Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lab 6.2.3 Controlling A DR-BDR Election
Caricato da
dhesand100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
92 visualizzazioni6 paginelab about controlling a DR-BDR Election in OPSF Routing Protocol
Titolo originale
Lab 6.2.3 Controlling a DR-BDR Election%0A
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentolab about controlling a DR-BDR Election in OPSF Routing Protocol
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
92 visualizzazioni6 pagineLab 6.2.3 Controlling A DR-BDR Election
Caricato da
dhesandlab about controlling a DR-BDR Election in OPSF Routing Protocol
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 6
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6
CCNA Discovery
Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise
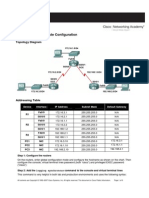
Lab 6.2.3 Controlling a DR/BDR Election
Device
Fast Ethernet 0/0
IP Address
Loopback0 IP
Address Network Statements
R1
192.168.1.1/24 10.0.3.1/32 192.168.1.0
R2
192.168.1.2/24 10.0.2.1/32 192.168.1.0
R3
192.168.1.3/24 10.0.1.1/32 192.168.1.0
Objectives
Configure OSPF routing on all routers.
Verify OSPF routing using show commands.
Configure loopback addresses to dictate DR/BDR election.
Verify DR/BDR election.
CCNA Discovery
Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 2 of 6
Background / Preparation
This lab focuses on the configuration of multiple OSPF routers attached to a muti-access Ethernet network to
control the outcome of the DR/BDR election. The lab uses Cisco IOS commands.
Any router that meets the interface requirements displayed on the above diagram may be used. For example,
router series 800, 1600, 1700, 1800, 2500, 2600, 2800, or any combination can be used.
The information in this lab applies to 1841 routers. Other routers may be used; however, command syntax
may vary. Depending on the router model, the interfaces may differ. For example, on some routers Serial 0
may be Serial 0/0, Serial 0/0/0 and Ethernet 0 may be FastEthernet 0/0. Any Cisco Catalyst switch may be
utilized. The default configuration of the switch will perform properly for this exercise.
The following resources are required:
One Cisco 2960 switch or other comparable switch
Three Cisco routers with at least 1 FastEthernet interface (preferably the same model number and
IOS version)
One Windows-based PC with a terminal emulation program
At least one RJ -45-to-DB-9 connector console cable to configure the routers
Three straight-through Ethernet cables to connect the routers to the switch
NOTE: Make sure that the routers and the switches have been erased and have no startup configurations.
Instructions for erasing both switch and router are provided in the Lab Manual, located on Academy
Connection in the Tools section.
NOTE: SDM Enabled Routers If the startup-config is erased in an SDM enabled router, SDM will no longer
come up by default when the router is restarted. It will be necessary to build a basic router configuration using
IOS commands. The steps provided in this lab use IOS commands and do not require the use of SDM. If you
wish to use SDM, refer to the instructions in the Lab Manual, located on the Academy Connection in the Tools
section or contact your instructor if necessary.
Step 1: Connect the equipment
Connect each of the router Fa0/0 interfaces to any port on the switch using a straight-through cable.
Step 2: Perform basic configuration on the routers
a. Connect a PC to the console port of the router to perform configurations using a terminal emulation
program.
b. Configure Routers 1, 2, and 3 with a hostname, and console, Telnet, and privileged passwords
according to the table diagram.
Step 3: Configure single area OSPF routing on the routers
Configure basic OSPF routing on the routers. All networks are in Area 0.
R1( conf i g) #router ospf 1
R1( conf i g- r out er ) #network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
R2( conf i g) #router ospf 1
R2( conf i g- r out er ) #network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
R3( conf i g) #router ospf 1
R3( conf i g- r out er ) #network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
CCNA Discovery
Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 3 of 6
Step 4: Verify current OSPF operation
a. Now that the Ethernet interfaces and OSPF have been configured, OSPF should be operational
between the routers. Because this is a multi-access network, a DR/BDR election should have
occurred.
b. Use the show ip ospf neighbor command on all the routers to verify operation. The output
should be similar to what is shown below.
R1#show ip ospf neighbor
Nei ghbor I D Pr i St at e Dead Ti me Addr ess I nt er f ace
192. 168. 1. 2 1 FULL/ BDR 00: 00: 38 192. 168. 1. 2 Fast Et her net 0/ 0
192. 168. 1. 3 1 FULL/ DR 00: 00: 35 192. 168. 1. 3 Fast Et her net 0/ 0
Do all routers show that they have established a neighbor relationship with the other routers?
__________
c. Use the show ip ospf neighbor detail command on R1 to determine which routers are the
DR and BDR.
Which router is the DR? ___________
Which router is the BDR? __________
What factor determined which router was the DR and which was the BDR in this scenario?
________________________________________________________________________________
Step 5: Configure router loopback interfaces
a. Configuring loopback interfaces for OSPF operation serves two purposes:
1) Because loopback interfaces are logical interfaces and never go down, it ensures that the router
ID will never change.
2) Configuring loopback interfaces allows control over the DR/BDR election.
b. Configure the loopback interfaces as shown in the addressing table on the first page.
R1( conf i g) #interface loopback 0
R1( conf i g- i f ) #ip address 10.0.3.1 255.255.255.255
R1( conf i g- i f ) #end
R2( conf i g) #interface loopback 0
R2( conf i g- i f ) #ip address 10.0.2.1 255.255.255.255
R2( conf i g- i f ) #end
R3( conf i g) #interface loopback 0
R3( conf i g- i f ) #ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.255
R3( conf i g- i f ) #end
c. Use the show ip ospf neighbor detail command on R1 to view the DR/BDR status.
Have the DR and BDR routers changed? __________
d. Once elected, the DR and the BDR do not change unless the interfaces all cycle or the OSPF
processes are reset. Use the clear ip ospf 1 process command on all routers to reset the
OSPF processes.
NOTE: If the clear ip osfp 1 process command does not result in the loopback addresses
determining the router ID and DR/BDR status, use the reload command from the privileged EXEC
prompt on each router. Be sure to save the configuration on each router before issuing the reload
command.
CCNA Discovery
Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 4 of 6
e. After the processes have been reset, use the show ip ospf neighbor detail command to
recheck the DR/BDR status.
R1#show ip ospf neighbor detail
Nei ghbor 10. 0. 1. 1, i nt er f ace addr ess 192. 168. 1. 3
I n t he ar ea 0 vi a i nt er f ace Fast Et her net 0/ 0
Nei ghbor pr i or i t y i s 1, St at e i s FULL, 6 st at e changes
DR i s 192. 168. 1. 1 BDR i s 192. 168. 1. 2
Opt i ons i s 0x52
LLS Opt i ons i s 0x1 ( LR)
Dead t i mer due i n 00: 00: 34
Nei ghbor i s up f or 00: 11: 55
I ndex 2/ 2, r et r ansmi ssi on queue l engt h 0, number of r et r ansmi ssi on 0
Fi r st 0x0( 0) / 0x0( 0) Next 0x0( 0) / 0x0( 0)
Last r et r ansmi ssi on scan l engt h i s 0, maxi mumi s 0
Last r et r ansmi ssi on scan t i me i s 0 msec, maxi mumi s 0 msec
Nei ghbor 10. 0. 2. 1, i nt er f ace addr ess 192. 168. 1. 2
I n t he ar ea 0 vi a i nt er f ace Fast Et her net 0/ 0
Nei ghbor pr i or i t y i s 1, St at e i s FULL, 6 st at e changes
DR i s 192. 168. 1. 1 BDR i s 192. 168. 1. 2
Opt i ons i s 0x52
LLS Opt i ons i s 0x1 ( LR)
Dead t i mer due i n 00: 00: 31
Nei ghbor i s up f or 00: 11: 57
I ndex 1/ 1, r et r ansmi ssi on queue l engt h 0, number of r et r ansmi ssi on 0
Fi r st 0x0( 0) / 0x0( 0) Next 0x0( 0) / 0x0( 0)
Last r et r ansmi ssi on scan l engt h i s 0, maxi mumi s 0
Last r et r ansmi ssi on scan t i me i s 0 msec, maxi mumi s 0 msec
Which router is now the DR? ____________
Which router is now the BDR? ___________
What factor determined which router was elected as the DR?
__________________________________________________________
Step 6: Use router interface priority to determine DR election
a. Another method that is used to determine the DR/BDR election is router interface priority. Use the
show ip ospf interface command to determine the default priority settings on the routers.
R1#show ip ospf interface
Fast Et her net 0/ 0 i s up, l i ne pr ot ocol i s up
I nt er net Addr ess 192. 168. 1. 1/ 24, Ar ea 0
Pr ocess I D 1, Rout er I D 10. 0. 3. 1, Net wor k Type BROADCAST, Cost : 1
Tr ansmi t Del ay i s 1 sec, St at e DR, Pr i or i t y 1
Desi gnat ed Rout er ( I D) 10. 0. 3. 1, I nt er f ace addr ess 192. 168. 1. 1
Backup Desi gnat ed r out er ( I D) 10. 0. 2. 1, I nt er f ace addr ess 192. 168. 1. 2
Ti mer i nt er val s conf i gur ed, Hel l o 10, Dead 40, Wai t 40, Ret r ansmi t 5
oob- r esync t i meout 40
Hel l o due i n 00: 00: 03
Suppor t s Li nk- l ocal Si gnal i ng ( LLS)
I ndex 1/ 1, f l ood queue l engt h 0
Next 0x0( 0) / 0x0( 0)
Last f l ood scan l engt h i s 1, maxi mumi s 2
Last f l ood scan t i me i s 0 msec, maxi mumi s 0 msec
Nei ghbor Count i s 2, Adj acent nei ghbor count i s 2
Adj acent wi t h nei ghbor 10. 0. 1. 1
CCNA Discovery
Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 5 of 6
Adj acent wi t h nei ghbor 10. 0. 2. 1 ( Backup Desi gnat ed Rout er )
Suppr ess hel l o f or 0 nei ghbor ( s)
What is the default interface priority for the Fa0/0 interfaces? _____________
b. Configure interface priorities on R1 and R2 to determine the DR/BDR election results.
R1( conf i g) #interface fa0/0
R1( conf i g- i f ) #ip ospf priority 25
R1( conf i g- i f ) #end
R2( conf i g) #interface fa0/0
R2( conf i g- i f ) #ip ospf priority 50
R2( conf i g- i f ) #end
c. Use the show ip ospf neighbor command to determine the DR and BDR.
Have the DR and the BDR changed? __________
d. Use the clear ip ospf 1 process command on all of the routers to reset the OSPF processes.
e. Again use the show ip ospf neighbor command to determine which router is the DR and which
is the BDR.
Which router is now the DR? ___________
Which router is now the BDR? __________
f. Use the show ip ospf interface command again on R1 and R2 to confirm the priority settings
and DR/BRD status on the routers.
R1#show ip ospf interface
Fast Et her net 0/ 0 i s up, l i ne pr ot ocol i s up
I nt er net Addr ess 192. 168. 1. 1/ 24, Ar ea 0
Pr ocess I D 1, Rout er I D 10. 0. 3. 1, Net wor k Type BROADCAST, Cost : 1
Tr ansmi t Del ay i s 1 sec, St at e BDR, Pr i or i t y 25
Desi gnat ed Rout er ( I D) 10. 0. 2. 1, I nt er f ace addr ess 192. 168. 1. 2
Backup Desi gnat ed r out er ( I D) 10. 0. 3. 1, I nt er f ace addr ess 192. 168. 1. 1
Ti mer i nt er val s conf i gur ed, Hel l o 10, Dead 40, Wai t 40, Ret r ansmi t 5
oob- r esync t i meout 40
Hel l o due i n 00: 00: 00
Suppor t s Li nk- l ocal Si gnal i ng ( LLS)
I ndex 1/ 1, f l ood queue l engt h 0
Next 0x0( 0) / 0x0( 0)
Last f l ood scan l engt h i s 0, maxi mumi s 2
Last f l ood scan t i me i s 0 msec, maxi mumi s 0 msec
Nei ghbor Count i s 2, Adj acent nei ghbor count i s 2
Adj acent wi t h nei ghbor 10. 0. 1. 1
Adj acent wi t h nei ghbor 10. 0. 2. 1 ( Desi gnat ed Rout er )
Suppr ess hel l o f or 0 nei ghbor ( s)
R2#show ip ospf interface
Fast Et her net 0/ 0 i s up, l i ne pr ot ocol i s up
I nt er net Addr ess 192. 168. 1. 2/ 24, Ar ea 0
Pr ocess I D 1, Rout er I D 10. 0. 2. 1, Net wor k Type BROADCAST, Cost : 1
Tr ansmi t Del ay i s 1 sec, St at e DR, Pr i or i t y 50
Desi gnat ed Rout er ( I D) 10. 0. 2. 1, I nt er f ace addr ess 192. 168. 1. 2
Backup Desi gnat ed r out er ( I D) 10. 0. 3. 1, I nt er f ace addr ess 192. 168. 1. 1
Ti mer i nt er val s conf i gur ed, Hel l o 10, Dead 40, Wai t 40, Ret r ansmi t 5
oob- r esync t i meout 40
Hel l o due i n 00: 00: 00
Suppor t s Li nk- l ocal Si gnal i ng ( LLS)
CCNA Discovery
Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 6 of 6
I ndex 1/ 1, f l ood queue l engt h 0
Next 0x0( 0) / 0x0( 0)
Last f l ood scan l engt h i s 1, maxi mumi s 2
Last f l ood scan t i me i s 0 msec, maxi mumi s 0 msec
Nei ghbor Count i s 2, Adj acent nei ghbor count i s 2
Adj acent wi t h nei ghbor 10. 0. 1. 1
Adj acent wi t h nei ghbor 10. 0. 3. 1 ( Backup Desi gnat ed Rout er )
Suppr ess hel l o f or 0 nei ghbor ( s)
Did the interface priority override the router ID in determining the DR/BDR? __________
Step 7: Reflection
List the criteria used from highest to lowest for determining the DR on an OSPF network.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Ccnpv6 Route Lab4-2Documento21 pagineCcnpv6 Route Lab4-2luderh123Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesDocumento9 pagine5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesJozeph Abod67% (3)
- 5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 On A Multiaccess NetworkDocumento6 pagine5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 On A Multiaccess Networkرافد البركيNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features - ILMDocumento12 pagine5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features - ILMرافد البركي75% (12)
- CCNPv6 ROUTE Lab4-3 Administrative Distance StudentDocumento16 pagineCCNPv6 ROUTE Lab4-3 Administrative Distance StudentWilliam WhitakerNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 8.3.3.6Documento10 pagineLab 8.3.3.6Justine DuranNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 5.2.3 Configuring Ripv2 With VLSM, and Default Route PropagationDocumento4 pagineLab 5.2.3 Configuring Ripv2 With VLSM, and Default Route Propagationmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring A Point-To-Point GRE VPN TunnelDocumento6 pagine7.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring A Point-To-Point GRE VPN TunnelBlyiremk83% (6)
- Configuring Multi-Area OSPFv3Documento16 pagineConfiguring Multi-Area OSPFv3etitahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab: Basic Static Route Configuration: Topology DiagramDocumento6 pagineLab: Basic Static Route Configuration: Topology Diagramchanda_banda272Nessuna valutazione finora
- IP Access Lists: Objective Lab TopologyDocumento5 pagineIP Access Lists: Objective Lab TopologyTomas Rodriguez RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocumento5 pagine6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANSergio MonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Router Igrp Configuration LabDocumento5 pagine3 Router Igrp Configuration LabSiddhant SingalNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.2.2.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring Dynamic NAT Instructions IG PDFDocumento2 pagine5.2.2.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring Dynamic NAT Instructions IG PDFblado1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Configure Static and Default Routing in GNS3Documento7 pagineConfigure Static and Default Routing in GNS3AngelaNessuna valutazione finora
- EIGRP AdvancesDocumento96 pagineEIGRP Advancesnenad20090% (1)
- 7.4.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv6 Routing Instructions IG PDFDocumento3 pagine7.4.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv6 Routing Instructions IG PDFJESUSCAMPONessuna valutazione finora
- 8.2.2.7 Cisco Packet TracerDocumento3 pagine8.2.2.7 Cisco Packet Tracerjstring69Nessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA 3 (v5.0) OSPF Practice Skills Assessment Exam Answer: Network DiagramDocumento22 pagineCCNA 3 (v5.0) OSPF Practice Skills Assessment Exam Answer: Network DiagramMark BrownNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA 2 RSE Practice Skills Assessment v5.2– PT 2015Documento11 pagineCCNA 2 RSE Practice Skills Assessment v5.2– PT 2015Hermo MedranoNessuna valutazione finora
- GNS3 Routing LabDocumento7 pagineGNS3 Routing LabTea KostadinovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco First Hop Redundancy Protocol by TanmoyDocumento38 pagineCisco First Hop Redundancy Protocol by TanmoyBIG BILLION DREAMSNessuna valutazione finora
- ROUTE Chapter 5 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)Documento10 pagineROUTE Chapter 5 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)AS2205Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 1 - Static RoutesDocumento9 pagineLab 1 - Static RoutesAndrew MaverickNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Router Configuration Commands GuideDocumento17 pagineCisco Router Configuration Commands GuideBazir AhamedNessuna valutazione finora
- TSHOOTDocumento25 pagineTSHOOTJeton Ahmeti100% (3)
- OSPF With Access ListDocumento8 pagineOSPF With Access ListdjmckcNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3.4.3 Part A: Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The EnterpriseDocumento5 pagineLab 3.4.3 Part A: Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The EnterpriseRano RenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Using GNS3 For Switching LabsDocumento7 pagineUsing GNS3 For Switching LabskinyNessuna valutazione finora
- ROUTE Chapter 4 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)Documento12 pagineROUTE Chapter 4 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)AS2205100% (5)
- Assessment System: Take Assessment - SWITCH Chapter 7 - CCNP SWITCH (Version 6.0)Documento7 pagineAssessment System: Take Assessment - SWITCH Chapter 7 - CCNP SWITCH (Version 6.0)sogunmola100% (1)
- CCNA 3 Discovery 4.0 Final ExamDocumento27 pagineCCNA 3 Discovery 4.0 Final ExamMamoona1680% (5)
- Cisco Certified Network AssociateDocumento96 pagineCisco Certified Network AssociateMohamed YagoubNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA 2 Exploration ERouting Final Exam Form2 V 4.0Documento19 pagineCCNA 2 Exploration ERouting Final Exam Form2 V 4.0sEcZxNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11 - Comprehensive Lab - txt-1Documento7 pagineChapter 11 - Comprehensive Lab - txt-1Arwin Ilagan33% (3)
- 6.2.3.10 Lab - Troubleshooting Multiarea OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 - ILM PDFDocumento29 pagine6.2.3.10 Lab - Troubleshooting Multiarea OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov95% (19)
- Labs Edited Labs Edited Task 1Documento44 pagineLabs Edited Labs Edited Task 1riche2040100% (1)
- Activity-6 Routing Informatio Protocol (RIP)Documento6 pagineActivity-6 Routing Informatio Protocol (RIP)raffy arranguezNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.2.5.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv6 Addressing InstructionsDocumento2 pagine8.2.5.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv6 Addressing Instructionsnarendra kumar bNessuna valutazione finora
- At Tshoot 642-832Documento249 pagineAt Tshoot 642-832_asdffgNessuna valutazione finora
- OSPF Practice Skills Assessment - Packet TracerDocumento13 pagineOSPF Practice Skills Assessment - Packet Tracerjohn doeNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA Final Project TastDocumento3 pagineCCNA Final Project Tastsathish77s100% (1)
- Route Case Study For CCNPDocumento2 pagineRoute Case Study For CCNPatiquebashirNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3: OSPF With Three RoutersDocumento6 pagineLab 3: OSPF With Three RoutersAmjad hassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Certified Security Professional A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandCisco Certified Security Professional A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Troubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsDa EverandTroubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Multiarea OspfDocumento13 pagineMultiarea OspfNavneetNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab - 5 - OSPFDocumento10 pagineLab - 5 - OSPFLipp00 M0MA100% (1)
- Ospf DR BDRDocumento5 pagineOspf DR BDRvelramsenNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab EIGRP 5Documento11 pagineLab EIGRP 5Danny Ricce EnriqueNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2.3.8 LabDocumento10 pagine6.2.3.8 LabAutumn TillmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) (Tutorial) - Packt HubDocumento13 pagineIntroduction To Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) (Tutorial) - Packt HubaaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Lab OSPF EncapsulationDocumento23 pagineCisco Lab OSPF EncapsulationMike OwlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 6.2.2 Configuring OSPF Authentication: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The EnterpriseDocumento4 pagineLab 6.2.2 Configuring OSPF Authentication: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The Enterprisemohammad_shahzad_iiuiNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNPv7 ROUTE Lab3-1 OSPF-Virtual-Links StudentDocumento12 pagineCCNPv7 ROUTE Lab3-1 OSPF-Virtual-Links Studentgarp579150% (2)
- CCN Expt 8 HKDocumento8 pagineCCN Expt 8 HKShailaja UdtewarNessuna valutazione finora
- OSPF Network Types: BroadcastDocumento76 pagineOSPF Network Types: BroadcastsamarendranNessuna valutazione finora
- Wi - Fi Control Robot Using Node MCU: January 2018Documento5 pagineWi - Fi Control Robot Using Node MCU: January 2018NayaaNessuna valutazione finora
- C6 User Manual en (V1.0.0)Documento10 pagineC6 User Manual en (V1.0.0)Pak UliNessuna valutazione finora
- In Ge Cmd5b1xxxmodDocumento6 pagineIn Ge Cmd5b1xxxmodNinh Quang TrườngNessuna valutazione finora
- Sharepoint Developer Interview QuestionsDocumento6 pagineSharepoint Developer Interview QuestionsSandeep VemulaNessuna valutazione finora
- RK3128 Datasheet V0.6Documento58 pagineRK3128 Datasheet V0.6ManishNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Example 5.1:, Nonlinear HZ or Multiples Thereof ForDocumento11 pagineComputer Example 5.1:, Nonlinear HZ or Multiples Thereof ForNguyễn Quang MinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Com 328 Review QuestionsDocumento1 paginaCom 328 Review QuestionsNjeru DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- 1500R Maintenance and TroubleshootingDocumento24 pagine1500R Maintenance and TroubleshootingKaushal DarjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Result - VAS - B Tech S5 (R& S) Dec 2019 PDFDocumento49 pagineResult - VAS - B Tech S5 (R& S) Dec 2019 PDFGjNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-1-Introduction To ComputersDocumento15 pagineCh-1-Introduction To Computersanand_gudnavarNessuna valutazione finora
- Alteryx API Developer Documentation SummaryDocumento2 pagineAlteryx API Developer Documentation SummaryAbhishek Dey DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Geh 6700Documento292 pagineGeh 6700Anis HamdaneNessuna valutazione finora
- BVADocumento4 pagineBVAHarshali Y. PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- CBORDocumento3 pagineCBORsweeti sahNessuna valutazione finora
- RFMD.: CATV Hybrid Amplifier Modules: Past, Present, FutureDocumento21 pagineRFMD.: CATV Hybrid Amplifier Modules: Past, Present, FutureSanthosh MechNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank Chapter 6 and Chapter 7Documento5 pagineQuestion Bank Chapter 6 and Chapter 7nooneNessuna valutazione finora
- Sound Level Meter: Model: SL-4012Documento2 pagineSound Level Meter: Model: SL-4012onurNessuna valutazione finora
- TCP Client Test Software - Simply Modbus SoftwareDocumento4 pagineTCP Client Test Software - Simply Modbus SoftwareSaber LeffiNessuna valutazione finora
- VB Script String FunctionsDocumento10 pagineVB Script String FunctionsG.C.ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Psocol 2003 PDFDocumento76 paginePsocol 2003 PDFJohn WallerNessuna valutazione finora
- GFK1645JDocumento704 pagineGFK1645JphuvtbuithuongNessuna valutazione finora
- COPA1 ST Sem TPDocumento422 pagineCOPA1 ST Sem TPNaveen NarnualNessuna valutazione finora
- Ica Lab (135) Iii-IDocumento87 pagineIca Lab (135) Iii-IesesesNessuna valutazione finora
- PLSQLDocumento54 paginePLSQLvenuoracle9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Artemis Mk5 User GuideDocumento36 pagineArtemis Mk5 User GuideHazem AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbide Series: Mid-Tower Gaming CaseDocumento48 pagineCarbide Series: Mid-Tower Gaming CaseRoger SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- An Improved Round Robin CPU Scheduling Algorithm BDocumento4 pagineAn Improved Round Robin CPU Scheduling Algorithm BAbduallah MustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Programmable Logic Controllers: PLC I/O Module Types and PLC Trainer ConfigurationDocumento11 pagineProgrammable Logic Controllers: PLC I/O Module Types and PLC Trainer Configurationemmaupik_221503348Nessuna valutazione finora
- Spend Less Time On Windows PC Migrations With Dell Migrate - Interactive PDFDocumento6 pagineSpend Less Time On Windows PC Migrations With Dell Migrate - Interactive PDFPrincipled TechnologiesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 Block Diagram Representation of Control SystemsDocumento57 pagineLecture 2 Block Diagram Representation of Control SystemsAmeer FauwazNessuna valutazione finora