.
Module II: Emission and Air Pollution
Automotive emissions and their role in air pollution, photochemical smog, Chemistry of smog formation, Combustion in homogeneous
mixtures, emission formation, Incomplete combustion formation of Hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide and oxides of nitrogen,
Aldehyde emissions of unregulated toxic pollutants such as benzene, 1, 3, butadiene etc.
Module III
Influence of engine design and operating parameters on S.I. engine exhaust emissions. Hydrocarbon Evaporative Emissions, Various
sources and method of their control, Canisters for controlling evaporative emissions, emission control system for S.I. engines, Blow by
control closed PCV system, Reduction of exhaust emissions / Various methods, fuels system design.
Module IV: Exhaust Treatment devices
Air injection into exhaust system, Thermal reactors, Catalytic converters. Stratified charge engines, Honda CVCC engine.
Diesel engine emissions: Source of emissions during combustion, Effect of Air injection timing on performance and formation. D.I. and
I.D.I. engines emissions, Diesel smoke, PM and RSPM emission.
Module V
Methods of reducing emission, Exhaust gas re-circulation smoke emission form diesel engines, Particulate Traps, Continuous
regeneration Traps (CRT).
Emission from CNG and LPG engines. Emission Instruments: Non-dispersive infrared analyzer, Gas chromatography, Flame ionization
Detector, Chemiluminescent analyser.
Examination Scheme:
Components A CT S/V/Q HA EE
Weightage (%) 5 10 8 7 70
CT: Class Test, HA: Home Assignment, S/V/Q: Seminar/Viva/Quiz, EE: End Semester Examination; Att: Attendance
Text & References:
Text:
R.P. Sharma and M.L. Mathur, Internal Combustion Engine, Dhanpat Rai Publications
V. Ganeshan, Internal Combustion Engine, Tata McGraw Hill
References:
Angli M Course., Automotive Engines, CBS Publications
Harper, Fuel Systems Emission Control, CBS Publication
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Advanced IC Engine Course Outline - 2019Documento3 pagineAdvanced IC Engine Course Outline - 2019Kumaran PalaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Automotive Fuels and Emission SyllabusDocumento2 pagineAutomotive Fuels and Emission SyllabusrajeevNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject Internal Combustion Engine Semester 5th Trade Mechanical Year 3rdDocumento25 pagineSubject Internal Combustion Engine Semester 5th Trade Mechanical Year 3rdKareem VazquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Alternate Fuels & EngineDocumento3 pagineAlternate Fuels & EnginecharulapNessuna valutazione finora
- PDFDocumento3 paginePDFAchal SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- IC New Course FileDocumento5 pagineIC New Course FiledearsaswatNessuna valutazione finora
- IC Engine Fuel and LubricationDocumento274 pagineIC Engine Fuel and Lubricationshivam57194Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ice Course PlanDocumento8 pagineIce Course PlanmallikarjunbpatilNessuna valutazione finora
- BE Syllabus of Mumbai Uni5Documento10 pagineBE Syllabus of Mumbai Uni5Rajendra B PawarNessuna valutazione finora
- IceDocumento3 pagineIceJaniNessuna valutazione finora
- AU204 CI Engines & CombustionDocumento3 pagineAU204 CI Engines & CombustionVivek Venugopal0% (1)
- List of Open Electives Offered by Automobile Engg BoardDocumento15 pagineList of Open Electives Offered by Automobile Engg BoardpurnaNessuna valutazione finora
- ME 204 Thermal Engineering KTUDocumento3 pagineME 204 Thermal Engineering KTUSunil BhaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocumento3 pagineInternal Combustion EnginescharulapNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 1 Course OutlineDocumento5 pagineForm 1 Course Outlinearslan khanNessuna valutazione finora
- AU 6th SEM - AU 21-22071021124330Documento12 pagineAU 6th SEM - AU 21-22071021124330Sumit VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocumento2 pagineInternal Combustion EnginesDhaval PanchalNessuna valutazione finora
- Ic Engine and Gas TurbineDocumento2 pagineIc Engine and Gas TurbineShaik YaseenNessuna valutazione finora
- AU201 SI Engines and CombustionDocumento3 pagineAU201 SI Engines and CombustionvaisakmctNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus For Intermediate Heat TransferDocumento3 pagineSyllabus For Intermediate Heat TransferShaurya PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Ic Engine SyllabusDocumento2 pagineIc Engine SyllabusMadhurjya SaikiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Documento3 pagineGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19AkashNessuna valutazione finora
- National University of Engineering Mechanical-Electrical Engineering ProgramDocumento2 pagineNational University of Engineering Mechanical-Electrical Engineering Programjimmy jimenez barriosNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus of The Subject Automotive Pollutants & Control L T P C 3 0 - 3Documento3 pagineSyllabus of The Subject Automotive Pollutants & Control L T P C 3 0 - 3siyalohia8Nessuna valutazione finora
- ME605 - Internal Combustion Engineering PDFDocumento3 pagineME605 - Internal Combustion Engineering PDFRajkumar SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 15me655 AeDocumento2 pagine15me655 Aeyoussef ibrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus I - C - Engines & CombustionDocumento2 pagineSyllabus I - C - Engines & CombustionZahir Ummer ZaidNessuna valutazione finora
- ME 21012 Fuels and Combustion CurriculumDocumento2 pagineME 21012 Fuels and Combustion Curriculumsameer gaikwadNessuna valutazione finora
- B.E Mechnical2009Documento64 pagineB.E Mechnical2009akshaybj4396Nessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion Generated Pollution-Notes PDFDocumento34 pagineCombustion Generated Pollution-Notes PDFbharathNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled NotesDocumento149 pagineUntitled NotesShashank BiligiNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Experiments: University of Mumbai, Mechanical Engineering (Third and Final Year) Revised Course (Rev-2012)Documento1 paginaList of Experiments: University of Mumbai, Mechanical Engineering (Third and Final Year) Revised Course (Rev-2012)Honey SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Anna University Semester II Syllabus (Regulation 2017)Documento10 pagineAnna University Semester II Syllabus (Regulation 2017)BENHAR ARVINDNessuna valutazione finora
- Exhaust Gas Analysis and Air Pollution: 5.1 Necessity of ExhaustDocumento1 paginaExhaust Gas Analysis and Air Pollution: 5.1 Necessity of ExhaustHoney SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Pass Marks: - 40: Detail Syllabus For Automobile EngineerDocumento7 paginePass Marks: - 40: Detail Syllabus For Automobile EngineerSaurav AdhikariNessuna valutazione finora
- ME604 (ICE>) Lecture NoteDocumento125 pagineME604 (ICE>) Lecture NoteKamna KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied ThermodynamicsDocumento2 pagineApplied ThermodynamicsLaxman RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Autotronics PDFDocumento3 pagineAutotronics PDFSiddhesh Kawalkar100% (1)
- Pvpsit Department of Mechanical Engineering PVP19Documento2 paginePvpsit Department of Mechanical Engineering PVP19Satya NarayanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2180210Documento2 pagine2180210mannuvpatelNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.32 & 4.33 TE & BE - Mech Engg 4Documento1 pagina4.32 & 4.33 TE & BE - Mech Engg 4Honey SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Alternative Fuels NotesDocumento9 pagineAlternative Fuels NotesParth MehraNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 1Documento13 pagine5 1gabrieltinNessuna valutazione finora
- Auto-Syllab MTech Admission 2012-13Documento25 pagineAuto-Syllab MTech Admission 2012-13Ratnakar PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- 2ME705-2-Internal Combustion Engine PDFDocumento2 pagine2ME705-2-Internal Combustion Engine PDFkrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ic PDFDocumento2 pagineIc PDFDeepak MehtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rto 2 Syllabus PDFDocumento11 pagineRto 2 Syllabus PDFParthNessuna valutazione finora
- Automobile - Full Notes - 6TH PDFDocumento179 pagineAutomobile - Full Notes - 6TH PDFShailesh RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Automobile Engineering Mod1Documento37 pagineAutomobile Engineering Mod1feriha khanNessuna valutazione finora
- M 89Documento2 pagineM 89navneetkpatil8409Nessuna valutazione finora
- Institute of Engineering & Technology, Devi Ahilya University, Indore, (M.P.), India. (Scheme Effective From July 2015)Documento2 pagineInstitute of Engineering & Technology, Devi Ahilya University, Indore, (M.P.), India. (Scheme Effective From July 2015)Subash AppuNessuna valutazione finora
- ME605-N-C Internal Combustion EngineDocumento3 pagineME605-N-C Internal Combustion Enginesnehalbhalerao20.booksNessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Documento3 pagineGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19AkashNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Developments in Ic Engines (Wankel Engine) : Theory of Internal Combustion Engines and EmissionsDocumento10 pagineModern Developments in Ic Engines (Wankel Engine) : Theory of Internal Combustion Engines and EmissionsZEDI gamingNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal Petrokimia Ivan AbrorDocumento10 pagineJurnal Petrokimia Ivan AbrorMuhamad Ivan AbrorNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Combustion EnginesDa EverandInternal Combustion EnginesConstantine ArcoumanisValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- NOx Emission Control Technologies in Stationary and Automotive Internal Combustion Engines: Approaches Toward NOx Free AutomobilesDa EverandNOx Emission Control Technologies in Stationary and Automotive Internal Combustion Engines: Approaches Toward NOx Free AutomobilesB. AshokNessuna valutazione finora
- At 6703 Automotive Pollution and Control 2 A& 16 MarksDocumento19 pagineAt 6703 Automotive Pollution and Control 2 A& 16 MarksDHILEEPAN0% (1)
- Gas Turbines: A Handbook of Air, Land and Sea ApplicationsDa EverandGas Turbines: A Handbook of Air, Land and Sea ApplicationsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (9)
- Advancement in Oxygenated Fuels for Sustainable Development: Feedstocks and Precursors for Catalysts SynthesisDa EverandAdvancement in Oxygenated Fuels for Sustainable Development: Feedstocks and Precursors for Catalysts SynthesisNessuna valutazione finora
- Ireland Profile - Timeline: A Chronology of Key EventsDocumento9 pagineIreland Profile - Timeline: A Chronology of Key EventsSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unconventional Machining LabDocumento1 paginaUnconventional Machining LabSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endorsement Letter From The Registrar of The University/Head of The Institute (Statement From Employer, On The Letter Head)Documento1 paginaEndorsement Letter From The Registrar of The University/Head of The Institute (Statement From Employer, On The Letter Head)Sanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rgpv-Bhopal Ojaswini Iii - SemesterDocumento7 pagineRgpv-Bhopal Ojaswini Iii - SemesterSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Annexure-1: (Signature of The Convener)Documento1 paginaAnnexure-1: (Signature of The Convener)Sanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Minute To Minute Programme For Blood Donation Camp 1 October 2015Documento2 pagineMinute To Minute Programme For Blood Donation Camp 1 October 2015Sanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurements and Controls Lab: Course Code: BTM 522 Credit Units: 01 Course Contents: List of ExperimentsDocumento1 paginaMeasurements and Controls Lab: Course Code: BTM 522 Credit Units: 01 Course Contents: List of ExperimentsSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Science and Metallurgy PDFDocumento1 paginaMaterial Science and Metallurgy PDFSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- B. Tech (MAE) - 2011 - (C)Documento173 pagineB. Tech (MAE) - 2011 - (C)Sanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Management: Course Code: BTM 706 Credit Units: 03 Course ObjectiveDocumento1 paginaMarketing Management: Course Code: BTM 706 Credit Units: 03 Course ObjectiveSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing Information Systems: Course Code: BTM 808 Credit Units: 04 Course ObjectiveDocumento1 paginaManufacturing Information Systems: Course Code: BTM 808 Credit Units: 04 Course ObjectiveSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine DesignDocumento1 paginaMachine DesignSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing MachinesDocumento1 paginaManufacturing MachinesSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine Drawing Lab: Course Code: BTM 321 Credit Units: 01 Course ContentsDocumento1 paginaMachine Drawing Lab: Course Code: BTM 321 Credit Units: 01 Course ContentsSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine Design Lab - Ii: Course Code: BTM 620 Credit Units: 01 Course ContentsDocumento1 paginaMachine Design Lab - Ii: Course Code: BTM 620 Credit Units: 01 Course ContentsSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing Machines Lab: Course Code: BTM 421 Credit Units: 01 Course ContentsDocumento1 paginaManufacturing Machines Lab: Course Code: BTM 421 Credit Units: 01 Course ContentsSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Manufacturing SystemsDocumento1 paginaManagement of Manufacturing SystemsSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Computers and Programming in CDocumento1 paginaIntroduction To Computers and Programming in CSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine Design Lab - I: Course Code: BTM 520 Credit Units: 01 Course ContentsDocumento1 paginaMachine Design Lab - I: Course Code: BTM 520 Credit Units: 01 Course ContentsSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial ManagementDocumento1 paginaFinancial ManagementSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Japanese - Iv: Course Code: BTM 447 Credit Units: 02 Course ObjectiveDocumento1 paginaJapanese - Iv: Course Code: BTM 447 Credit Units: 02 Course ObjectiveSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat and Mass TransferDocumento1 paginaHeat and Mass TransferSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion Engine Emissions: Course Code: BTM 709 Credit Units: 03 Course ObjectiveDocumento1 paginaCombustion Engine Emissions: Course Code: BTM 709 Credit Units: 03 Course ObjectiveSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gear Technology Lab: Course Code: BTM 822 Credit Units: 01 Course Contents: List of ExperimentsDocumento1 paginaGear Technology Lab: Course Code: BTM 822 Credit Units: 01 Course Contents: List of ExperimentsSanjay GomastaNessuna valutazione finora