Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lecture - 17 B - Identification - of - Plastics
Caricato da
dev11739Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lecture - 17 B - Identification - of - Plastics
Caricato da
dev11739Copyright:
Formati disponibili
IDENTIFICATION OF PLASTICS IDENTIFICATION OF PLASTICS
BY
SIMPLE METHODS
BY
SIMPLE METHODS
IDENTIFICATION TECHNIQUES
SIMPLE INSTRUMENTAL
IDENTIFICATION IDENTIFICATION IDENTIFICATION IDENTIFICATION
1. APPEARANCE 1. THERMAL ANALYZER
2. METHOD OF 2. GPC
FABRICATION
3. PENETRATION TO 3. X RAY DIFRACTIOMETER
HOT ROD AND
CUTTING WITH A 4. I. R. SPECTROSCOPY
KNIFE
5. NMR SPECTROSCOPY
4. FLOTATION TEST
5. SCRATCH RESISTANCE
6. COLOUR
7. ODOUR
8. TEAR
9 SOLUBILITY 9. SOLUBILITY
10. BURNING
CHARACTERISTICS
11. PYROLYSIS
12. MELTING POINT
13. CONFIRMATION TEST
.
HOW TO IDENTIFY A
PLASTIC ? PLASTIC ?
Look at the sample. Is it transparent, translucent or opaque?
Feel the sample Doesit bend? Canit bescratched? What doesthesurfacefeel Feel the sample. Does it bend? Can it be scratched? What does the surface feel
like?
Cut the sample with a sharp knife. Does it cut easily: Are the edge smooth or
j d i bl fl k jagged? Does it crumble or flake?
Subject the sample to a float test. Does it float or sink? (the test is invalid if
plastic foam. Wash with detergent solution initially to stop air bubbles adhering to p g y p g
surface.)
Try to burn a small piece of sample. What is the size and colour of flame? Is
smokeproduced? Domoltendripsfall fromsampleandcontinuetoburn? Isthe smoke produced? Do molten drips fall from sample and continue to burn? Is the
sample self-extinguishing? Is there any odour when flame has been extinguished?
SAFETY: Use only a small sample held with tongs or pliers. Hold sample over a
t l t Shift ti l d t h till i it d metal tray. Shift cautiously and not when still ignited.
BENDING TEST ( WITH MOULDED BAR)
PLASTICS BENDING BEHAVIOUR PLASTICS BENDING BEHAVIOUR
1. Polyethylene Bends, tends to remain
2. Polypropylene Unbends most of the way
3. Polystyrene Cracks but retains bend
4. ABS Bend tends to remain
5 PVC (Rigid) Bendseasilyandsprings 5. PVC (Rigid) Bends easily and springs
back quickly
6. Cellulose acetate Bend tends to remain
7. PMMA Cracks and splinters
8. Nylon Difficult to bend, springs back y , p g
9. Polycarbonate Tough to bend
THERMOPLASTICS
VISUAL OBSERVATION TEST VISUAL OBSERVATION TEST
Low gloss easily be scratched by nail - LDPE OR LLDPE
High gloss can be scratched by nail - HDPE
Highglosscannot bescratchedbynail PP High gloss cannot be scratched by nail - PP
DROPPING TEST
When a moulded component is dropped on hard surface
Metallic sound Dull sound etallic sou d ull sou d
PS, HIPS Cellulosics
SAN ABS Polyamides SAN, ABS Polyamides
PC, PPS PTFE,PMMA
PPO Polyacetal
Polysulphone PVC ,
Polyolefins
TEST TO DIFFERENTIATE
THERMOPLASTICS AND THERMOSETS
CUTTING TESTS
a) If a shaving can be pared off with knife, it may be a
th l ti thermoplastic.
Note:PMMA and Polystyrene are brittle and difficult to pare
b) If the material is rigid and will not pare off instead
flakes of powders, it may probably a thermoset plastic.
HOT ROD PENETRATION TEST HOT ROD PENETRATION TEST
Heat an electronic soldering iron to red hot and press against
the unknown sample.
) If th l ti t i l ft dth d t t a) If the plastic material softens, and the rod penetrates
the sample is thermoplastic.
b) If the plastic material does not soften and the rod does
not penetrate, the sample is thermoset plastic.
FLOTATION TEST
h h i l i d di When the material is dropped in water
Floats Sinks Floats Sinks
Polyolefins Other than
Polyolefins
N t Fill d l l fi d ll l f Note: Filled polyolefins and cellular foams are
exceptional for this test.
E gSinks Floats E.g.Sinks Floats
Talk filled PP PVC , PU
Glass filled PP and PS foams
PYROLYSIS TEST
HEAT THE SAMPLE IN AN IGNITION TUBE AND TEST THE PYROLYTIC VAPOUR WITH HEAT THE SAMPLE IN AN IGNITION TUBE AND TEST THE PYROLYTIC VAPOUR WITH
A MOISTENED INDICATOR PAPER.
ACID : TURNS BLUE LITMUS TO RED
BASE TURNS RED LITMUS TO BLUE BASE : TURNS RED LITMUS TO BLUE.
ACID VAPOURS
MAY COME FROM CARBOHYDRATE POLYMERS & THEIR DERIVATIVES . [E.G.,
CELLULOSE ACETATE]
HIGH ACID VAPOURS HIGH ACID VAPOURS
OFTEN INDICATES THE PRESENCE OF CHLORINE . [E.G., PVC OR RUBBER NEUTRAL
VAPORS]
EVOLVED FROM HYDRO CARBON POLYMERS, SILICONES AND SOME POLYESTERS
HYDROCHLORIDE.
ALKALINE VAPOURS
INDICATE THE PRESENCE OF N
2 .
E.G., POLYAMIDE, PUs, PROTEINS & AMINO
FORMALDEHYDE RESINS.
BURNING CHARECTERISTICS OF
THERMOPLASTICS
S. No. Plastic Flame Kind of Melt Odour
Material Characteristics smoke behaviour
1. PE Blue base yellow tip No smoke Drips Waxy
smell
2. PP Blue base and No smoke Drips Lubricating p g
yellow tip oil smell
3. PS Orange yellow Black soot No Merry gold
flame (Heavy smoke) dripping smell
4. HIPS -do -do -do- Burning rubber
smell
5 ABS do do do do 5. ABS -do -do -do- -do-
Note: ABS & HIPS can be differentiated by detection of Nitrogen by elemental analysis.
6. SAN -do- -do- -do- Merry gold
smell
Note: SAN & PS can be differentiated by detection of present of extra element Nitrogen.
S. No. Plastic Flame Kind of Melt Odour
Material Characteristics smoke behaviour
7. PVC Green edged flame emitting white burnt pungent
self extinguishing fume after edges smell
put off the charing of chlorine
flame
Note: A copper wire is heated to redness and the material is taken by the wire and ignited.
Bright green flame confirms presence of chlorine - PVC
8. Polyamides:
Nylon-6 Blue base yellow No smoke Burned face Burned
tip, spurting self bubbles and hair
extinguishing drips smell
Nylon-6,6 -do- -do- -do -do-
Nylon-6,10 -do- -do- -do- -do-
Nylon-11&12 -do- -do- -do- -do-
Note: The individual type of polyamides can be differentiated by melting temperature and
solubility.
Nylon 11 & 12 will not dissolve in formic acid at room temperature. But Nylon 11 will
dissolve in formic acid at elevated temperature.
S.No. Plastic Flame Kind of Melt Odour
Material Characteristics smoke behaviour
9. Cellulose -do- -do- -do- Rancid
Acetate butter Acetate butter
Butyrate or charred
milk smell
Cellulose Burns vigorously Black Sublimation Camper g y p
Nitrate with bright yellow smoke like camper smell
10. Polyester (thermoplastics)
PBT & PET Orange yellow flame Sooty Drips Fruity
spurting, self flame smell of
extinguishing ester
Note: Bothcanbedistinguishedbymeasuringmeltingtemperature Note: Both can be distinguished by measuring melting temperature.
11. PMMA Blue base yellow tip No smoke No driping Fruity
burns continuously but bubbling smell
on the burnt
surface
12. PC Orange yellow flame Black Burnt edge Phenolic
self extinguishing smoke chars smell
(Ink
smell) smell)
13. POM Pale blue flame No smoke Driping Pungent
burns continuously smell of
formaldehyde
14. PPS Orange yellow Black No Dripping H
2
S gas
flame self smoke but charring smell
extinguishing
15. PPO -do- -do- -do- Phenolic
Smell
Note: It can be differentiated with polycarbonate by pyroloising PPO, which emits brown gas
acidic in nature.
16. TPU
MDI based Blue base yellow No smoke Drips like Faint
resin tipburnscontinuously oil apple resin tip burns continuously oil apple
smell
TDI based Yellow flame self Black Drips very -do-
resin extinguishing smoke fast g g
17. PTFE Does not burn No smoke No dripping Pungent
smell of HF
N Wh h d l b Note: When heated strongly becomes transparent.
BURNING CHARECTERISTICS OF
THERMOSETS THERMOSETS
S. No. Plastics Flame Kind of Odour
Material Characteristics smoke
1. PF Self extinguishing No Charcoal smell
2. UF -do- No Fishy smell
3 MF d N d 3. MF -do- No -do-
Note: When the moulded component of all the three materials burn in the flame, the burnt surface
slightly swells and cracks.
4. Polyester Burns with orange Black Ester smell
(unsaturated) yellow flame burns smoke
continuously
5 E d d Ch dfl ll 5. Epoxy -do- -do- Charred flour smell
BURNING CHARACTERISTICS OF
ELASTOMERS
S.No TYPE OF POLYMER COLOUR OF FLAME ODOUR OTHER NOTABLE
& KIND OF SMOKE CHARACTERISTICS
1 POLY BUTYLENE YELLOW, BLUE BASE DISAGREEABLE , CHARS READILY
SMOKY SWEET
2 STYRENE - BUTADIENE BURNS CONTINUOUSLY PUNGENT SMELL OF CHARS , DRY
YELLOW SOOTY STYRENE POWDERY
3 EPDM NO SMOKE ,BLUE BASE WAXY SMELL DRY
YELLOW TIP POWDERY
4 N BR YELLOW SOOTY UNPLEASANT TACKY
5 BUTILE RUBBER (IIR) SMOKE FREE , CANDLE HYDROCARBON MELT &
LIKE SMELL TACKY
6 POLYISOPRENE (NR) YELLOW SOOTY PUNGENT LIKE CHARS &
BURNT RUBBER TACKY BURNT RUBBER TACKY
7 POLYCHLOROPRENE (CR) SELF EXTINGUISHING PUNGENT SMELL STRONGLY
YELLOW & SMOKY OF CHLORIN ACIDIC
8 SILICONE RUBBER BURNS CONTINUOUSLY NO ODOUR DRY WHITE
GLOW WITH WHITE SMOKE POWDERY GLOW WITH WHITE SMOKE POWDERY
9 EBONITE SMOKE FREE SULPHUR ODOUR CHARS
READILY
IDENTIFICATION BY PYROLYSIS TEST
This scheme is useful for identification of CR , NBR , SBR , NR / IR , IIR
type of rubbers
Test Procedure : Heat strongly 0.5gm of sample in a test tube until sample
begins to decompose and pass the fume in solution I and II and observe
change in colour initially and after heating.(Refer the following table)
SOLUTION - I : Dissolve one gram of p - dimethyl amino benzaldehyde in g p y y
5ml of HCl and add 10ml of ethylene glycol. Adjust the density to 0.851
gm /cc. By addition of methanol.
SOLUTION - II : Dissolve 2gm sodium citrate , 200mg of citric acid , 300mg
of bromocresol green and 300mg of metanil yellow in 500ml of water.
COLOUR REACTION WITH SOLUTION - I & II
RUBBER SOLUTION - I SOLUTION II
INITIAL AFTER HEATING
BLANK SOLUTION PALE YELLOW PALE YELLOW GREEN
CR YELLOW PALE YELLOW RED CR YELLOW PALE YELLOW RED
GREEN
NBR ORANGE RED RED GREEN
SBR YELLOW GREEN GREEN GREEN
NR / IR BROWN VIOLET BLUE GREEN
I I R YELLOW PALE BLUE GREEN GREEN
DROPLET FLOATS
DETERMINATION OF SPECIFIC GRAVITY
OF PLASTICS TEST METHOD ASTMD 792 OF PLASTICS TEST METHOD ASTM D 792
PROCEDURE:
Weight of empty specific gravity bottle : a gm
Weight of S. G. Bottle+Material : bgm Weight of S. G. Bottle Material : b gm
Weight of the material +S. G. bottle +liquid: c gm
Weight of the S. G. Bottle +Liquid : d gm
Weight of the material (b-a) : e gm g ( ) g
Specific Gravity of the material : e x D
(e + d) - c
Where D - specific gravity of the liquid taken for testing
Densityof thematerial: Density of the material:
specific gravity of the material x 0.999 (gm/cc)
DENSITY & MELTING POINT OF PLASTICS
S. NO. POLYMER ABBREVATION DENSITY MELTING
gm/cc POINT Deg. C
I POLYOLEFINS I. POLYOLEFINS
1. Low density Polyethylene LDPE 0.91 - 0.92 110
2. High density Polyethylene HDPE 0.94 - 0.96 130
3. Linear low density polyethylene LLDPE 0.91 - 0.93 125
4. High Molecule HDPE HMHDPE 0.94 - 0.97 135
5. Ultra High Molecular HDPE UHMHDPE 0.97 130
6. Polypropylene PP 0.89 - 0.91 160
II CHLORINATED POLYMERS II. CHLORINATED POLYMERS
1. Poly vinyl chloride PVC 1.38 - 1.41 160 - 220
2. Poly vinyledene chloride PVDC 1.65 - 1.75 190 - 200 y y
3. Chlorinated PVC PVCC 1.44 - 1.47 200 - 210
4. Co-polymer of vinyl chloride & PVC Co VA 1.16 - 1.36 130
Vinyl Acetate Vinyl Acetate
5. Poly vinyl Alcohol PVAI 1.21 - 1.32 218
6. Poly vinyl Acetate PVAc 1.17 - 1.26 175
III. FLUORINATED POLYMERS
1. Polyvinyl fluoride PVF 1.44 200
2. Poly vinyledene Fluoride PVDF 1.76 - 1.771 172
3. Poly chloro tri fluoro ethylene PCTFE 2.10 - 2.20 210
4. Poly Tetra Fluoro ethylene PTFE 2.10 - 2.30 320
IV. POLY STYRENE & CO-POLYMERS
1. Acrylonitrile-Butadiene styrene ABS 1.07 - 1.10 200 - 210
2. Styrene Acrylo nitrile SAN 1.06 200
3 l S 104 10 190 3. Polystyrene PS 1.04 - 1.07 190
V. POLYAMIDES
1. Nylon 6 PA 6 1.10 - 1.16 215
2. Nylon 66 PA66 1.09 - 1.14 265
3 N l 11 PA11 104 110 190 3. Nylon 11 PA11 1.04 - 1.10 190
4. Nylon 12 PA12 1.01 - 1.02 180
5. Nylon 6,10 PA6,10 1.07 - 1.09 210
VI. ACRYLIC POLYMERS
1. Polymethamethacrylate PMMA 1.17 - 1.20 190 y y
2. Polyacrylonitrile PAN 1.16 - 1.19 -
VII ACETAL POLYMERS VII. ACETAL POLYMERS
1. Polyoxym,ethylene(homo) POM 1.43 175
2. Polyoxymethylene (Co) POM 1.41 163
VIII. ESTERS
1 Polycarbonate PC 12 220 1. Polycarbonate PC 1.2 220
2. Poly ethylene terepthalate PET 1.37 255
3. Poly butylene terepthalate PBT 1.32 225
IX. POLYURETHANES
1 Polyurethane(Linear) PUR 117 122 150 185 1. Polyurethane (Linear) PUR 1.17 - 1.22 150 - 185
X. CELLULOSIC POLYMERS
1. Cellulose acetate CA 1.25 - 1.35 230 1. Cellulose acetate CA 1.25 1.35 230
2. Cellulose acetate butyrate CAB 1.15 - 1.25 180
3. Cellulose noitrate CN 1.58 - 1.66 -
4. Cellulose propinate CP 1.20 - 1.24 -
XI. HEAT RESISTANCE POLYMERS
1. Poly phenylene oxide PPO 1.06 262
2. Poly phenylene sulphide PPS 1.35 290
3. Poly sulphone PSU 1.24 260
4. Poly imide PI 1.42 -
5. Poly ether ether ketone PEEK 1.27 335
THANK YOU THANK YOU
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- KEY Macromolecules Chart 2015Documento4 pagineKEY Macromolecules Chart 2015Joshua BernilNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 - Reactions Energy WorksheetDocumento4 pagineLesson 1 - Reactions Energy WorksheetAvakoalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Relationships Between The Surface Texture of Flexographic Printing Plates and The Printability of Kraft PaperDocumento11 pagineRelationships Between The Surface Texture of Flexographic Printing Plates and The Printability of Kraft PaperQuý Đình Mai MaiNessuna valutazione finora
- AntimonyDocumento72 pagineAntimony沈益Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ex: # 01: A Sample of Dry Anthracite Has The Following: 44kg CODocumento12 pagineEx: # 01: A Sample of Dry Anthracite Has The Following: 44kg COnicoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Urinalysis and Body Fluids 5th Edition StrasingerDocumento23 pagineTest Bank For Urinalysis and Body Fluids 5th Edition StrasingerMarcSmithyoqz100% (33)
- Elements Compounds MixturesDocumento55 pagineElements Compounds MixturesFatima ?Nessuna valutazione finora
- Static and Mobile Pressure Vessels Rules OverviewDocumento22 pagineStatic and Mobile Pressure Vessels Rules Overviewsatnam1979100% (1)
- 4th - QTR - Result2013-14 PDFDocumento39 pagine4th - QTR - Result2013-14 PDFdev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6Documento48 pagine6dev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4th - QTR - Result2013-14 PDFDocumento39 pagine4th - QTR - Result2013-14 PDFdev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ministry of Culture: Required: District Youth CoordinatorsDocumento1 paginaMinistry of Culture: Required: District Youth Coordinatorsdev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notification SAIL Management Trainee PostsDocumento9 pagineNotification SAIL Management Trainee PostsAnusha PalakurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- 4th - QTR - Result2013-14 PDFDocumento39 pagine4th - QTR - Result2013-14 PDFdev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd SCH 2013-14 PDFDocumento67 pagine2nd SCH 2013-14 PDFdev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1.1polymers in Everyday Things - Contact LensesDocumento5 pagine3.1.1polymers in Everyday Things - Contact LensesDhif MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd SCH 2013-14 PDFDocumento67 pagine2nd SCH 2013-14 PDFdev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4 PDFDocumento12 pagine4 PDFdev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4th - QTR - Result2013-14 PDFDocumento39 pagine4th - QTR - Result2013-14 PDFdev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5 2014 PDFDocumento11 pagine5 2014 PDFRajesh Kumar ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Treatment of Waste Water: Presented By:-Vinai Agarwal (Bt10Che084)Documento10 pagineChemical Treatment of Waste Water: Presented By:-Vinai Agarwal (Bt10Che084)dev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- Flow Chart Heat Equation (BT10CHE051) Prashant MeenaDocumento1 paginaFlow Chart Heat Equation (BT10CHE051) Prashant Meenadev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
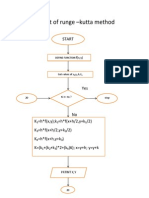
- Flow Chart of Runge - Kutta Method: StartDocumento1 paginaFlow Chart of Runge - Kutta Method: Startdev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- GATE 2016 Certificate From PrincipalDocumento1 paginaGATE 2016 Certificate From PrincipalPraveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture - 18 Applied Rheology 2Documento7 pagineLecture - 18 Applied Rheology 2dev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- Block Diagram ReductionDocumento7 pagineBlock Diagram ReductionMahendra Sutar100% (1)
- Ozone DisinfectionDocumento7 pagineOzone DisinfectionKwang Je LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Sewage Sludge Incineration Processes and Emissions RegulationsDocumento53 pagineSewage Sludge Incineration Processes and Emissions RegulationsTaufik Abdillah Natsir100% (1)
- Cen 03 - 2014Documento12 pagineCen 03 - 2014dev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture - 19 Applied Rheology 3Documento10 pagineLecture - 19 Applied Rheology 3dev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture - 17 A - Identification of PlasticsDocumento3 pagineLecture - 17 A - Identification of Plasticsdev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- Advantage Plus Consent LetterDocumento1 paginaAdvantage Plus Consent Letterdev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- 02 5Documento18 pagine02 5dev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture - 20 Applied Rheology 4Documento9 pagineLecture - 20 Applied Rheology 4dev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Rheology in Polymer ProcessingDocumento11 pagineApplied Rheology in Polymer Processingdev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture - 16 Applied Rheology in Polymer ProcessingDocumento12 pagineLecture - 16 Applied Rheology in Polymer Processingdev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture - 15 Decorating PlasticsDocumento24 pagineLecture - 15 Decorating Plasticsdev11739Nessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Internal Energy at the Microscopic LevelDocumento4 pagineUnderstanding Internal Energy at the Microscopic Levelaknauriyal2013Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Effect of Different Alkalinity Levels On Litopenaeus Vannamei Reared With Bio Oc Technology (BFT)Documento17 pagineThe Effect of Different Alkalinity Levels On Litopenaeus Vannamei Reared With Bio Oc Technology (BFT)Manu MorpheusNessuna valutazione finora
- June 2017 (v1) QP - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSEDocumento12 pagineJune 2017 (v1) QP - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSEbandana dekaNessuna valutazione finora
- Epicon T 500Documento12 pagineEpicon T 500Mugilrajan DevarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohol DistillationDocumento4 pagineAlcohol DistillationprocesspipingdesignNessuna valutazione finora
- The Radio Chemistry of Mercury - Us AECDocumento211 pagineThe Radio Chemistry of Mercury - Us AEClondonbluetopazNessuna valutazione finora
- Dualistic Properties of Cosmetic Formulations Based On Phenylpropanoids From Ajuga Reptans PDFDocumento11 pagineDualistic Properties of Cosmetic Formulations Based On Phenylpropanoids From Ajuga Reptans PDFjohannes karcherNessuna valutazione finora
- UV-Curing Screen InksDocumento2 pagineUV-Curing Screen InksJavier RealNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Information Sheet: Alloy Cusn12Documento1 paginaProduct Information Sheet: Alloy Cusn12Hawraa AlbahadlyNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Emission AbsorptionDocumento6 pagine6 Emission AbsorptionArya RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Niton XRF V Fire Assay App NoteDocumento2 pagineNiton XRF V Fire Assay App Notedarioharloc2272Nessuna valutazione finora
- This Document Certifies That: Precision Polymer Engineering Limited (PPE)Documento2 pagineThis Document Certifies That: Precision Polymer Engineering Limited (PPE)JuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Urine Analysis I: Chemical Examination: Lenka Fialová & Martin VejražkaDocumento9 pagineUrine Analysis I: Chemical Examination: Lenka Fialová & Martin VejražkaGeffrey S. QuilalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Brochure TDS RedicoteE 11Documento1 paginaBrochure TDS RedicoteE 11Rabin BeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Fighting - BasicDocumento1 paginaFire Fighting - BasicCostisNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipe identification color codingDocumento1 paginaPipe identification color codingขุน แสนNessuna valutazione finora
- Marcet Boiler Experiment LabsheetDocumento8 pagineMarcet Boiler Experiment LabsheetWan NurdyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016-04 - Broschuere - Innovative - Oberflaechensysteme - Klein R3RDocumento16 pagine2016-04 - Broschuere - Innovative - Oberflaechensysteme - Klein R3RRico MalibiranNessuna valutazione finora
- Carboxylic Acid & NitrilesDocumento19 pagineCarboxylic Acid & NitrilesDante Luis SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7: Practical Considerations in Modeling: With Examples From Other ChaptersDocumento38 pagineChapter 7: Practical Considerations in Modeling: With Examples From Other ChaptersHectistyleNessuna valutazione finora
- AQUACID 101 EX Lote 1020015695 & BPY0021-01Documento1 paginaAQUACID 101 EX Lote 1020015695 & BPY0021-01Julio . CNessuna valutazione finora
- BASF Pharma Solutions - Main Product Catalog - WebDocumento44 pagineBASF Pharma Solutions - Main Product Catalog - WebŽeljko StanojkovskiNessuna valutazione finora