Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Makalah AAS NovA 300 Bing
Caricato da
Ahmad Fadil DjamilCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Makalah AAS NovA 300 Bing
Caricato da
Ahmad Fadil DjamilCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry (AAS) or atomic absorption
Spectrophotometryis one type of analysis spektrofometri where the
measurement basis is themeasurement of the absorption of a beam by an atom, the
rays are not absorbed,transmitted and converted into electrical signals that
are measurable. AAS was first introduced by the Welsh (Australia) in 1955. AAS is
a popular method for analysis of metals, since in addition to simple, it is
also sensitive and selective. The development of science and technology today have
an impact on furtherincreasing the knowledge and the capacity of human
beings. How much does each man more demanded and is directed towards science
and technology in all areas. Do not miss also a chemistry that is identical to
the science of mikropun did not escapefrom this SCIENCE and
TECHNOLOGY perkebangan sosrotan. Lately, the SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY
SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY has been born who could facilitate thepurposes
of chemical analysis. One form of this SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY advancesthat
are now commonly known as atomic absorption tools which are very supportive ina
chemical analysis by the method of atomic absorption Spectroscopic (SSA).
Chemists have long been used as an aid in identifying chemical substances. Atomic
absorption, which have been known many years ago. Nowadays the use of
spectrophotometry measurements implies the absorption of light
energy away by achemical system as a function of the wavelength
of the radiation, similarly the lone
absorption measurement at a certain gelomabng. Extension of the atomic
absorptionspectrophotometry to the other original elements of the
result development of flameemission spectroscopy. When properly illuminated, can
be seen occasionallydrop-drops of sample that has not been evaporated out of
the top of the flame, and gas-gas flame was terencerkan by the
air entrance respectively as a result of low pressure created by the high speed
of the optical system, anyway it's not but the entirenayala but only manage an area
with a certain distance on the cusp of the burner.
In addition with the method of atomic
absorption elements with low excitation energycan also be
analyzed by flame photometry, but for elements with high excitationenergy can only
be done with the fotomeetri flame. For analisisi with the resonancespectral
line between 400-800 nm, flame photometry is useful, while between 200-
300nm, the AAS method better than flame photometry. For the
qualitative analysis, the preferred method of flame photometry of AAS,
because cathode lamps require specificAAS (hallow cathode). Kemonokromatisan in
AAS is the main requirement. A change intemperature of a flame will interfere
with the process of excitation so that analysis canberfarisasi flame photometry in the
result. In terms of operating costs, more
expensivethan AAS flame photometry berfilter. It can be said that
the flame photometry methodand AAS are complementary of each other.
1.2 scope
Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) is a
procedure for spectro analyticalpenentuankualitatif and quantitative chemical
elements that employ optical radiationabsorption (light) by free the atoms
in the gas. In a chemical analysis technique useduntukmenentukan the
concentration of specific elements (analyte) in the sample to be analyzed.AAS can
be used to determine more than 70 different elements dalamlarutanor directly on
the solid sample.
1.3 the benefits of writing
As for the Benefits expected from this paper writing in addition to fulfill
the duties ofteachers of subjects, also aims to be the writer or the reader can find
out more abouthow the method or basic principles of Atomic
Absorption Spectroscopy (SSA) itself, in addition so that we can see the extent to
which efficiency from the use of this methodif seen from the advantages
and shortcomings and also knowing how to operate toolsAAS novA 300
CHAPTER II
THEORY
2.1 a Brief theory of Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (SSA)
A short history of atomic absorption was first observed by Frounhofer, who at the
timeworked on the black lines on spetrum of the Sun. While
the mememfaatkan principle in the field of atomic absorption analysis is
an Australia named Alan Walsh in 1995.Before chemists depends a lot on ways or
methods of analyst spektrografikspektrofotometrik. Some of the ways this is a
difficult and time consuming, then immediately in the substitute with atomic
absorption Spectroscopy or AtomicAbsorption Spectroscopy (ASS). This method is
very appropriate for the analysis of substances at low concentration. This
technique has several advantages compared to
conventional emission spectroscopy method.Indeed apart from the atomic
absorptionmethod, the elements with the energy excitation can be also analyzed
by flamephotometry, but to share elements with high excitation energy can only be
done withflame photometry for analysis with the line resonance spectrum between
400-800 nm,flame photometry is useful while between 200-
300 nm method ASS better than flamephotometry.For the qualitative analysis, the
flame photometry method is preferablefrom
the ASS, because cathode lamps require specific ASS (hallow cathode).kemonokro
matisan in the ASS is a major preoccupation. In terms of the cost of the more
expensive of the AAS flame photometry berfilter. It can be said that
the flamephotometry method and AAS is the komplomenter of each other.
Other components of an atomic absorption spectrophotometer is konfensional
nature.Monokromator can not as expensive as a regular spectrophotometer
monokromator commensurate quality, because less is required. The only
requirement is that the monokromator skip the line selected, without the
resonant coupled to otherlines in the spectrum of the light source arising from the
cathode metal or gas lags.
Principled methods of AAS on absorption of light by atoms. The atoms absorb
light at particular wavelength, depending on the nature of elemental. E.g. Sodium
absorbs at 589 nm, uranium at. 358,5 nm where as potassium at 766,5 nm. Light on
this wave has enough energy to change the electronic level of an atom. With
theabsorption of energy, means gaining more energy, an atom in the ground
state energylevel is raised to the level of excitation. Excitation levels are varied. For
example the element with atomic number 11 Na has the electron
configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1,basic level for valence electrons, meaning it does not
have any 3S the excess energy.These electrons can be excited by the energy of
ascent 3 p or 4 p 2.2 eV ascent with the energy of 3.6 eV, each corresponding
to a wavelength 589nm and 330 nm. We can choose among these wavelengths that
produce the sharp spectral lines with maximum intensity, known for its line
of resonance. Other lines that are not line resonancespectrum can be associated
with energy levels of molecules, usually in the form ofRibbon-Ribbon width or line is
not derived from a basic level of excitation caused the process atomisasinya.
The Notion Of Atomic Absorption Spectrometry Atomic absorption
spectrophotometry (AAS) is a method of analysis for the determination
of elements and metals, metalloids, based on absorption (absorption) of
radiation by atoms of these elements-free. About 67 items have can be
determined by means AAS. A lot of determination of metalelements previously
done with the method polarografi, then with UV VIS Spectrophotometric methods,
many are now replaced by the method of AAS.
The principle of measurement with the method of AAS is the absorption of UV
light orVis by metal atoms in the ground state are contained in "the Atomic-
forming". UV raysor Vis that diabsorpsi comes from emeisi light metal found on
the source of energy"HOLLOW CATHODE".
The rays emanating from the "HOLLOW CATHODE" is absorbed by the atoms of the
metals contained in the flame, so that the configuration of the atoms become excited
state. If the electron returns to the ground state "GROUND STATE" then it
will emit its light. The magnitude of the diemisikan light intensity is proportional to
theconcentration of the sample (in the form of atom) found on the flame.
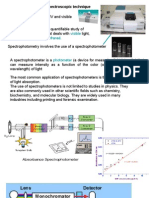
There are five basic component tools SSA:
1) SOURCE of LIGHT, usually in the form of "HOLLOW CATHODE"
that emit the rays of the spectrum absorbed by atoms.
2) Flame, is the absorption cells produce samples of atoms
3) Monokromator, for mendispersikan beam with a specific wavelength
4) detector, to measure the intensity of the signal and amplify beams
5) Readout, the bigger picture shows the reading after processed by electronic tools
Like a General on quantitative analysis, spectrometer equipment a sample based on
thelaw of Lambert-Beer, namely:
A = b C
Description: A = absorbance
- = molar absorptivitas
-b = width of samples crossed rays
-C = concentration of a substance
Formula Beer Lambert law showed that the magnitude of the absorbance value is
directly proportional (linearly) with concentration. Based on research, kelinieranBeer-
Lamber Saturday law generally is limited to the value of absorban 0.2 to 0.8.
Beer Lambert law can be applied to the standard
method and standard additionmethod.
THE USUAL STANDARD STANDARD ADDITION
1.1. Measurement of the samples and standards are carried
out separately 1.measurement of the samples and standards are carried
out simultaneously
1.2. On its calibration curve there is just slop 2. on its calibration curve other
thanthere's slop there is also intersep
1.3. Determination the concentration of direct diplotkan to sample calibration
curve 3.determination of concentration sample calibration
curve to diplotkan indirectly
1. Basic principles of b.
The basic principle of the measurement by AAS is the decomposition of
molecules intoatoms with rock energy from fire or electricity. Atom in ground
state can soak up raysemitted by the source, at this stage will be on Atomic excited
state. The rays are not absorbed by the atoms will be forwarded and emitted at the
detector, and thenconverted into a signal that is measurable. The wavelength
of the light depends on theelectron configuration of the atoms and
the intensitasnya depends on the number ofatoms in the ground state, so AAS can
be used for both qualitative and quantitativeanalysis.
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry (AAS) is a method of analysis that is based
onthe process of absorption of radiation energy by atoms which are at the level
ofprimary energy (the ground state).
The absorption of the tereksitasinya of electrons in the atom's skin to the level
ofhigher energy. This situation is unstable, the electrons are going back
to basic energy level while removing the energy in the form of radiation.
In AAS, atoms are free to interact with the various forms of energy such as heat
energy, electromagnetic energy, chemical energy and electrical energy. This
interactiongives rise to the processes in
the free atom absorption and generating emissions (emission) radiation and heat.
The emitted radiation is distinctive because it has the characteristics
of a wavelength for each free atoms.
The absorption or emission of radiation due to electronic transitions, i.e. the
displacement of atoms, the electron energy levels to other energy levels.
Radiation absorption occurs when there is an mengabsorpsi electron energy of
radiation so that the switch to a higher energy level. Emissions occur when there
is anelectron moves to a lower energy level so a release of energy in the form of
radiation.
The wavelength of the radiation that causes excitation excitation level to level-1 is
called the resonance wavelength. This radiation comes from the element
ofmetal/metalloid.
Resonance radiation from element X can only be diabsorpsi by an
X atoms, otherwiseatoms X cannot be mengabsorpsi the
resonance radiation element Y. None of theelements in a periodic arrangement
of resonance radiation equal to other elements.
This led to a very specific method of AAS and almost free of interference because of
thefrequency of the radiation that is absorbed is characteristic for
each element.Distractions will only occur if the length of the resonance radiation of
two elements that are adjacent to each other.
c. type and type of AAS
There are three ways of atomisasi (the formation of atoms) within the AAS:
1. Atomisasi with a flame
A heated metal compounds will form the metal atoms at a temperature of
approximately 1700 C or more. The samples are in the shape of a liquid will be
doneatomisasi by way of embodying the fluid into the flame of the
gas fuel mixture. The high temperature of the flame is
required for each different elements of a atomisasi.Some elements can be
determined with a flame from a gas mixture that is different butthe use of fuel
and oxidant are different will give different sensitivity.
The terms of the gas that can be used in atomisasi with a flame:
Gas Mixture gives the temperature of the flame according to atomisasi items will be
analyzed
Not dangerous for example are not easy to cause an explosion.
Gas is reasonably safe, non-toxic and easily controlled
Pure and clean enough Gas (UHP)
The gas mixture is the most commonly used are air: C2H2 (1900
2000 flametemperature c), N2O: C2H2 (flame temperature of 2700-
3000 C), air: propane (1700 1900 flame temperature c). Number of atoms in
the flame depends on thetemperature of the flame. Flame temperature depending
on the comparison of gas fuel and oxidant.
Things to watch out for on a atomisasi with a flame:
1. the standards and samples must be prepared in the form of solution and quite
stable. It is recommended in a solution with a low acidity to prevent corrosion.
2. Atomisasi do with a flame from a gas mixture that corresponds to the element that
is analyzed.
3. the requirements when using the organic solvent:
Not easy to explode when it hit the heat
Have specific gravity > 0.7 g/mL
Have a boiling point > 100 C
Have a high flash point
Do not use hydrocarbon solvents
Making free with the use of atoms in the flame (Flame AAS)
Example: an aqueous solution of the MX, after dinebulisasi into
the spray chamber so as to form an aerosol is then brought into the flame of the
gas mixture by oxidant and fuel going through the process of atomisasi
2. Atomisasi without a flame
Atomisasi without a flame is carried out by the electrical energy flow in a
carbon rod(CRA Carbon Rod Atomizer) or tubes of
carbon (Graphite Tube Atomizer GTA) with two electrodes.
The sample was submitted to the CRA or GTA. An electric current is applied so
that the rod or tube becomes hot (the temperature rises to height) and the
elements analysedwill be teratomisasi. The temperature can be regulated up
to 3000 C. the samplesolution warming through three stages, namely:
Phase drying (drying) to evaporate the solvent
Pengabuan (ashing), the temperature of the furnace is raised gradually until
it occursthe decomposition and evaporation of the organic compound that is present
in the samples so retrieved metal oxide or a salt
Pengatoman (atomization)
3. formation of compounds with hydride Atomisasi
Atomisasi with the formation of the hydride compounds made
to items As, Se, Sbwhich is easy to decompose when heated at a temperature
of more than 800 c soatomisasi done by forming a hybrid compound
of gaseous or break down into atomsthrough the reaction of SnCl2 or as
NaBH4 reduction by, for example, mercury (Hg).
Parts of the Spectrometry AAS and its function
a resonance Radiation Sources.
Resonance radiation source used is
a hollow cathode lamp (the Hollow Cathode Lamp) or Electrodeless Discharge Tube
(EDT). Electrode hollow cathode lamp usually consist ofa
hollow cathode and tungsten coated with pure elements or a mix of the
pure elementdesired.
Tanung lights and window (window) is made of silica or quartz, filled with
a filler gasthat can produce ionization process. Gas fillers normally used is Ne, Ar
or He.
Resonance radiation emission occurs when the two electrodes is given
the voltage, the electric current that occur cause ionization of gas-gas filler. Ions
are positively chargedgas is shooting up the atoms that are present in the
cathode causing the atomstereksitasinya. The excited atoms are unstable and will go
back to the basic level by releasing energy in the form
of eksitasinya radiation. This radiation that is passedthrough the atom that is
in flames.
b. Atomizer
Atomizer comprising Nebulizer system
(spray), spray chamber and burner (burnersystem)
Nebulizer works to convert the solution into an aerosol (mist with a grain size
ofparticles of 15 20 m) and how to draw the solution through the capillaries (due
tothe effects of air flow) and suctioning gas fuel and oxidant, sprayed into
the Chamberof the spray. The mist particles finer then a mixed gas flow along the
fuel, go into a flame, while the great fog point streamed through the sewer.
Spray chamber serves to create a
homogenous mixture between gas fuel and oxidant,aerosols containing examples
of prior to entering the burner.
The Burner is just going on atomisasi i.e. changing mist/salt steam items will be
analyzed into normal atoms in the flame.
c. Monokromator
After the resonance radiation from a
hollow cathode lamp Atomic populations throughthe flame, the energy of the
radiation is partly absorbed and partly succeeded. The fraction of radiation that is
separated from other radiation continues. The election orthe separation
of the radiation is done by monokromator.
Monokromator serves to separate the resonance radiation which has
experienced theabsorption of other radiation-radiation. Other radiation comes from a
hollow cathodelamps, hollow cathode lamps are gas filler or
metal dopants in hollow cathode lamp.Monokromator consists of optical systems,
namely, mirrors and grille openings.
d. Detector
The detector function measures the radiation transmitted by the sample
and measure the intensity of the radiation in the form of electrical energy.
e. Rekorder
The electric signal coming out of the detector device which can be accepted
bydescribing the absorption curve automatically.
f. Cathode Lamp
Cathode lamps are light sources on AAS. Cathode lamp has a lifetime
of consumptionage or for 1000 hours. Cathode lamps on each item to be
tested varies depending on the items to be tested, such as lamp cathode Cu, can
only be used for the measurement of elemental Cu cathode Lamps. is divided into
two kinds, namely:
Cathode Monologam lamp: used to measure 1 item
Cathode Multilogam lamp: used for the measurement of some metals at once, it's
just that much more expensive.
Socket on the cathode lights are a more prominent black, used to facilitate
theinstallation of cathode lights when lights are inserted into a socket on
the AAS. Theblack part is part of the most prominent of the four other iron.
Cathode lamp serves as a light source to provide energy so that the
metal elementwhich will be tested, will be easily excited. Duct tape was added, so
that there is noempty space to exit gas influx from outside and from inside
the gas discharge, becausewhen there is gas coming out from the inside can
cause toxicity in the environment.
Cathode lamp is maintenance of way when once completed is used,
then the lightsdisconnected from the socket on the main unit lights, and AAS are
put in placebusanya inside the box again, and the storage box is closed again. We
recommend that you use when you are finished, the length of time the usage note.
g. Gas tube
The gas tube on the AAS is used gas cylinders containing acetylene gas. Acetylene
Gas on AAS has a temperature range of 20,000 K, and there are also gas
cylinders containing the gas N2O hotter than acetylene gas, with a temperature
range of 30,000 K. Regulators on acetylene gas cylinders for setting the number of
gases to be issued, and the gas in the tube. Spedometer on the right side of the
regulator is apressure balance inside the tube.
Testing for the detection of leak or whether the gas tube, by exposing the ears to
near the gas regulator and given a little bit of water, to pengecekkan. When sound or
air, it is menendakan that the gas cylinder is leaking and there is gas coming
out. Other things that can be done is to give a little soapy water on the top
of the regulator and see if there are any air bubbles are formed. If there is,
then the positive gas tubeleaked. Preferably pengecekkan leaks, do not use the
oil, because the oil will can causeclogged gas line. The Gas in the tube can come
out because it caused in the tube onthe bottom of the tube contains acetone which
can make easy gas will come out, in addition to the gas also has pressure.
h. Ducting
Ducting is the chimney to suck up the smoke or residual combustion on AAS,
whichdirectly connected on the outside of the chimney on the roof of the building, so
thatthe smoke generated by the AAS, not harmful to the environment. The
smoke resulting from the combustion of the AAS, processed in such a way in
the ducting, the resultingpollution to harmless.
How to maintenance of the ducting, i.e. by closing the ducting horizontally, so
that the top can be tightly closed, so there will be no insects or other
animals that can get into the ducting. Because if there are insects or other
animals that entered into the ducting, then it can cause ducting is clogged.
The use of ducting that is, pressing a small part on a leaning towards the ducting,
because when straight horizontally, signaling the ducting is covered. Ducting serves
tosuck the combustion occurs at AAS, and remove it through the chimney connected
toducting
i. Compressor
The compressor is a tool that is separate to the main unit, because this tool works
forsupplying the air needs to be used by AAS at the combustion of
atoms. Compressor has 3 buttons pressure balance, where in the black box is
the ON-OFF button, the middle section is a spedo of small air to be issued, or serve
as a pressure balance, whilethe right button merupakantombol settings to set
multiple/at least the air will besprayed into the burner. Section on the rear of the
compressor air is used as storageafter after the use of AAS.
This tool serves to filter the air from outside, so that the net position to the
right., is an open position, and position it to the left position closed. Water vapor is
released, it willsplatter and could result in the floor taut around a wet, therefore
it should be on whenpressed to the
right section, preferably accommodated with laps, so the floor does not get wet
and water vapor will be absorbed into the lap.
j. Burner
The most important part is the Burner inside the main unit, because
the burner serves as a place of acetylene gas, pancampuran and aquabides, in
order to be mixed evenly, and can be burned in cigarette lighters are nice
and evenly. Holes in the burner, anaperture of cigarette lighters, where the pit is the
beginning of the process ofpengatomisasian the flame.
Maintenance burner that is after the completion of the measurement is done,
theaspirator hose inserted into the bottle containing
the aquabides for approximately 15 minutes, it is the process of leaching on
the aspirator and the burner after completionof usage. Aspirator hose used to
suck or suck the solution samples and standards thatwill be
tested. Aspirator hose is part of the orange-colored hose on the right
sideburner. While the left hose, hose to
siphon the gas acetylene. Metal is metal that will be tested in the form of the
solution and must be dissolved in advance using a solution ofconcentrated nitric
acid. Metals in the solution, will experience low energy excitation ofthe energy high.
The value of the excitation of each metal has a different value. The
resulting flame colorvaries depending on the level
of metal concentrations measured. When red fire color, then it indicates
that too much gas. And the color blue, the most fire is the colour offire, the
most good, and most of the heat.
k. Exile on AAS
Exile on AAS is stored in drigen and is
placed separately on AAS. Exhaust exhaust hoseis connected to the circular which
was made in such a way, so that the rest of the exilesbefore rising again to the
top, because when this happens it can shut down the processpengatomisasian the
flame at the time of measurement the sample, so that the resulting curve will look
bad. Place a container of exile (drigen) is placed on a Board thatis also
equipped with a light indicator. When the lamp indicator lights up, indicating that the
tool or api on the process of AAS pengatomisasian turned on, and is the continuation
of the process of pengatomisasian the flame. In addition, the Board also
serves to place waste containers or not tersenggol away. If the exile is full,
the contentsinside the container do not empty, but will stay at made a little, so as not
to dry.
Procedure
1. Open valve / gas regulator used
2. Air compressor valve (located below) and compressor shut in on it
3. Instruments on it (there is a button on the right of the green color tool)
4. Wait until the display "AAS novA 300" appears.
5. Click "HCl TURRED", place the position of the arrow on the position of the
lights (if you want to replace the lamp select "CHANGE" and select the elements that
would be tested) and then click OK - OK to the start menu
6. Click "METHOD DEVELOPMENT" click OK
7. Click "SPECTROPHOTOMETER", "OPTICAL PARAMETER" make sure that is
analyzed in an active state, click the "ENERGY" or "GAJN" and make sure the
energy around 60-80 then ok
8. Click "CALIBRATION", "CALIBRATION STANDARD" click "CONDITION"
notice "NO.OFF SATNDARD" adjust the amount of the standard to be analyzed.
Click the "Table", "CLEAR THE TABLE", click "CAL-STANO". 1. Click "CHANGE"
select "CONCENTRATION" if there is already a number, "DELETE", and then
replace it with a new number. "ENTER", the same thing is done for the other
standards. Click OK again
9. Click "SAMPLES" select lines enabling filled replace the sample data by
clicking "CHANGE" enter the name of the sample you click OK then OK again.
10. Blower in on it
11. Click "FLAME", click on "TEST THE WATER" notice must be aerosolized
form (only appears when a new tool is operated) TEST END.
12. To light the burner, click "EGNITE FLAME", wait until the burner flame
appears, click OK.
13. Click "CALIBRATION" and "STANDARD CALIBRATION", "TABLE", select
"START / ABS", OK.
14. Follow the instructions on the screen. Click OK.
"ALWAYS REMEMBER AQUADEST WILL REPLACE THE ENTIRE SOLUTION"
15. Click "SAMPLES", select the name of the sample that you want to measure,
select the "LINE" and "SAMPLE RUN" click OK until the instruction the monitor.
Follow the instructions to complete.
16. Click OK, then OK again until the start menu
17. Click "FLAME" and "EXTINGUISH", click OK
18. When done click "EXIT", then the instrument is turned off by pressing the
right tools.
D. Benefits/Advantages Of AAS
The advantages are: the AAS method
Specific
Limit (limit) detection of low
From one same substance, some different elements can be measured
Measurement can be directly made to the solution of
the sample (sample preparationbefore the measurement is simpler, except
when there is a bully)
Can be applied to many types of items in many different types of examples.
The rates that can be specified is very broad (mg/L up to percent)
E. Shortcomings Method AAS
Analysis using AAS is a weakness, because there are several sources of
error, includingthe error Source: measurements may occur on measurements using
the SSA may bepredicted as follows:
1. Less perfect sample preparation, such as:
-The process of destruction is less than perfect
-The level of acidity of the samples and not similarly blanko
The error matrix, this is due to the existence of a difference matrix sample
and matrix of standards
The flow of the sample at the burner are not the same pace or there is blockage
in the course of the flow of the sample.
1. chemical Disorders such as:
-Dissociation is not perfect
-Ionization
-Formation of refraktori compounds
F. Application Of Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (SSA) In The Chemical Analysis
For atomic absorption method has been applied to the determination
of approximately 60 elements, and this technique is the main tool in the study
of metal which includetracing in the environment and
in biological samples. Often these techniques are also useful in cases
where the metal is at a sufficient level in the sample, but just a littletersediasedia in
the analysis of samples, sometimes such cases with metaloprotein for example. The
first reports about the role of biologically important for nickel based
ondetermination by atomic absorption that urease enzyme from the organism, at
least on two nickel ions per molecule of protein. Often the first stage in the analysis
of biologicalsamples is mengabukan to damage organic
ingredients. Pengabuan base with a nitric
acid and perchlorate often preferable than dry Recalling pengabuan shrink due
toevaporate from certain tracing elements (dry pengabuan sheer was the installation
ofthe samples in one furnace to oxidize organic material). Then the atomic
absorptionlarytan pengabuan base or against a solution made from
the residue dried pengabuan.
A major facet of the atomic absorption of course is the sensitivity. In a sense, atomic
absorption blatant free from distractions once. The electronic energy levels of an
atomwas a unit for that element. This means that no
two elements which demonstrate thespectral lines of
the exact same wavelength. Often times there are lines for an item that is very close
to some of the other elements, but it is common to find a resonance line isfor
a particular element, if there is no spectral interference by other elements in the
sample.
A major disruption in the atomic absorption is the effect matrix that affects the
process of pengatoman. Good away dissociation into atoms at a given
temperature and the rate of the process depends on the
overall composition of all samples. For example if an aqueous solution of
calcium chloride dikabutkan and dissolved particles of
solid CaCl2dissociates finely produced atoms of Ca with a lot easier
than paertikel calciumphosphate Ca3 (PO4), 2.
With the advances in science that dieksistensikan with the increasing number of
research publications in the field of atomic absorption spectroscopy, it appears
that the dwarf in atomic absorption spectroscopy is still in the ranks of the refinement
G. Disturbances In The AAS Method
Chemical Disorder
Chemical disorder occurs when the items analyzed experiencing a chemical
reactionwith the anion or ketion certain refraktori compounds, so not all analytes can
beteratomisasi. To overcome this disorder can be done in two ways, namely: 1) use
of a higher flame temperature, 2) addition of other chemicals that can release
the cation oranion bullies from their bonds with analytes. Other
chemical substances that are added to a
substance called liberators (Releasing Agent) or protective substances (ProtectiveAg
ent).
Disturbance Of Matrix
This disorder occurs when samples contain a lot of salt, acid or when ayau solvent
useddoes not use the standard substances, solvents or when the temperature of
the flameto a solution of the sample and the standards are
different. Qualitative analysis in this disorder is not too problematic, but it is
very annoying in quantitative analysis. To overcome this disorder in quantitative
analysis can be used the way the analysis of the addition of satandar (a
standard Adduct).
Disturbance Of Ionization
Disorders of ionization occurs when the temperature of the flame is high enough so
that it is able to release the electrons from a neutral atom to form positive ions. The
formation of this ion reduced the number of neutral atoms, so cue the absorption will
be reduced as well. To solve this problem can be done by adding a solution of an
easilyionized elements or atoms which are more electropositive character of atoms
that were analyzed, such as Cs, Rb, K, and Na. This addition can reach 100 to
2000 ppm.
Absorption Of Background (Back Ground)
Plural form of Background (Back Ground) is a term used to indicate the presence
ofvarious influences, from absorption by the flame, molecular absorption,
and scatteringof light.
CHAPTER III
COVER
3.1 Conclusions
Pejelasan-explanation of the foregoing the conclusion that can be drawn:
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy based on the amount of energy absorbed
byneutral atoms in a gas.
In order for the intensity of the early rays (Po) and the rays passed on (P) can be
measured, then the energy rays of pengeksitasi must match
the Atomic excitationenergy absorber and absorber of energy is obtained through a
hollow cathode lamplight.
SSA has a high accuracy on qualitative analysis.
AAS novA 300 has many advantages compared to other types of AAS
3.2 Advice
On this occasion the author suggested to all those who feel to have a share in the
development of education in order to support things that smelled of technology
toease the development of education can be further enhanced. It aims to improve
the quality of our national education. In addition it should all sides should be further
enhanced to mention a sense of concern for science technology to the fore we
canrealize a society that soulless technology.
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry (SSA) is a tool used in the methods of
analysisfor the determination of the elements of
metal and metalloid that measurement based on the absorption
of specific wavelengths of light by atoms of the metal in a State
ofnon (Skooget al., 2000). This method is very appropriate for the analysis of
substancesat low concentration. This technique has several advantages compared
to conventionalemission spectroscopy method. Indeed apart from the atomic
absorption method, withelements of low energy excitation
of unsurdengan can also be analyzed by flamephotometry, flame photometry,
however not suitable for
elements with high excitationenergy. Flame photometry has the
optimum measurement range at a wavelength of400-800 nm, while
the AAS have the optimum measurement range at a wavelength of200-300 nm
(Skoog et al., 2000).For the qualitative analysis, the preferred method
offlame photometry of AAS,
since specific cathode memerlukanlampu AAS (hallowcathode). Kemonokromatisan i
n the AASmerupakan the main
requirement. A flametemperature changes akanmengganggu process
of excitation so that analysis of flamephotometry berfilter.It can be said that
the flame photometry method and AASmerupakankomplementer each other.
Principled methods of AAS on the absorption of light by atoms, atom-
atommenyerapthe light at a particular wavelength,
depending padasifat elemental. E.g. Sodiumabsorbs at 589 nm, uranium in
358, 5nm whereas potassium at 766,5 nm. Light onthis
wave mempunyaicukup energiuntukmengubah electronic energy levels of an
atom.Denganabsorpsi energy, means gaining
more energy, a basic padakeadaan atomicenergy level is raised to the level
of excitation. Any of various tingkateksitasinya levels.For example the
element Na with an
atomic electron configuration 11mempunyai noor1s1 2p6 2s2 3s1, basic
level for electronvalensi 3s, meaning do not have excess energy.Ascent
to dapattereksitasi Elektronini 3 p with energy 2.2 eV or ascent to the 4 p with an
energy of 3.6 eV, each corresponding to a wavelength 589nm and 330 nm. We can
choose between this yangmenghasilkan line wavelength spectrum that is sharp
andwith maximum intensity, yangdikenal with the line resonance. Other lines that are
notgarisresonansi can be either Ribbon-Ribbon width or line is not derived from the
basiceksitasitingkat that caused the atomisasinya.In the light of
certain wavelengths is passed on suatusel containing free atoms in
question then the sebagiancahaya will beabsorbed and the intensity of the
absorption will be compared to the number of atoms in a metal-free lurusdengan on
the antaraabsorbansi Relationship with the cells.concentration derived from: 1.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Laser Metrology in Fluid Mechanics: Granulometry, Temperature and Concentration MeasurementsDa EverandLaser Metrology in Fluid Mechanics: Granulometry, Temperature and Concentration MeasurementsNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Spectroscopy AnalysisDocumento16 pagineAtomic Spectroscopy AnalysisMiftahul JannahNessuna valutazione finora
- Shining a Light on Cool Standards: Infrared Spectroscopy Theory Explored.Da EverandShining a Light on Cool Standards: Infrared Spectroscopy Theory Explored.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocumento6 pagineAtomic Absorption SpectrosShajith Ahamed ANessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDa EverandOptical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 11 Applications of AAS and AESDocumento22 pagineUnit 11 Applications of AAS and AESNathanian75% (4)
- Introduction to Infrared and Raman SpectroscopyDa EverandIntroduction to Infrared and Raman SpectroscopyNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 10 Atomic Emission SpectrometryDocumento26 pagineUnit 10 Atomic Emission SpectrometryVelpuri Venkatappaiah67% (3)
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy: Elena SevostianovaDocumento7 pagineAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy: Elena Sevostianovaodunmoolorun dorcasNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Emission SpectrosDocumento14 pagineAtomic Emission SpectrosGjelo CachoNessuna valutazione finora
- Neutron Activation Analysis (INAA and RNAA)Documento4 pagineNeutron Activation Analysis (INAA and RNAA)Marco Antonio Enriquez QuirogaNessuna valutazione finora
- Progress in Analytical Atomic Spectroscopy: Volume 6Da EverandProgress in Analytical Atomic Spectroscopy: Volume 6C L ChakrabartiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cook BookDocumento138 pagineCook BookAbdul Manan SaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Characterization of Nanoparticles: Measurement Processes for NanoparticlesDa EverandCharacterization of Nanoparticles: Measurement Processes for NanoparticlesVasile-Dan HodoroabaNessuna valutazione finora
- AaesDocumento14 pagineAaesAbdeta BogaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide-Lines to Planning Atomic Spectrometric AnalysisDa EverandGuide-Lines to Planning Atomic Spectrometric AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (5)
- Atomic Emission Spectroscopy AsaDocumento16 pagineAtomic Emission Spectroscopy AsaMark Cliffton Badlon100% (1)
- Atomic Mass SpectrosDocumento40 pagineAtomic Mass Spectrosjohnpaul varonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Spectroscopy and Types LectureDocumento8 pagineSpectroscopy and Types LectureAnisam AbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Term Paper OF Physics: Submitted To: Submitted byDocumento11 pagineTerm Paper OF Physics: Submitted To: Submitted bynirbhymynameNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Spectroscopy 1Documento40 pagineAtomic Spectroscopy 1SOURAV BHATTACHARYANessuna valutazione finora
- Hacettepe University Department of Chemical Engineering KMÜ 359 Instrumental Analysis Laboratories Experiment 5 Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocumento13 pagineHacettepe University Department of Chemical Engineering KMÜ 359 Instrumental Analysis Laboratories Experiment 5 Atomic Absorption SpectrosGamze IdeNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 7 Flame PhotometryDocumento32 pagineUnit 7 Flame PhotometryRia Agnez100% (8)
- Atomic Absorption SpectrometryDocumento36 pagineAtomic Absorption SpectrometryZubair KambohNessuna valutazione finora
- InTech-Atomic Absorption Spectrometry AasDocumento13 pagineInTech-Atomic Absorption Spectrometry Aastaufany99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy: Basic PrincipleDocumento7 pagineAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy: Basic PrincipleSubhecchha BaidyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy - SeminarDocumento8 pagineAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy - Seminarbolaji4411Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry (AAS)Documento4 pagineAtomic Absorption Spectrophotometry (AAS)Kurnia JayantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mass Spectromet-WPS OfficeDocumento4 pagineMass Spectromet-WPS OfficeMeena AliNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM 312 Note Instrumental-1Documento16 pagineCHM 312 Note Instrumental-1makisami62Nessuna valutazione finora
- 947pm - 55.EPRA JOURNALS 8582Documento6 pagine947pm - 55.EPRA JOURNALS 8582Vishal GoelNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocumento4 pagineAtomic Absorption SpectrosAye Ei MonNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption and Emission SpectrosDocumento10 pagineAtomic Absorption and Emission SpectrosQasim Jalali NanotiNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocumento62 pagineAtomic Absorption SpectrosJamal HamadNessuna valutazione finora
- Capitulo 6Documento32 pagineCapitulo 6kevin abrilNessuna valutazione finora
- Spectroscopy: Classification of MethodsDocumento8 pagineSpectroscopy: Classification of Methodsabdulla ateeqNessuna valutazione finora
- Absorçãoatomicaftheory ChamaDocumento81 pagineAbsorçãoatomicaftheory ChamaelenitabastosNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 Atomic Absorption SpectroscDocumento22 pagineAssignment 1 Atomic Absorption Spectroscpakpolitics206Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 9 Atomic AbsorptionDocumento26 pagineUnit 9 Atomic AbsorptionNathanianNessuna valutazione finora
- Spectroscopic TechniqueDocumento24 pagineSpectroscopic TechniqueJubair Al-rashidNessuna valutazione finora
- Aes Lecture NoteDocumento5 pagineAes Lecture NoteEmmanuella OffiongNessuna valutazione finora
- Spectroscopy OvrviewDocumento164 pagineSpectroscopy OvrviewKim Phillips100% (1)
- Spectrophotometry and ColorimetryDocumento5 pagineSpectrophotometry and ColorimetryHarish.UNessuna valutazione finora
- AtomicDocumento3 pagineAtomicRashidNessuna valutazione finora
- Aas Introduction 2022Documento6 pagineAas Introduction 2022Korir DennisNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic SpectrosDocumento23 pagineAtomic SpectrosJean Kimberly AgnoNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption SpectrometryDocumento9 pagineAtomic Absorption SpectrometryRisnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical SpectrosDocumento7 pagineOptical SpectrosgayaxniNessuna valutazione finora
- Sem & AasDocumento6 pagineSem & Aasblakk archimedesNessuna valutazione finora
- Determination of Heavy Metal Concentration by Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocumento2 pagineDetermination of Heavy Metal Concentration by Atomic Absorption SpectrosNandhini D PNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Aes Lecture NoteDocumento6 pagineFinal Aes Lecture NoteEmmanuella OffiongNessuna valutazione finora
- Spectral Methods. Absorption Spectroscopic MethodsDocumento14 pagineSpectral Methods. Absorption Spectroscopic MethodsKenan SeneliyevNessuna valutazione finora
- Prac 1 340Documento17 paginePrac 1 340phiwayinkosi PwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Emission SpectrometryDocumento21 pagineAtomic Emission SpectrometryArslan Muhammad EjazNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5Documento33 pagineUnit 5sankar velisettyNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Spectroscopy Sahin EbookDocumento11 pagineAtomic Spectroscopy Sahin EbookWW JeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocumento30 pagineAtomic Absorption SpectrosRashed BiswasNessuna valutazione finora
- Proposal Fearless FaithDocumento24 pagineProposal Fearless FaithAhmad Fadil DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Product PDFDocumento1 paginaDesign Product PDFAhmad Fadil DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Dear Khun BoonyaritDocumento1 paginaDear Khun BoonyaritAhmad Fadil DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Print LCDDocumento10 paginePrint LCDAhmad Fadil DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Caption LaserDocumento8 pagineCaption LaserAhmad Fadil DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Caption LaserDocumento8 pagineCaption LaserAhmad Fadil DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Uses of Mass SpectrometryDocumento4 pagineLesson Plan: Lesson: Uses of Mass SpectrometryMarcTnn100% (1)
- Final Quantum 2020Documento2 pagineFinal Quantum 2020ANessuna valutazione finora
- Ii. Content Iii. Learning Resources: Pencil/ Pen Crayon or Colored PencilsDocumento2 pagineIi. Content Iii. Learning Resources: Pencil/ Pen Crayon or Colored Pencilsjanice alquizarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bohr Atom Lesson PlanDocumento5 pagineBohr Atom Lesson Planjaidy morgadez100% (1)
- Atomic StructureDocumento162 pagineAtomic StructurevaughanNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Questions On LN 5Documento4 paginePractice Questions On LN 5gokharNessuna valutazione finora
- Clssification PDFDocumento24 pagineClssification PDFKarthik HNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 3 13 MC Practice-1Documento13 pagineTopic 3 13 MC Practice-1Keshav AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Guide Nuclear Model of AtomDocumento2 pagineLesson Guide Nuclear Model of AtomGrace RabinaNessuna valutazione finora
- PHET Rutherfords Scattering - 1769974724Documento3 paginePHET Rutherfords Scattering - 1769974724Robert ColemanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Ncert NotesDocumento35 pagineChemistry Ncert Notesvandana dehankarNessuna valutazione finora
- B17CA Student Guide v3Documento186 pagineB17CA Student Guide v3Elcan AlmammadovNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1! Describing Chemical Bonds - Valence Bond TheoryDocumento4 pagine1.1! Describing Chemical Bonds - Valence Bond TheorySadeeq ArtxzNessuna valutazione finora
- IR and Raman Spectroscopy of Organometallic Compounds-HCDocumento38 pagineIR and Raman Spectroscopy of Organometallic Compounds-HCrakesh1521100% (2)
- Principle of Photo Electron SpectrosDocumento9 paginePrinciple of Photo Electron SpectrosAbdul BaasitNessuna valutazione finora
- Draw LewisDocumento3 pagineDraw LewisclrgeekNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem XRD Diff Lecture 6Documento71 pagineChem XRD Diff Lecture 6Công Bùi ChíNessuna valutazione finora
- GC - Quiz 3Documento214 pagineGC - Quiz 3ghusto100% (1)
- Chapter#1: Choose The Best AnswerDocumento2 pagineChapter#1: Choose The Best AnswerMohammad AshfaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Name: Basic Electronics: B.Tech First YearDocumento25 pagineCourse Name: Basic Electronics: B.Tech First YearNeha GabaNessuna valutazione finora
- NMRDocumento30 pagineNMRBharatula Suryamani Shankar ee19b013Nessuna valutazione finora
- Konfigurasi ElektronDocumento4 pagineKonfigurasi ElektronGalih NugrohoNessuna valutazione finora
- 09 - Electron MicrosDocumento63 pagine09 - Electron Microsnayonaega100% (2)
- CH2 ReviewQuastions ExersisesDocumento6 pagineCH2 ReviewQuastions ExersisestamarNessuna valutazione finora
- All Chemistry Worksheets Chapter 5 8 PDF FreeDocumento92 pagineAll Chemistry Worksheets Chapter 5 8 PDF Freea-chi chen100% (1)
- Origin of ElementsDocumento27 pagineOrigin of ElementsJoanna Ruth SeproNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM14.1 ReportDocumento25 pagineCHEM14.1 Reportjoanne_chioNessuna valutazione finora
- 10-07-2022 - JR - Super60 (Incoming) - Jee-Adv (2020-P2) - WTA-06 - Q. PaperDocumento18 pagine10-07-2022 - JR - Super60 (Incoming) - Jee-Adv (2020-P2) - WTA-06 - Q. PaperAnil KonkatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Physics Is The Field ofDocumento1 paginaAtomic Physics Is The Field ofvcespecialistmathsNessuna valutazione finora
- Water-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Da EverandWater-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersDa EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressDa EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityDa EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyDa EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (21)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookDa EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNessuna valutazione finora
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookDa EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisDa EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Lees' Process Safety Essentials: Hazard Identification, Assessment and ControlDa EverandLees' Process Safety Essentials: Hazard Identification, Assessment and ControlValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- Physical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersDa EverandPhysical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Operational Excellence: Journey to Creating Sustainable ValueDa EverandOperational Excellence: Journey to Creating Sustainable ValueNessuna valutazione finora
- Phase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringDa EverandPhase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- Pharmaceutical Blending and MixingDa EverandPharmaceutical Blending and MixingP. J. CullenValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Engineering Design for Process SafetyDa EverandGuidelines for Engineering Design for Process SafetyNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsDa EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationDa EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (18)
- Principles and Case Studies of Simultaneous DesignDa EverandPrinciples and Case Studies of Simultaneous DesignNessuna valutazione finora
- The HAZOP Leader's Handbook: How to Plan and Conduct Successful HAZOP StudiesDa EverandThe HAZOP Leader's Handbook: How to Plan and Conduct Successful HAZOP StudiesNessuna valutazione finora
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksDa EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyDa EverandGuidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyNessuna valutazione finora
- Recognizing Catastrophic Incident Warning Signs in the Process IndustriesDa EverandRecognizing Catastrophic Incident Warning Signs in the Process IndustriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesDa EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (14)
- Pharmaceutical Excipients: Properties, Functionality, and Applications in Research and IndustryDa EverandPharmaceutical Excipients: Properties, Functionality, and Applications in Research and IndustryOtilia M. Y. KooNessuna valutazione finora