Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
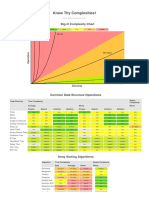
The Running Times: O (log (n) ) O (n) O (α (n) ) O (log (n) ) O (log (n) ) O (log (n) ) O (log (n) )
Caricato da
dinban1Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The Running Times: O (log (n) ) O (n) O (α (n) ) O (log (n) ) O (log (n) ) O (log (n) ) O (log (n) )
Caricato da
dinban1Copyright:
Formati disponibili
THE RUNNING TIMES
2013 Mid-Term
A. Deleting an element from a map with n elements: O(log(n))
B. Constructing a heap from a vector with n elements: O(n)
C. Performing union() on a disjoint set instance with n elements: O(1)
D. Performing find() on a disjoint set instance with n elements: O((n))
E. Performing upper_bound() on a map with n elements: O(log(n))
F. Inserting an element into a map with n elements: O(log(n))
G. Performing pop() on a heap with n elements: O(log(n))
H. Performing push() on a heap with n elements: O(log(n))
2012 Mid-Term
A. Sorting a vector using insertion sort. O(n2)
B. Sorting a vector using heap sort. O(n log n)
C. Calling Push() on a heap. O(log n)
D. Creating a heap from a random vector. O(n)
E. Calling Pop() on a heap. O(log n)
F. Printing all elements of a map in order. O(n)
G. Printing all subsets of a set. O(2n)
H. Calling Union() on a disjoint set. O(1)
I. Deleting an element from a map. O(log n)
J. Printing all pairs of elements in a vector of integers. O(n2)
K. Inserting an element into a map. O(log n)
L. Sorting a vector using selection sort. O(n2)
M. Sorting a vector using bubble sort. O(n2)
N. Calling Find() on a disjoint set. O((n))
O. Sorting a vector using STL multisets. O(n log n)
P. Enumerating all 2-disk failures in an n-disk system. O(n2)
2009 Mid-Term
A. Inserting an element into a map. Same as a balanced binary tree: O(log2(n)).
B. Creating a heap from a vector. This is where a heap excels over a set or map, because you can create a heap
from a vector in linear time: O(n).
C. Finding the minimum element of a priority queue. The minimum element is at the root of the heap: O(1).
D. Inserting an element into a priority queue. Add the new element to the back of the vector and percolate up:
O(log2(n)).
E. Appending an element to a vector. This is a constant time operation: O(1).
F. Counting the number of unique elements of a multiset. You need to traverse the multiset with an iterator: O(n).
G. Creating a sorted vector from a multiset that has n elements. Again, this simply requires traversing the multiset
with an iterator: O(n).
H. Sorting a nearly sorted vector using selection sort. There is no advantage to having the vector nearly sorted --
selection sort still takes O(n2) operations.
I. Deleting an element from a list: O(1).
J. Sorting a nearly sorted vector using insertion sort. This is where insertion sort does well: O(n).
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27Da EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27Nessuna valutazione finora
- INFO1905 Cheat Sheet FinalDocumento2 pagineINFO1905 Cheat Sheet FinalJeffreyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentDa EverandMathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentNessuna valutazione finora
- EECS 211 STL Summary PDFDocumento9 pagineEECS 211 STL Summary PDFsvetlanapmfNessuna valutazione finora
- Discrete Series of GLn Over a Finite Field. (AM-81), Volume 81Da EverandDiscrete Series of GLn Over a Finite Field. (AM-81), Volume 81Nessuna valutazione finora
- Data StructureDocumento13 pagineData StructureOporajitaNessuna valutazione finora
- CDS S9Documento9 pagineCDS S9Jaydeep SNessuna valutazione finora
- hw03 Solution PDFDocumento7 paginehw03 Solution PDFsiddharth1k0% (1)
- Chang Final PracticeDocumento10 pagineChang Final PracticeCrystalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sorting in Linear Time: Counting-SortDocumento7 pagineSorting in Linear Time: Counting-Sortcristi_pet4742Nessuna valutazione finora
- Comp 352 Study GuideDocumento16 pagineComp 352 Study GuideAleksander GjokaNessuna valutazione finora
- CDS Q9Documento6 pagineCDS Q9Jaydeep SNessuna valutazione finora
- BCA-2Sem Data StructureDocumento30 pagineBCA-2Sem Data StructureSHAMBHU JHANessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 - ECE391 - Ch3 - Vectors - Lists - and SequencesDocumento11 pagine2021 - ECE391 - Ch3 - Vectors - Lists - and SequencesHoang TranNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IiiDocumento37 pagineUnit IiiSeshu ChakravarthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Merge Sort SeminarDocumento22 pagineMerge Sort SeminarChaitanya BharadwajNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract Data Types: COMP2015 HKBU/CS/JF/2023 1Documento73 pagineAbstract Data Types: COMP2015 HKBU/CS/JF/2023 1mars chouNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 1 Module7 (Complexity Analysis)Documento1 paginaWeek 1 Module7 (Complexity Analysis)Srinivas JayanthiNessuna valutazione finora
- GATE QuestionsDocumento96 pagineGATE QuestionsAkhil Verma100% (1)
- Ds UNIT-1 Gate BitsDocumento8 pagineDs UNIT-1 Gate Bitslakshmi lNessuna valutazione finora
- GATE Questions 16-7-13Documento106 pagineGATE Questions 16-7-13shinde_jayesh2005100% (1)
- DS AssignmentDocumento4 pagineDS AssignmentkalpanasripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Aoa ExtcDocumento32 pagineAoa ExtcchhayanarvekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit V: 1 A. Define Sorting. Discuss The Complexities of Selection, Insertion and Bubble Sort?Documento23 pagineUnit V: 1 A. Define Sorting. Discuss The Complexities of Selection, Insertion and Bubble Sort?Siva Jyothi ChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Capgemini Section-1: SyllabusDocumento42 pagineCapgemini Section-1: SyllabusHERE'S THE SOLUTIONNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment - IA Linked Lists SolutionsDocumento8 pagineAssignment - IA Linked Lists SolutionsVikalp HandaNessuna valutazione finora
- DS MCQDocumento4 pagineDS MCQbarunduariNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT IIIaDocumento37 pagineUNIT IIIaSeshu ChakravarthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Final ExercisesDocumento13 pagineFinal ExercisesAshish DarjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Stacks and QueuesDocumento45 pagineStacks and QueuesthiruNessuna valutazione finora
- GATE Questions 18-7-14 GateDocumento116 pagineGATE Questions 18-7-14 GateDELFIN BIJUNessuna valutazione finora
- Nodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Computer Science Engineering 2008Documento20 pagineNodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Computer Science Engineering 2008jayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Key P1Documento3 pagineKey P1James RobertNessuna valutazione finora
- AQU Data Structures First ExamDocumento7 pagineAQU Data Structures First ExamMohammadNessuna valutazione finora
- A6c 8Documento5 pagineA6c 8jvashisht81Nessuna valutazione finora
- Linear (Or Ordered) Lists ADT: Instances Are of The FormDocumento33 pagineLinear (Or Ordered) Lists ADT: Instances Are of The FormKushal GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sorting: - Review of Sorting - Merge Sort - SetsDocumento31 pagineSorting: - Review of Sorting - Merge Sort - SetsabirhNessuna valutazione finora
- Xy WZ - Xy+wz.Documento3 pagineXy WZ - Xy+wz.Vikash KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ in DAADocumento3 pagineMCQ in DAAkamakshi2Nessuna valutazione finora
- 9.map 1 HashTableDocumento31 pagine9.map 1 HashTableGaith RjoubNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes COMP3506Documento17 pagineLecture Notes COMP3506JackNessuna valutazione finora
- Aim: C++ Program To Implement Linked List and Its Operations Algorithm: Step 1Documento3 pagineAim: C++ Program To Implement Linked List and Its Operations Algorithm: Step 1Elamparithi ManiezhilanNessuna valutazione finora
- File - 884729453 - 1694060717 - Stack&queue 10 MCQDocumento3 pagineFile - 884729453 - 1694060717 - Stack&queue 10 MCQRakesh SNessuna valutazione finora
- 2023 CSC10004 22CLC03 HW02 AlgorithmEfficiencyDocumento4 pagine2023 CSC10004 22CLC03 HW02 AlgorithmEfficiencyDuy BảoNessuna valutazione finora
- MATHEMATICSDocumento11 pagineMATHEMATICSNaveeshvaran NagulanNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structure SlidesDocumento100 pagineData Structure SlidesAnirban SadhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Vector Built-In FunctionsDocumento3 pagineVector Built-In FunctionsTanzil AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- L05 PDFDocumento4 pagineL05 PDFMarcos ShepardNessuna valutazione finora
- Maps in C++Documento3 pagineMaps in C++collegian youtuberNessuna valutazione finora
- Collection CheatsheetDocumento12 pagineCollection Cheatsheetswapnil_pingale28Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 5: Linear Sorting: ReviewDocumento5 pagineLecture 5: Linear Sorting: ReviewVan Vy HongNessuna valutazione finora
- FDS Unit 3 and 4 MCQ'sDocumento103 pagineFDS Unit 3 and 4 MCQ'sTejas PawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Handout 1Documento4 pagineHandout 1Vinod PartiharNessuna valutazione finora
- ListDocumento92 pagineListkparisa057525Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 2 OHTA StudentDocumento13 pagine1 2 OHTA StudentPame CorralNessuna valutazione finora
- CPSC Algorithms Cheat SheetDocumento6 pagineCPSC Algorithms Cheat SheetRya KarkowskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Open in 2022 PDFDocumento11 pagineOpen in 2022 PDFstargazxrNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction Protocol of Circle Area and Circumference in GeogebraDocumento3 pagineConstruction Protocol of Circle Area and Circumference in GeogebraJanak Singh KarkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Stack QueueDocumento7 pagineStack QueueYash JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.1 Arrays Lists and TreesDocumento23 pagine2.1 Arrays Lists and TreesStanley WangNessuna valutazione finora
- Powerconnect-2808 User's Guide En-UsDocumento184 paginePowerconnect-2808 User's Guide En-UsrohightNessuna valutazione finora
- Top 100 Networking Interview Questions & AnswersDocumento73 pagineTop 100 Networking Interview Questions & Answersdinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Video Over DOCSIS (VDOC) TutorialDocumento81 pagineVideo Over DOCSIS (VDOC) Tutorialdinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ansible For Aws SampleDocumento106 pagineAnsible For Aws SamplewalkertraylorNessuna valutazione finora
- Shell Scripting For Network EngineersDocumento26 pagineShell Scripting For Network Engineersdinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco 2600 Memory Guide: BootromDocumento4 pagineCisco 2600 Memory Guide: Bootromdinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Powerconnect-2808 User's Guide En-UsDocumento184 paginePowerconnect-2808 User's Guide En-UsrohightNessuna valutazione finora
- MPLS Segment Routing: Driving A Modern Approach To MPLS TransportDocumento12 pagineMPLS Segment Routing: Driving A Modern Approach To MPLS Transportdinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Programmability Open NX-OSDocumento285 pagineProgrammability Open NX-OSdinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Juniper / Cisco Interoperability Tests: August 2014Documento9 pagineJuniper / Cisco Interoperability Tests: August 2014dinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 04-Cisco IOS-XR Overview PDFDocumento90 pagine04-Cisco IOS-XR Overview PDFBerrezeg MahieddineNessuna valutazione finora
- HC 43 Xasr 9 KbookDocumento806 pagineHC 43 Xasr 9 Kbookdinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- CSC13 Asr-9000Documento99 pagineCSC13 Asr-9000dinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Networkers 2002 - Rst360 - Troubleshooting Ip Multicast PDFDocumento232 pagineCisco Networkers 2002 - Rst360 - Troubleshooting Ip Multicast PDFdinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Optical The Transmode WayDocumento86 paginePacket Optical The Transmode Waydinban1100% (1)
- Cisco IOS Debug Command Reference - Commands A Through DDocumento666 pagineCisco IOS Debug Command Reference - Commands A Through DscorcdNessuna valutazione finora
- MPLS Segment Routing: Driving A Modern Approach To MPLS TransportDocumento12 pagineMPLS Segment Routing: Driving A Modern Approach To MPLS Transportdinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Server Managing Mind MapDocumento1 paginaServer Managing Mind Mapdinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco VoIP Q/ADocumento2 pagineCisco VoIP Q/Adinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Segment RoutingDocumento8 pagineIntroduction To Segment Routingdinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- NFVDocumento1 paginaNFVSaurabhNessuna valutazione finora
- SM Fibre SelectionDocumento2 pagineSM Fibre SelectionkhotrucNessuna valutazione finora
- Gigabit Ethernet Optical SpecficationsDocumento4 pagineGigabit Ethernet Optical Specficationsdinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- SPEED-DCM eDocumento1 paginaSPEED-DCM edinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- DWDM PrincipleDocumento83 pagineDWDM Principlephucdinhnguyen100% (5)
- AP 2600 Get StartDocumento38 pagineAP 2600 Get StartgovindarajnmcaNessuna valutazione finora
- Conda Cheatsheet PDFDocumento2 pagineConda Cheatsheet PDFdinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- ASR 9000 Series Punt Fabric Data Path Failures Troubleshoot GuideDocumento29 pagineASR 9000 Series Punt Fabric Data Path Failures Troubleshoot Guidedinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Know Thy Complexities!: Big-O Complexity ChartDocumento2 pagineKnow Thy Complexities!: Big-O Complexity ChartDhruvaSNessuna valutazione finora
- Lax CLT: Boarding PassDocumento2 pagineLax CLT: Boarding Passdinban1Nessuna valutazione finora
- SOP No. 6Documento22 pagineSOP No. 6Eli CohenNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 1 6Documento45 pagineMath 1 6Dhamar Hanania Ashari100% (1)
- Ground Vibration1Documento15 pagineGround Vibration1MezamMohammedCherifNessuna valutazione finora
- Tecplot 360 2013 Scripting ManualDocumento306 pagineTecplot 360 2013 Scripting ManualThomas KinseyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Ton Per Hour Electrode Production LineDocumento7 pagine1 Ton Per Hour Electrode Production LineMohamed AdelNessuna valutazione finora
- Teralight ProfileDocumento12 pagineTeralight ProfileMohammed TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Engineering PEEDocumento3 pagineTechnical Engineering PEEMariano Acosta Landicho Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Self-Instructional Manual (SIM) For Self-Directed Learning (SDL)Documento28 pagineSelf-Instructional Manual (SIM) For Self-Directed Learning (SDL)Monique Dianne Dela VegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Review Solar Tower Technology PDFDocumento43 pagineGlobal Review Solar Tower Technology PDFmohit tailorNessuna valutazione finora
- RWJ Corp Ch19 Dividends and Other PayoutsDocumento28 pagineRWJ Corp Ch19 Dividends and Other Payoutsmuhibbuddin noorNessuna valutazione finora
- Manulife Health Flex Cancer Plus Benefit IllustrationDocumento2 pagineManulife Health Flex Cancer Plus Benefit Illustrationroschi dayritNessuna valutazione finora
- Enumerator ResumeDocumento1 paginaEnumerator Resumesaid mohamudNessuna valutazione finora
- Stainless Steel 1.4404 316lDocumento3 pagineStainless Steel 1.4404 316lDilipSinghNessuna valutazione finora
- CENT - Company Presentation Q1 2020 PDFDocumento22 pagineCENT - Company Presentation Q1 2020 PDFsabrina rahmawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- SDM Case AssignmentDocumento15 pagineSDM Case Assignmentcharith sai t 122013601002Nessuna valutazione finora
- VB 850Documento333 pagineVB 850Laura ValentinaNessuna valutazione finora
- CPM W1.1Documento19 pagineCPM W1.1HARIJITH K SNessuna valutazione finora
- Statable 1Documento350 pagineStatable 1Shelly SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk and Uncertainty in Estimating and TenderingDocumento16 pagineRisk and Uncertainty in Estimating and TenderingHaneefa ChNessuna valutazione finora
- Flyer Manuale - CON WATERMARK PAGINE SINGOLEDocumento6 pagineFlyer Manuale - CON WATERMARK PAGINE SINGOLEjscmtNessuna valutazione finora
- 254 AssignmentDocumento3 pagine254 AssignmentSavera Mizan ShuptiNessuna valutazione finora
- BS As On 23-09-2023Documento28 pagineBS As On 23-09-2023Farooq MaqboolNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 123 RevisedDocumento23 pagineChapter 123 RevisedCristy Ann BallanNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Management - Pgpmi - Class 12Documento44 pagineMarketing Management - Pgpmi - Class 12Sivapriya KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Land Use Paln in La Trinidad BenguetDocumento19 pagineLand Use Paln in La Trinidad BenguetErin FontanillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics 2 First Quarter - Module 5 "Recognizing Money and Counting The Value of Money"Documento6 pagineMathematics 2 First Quarter - Module 5 "Recognizing Money and Counting The Value of Money"Kenneth NuñezNessuna valutazione finora
- Freqinv 3g3fv Ds 01oct2000Documento20 pagineFreqinv 3g3fv Ds 01oct2000Mohd Abu AjajNessuna valutazione finora
- Reverse Osmosis ProcessDocumento10 pagineReverse Osmosis ProcessHeshamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11 Walter Nicholson Microcenomic TheoryDocumento15 pagineChapter 11 Walter Nicholson Microcenomic TheoryUmair QaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Si KaDocumento12 pagineSi KanasmineNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine Learning: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learn Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence & Neural Networks Step by StepDa EverandMachine Learning: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learn Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence & Neural Networks Step by StepValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (19)
- Learn Python Programming for Beginners: Best Step-by-Step Guide for Coding with Python, Great for Kids and Adults. Includes Practical Exercises on Data Analysis, Machine Learning and More.Da EverandLearn Python Programming for Beginners: Best Step-by-Step Guide for Coding with Python, Great for Kids and Adults. Includes Practical Exercises on Data Analysis, Machine Learning and More.Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (34)
- Clean Code: A Handbook of Agile Software CraftsmanshipDa EverandClean Code: A Handbook of Agile Software CraftsmanshipValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (13)
- Once Upon an Algorithm: How Stories Explain ComputingDa EverandOnce Upon an Algorithm: How Stories Explain ComputingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (43)
- Excel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceDa EverandExcel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleDa EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (16)
- Python Programming For Beginners: Learn The Basics Of Python Programming (Python Crash Course, Programming for Dummies)Da EverandPython Programming For Beginners: Learn The Basics Of Python Programming (Python Crash Course, Programming for Dummies)Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Understanding Software: Max Kanat-Alexander on simplicity, coding, and how to suck less as a programmerDa EverandUnderstanding Software: Max Kanat-Alexander on simplicity, coding, and how to suck less as a programmerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (44)
- GAMEDEV: 10 Steps to Making Your First Game SuccessfulDa EverandGAMEDEV: 10 Steps to Making Your First Game SuccessfulValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (12)
- How to Make a Video Game All By Yourself: 10 steps, just you and a computerDa EverandHow to Make a Video Game All By Yourself: 10 steps, just you and a computerValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Blockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsDa EverandBlockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (24)
- Coders at Work: Reflections on the Craft of ProgrammingDa EverandCoders at Work: Reflections on the Craft of ProgrammingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (151)
- Nine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersDa EverandNine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (7)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsDa EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- The Advanced Roblox Coding Book: An Unofficial Guide, Updated Edition: Learn How to Script Games, Code Objects and Settings, and Create Your Own World!Da EverandThe Advanced Roblox Coding Book: An Unofficial Guide, Updated Edition: Learn How to Script Games, Code Objects and Settings, and Create Your Own World!Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Software Development: BCS Level 4 Certificate in IT study guideDa EverandSoftware Development: BCS Level 4 Certificate in IT study guideValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- What Algorithms Want: Imagination in the Age of ComputingDa EverandWhat Algorithms Want: Imagination in the Age of ComputingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (41)
- Django Unleashed: Building Web Applications with Python's FrameworkDa EverandDjango Unleashed: Building Web Applications with Python's FrameworkNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Engineering at Google: Lessons Learned from Programming Over TimeDa EverandSoftware Engineering at Google: Lessons Learned from Programming Over TimeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- Python for Data Analysis: A Beginners Guide to Master the Fundamentals of Data Science and Data Analysis by Using Pandas, Numpy and IpythonDa EverandPython for Data Analysis: A Beginners Guide to Master the Fundamentals of Data Science and Data Analysis by Using Pandas, Numpy and IpythonNessuna valutazione finora


![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)