Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Bab II Strategic Asset Management Framework-Rev
Caricato da
FatimaAgatsDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bab II Strategic Asset Management Framework-Rev
Caricato da
FatimaAgatsCopyright:
Formati disponibili
STRATEGI PENGELOLAAN ASET 18
BAB II
STRATEGIC ASSET MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK
Tujuan Pembelajaran Umum Bab II :
Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan apa yang dimaksud dengan Kerangka Strategi Manajemen
Aset
Tujuan Pembelajaran Khusus Bab II:
Mahasiswa mampu menjelaskan latar belakang, ruang lingkup, perencanaan, dan
implementasi dari strategi manajemen aset
2.1. Latar Belakang dan Ruang Lingkup dari Strategic Asset Management
Framework
Tujuan Pembelajaran Umum Sub- Bab 2.1 :
Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan latar belakang dan ruang lingkup dari Strategic Asset
Management Framework
Tujuan Pembelajaran Khusus Sub- Bab 2.1 :
1. Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan latar belakang dari Strategic Asset Management
Framework
2. Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan ruang lingkup dari Strategic Asset Management
Framework
2.1.1 Latar Belakang Strategic Asset Management Framework
Managing Organization assets requires a strategic approach, to enable Organization to
meet community needs, provide and sustain public assets and to achieve service outcomes.
Asset management assists Organization, through its agencies, to meet its desired outcomes
effectively and efficiently by:
STRATEGI PENGELOLAAN ASET 19
a. making the best possible use of existing assets;
b. maximizing value for money when investing in new assets; and
c. making decisions to invest in, retain or divest assets that take into consideration and
protect the needs of current and future generations.
This Strategic Asset Management Framework is designed to assist agencies to make
informed decisions on the assets it needs to support service delivery. It builds on the 1998
policy Strategic Asset Management Policy An Overview.
The key objectives of the Strategic Asset Management Framework are:
a) to integrate the Organizations asset management policies and make them more
accessible ;and
b) to make stronger links between planning asset needs and implementing asset decisions.
The Framework also highlights the need for agencies to ensure that their corporate planning
processes are integrated with their asset planning processes. In this context, agencies are
also encouraged to explore alternative solutions to purchasing new assets or retaining any
existing assets that are under-performing or under-utilised.
This Framework document outlines the major components of asset management, and shows
the broad relationships between them. In addition, supporting policies have been developed
to provide guidance for each component.
2.1.2 Ruang Lingkup Strategic Asset Management Framework
This Strategic Asset Management Framework is to be applied by general Organization
agencies, public financial corporations and public non-financial corporations in accordance
with all relevant legislation, Treasurers Instructions and related Organization policies.
However, agencies that are required, by legislation, to produce Statements of Corporate
Intent (SCI) and Strategic Development Plans (SDP) are not bound by this policy, but are
STRATEGI PENGELOLAAN ASET 20
expected to adopt the principles of the Framework in meeting their statutory obligations,
although there are several reporting requirements, predominantly relating to the capital
investment process, with which all agencies are expected to comply. Further guidance
about reporting requirements is provided in Strategic Asset Plans.
CORPORATE
PLANNING
STRATEGIC
PLANNING
STRATECIC
ASSET
PLANS
Agency
Mission
Corporate
Plan
Strategic
Asset
Management
Plan
Acquisition
Community
Demand
Service
Delivery
Strategy
Human
Resources
Plan
Operation &
Maintenance
Service
Delivery
Information
Technology
Plan
Disposal
Financial
Plan
Alternative Solution
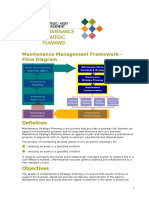
Gambar 2.1. Strategic Asset Management Framework
(Sumber : Department of Treasury and Finance - Tasmania , 2004)
In addition, as agencies vary widely in terms of their size and nature, the Framework may
have limited application to some agencies. In this context, each agency should adopt a
common sense approach towards implementation. Any document that is developed to meet
external reporting requirements should be clear and concise, and prepared to an appropriate
level of length and detail.
If there is any doubt about the applicability of any aspect of the Strategic Asset
Management Framework, or how to address any reporting requirement, please contact your
Department of Treasury and Finance analyst for advice.
STRATEGI PENGELOLAAN ASET 21
Where an Information and Communications Technology (ICT) project is being considered,
the agency should also consult the Office of e-Organization in the Department of the
Premier and Cabinet and the Organization Procurement Division of the Department of
Treasury and Finance.
2.2. Perencanaan dalam Strategic Asset Management Framework
Tujuan Pembelajaran Umum Sub- Bab 2.2 :
Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan perencanaan dalam Strategic Asset Management
Framework
Tujuan Pembelajaran Khusus Sub- Bab 2.2 :
1. Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan Corporate Planning
2. Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan Asset Planning
3. Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan The Strategic Asset Plan
2.2.1 Corpoorate Planning
Corporate planning has an important influence on asset management.
Agencies invest in, and retain, the capital resources required to deliver agreed levels of
services to achieve the desired outcomes.
The resources utilized by the agency should be clearly aligned with the agencys desired
outcomes, and at least one goal in the Organizations strategic planning framework.
Agencies performance against these agency-level outcomes is assessed using key
effectiveness and efficiency indicators.
Gambar 2.1. illustrates how agencies may conduct planning at strategic and business
levels, to identify and secure the resources required to deliver agreed services through
Outcome Based Management (OBM). Such planning, which may include consultation with
the community or key stakeholders, is usually conducted on a cyclical basis, perhaps every
two to three years.
STRATEGI PENGELOLAAN ASET 22
Corporate Planning identifies the specific programs and provides details on services that an
agency intends to deliver during a financial year and the means by which these will be
delivered. Within the context of the agency's longer term (i.e. strategic) plan, it builds on
the performance review of the preceding year and anticipates and works toward the services
and results identified in the RSP (Results and Services Plan).
2.2.2 Asset Planning
Asset planning, management and review should be undertaken on a cyclical basis, in
association with corporate and other planning activities.
The asset planning process should draw on the information gathered from the business and
operational planning processes, which should be conducted around human, information,
financial and physical resourcing needs, either to develop or to meet the level of services
(or output targets) agreed with Organization from within an approved level of funding.
This planning is largely undertaken internally by the agency, although key decisions to
invest or dispose of significant assets must be endorsed by the Organizations Expenditure
Review Committee. Consideration should be given to seeking community input to the asset
planning process, where community support for strategic asset management decisions is
critical to ensuring cost-effective implementation.
The broad asset needs identified through the asset planning, management and review
processes should be highlighted in the agencys strategic asset plan, which should then be
articulated through appropriate capital investment, maintenance, and/or asset disposal
planning processes.
2.2.3 The Strategic Asset Plan
STRATEGI PENGELOLAAN ASET 23
The asset planning process should result in the formulation of a Strategic Asset Plan
(Gambar 2.1.).
This plan is the means by which an agency aligns its asset portfolio to Organization desired
outcomes. It defines the strategic actions that it intends to implement to ensure that its
assets best meet its service delivery requirements. A common sense approach should be
taken to determine the appropriate level of detail and complexity at which the planning
process is undertaken.
Asset planning balances the service delivery potential, and cost, of existing assets against
the cost of other resources required to achieve agency service objectives, timeframes and
budgets. Non asset solutions should also be considered at this point.
Strategies for the management of individual assets and portfolios should be based on
defined service delivery objectives.
The primary stages for an agency to develop a Strategic Asset Plan are:
a) to demonstrate a need to acquire physical assets from the business planning process,
after
b) consideration of alternative solutions that do not require assets, such as changes to
service delivery;
c) to identify the agencys ideal asset mix;
d) to review the agencys existing assets, in terms of reviewing and optimising existing
capacity, asset performance and the condition of existing assets at an appropriate
level of detail;
e) to undertake a gap analysis between the ideal and the existing asset mix; and
f) to summarize the conclusions formed from this planning process in the Strategic
Asset Plan.
The resulting plan should outline the capital investment, maintenance and asset disposal
implications for the agency over the short- to medium-term.
STRATEGI PENGELOLAAN ASET 24
2.3. Implementasi dari Strategic Asset Management Framework
Tujuan Pembelajaran Umum Sub- Bab 2.3 :
Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan implementasi dari Strategic Asset Management
Framework
Tujuan Pembelajaran Khusus Sub- Bab 2.3 :
1. Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan Delivering the Strategic Asset Plan
2. Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan Capital Investment Plan
3. Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan Maintenance Plan
4. Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan Asset Disposal Plan
2.3.1 Delivering the Strategic Asset Plan
The key processes to implement each of the capital investment, maintenance, and asset
disposal implications that were identified in the Strategic Asset Plan.
2.3.2 Capital Investment Plan
The capital investment plan details the new assets, or the major changes required to support
the agencys service delivery.
This plan should address all relevant factors, including flexible long-term service delivery
requirements, demographic trends, periodic refurbishment, life cycle costing and the impact
on future budgets, Organization priorities, and the risks of change to service delivery
requirements.
The primary stages for an agency in managing the capital investment implications of the
Strategic Asset Plan are:
STRATEGI PENGELOLAAN ASET 25
a. to identify capital investment implications arising from the agencys business and asset
strategic planning processes;
b. for the agency to undertake sufficiently rigorous evaluation of proposed new assets, to
justify its inclusion of the proposals in the 10-year capital investment plan, which may
include consideration of financing options such as Public Private Partnerships (PPPs)3;
c. to develop sufficient project definition, to establish a clear understanding of the project
and a plan for its implementation, and determine whether the project is sufficiently
defined to proceed into detailed design and documentation;
d. to deliver the project; and
e. after commissioning has been completed, to undertake a review of the projects
readiness for service.
Further guidance on the capital investment process is available from the policy document
Capital Investment Policy.
2.3.3. Maintenance Plan
Agencies must ensure existing assets sustain service delivery and are appropriately
maintained, operated and fully utilized.
Through asset management, agencies should plan and undertake maintenance programs for
all assets. A Maintenance Plan should be developed to identify existing maintenance
requirements, and the approach to manage these requirements within approved funding
limits. As part of this plan, assets should be retained in, or restored to, conditions that are
specified to support service delivery.
Maintenance Plans need to be consistent with the Strategic Asset Plan, and aligned with
investment and disposal plans and properly accounted for in agency budgets. Issues relating
to under-utilization of assets, the suitability and accessibility of assets, and the recurrent
costs associated with the asset should be fed back into the asset planning process.
STRATEGI PENGELOLAAN ASET 26
The primary stages for an agency in managing the maintenance implications of the
Strategic Asset Plan are:
a. to review the current maintenance program in the light of the issues raised in the asset
b. planning process;
c. to assess the risks inherent within the current maintenance program;
d. to prioritise maintenance needs;
e. to define the appropriate balance between maintenance that should be undertaken in the
f. short-term, and that which may be deferred;
g. to define the available funding resources; and
h. to prepare a maintenance schedule, aiming to ensure that assets are maintained in a cost
effective manner with minimal disruption to the occupants, or the delivery of services.
Further guidance on maintenance is provided in the Maintenance Policy.
2.3.4. Asset Disposal Plan
Agencies should develop contingency plans for asset disposal at the end of the assets
useful life. Disposal of assets can release capital for other uses, and there may be grounds
or incentives for agencies to dispose of surplus capital stock, or to relocate, where the value
of the asset is greater when used for other purposes. Alternatives to closure of under-
utilised or under-performing assets should be considered.
The primary stages for an agency to manage the asset disposal implications of the Strategic
Asset Plan are:
1. to evaluate surplus assets for potential disposal;
2. to implement the disposal process; and
3. to review the effectiveness of the disposal process.
Further guidance on asset disposal processes is available from the Asset Disposal Policy
RANGKUMAN
STRATEGI PENGELOLAAN ASET 27
1. Managing Organization assets requires a strategic approach, to enable Organization
to meet community needs, provide and sustain public assets and to achieve service
outcomes. Asset management assists organization, through its agencies, to meet its
desired outcomes effectively and efficiently.
2. The key objectives of the Strategic Asset Management Framework are to integrate the
Organizations asset management policies and make them more accessible ;and to
make stronger links between planning asset needs and implementing asset decisions.
3. Perencanaan dalam Strategic Asset Management Framework terdiri dari Corporate
Planning, Asset Planning, dan The Strategic Asset Plan
4. Implementasi dalam Strategic Asset Management Framework terdiri dari Delivering
the Strategic Asset Plan, Capital Investment Plan, Maintenance Plan dan Asset
Disposal Plan
5. The key processes to implement each of the capital investment, maintenance, and asset
disposal implications that were identified in the Strategic Asset Plan.
6. The capital investment plan details the new assets, or the major changes required to
support the agencys service delivery. The plan should address all relevant factors,
including flexible long-term service delivery requirements, demographic trends,
periodic refurbishment, life cycle costing and the impact on future budgets,
Organization priorities, and the risks of change to service delivery requirements.
7. Maintenance Plans need to be consistent with the Strategic Asset Plan, and aligned with
investment and disposal plans and properly accounted for in agency budgets. Issues
relating to under-utilization of assets, the suitability and accessibility of assets, and the
recurrent costs associated with the asset should be fed back into the asset planning
process.
8. Disposal of assets can release capital for other uses, and there may be grounds or
incentives for agencies to dispose of surplus capital stock, or to relocate, where the
value of the asset is greater when used for other purposes.
LATIHAN / SOAL
STRATEGI PENGELOLAAN ASET 28
1. Jelaskan dengan apa yang disebut sebagai tujuan dari Strategic Asset Management
Framework!
2. Jelaskan bagaimana implementasi dari manajemen strategis dapat digunakan oleh
organisasi untuk pengelolaan asetnya!
3. Sebutkan apa yang dimaksud dengan bagian dari implementasi Strategic Asset
Management ?
LEMBAR PRE-TEST
Mencoba mengingatkan manajemen strategis aset seperti yang dipelajari dalam bab I dan
bagaimana kerangka dalam manajemen strategis aset dapat diterapkan dalam suatu
organisasi untuk mencapai tujuan
LEMBAR POST-TEST
Setelah mempelajari pengertian dan ruang lingkup tentang kerangka manajemen stategis
asset dalam pengelolaan aset maka mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan pemahaman dan
pengetahuannya bagaimana kerangka pengelolaan aset suatu organisasi
DAFTAR PUSTAKA
1. Macnair , Gordon Ordon E., SR/WA, AACI, P. APP, (2 0 1 0 ), Right of Way , July /
August
2. .., Developing Strategic Asset Management Plans-Department of Treasury
and Finance (2004), Tasmania ,
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Low Budget Music Promotion and PublicityDocumento41 pagineLow Budget Music Promotion and PublicityFola Folayan100% (3)
- Poetry UnitDocumento212 paginePoetry Unittrovatore48100% (2)
- Fiscal Management TechniquesDocumento34 pagineFiscal Management TechniquesadityaapNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Asset Management FrameworkDocumento16 pagineStrategic Asset Management FrameworkReisya El ShaninaNessuna valutazione finora
- Top Activist Stories - 5 - A Review of Financial Activism by Geneva PartnersDocumento8 pagineTop Activist Stories - 5 - A Review of Financial Activism by Geneva PartnersBassignotNessuna valutazione finora
- SFM PDFDocumento328 pagineSFM PDFZainNessuna valutazione finora
- Capital Investment DecisionsDocumento62 pagineCapital Investment DecisionsVijay GandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 IT - Sheilding Guide PDFDocumento40 pagine2016 IT - Sheilding Guide PDFlazarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Assets Sample ProblemsDocumento4 pagineBiological Assets Sample ProblemsKathleenNessuna valutazione finora
- Rationale For, and Use Of, Asset Management Maturity AssessmentsDocumento11 pagineRationale For, and Use Of, Asset Management Maturity AssessmentsChaouch NajehNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Signal and Power Integrity PDFDocumento46 pagineFundamentals of Signal and Power Integrity PDFjaltitiNessuna valutazione finora
- Projects: Dairy Farms From Vision To SuccessDocumento8 pagineProjects: Dairy Farms From Vision To SuccessAditya Kumar DwivediNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Planning and ForecastingDocumento36 pagineFinancial Planning and ForecastingSana Khatri100% (1)
- Project AppraisalDocumento18 pagineProject AppraisalGaurav BundelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Saep 60 PDFDocumento19 pagineSaep 60 PDFRami ElloumiNessuna valutazione finora
- SAMF OverviewDocumento16 pagineSAMF OverviewDedi Pramono100% (1)
- Key Stages of Asset Management LifecycleDocumento5 pagineKey Stages of Asset Management LifecyclequyenhuynhhaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.1 Populating Asset Management PlansDocumento6 pagine2.1 Populating Asset Management PlansmohitreddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Approaches and Techniques in BudgetingDocumento8 pagineApproaches and Techniques in Budgetinghijkayelmnop89% (9)
- Guidelines Physical Asset Management: Section IDocumento169 pagineGuidelines Physical Asset Management: Section IAlexis VinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 08 - Change in Accounting Policy: Problem 8-1 (AICPA Adapted)Documento5 pagineChapter 08 - Change in Accounting Policy: Problem 8-1 (AICPA Adapted)Kimberly Claire AtienzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Caterpillar Space Mining Portfolio Management PlanDocumento10 pagineCaterpillar Space Mining Portfolio Management PlanluganloveNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance BudgetingDocumento2 paginePerformance BudgetingPankaj2cNessuna valutazione finora
- Sabp A 043 PDFDocumento44 pagineSabp A 043 PDFWalid MegahedNessuna valutazione finora
- Asterisk NowDocumento82 pagineAsterisk Nowkambojk100% (1)
- Strategic Project ManagementDocumento17 pagineStrategic Project ManagementAnupamaa Singh100% (2)
- A Comprehensive Study On Financial Planning and ForecastingDocumento31 pagineA Comprehensive Study On Financial Planning and ForecastingInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Saep 60Documento19 pagineSaep 60R. P. SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Asset ManagementDocumento14 pagineAsset ManagementMeraj AhamadNessuna valutazione finora
- SAM 4.1. Maintenance Strategic PlanningDocumento12 pagineSAM 4.1. Maintenance Strategic PlanningRechian Hapsari50% (2)
- 01 ASSET AssetManagementSeriesPart1Documento11 pagine01 ASSET AssetManagementSeriesPart1reyzknight100% (1)
- Brochure - Work Improvements in Small EnterprisesDocumento16 pagineBrochure - Work Improvements in Small EnterprisesZuleika Soave GuaranyNessuna valutazione finora
- BBC Programme Strategic Assessment Template 2018Documento12 pagineBBC Programme Strategic Assessment Template 2018Our World SmileNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Appraisal 1Documento3 pagineProject Appraisal 1Paras MongiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Page 1 of 2Documento2 paginePage 1 of 2Lance daguhoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Topic 1 Notes Strategy Implementation and Budget ProcessDocumento6 pagineMidterm Topic 1 Notes Strategy Implementation and Budget ProcesslanoyjessicaellahNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Implementation UnitDocumento30 pagineStrategic Implementation Unitwruttika jadhavNessuna valutazione finora
- Fampulme - The Planning Functions of The ControllershipDocumento22 pagineFampulme - The Planning Functions of The ControllershipCarla Pianz FampulmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4 - OMCDocumento10 pagineLecture 4 - OMCDorwin RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment2 EngManDocumento5 pagineAssignment2 EngManNick RamNessuna valutazione finora
- 0911 Transpo Strategic Plan Inst FinalwithcoverDocumento22 pagine0911 Transpo Strategic Plan Inst FinalwithcoverSileshi ShibruNessuna valutazione finora
- (Term Paper) Budgeting As An Instrument of MCSDocumento27 pagine(Term Paper) Budgeting As An Instrument of MCSSaiyan IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Financial PlanningDocumento19 pagine2 Financial Planningravic25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assetivity Asset Management Strategy TemplateDocumento14 pagineAssetivity Asset Management Strategy TemplateShashannk DoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- A Portfolio Approach To Programme Management & Project DesignDocumento5 pagineA Portfolio Approach To Programme Management & Project DesignMelina SawyerNessuna valutazione finora
- BSBPMG514Documento21 pagineBSBPMG514tvatNessuna valutazione finora
- LU 2 Strategy Implementation and Business Models 1Documento29 pagineLU 2 Strategy Implementation and Business Models 1stibalowNessuna valutazione finora
- IM Module 2 PlanningDocumento7 pagineIM Module 2 PlanningDan Alfonso de TablanNessuna valutazione finora
- Developing The FirmDocumento14 pagineDeveloping The FirmMagnificient EchoNessuna valutazione finora
- FS Notes Budgetary Control & MiscellaneousDocumento8 pagineFS Notes Budgetary Control & MiscellaneousMuditNessuna valutazione finora
- Restructuring Notification 09mar2020Documento19 pagineRestructuring Notification 09mar2020DAG SS2Nessuna valutazione finora
- D I S 5 M, 2018: Eployment and Mplementation TageDocumento51 pagineD I S 5 M, 2018: Eployment and Mplementation Tagesaad aliNessuna valutazione finora
- BSBOPS502 Task 1 - Jacob Lloyd JonesDocumento10 pagineBSBOPS502 Task 1 - Jacob Lloyd JonesBui AnNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank Strategic Planning and Budgeting ProcessDocumento18 pagineBank Strategic Planning and Budgeting ProcessBaby KhorNessuna valutazione finora
- B.4.9. Criteria For Appraisal of The Financial Investment in IS&T ProjectsDocumento4 pagineB.4.9. Criteria For Appraisal of The Financial Investment in IS&T Projectsmaga2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Capacity Development Agenda - ELADocumento110 pagineCapacity Development Agenda - ELAJonathan Arandia LitangNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5Documento14 pagineModule 5Shweta JambhulkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 FinalDocumento83 pagineUnit 4 FinalVidhyamahaasree DNessuna valutazione finora
- SFM Ch.1 Introduction To Strategy and Financial Mgmt.Documento7 pagineSFM Ch.1 Introduction To Strategy and Financial Mgmt.141. Siddiqui RizwanNessuna valutazione finora
- BudgetingDocumento20 pagineBudgetingSanjeevNessuna valutazione finora
- MB 0045Documento32 pagineMB 0045Kawal Preet Singh OberoiNessuna valutazione finora
- TAM ManualDocumento392 pagineTAM ManualMaidan KimyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparation of Budget For Schools and CollegesDocumento12 paginePreparation of Budget For Schools and Collegesmerin sunilNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning Technical ActivitiesDocumento31 paginePlanning Technical ActivitiesClaraise VivienNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-3 (Economic Environment)Documento33 pagineUnit-3 (Economic Environment)Rajat PawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategy Implementation: UNIT-4Documento19 pagineStrategy Implementation: UNIT-4VIVEK KUMAR SINGH 13Nessuna valutazione finora
- Organization Strategy and Project Selection: Dima Mostafa Hajaia 5190002Documento58 pagineOrganization Strategy and Project Selection: Dima Mostafa Hajaia 5190002Rand Nasa'aNessuna valutazione finora
- Stone As A Building Material: LateriteDocumento13 pagineStone As A Building Material: LateriteSatyajeet ChavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Convection Transfer EquationsDocumento9 pagineConvection Transfer EquationsA.N.M. Mominul Islam MukutNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Investigatory Project (R)Documento23 pagineChemistry Investigatory Project (R)BhagyashreeNessuna valutazione finora
- Iaea Tecdoc 1092Documento287 pagineIaea Tecdoc 1092Andres AracenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Midi Pro Adapter ManualDocumento34 pagineMidi Pro Adapter ManualUli ZukowskiNessuna valutazione finora
- This Study Resource Was: For The Next 6 ItemsDocumento9 pagineThis Study Resource Was: For The Next 6 ItemsJames CastañedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gomez-Acevedo 2010 Neotropical Mutualism Between Acacia and Pseudomyrmex Phylogeny and Divergence TimesDocumento16 pagineGomez-Acevedo 2010 Neotropical Mutualism Between Acacia and Pseudomyrmex Phylogeny and Divergence TimesTheChaoticFlameNessuna valutazione finora
- Feed-Pump Hydraulic Performance and Design Improvement, Phase I: J2esearch Program DesignDocumento201 pagineFeed-Pump Hydraulic Performance and Design Improvement, Phase I: J2esearch Program DesignJonasNessuna valutazione finora
- Aditya Birla GroupDocumento21 pagineAditya Birla GroupNarendra ThummarNessuna valutazione finora
- in 30 MinutesDocumento5 paginein 30 MinutesCésar DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Upes School of Law Lac & Adr Association: PresentsDocumento7 pagineUpes School of Law Lac & Adr Association: PresentsSuvedhya ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- BSBITU314 Assessment Workbook FIllableDocumento51 pagineBSBITU314 Assessment Workbook FIllableAryan SinglaNessuna valutazione finora
- RMC 102-2017 HighlightsDocumento3 pagineRMC 102-2017 HighlightsmmeeeowwNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus PDFDocumento3 pagineSyllabus PDFBibin Raj B SNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern and Nonlinear OpticsDocumento181 pagineModern and Nonlinear Opticssoma_venuNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical Chem Lab #3Documento4 pagineAnalytical Chem Lab #3kent galangNessuna valutazione finora
- 5066452Documento53 pagine5066452jlcheefei9258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hydro Electric Fire HistoryDocumento3 pagineHydro Electric Fire HistorygdmurfNessuna valutazione finora
- Civ Beyond Earth HotkeysDocumento1 paginaCiv Beyond Earth HotkeysExirtisNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.SDH Basics PDFDocumento37 pagine1.SDH Basics PDFsafder wahabNessuna valutazione finora
- ADC of PIC MicrocontrollerDocumento4 pagineADC of PIC Microcontrollerkillbill100% (2)
- Form Expense ClaimDocumento2 pagineForm Expense Claimviedelamonde_3868443Nessuna valutazione finora