Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Subject: Type of Lesson: Grade: Csec Obj:: Student Instructional Material
Caricato da
Chris McLean0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
9 visualizzazioni9 pagineStates of Matter
Titolo originale
l2PDF
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoStates of Matter
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
9 visualizzazioni9 pagineSubject: Type of Lesson: Grade: Csec Obj:: Student Instructional Material
Caricato da
Chris McLeanStates of Matter
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 9
Subject: Chemistry Type of Lesson: Practical Activity, Discussion
Grade: 10 CSEC OBJ: A 1.2 Explain the difference et!een
the three states of matter in terms of
ener"y and arran"ement of particles
Term: Christmas UNIT: 1 #tates of $atter
urat!on: %0 minutes Lesson: " &i'uid ( )aseous state of *ater
#ee$: 1
Objectives
As a result of this lesson, you !ill e ale to:
1+ ,utline the physical properties of !ater in the li'uid state.
2+ Explain ho! li'uid particles ehave in terms of -inetic ener"y and
other associated physical properties.
.+ /se dra!in"s and flo! dia"rams to sho! the arran"ement of
particles of matter in the li'uid state of !ater and compare this to
the arran"ement of particles in the solid state of !ater.
0+ Discuss !hy the heat ener"y re'uired for chan"in" !ater from the
li'uid state to the "aseous state is relatively lar"e.
1+ Explain ho! the processes of evaporation and coolin" are rou"ht
aout y chan"in" the state of matter.
Prerequisite Student Knowledge
1+ 2ou should e a!are that the properties of matter can chan"e.
2+ 3here are physical and chemical chan"es !hich may occur to
chan"e matter from one state to another.
Important Points
1+ *ater in the solid state is called ice and it can chan"e to a li'uid state
!hich !e call !ater y a physical chan"e called meltin". $eltin"
occurs !hen !ater in the solid state "ains ener"y to chan"e the
arran"ement of the particles into li'uid !ater.
Key Terms
meltin" point oilin" point free4in" point
Student Instructional Material 1
Challenge Areas
Distin"uish et!een meltin" point5 free4in" point and oilin" point
quipment!"aterial #eeded$
Containers of varyin" shapes and si4es, pencil crayons, thermometer
#ote to Student$
1+ 6or a pure sustance, the meltin" point and free4in" point occur at
the same temperature
#hape is a physical property of a sustance
2
Introduction
1) Introductory %ct!&!ty
a. &oo- at a "lass of ice. *hat do you oserve7
*rite this para"raph in your note noo-.
i. 3he states of matter can e chan"ed dependent on conditions of
temperature and pressure. 3emperature and pressure can affect the
arran"ement of the particles, the types of forces et!een the particles and the
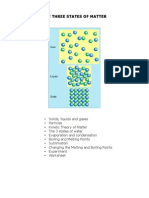
types of motion !hich the particles under"o. *ater exists in three states: solid,
li'uid and "as and is ale to chan"e its state dependent on the temperature and
pressure conditions.
ii. 8n this lesson !e !ill focus on the chan"e in state of !ater from a solid to
a li'uid and from a li'uid to a solid.
2) %ct!&!ty: Investigating the energy changes which occur when the temperature of water
changes.
a. 2our teacher !ill place you in "roups of threes and you !ill e provided !ith a
heat source, thermometer, 100 " ice, 110 cm
.
!ater at room temperature.
. Carry out the follo!in" steps outlined in *or-sheet 2.1 and record your results
usin" a data tale:
#or$s'eet "(1
%!m: Investigating the energy changes which occur when the
temperature of water changes
%pparatus: heat source, thermometer, 100 " ice, 110 cm
room temperature
)et'od
1+ Place the 110 cm
and place the ea-er and its contents on a tripod stand over the
9unsen urner or hot plate.
2+ 3a-e the temperature of the ice:!ater mixture usin" the
thermometer. 9e careful not to use the thermometer as a stirrin"
rod and not to ma-e it touch the ottom or sides of the ea-er.
Allo! it to remain in the mixture for aout .0 seconds, measure
and record the temperature in the data tale.
.+ &i"ht the 9unsen urner and ad;ust it to a medium flame.
$easure and record the temperature of the mixture every .0
seconds. /se a stirrin" rod to stir the ice and !ater efore
ma-in" each temperature readin". Also, record the physical state
Description Explanation
Student Instructional Material
%arning
1. Do not use the
thermometer as a
stirring rod.
2. Do not make the
thermometer touch
the bottom or sides of
the beaker
.
of the !ater at each .0 second interval.
0+ Continue until the !ater e"ins to oil for aout . minutes.
*esu+ts
Complete the follo!in" tale !ith your results and share your results
!ith the !hole class:
Tab+e 1 ,eat!n- ata and Obser&at!ons
T!me !n m!nutes
Temperature .
/
C0
1'ys!ca+ State
0.0
3he teacher !ill "uide you in an exercise to ma-e a temperature:time
"raph.
Interpretat!on
After completin" the "raph, your teacher !ill "uide you in
interpretin" your "raph. Ans!er the follo!in" 'uestions:
1+ ,serve your "raph and note !here the curve is flat. *hat is the
temperature of the !ater and the physical state at that point7
Explain !hat you thin- mi"ht have een happenin" to the !ater
at that point.
2+ <o! do the flat portions on the "raph relate to the meltin" point
and oilin" points of !ater7
.+ 8dentify the processes y !hich !ater chan"es from a solid to a
Student Instructional Material
%arning
This activity should take
about 10 minutes.
Ensure that the units of
measurement which
were used for time and
temperature are
appropriate.
Do not connect the data
points with a straight
line.
0
li'uid and then from a li'uid to a "as.
0+ Explain !hat happens to the particles of !ater as it chan"es state
from ice to li'uid !ater.
&ody o' (esson
10 Group 2or$ 3
In4u!ry5based
+earn!n-
a( 6our
teac'er
2!++
re&!e2
2!t' you
2'at
p'ys!ca+
propert!es
of
substance
s are(
. ,utlin
e the
physical
properties
of !ater in
the li'uid
and solid
state in
terms of
the
arran"eme
nt of
particles,
motion of
the
particles,
Student Instructional Material 1
shape and
volume.
c. 2our
teacher
!ill
demonstra
te ho! to
represent
particle
arran"eme
nts on a
dia"ram as
you
descrie
the
arran"eme
nt to the
class. 2ou
!ill then
e allo!ed
to
complete
the tale
elo!
usin" the
specified
headin"s.
d. Complete
the follo!in" tale in
*or-sheet 2.2:
#or$s
'eet
"(":
Physical state: #olid
Property
#hape
=olume
Arran"ement of
Particles
Compressiility
Student Instructional Material >
Physical state: &i'uid
Property Description Explanation
#hape
=olume
Arran"ement of
Particles
Compressiility
2+ !scuss!on of %ct!&!ty
a. 2our teacher !ill explain that the temperature of matter, in this case !ater, is an
indirect measure of the avera"e -inetic ener"y of the particles that ma-e up that
matter. 3herefore, the temperature of the !ater:ice mixture "ives an indication of the
-inetic ener"y of the !ater molecules at that particular temperature. 3he hi"her the
temperature the faster the !ater molecules ?particles+ are movin".
. 2our teacher !ill then illustrate this movement of the !ater molecules usin"
circles and arro! dia"ram.
c. 2our teacher !ill explain that: *ater in the solid state can chan"e to a li'uid state
y addin" heat. 3he temperature at !hich a solid melts to form a li'uid is called its
meltin" point. 3he temperature at !hich ice melts is 0
0
C. 3his means that ice: the
solid state of !ater, can exist elo! this temperature ut !ill e"in to chan"e state
from a solid to a li'uid at 0
0
C @ this is referred to as its meltin" point. *hen li'uid
!ater chan"es to ice: solid state, it loses heat ener"y, so the temperature ecomes
lo!er, the motion of the particles ecomes more restricted and this is referred to as
coolin" or free4in" temperature. 3he temperature at !hich the !ater e"ins to chan"e
to ice is called its free4in" point.
d. 2ou should e ale to determine from your experiment that !ater can chan"e from
a li'uid to steam if more heat is added to cause the -inetic ener"y of the molecules to
further increase.
Student Instructional Material A
Closure
In5C+ass %ss!-nments
1+ Ans!er the follo!in" 'uestions:
a. Dra! dia"rams to illustrate the chan"e in state of particles of ice and !ater from
the solid to the li'uid state. 9e sure to include explanations in your dia"ram.
. Differentiate et!een the solid state of matter and the li'uid state of matter usin"
the particle theory of matter.
Out5of5C+ass %ss!-nment
1+ 8dentify the physical properties that you could use to tell the difference et!een the
follo!in" pairs of matter:
a. charcoal and sno!
b. lead and copper
c. salt and su"ar
d. vine"ar and !ater
e. "rape:nut ice:cream and vanilla ice:cream.
2+ Descrie the physical chan"e that is ta-in" place in each of the follo!in":
a. A pot of chic-en soup ules and steams on the stove.
b. &i'uid candle !ax drips and ecomes hard.
c. 3he car !indscreen e"ins to Bfo"C on the inside.
Supplemental
G+ossary of Terms
1'ys!ca+
propert!es
Characteristics that can e oserved
!ithout chan"in" the composition of
matter. Physical properties include
colour, odour, taste, density, soluility,
meltin" point and oilin" point.
1art!c+e t'eory $atter is made up of particles.
)e+t!n- po!nt 3he meltin" point of a sustance is the
temperature at !hich it chan"es from
the solid state to the li'uid state at
atmospheric pressure
,r
3he temperature at !hich a solid and its
li'uid exist to"ether in e'uilirium.
Student Instructional Material %
CSEC 7uest!ons
1+ Explain !hy more heat ener"y is necessary to chan"e !ater from a li'uid to !ater vapour
!hile less heat ener"y is re'uired to chan"e it from ice to li'uid !ater. D% mar-sE.
2+ #tate the difference et!een oilin" point and free4in" point.D 0 mar-sE.
*ecommended )ater!a+s
3extoo-, "raph paper, thermometer, stirrin" rod, ea-er, ice and pure !ater.
B!b+!o-rap'y
Atherton, $. and &a!rence, F., Chemistry for the Cariean: A CGC course. Fohn $urray.
Student Instructional Material H
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Algebra Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineAlgebra Cheat SheetDino97% (72)
- Kitchen Chemistry: Cool Crystals, Rockin’ Reactions, and Magical Mixtures with Hands-On Science ActivitiesDa EverandKitchen Chemistry: Cool Crystals, Rockin’ Reactions, and Magical Mixtures with Hands-On Science ActivitiesNessuna valutazione finora
- Flotation and Buoyancy ExplainedDocumento35 pagineFlotation and Buoyancy ExplainedChris McLean100% (1)
- Redox ReactionsDocumento7 pagineRedox ReactionsChris McLean0% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersNessuna valutazione finora
- Gating ManualDocumento84 pagineGating Manualmr.nguyenk100% (4)
- Gear CalculationDocumento58 pagineGear CalculationSachin KubasadNessuna valutazione finora
- 07 - Melting PointDocumento4 pagine07 - Melting Pointm_k_tripathy100% (2)
- 2210 - Melting Points and Mixed Melting PointsDocumento13 pagine2210 - Melting Points and Mixed Melting PointsAmalia Siller0% (1)
- Calorimetry Lab SEDocumento13 pagineCalorimetry Lab SEOindrilla Chakrabarty73% (11)
- St. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 4E Science (Physics) Chapter 14 Sound NotesDocumento6 pagineSt. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 4E Science (Physics) Chapter 14 Sound NotesMsLiewNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthing CalculationDocumento4 pagineEarthing CalculationNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Charles' Law ExplainedDocumento2 pagineCharles' Law ExplainedQueencess Ara TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Evapco Evaporative Condenser Engineering ManualDocumento32 pagineEvapco Evaporative Condenser Engineering Manualrodolfocv923590% (1)
- Aerodynamic Characteristics of NACA 4412 AirfoilDocumento19 pagineAerodynamic Characteristics of NACA 4412 AirfoilMuhammad HattaNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Science QuestionsDocumento40 pagineMaterial Science QuestionsLucky KapoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Loading LPG CalculationsDocumento12 pagineLoading LPG CalculationsJohn Green67% (3)
- Ionic and Covalent Compounds LabDocumento11 pagineIonic and Covalent Compounds Labapi-248698708100% (1)
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 1: Behavior of GasesDocumento32 pagineScience: Quarter 4 - Module 1: Behavior of GasesJoem Nicodemus Samonte83% (6)
- Dual Plate Check ValveDocumento38 pagineDual Plate Check ValveVikas Kumar PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry IGCSE GuideDocumento36 pagineChemistry IGCSE GuideFolk NarongritNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Thermal Equilibrium: Heat Transfer and TemperatureDocumento51 pagineUnderstanding Thermal Equilibrium: Heat Transfer and TemperatureZul Fahmi Mohamad SapawiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapt 15 LabDocumento4 pagineChapt 15 Labcledus2139267% (3)
- Observing Chemical Changes: Purpose: MaterialDocumento2 pagineObserving Chemical Changes: Purpose: Materialctremblaylcsd150Nessuna valutazione finora
- 08 Specific Heat CapacityDocumento11 pagine08 Specific Heat CapacityZoelFikar Fahmi67% (3)
- Physical Properties of Matter: ExperimentDocumento4 paginePhysical Properties of Matter: Experimentch chNessuna valutazione finora
- Week OneDocumento13 pagineWeek Oneapi-364434145Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ch.1-Matter in Our Surroundings 9th SolvedDocumento50 pagineCh.1-Matter in Our Surroundings 9th SolvedVikash SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- G10_SSLM_Q4_W2_APOSTOL_EVALUATED_EDITED-1Documento4 pagineG10_SSLM_Q4_W2_APOSTOL_EVALUATED_EDITED-1Gacha FluffyNessuna valutazione finora
- Science - The Three States of MatterDocumento11 pagineScience - The Three States of Matterapi-246187169Nessuna valutazione finora
- DL WorkDocumento2 pagineDL WorkyesNessuna valutazione finora
- U15 S1-2 HW Packet 1-7Documento19 pagineU15 S1-2 HW Packet 1-7Rohith GudatiNessuna valutazione finora
- StatesDocumento5 pagineStatesoffenberg1Nessuna valutazione finora
- XaDocumento8 pagineXaYongguk BangNessuna valutazione finora
- EXercise 2 (Recrystallization and Melting Point Determination)Documento3 pagineEXercise 2 (Recrystallization and Melting Point Determination)Cherryl SurigaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Expansion & Temperature ScalesDocumento28 pagineThermal Expansion & Temperature ScalesJames Trick Ocampo Valera0% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Lab - Determine Melting PointsDocumento9 pagineOrganic Chemistry Lab - Determine Melting PointssoulsodaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Law ReportDocumento24 pagineGas Law ReportFranko VujicicNessuna valutazione finora
- States of MatterDocumento5 pagineStates of MatterMichaela JohanntgesNessuna valutazione finora
- OrgChem Prelim ManualDocumento13 pagineOrgChem Prelim ManualCHEA MICH L. ABELLANONessuna valutazione finora
- Matter: Unit 5Documento16 pagineMatter: Unit 5al sigmanovaNessuna valutazione finora
- ScienceSLM G10 Q4 M1 Behavior-of-Gases-v-3.0Documento31 pagineScienceSLM G10 Q4 M1 Behavior-of-Gases-v-3.0matilendoabubakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Determine Melting Points with Mel-Temp ApparatusDocumento3 pagineDetermine Melting Points with Mel-Temp ApparatusNadherdaman AlshamaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 8 Q1 Week 6 7Documento13 pagineScience 8 Q1 Week 6 7Rachelle Mitch R. TamparongNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 7 3Documento5 pagineExperiment 7 3deborah07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Miranda, Marilyn, Teodoro, Nowell Neill D: CHM142L Organic Chemistry 1 Laboratory 2 Quarter SY 2013-2014Documento5 pagineMiranda, Marilyn, Teodoro, Nowell Neill D: CHM142L Organic Chemistry 1 Laboratory 2 Quarter SY 2013-2014Neill TeodoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry I Melting Point DeterminationDocumento10 pagineOrganic Chemistry I Melting Point DeterminationSmart TirmiziNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan 4Documento5 pagineLesson Plan 4api-177378486Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideDocumento39 pagineChapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideMuhd Rifaie RodzilNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Chemistry DLP F4Documento79 pagineNotes Chemistry DLP F4Aleisha SofeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement of Physical Properties: Substance Density in G/ML at 20 CDocumento8 pagineMeasurement of Physical Properties: Substance Density in G/ML at 20 Cمحمد العراقيNessuna valutazione finora
- Definitions and MCQs of Ninth Class Chemistry (States of Matter)Documento6 pagineDefinitions and MCQs of Ninth Class Chemistry (States of Matter)Sajid AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 WorksheetDocumento4 pagineLesson 1 Worksheetapi-239996848Nessuna valutazione finora
- Activity # 1 States of Matter (Basic)Documento6 pagineActivity # 1 States of Matter (Basic)ArebeeJayBelloNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Class 7 2022Documento95 pagineHeat Class 7 2022Theia JacobNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapt 15 LabDocumento4 pagineChapt 15 Labcledus21392Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Law ExpDocumento6 pagineGas Law ExpRonet Lopez RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Rising - Demonstration and InvestigationDocumento4 pagineWater Rising - Demonstration and InvestigationSorna KailashNessuna valutazione finora
- FeCu Mole Lab Honors ChemDocumento6 pagineFeCu Mole Lab Honors ChemMegan LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry Laboratory: Basra University College of Science and Technology Pharmacy DepartmentDocumento12 pagineOrganic Chemistry Laboratory: Basra University College of Science and Technology Pharmacy DepartmentcrtgyhujikNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 16 (Specific Heat of Copper)Documento4 pagineLab 16 (Specific Heat of Copper)tua87538Nessuna valutazione finora
- Q1 Week 4 - Module 11 Heat and TemperatureDocumento19 pagineQ1 Week 4 - Module 11 Heat and TemperatureJoana Cressel Paballa GratilNessuna valutazione finora
- SDLP-Charles'-Law 3Documento6 pagineSDLP-Charles'-Law 3Jessica SudioNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2, Lesson 1: Heat, Temperature, and Conduction: Key ConceptsDocumento13 pagineChapter 2, Lesson 1: Heat, Temperature, and Conduction: Key ConceptshanieNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2, Lesson 1: Heat, Temperature, and Conduction: Key ConceptsDocumento90 pagineChapter 2, Lesson 1: Heat, Temperature, and Conduction: Key ConceptsPeterNessuna valutazione finora
- ParticleDocumento143 pagineParticlespamiplviewNessuna valutazione finora
- Penabur International School - 8 - Gasses Law, Thermal Transfer - 1 - (Test) - Soal Siswa - RegaDocumento7 paginePenabur International School - 8 - Gasses Law, Thermal Transfer - 1 - (Test) - Soal Siswa - RegaFaber O.MNessuna valutazione finora
- Temperature and Thermal Energy ExplainedDocumento8 pagineTemperature and Thermal Energy ExplainedJessa Sumaylo CalambaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hot Globe and No Greenery Courtesy of the Carbon Hater's CultDa EverandHot Globe and No Greenery Courtesy of the Carbon Hater's CultNessuna valutazione finora
- Single Page Integral Table PDFDocumento2 pagineSingle Page Integral Table PDFEduardo MazariegosNessuna valutazione finora
- Sychronous CounterDocumento7 pagineSychronous CounterChris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistical Tables: Useful FormulaeDocumento5 pagineStatistical Tables: Useful FormulaeChris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Alg SolveRatIneq SolutionsDocumento10 pagineAlg SolveRatIneq SolutionsChris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol Anal 25 SIMDocumento7 pagineVol Anal 25 SIMChris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Multi SimDocumento713 pagineMulti SimBiswajit DebnathNessuna valutazione finora
- Alg SolveLogEqnsDocumento8 pagineAlg SolveLogEqnsStarijaNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Collector (Emitter Follower) AmplifierDocumento24 pagineCommon Collector (Emitter Follower) AmplifierBaljeet Singh SinwarNessuna valutazione finora
- DynamoDocumento28 pagineDynamoChris McLean0% (1)
- Reactivity of Metals SIMDocumento7 pagineReactivity of Metals SIMChris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- ComputingLimits SolutionsDocumento9 pagineComputingLimits SolutionsChris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Alg InverseFunctionsDocumento10 pagineAlg InverseFunctionsChris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Limits AssignmentsDocumento25 pagineLimits AssignmentsChris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebra CombinedFunctionsDocumento9 pagineAlgebra CombinedFunctionsChris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- College Algebra, Problems (Dawkins)Documento45 pagineCollege Algebra, Problems (Dawkins)joaoguitarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Vision of VolunteerismDocumento71 pagineVision of VolunteerismJosh LawrenceNessuna valutazione finora
- CalcII HydrostaticPressure AssignmentsDocumento4 pagineCalcII HydrostaticPressure AssignmentsUmer Iftikhar AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- ComputingLimits SolutionsDocumento9 pagineComputingLimits SolutionsChris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Engine Controls & SensorsDocumento9 pagineEngine Controls & Sensorsrudey18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computing LimitsDocumento9 pagineComputing LimitsChris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer Monomers and Their UsesDocumento8 paginePolymer Monomers and Their UsesChris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- M3SIM Reactivity 5Documento4 pagineM3SIM Reactivity 5Chris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- M3SIM Reactivity 5Documento4 pagineM3SIM Reactivity 5Chris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Trends in The Periodic TableDocumento24 pagineTrends in The Periodic TableChris McLeanNessuna valutazione finora
- E3 Fall 04Documento8 pagineE3 Fall 04Andriy ZetrumNessuna valutazione finora
- Weber Carb Troubleshooting GuideDocumento8 pagineWeber Carb Troubleshooting Guideleechyza100% (1)
- Zener BZX83CDocumento2 pagineZener BZX83CPelotaDeTrapoNessuna valutazione finora
- WRS 2008 CatalogDocumento34 pagineWRS 2008 CatalogYimmy Alexander Parra MarulandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Medicines ListDocumento24 pagineEssential Medicines ListJoshua Kevin Carl Tabar-GolpeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mutu Manajemen PDFDocumento238 pagineMutu Manajemen PDFirdawanNessuna valutazione finora
- R717 (Ammonia) Pressure Temperature ChartDocumento2 pagineR717 (Ammonia) Pressure Temperature ChartNeoZeruelNessuna valutazione finora
- C5Documento4 pagineC5Vilma Puma InostrozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Optional Strain Rate Forms For The Johnson CookDocumento17 pagineOptional Strain Rate Forms For The Johnson CookTien KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Determination of sulphites in water and wastewater by iodide-iodate titrationDocumento2 pagineDetermination of sulphites in water and wastewater by iodide-iodate titrationHimanshu ChaturvediNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM111 Week 4.2 - Chemical Bonds and Compounds Part 2 - Covalent Bond ModelDocumento17 pagineCHEM111 Week 4.2 - Chemical Bonds and Compounds Part 2 - Covalent Bond ModelKharl Roei SalvadorNessuna valutazione finora
- ACT Reading Practice TestsDocumento81 pagineACT Reading Practice TestsYann VautrinNessuna valutazione finora
- Rainbow FireDocumento4 pagineRainbow FireSilvia MariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Valvoline Lithium Ep2 GreaseDocumento1 paginaValvoline Lithium Ep2 GreaseDicky PratamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cutting Fluids and Machining ProcessesDocumento19 pagineCutting Fluids and Machining Processescasey rimNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO 4406 Fluid Cleanliness GuideDocumento1 paginaISO 4406 Fluid Cleanliness GuideJai BhandariNessuna valutazione finora
- Griffiths Chapter 2: Dan Wysocki February 19, 2015Documento6 pagineGriffiths Chapter 2: Dan Wysocki February 19, 2015akjsdnfNessuna valutazione finora
- Gcse 239/01 Additional Science: Foundation Tier Biology 2 A.M. THURSDAY, 13 January 2011 45 MinutesDocumento12 pagineGcse 239/01 Additional Science: Foundation Tier Biology 2 A.M. THURSDAY, 13 January 2011 45 MinutessureshthevanNessuna valutazione finora
- Macromolecules: Question Paper 1Documento8 pagineMacromolecules: Question Paper 1Bridgette LombardNessuna valutazione finora
- U4 - WeldingDocumento59 pagineU4 - WeldingAnonymous LM9RaUA4yNessuna valutazione finora
- ApplicationNote PH Measurement JamJellies EN 30538204Documento4 pagineApplicationNote PH Measurement JamJellies EN 30538204MarcinNessuna valutazione finora
- ENSCO DS6 - Unit320P04DS6 - SNDS6320D - Mud Pump D - Abnormal - 25506970Documento5 pagineENSCO DS6 - Unit320P04DS6 - SNDS6320D - Mud Pump D - Abnormal - 25506970mohamed hamedNessuna valutazione finora
- 200 ML of Water and 300 ML of Water Into Container B, C and D RespectivelyDocumento3 pagine200 ML of Water and 300 ML of Water Into Container B, C and D RespectivelyAlexandra ChiengNessuna valutazione finora