Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Analog Computers
Caricato da
zeronega71Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Analog Computers
Caricato da
zeronega71Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Analog Computers
Analog computers are used to process analog data. Analog data is of continuous nature
and which is not discrete or separate. Such type of data includes temperature, pressure,
speed weight, voltage, depth etc. These quantities are continuous and having an infinite
variety of values.
It measures continuous changes in some physical quantity e.g. The Speedometer of a
car measures speed, the change of temperature
is measured by a Thermometer, the weight is measured by Weights machine. These
computers are ideal in situations where data can be accepted directly from measuring
instrument without having to convert it into numbers or codes.
Analog computers are the first computers being developed and provided the basis for
the development of the modern digital computers. Analog computers are widely used for
certain specialized engineering and scientific applications, for calculation and
measurement of analog quantities. They are frequently used to control process such as
those found in oil refinery where flow and temperature measurements are important.
They are used for example in paper making and in chemical industry. Analog computers
do not require any storage capability because they measure and compare quantities in
a single operation. Output from an analog computer is generally in the form of readings
on a series of dial (Speedometer of a car) or a graph on strip chart.
Digital Computers
A Digital Computer, as its name implies, works with digits to represent numerals, letters
or other special symbols. Digital Computers operate on inputs which are ON-OFF type
and its output is also in the form of ON-OFF signal. Normally, an ON is represented by a
1 and an OFF is represented by a 0. So we can say that digital computers process
information which is based on the presence or the absence of an electrical charge or we
prefer to say a binary 1 or 0.
A digital computer can be used to process numeric as well as non-numeric data. It can
perform arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division and
also logical operations. Most of the computers available today are digital computers.
The most common examples of digital computers are accounting machines and
calculators.
The results of digital computers are more accurate than the results of analog computers.
Analog computers are faster than digital. Analog computers lack memory whereas
digital computers store information. We can say that digital computers count and analog
computers measures.
Hybrid Computers
A hybrid is a combination of digital and analog computers. It combines the best features
of both types of computers, i-e. It has the speed of analog computer and the memory
and accuracy of digital computer. Hybrid computers are used mainly in specialized
applications where both kinds of data need to be processed. Therefore, they help the
user, to process both continuous and discrete data. For example a petrol pump contains
a processor that converts fuel flow measurements into quantity and price values. In
hospital Intensive Care Unit (ICU), an analog device is used which measures patient's
blood pressure and temperature etc, which are then converted and displayed in the
form of digits. Hybrid computers for example are used for scientific calculations, in
defense and radar systems.
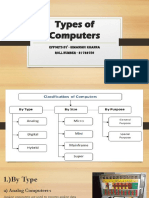
The Types of computer
Computers are divided into three types according to their structure, speed and architecture.
Analog Computers
Digital Computers
Hybrid Computers
Analog computers:
The computers which provide us continuous information are called analog computers.
Analog computers represent physical quantities in the form of waves or in continuous form.
Examples:
Thermometer is the example of analog computers because it measures the length of a mercury
column continuously.
A traditional clock is the example of analog computers because the needle of clock covers the
distance of dial continuously. Weight machine and Speedo meter are other examples of analog
computers.
Characteristics of the analog computers:
1. These computers have no state
The Speed of analog computer is fast
These computers are not reliable
These computers became the base for digital computers
These computers are difficult to operate and use
These computers are easy to develop
These computers have small memory
Digital Computers:
The computers which present physical quantities with the help of symbols or numbers and
provide us discrete information are called digital computers.
Examples:
Digital watch, digital petrol stations and the computer, which we use nowadays, are the
examples of digital computers
Characteristics of the digital computers:
Digital computers have two states On (0) and Off (1).
These computers are easy to use.
Human being like to use digital computers.
These computers are reliable.
Digital computers have big memory.
Working speed of digital computers is slower as compared to analog computers.
These computers are further divided into different categories such as personal computers,
Mainframe computers and super computers.
Hybrid Computers:
The computers which have qualities of both digital and analog computers are called hybrid
computers.
Hybrid computer has the speed of analog and the accuracy of digital computer.
Example:
In ICU (Intensive care unit) of a hospital hybrid computers are used. These computers analog
quality controls the temperature of the room digital quality informs the doctor about the blood
pressure, temperature and physical status of the patient.
In Cement factory a hybrid computer is used where all calculations are performed by the digital
computers; and actions like increase of material are performed by the analog computers.
Characteristics of the Hybrid computers:
These computers are reliable and provide accurate result.
These computers are fast and speedy.
Personal Computers/Desktop computers:
These are small size computers and are used by a single user. Desktop computers are also
called Personal computers or PC. We can use these computers easily in offices, colleges, schools,
universities, homes, and factories.
Characteristics of Desktop computers:
These computers have fast speed and accuracy
Small in size
Easy to operate
These computers are easy to move
These computers are cheaper
We can use desktop computers as a single user and multi-user environment
Laptop Computers/Notebook:
Lap top computers are another category of personal computers. These computers are small in
size and light packed in. These computers are moveable because they work on batteries and
can operate without an external power source. Laptop computers are also called Notebook
computers because the size of these computers is about one- inch notebook and weight is from
four to eight pounds.
Analog Computers
Analog Computer is a computing device that works on continuous range of values. The results
given by the analog computers will only be approximate since they deal with quantities that
vary continuously. It generally deals with physical variables such as voltage, pressure,
temperature, speed, etc.
Digital Computers
On the other hand a digital computer operates on digital data such as numbers. It uses binary
number system in which there are only two digits 0 and 1. Each one is called a bit.
The digital computer is designed using digital circuits in which there are two levels for an input
or output signal. These two levels are known as logic 0 and logic 1. Digital Computers can give
more accurate and faster results.
Digital computer is well suited for solving complex problems in engineering and technology.
Hence digital computers have an increasing use in the field of design, research and data
processing.
Based on the purpose, Digital computers can be further classified as,
General Purpose Computers
Special Purpose Computers
Special purpose computer is one that is built for a specific application. General purpose
computers are used for any type of applications. They can store different programs and do the
jobs as per the instructions specified on those programs. Most of the computers that we see
today, are general purpose computers.
Hybrid Computers
A hybrid computer combines the desirable features of analog and digital computers. It is mostly
used for automatic operations of complicated physical processes and machines. Now-a-days
analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog converters are used for transforming the data into
suitable form for either type of computation.
For example, in hospitals ICU, analog devices might measure the patients temperature, blood
pressure and other vital signs. These measurements which are in analog might then be
converted into numbers and supplied to digital components in the system. These components
are used to monitor the patients vital sign and send signals if any abnormal readings are
detected. Hybrid computers are mainly used for specialized tasks.
Types of Computers based on Configuration
There are four different types of computers when we classify them based on their performance
and capacity. The four types are
Super Computers
When we talk about types of computers, the first type that comes to our mind would be Super
computers. They are the best in terms of processing capacity and also the most expensive ones.
These computers can process billions of instructions per second. Normally, they will be used for
applications which require intensive numerical computations such as stock analysis, weather
forecasting etc. Other uses of supercomputers are scientific simulations, (animated) graphics,
fluid dynamic calculations, nuclear energy research, electronic design, and analysis of geological
data (e.g. in petrochemical prospecting). Perhaps the best known super computer
manufacturer is Cray Research. Some of the "traditional" companies which produce super
computers are Cray, IBM and Hewlett-Packard.
Mainframe Computers
Mainframe computers can also process data at very high speeds vi.e., hundreds of million
instructions per second and they are also quite expensive. Normally, they are used in banking,
airlines and railways etc for their applications.
Mini Computers
Mini computers are lower to mainframe computers in terms of speed and storage capacity.
They are also less expensive than mainframe computers. Some of the features of mainframes
will not be available in mini computers. Hence, their performance also will be less than that of
mainframes.
Micro Computers
The invention of microprocessor (single chip CPU) gave birth to the much cheaper
microcomputers. They are further classified into
Desktop Computers
Laptop Computers
Handheld Computers(PDAs)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Classification of ComputersDocumento2 pagineClassification of Computerseduardo acuniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dhaka International University, Dhaka: Generation of Computer'sDocumento8 pagineDhaka International University, Dhaka: Generation of Computer'sMehedi Hasan MirazNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 11 Computer Science Complete Notes by Binod RijalDocumento34 pagineClass 11 Computer Science Complete Notes by Binod RijalParakram Kharel100% (1)
- Tle-Lesson 3Documento33 pagineTle-Lesson 3Sophrina Jazmynrose CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To ICTDocumento11 pagineIntroduction To ICTJohanita Juliana ManaluNessuna valutazione finora
- Wearable Computing Past, Present and Future: Gurjeet SinghDocumento43 pagineWearable Computing Past, Present and Future: Gurjeet SinghSonu PuriNessuna valutazione finora
- The History of Computers: Michelle P. Navarro Tle-Ict TeacherDocumento95 pagineThe History of Computers: Michelle P. Navarro Tle-Ict TeacherMichelle NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- Text Book On Instrumentation Update Latest09Documento136 pagineText Book On Instrumentation Update Latest09ابزار دقیقNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Generations Assignment RefinedDocumento6 pagineComputer Generations Assignment Refinedbasit_gee100% (2)
- Types of Computer: Analog ComputersDocumento2 pagineTypes of Computer: Analog ComputersJohnAmielAlmeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of ComputerDocumento1 paginaTypes of Computersweetktz789Nessuna valutazione finora
- LESSON 1 Different Types of Computer Base On The Basis of WorkDocumento1 paginaLESSON 1 Different Types of Computer Base On The Basis of WorkCliodesh RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog, Digtal, Hybrid Unit 1Documento1 paginaAnalog, Digtal, Hybrid Unit 1Simar ZuluNessuna valutazione finora
- Characteristics of The Analog ComputersDocumento5 pagineCharacteristics of The Analog Computersmanju_csNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Computers Based On Principles of OperationDocumento6 pagineTypes of Computers Based On Principles of OperationMayank Jain NeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3 Types of ComputerDocumento12 pagineLesson 3 Types of ComputerMAUREEN MEDESNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification & Types of ComputersDocumento10 pagineClassification & Types of ComputersMudasir Abbas PhulpotoNessuna valutazione finora
- 이 동 혁 해찬What are Different Types of ComputerDocumento23 pagine이 동 혁 해찬What are Different Types of ComputerCJ Hernandez BorretaNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of ComputerDocumento16 pagineClassification of Computerlarkej51Nessuna valutazione finora
- Types of ComputerDocumento4 pagineTypes of ComputerHenson JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Computers-1Documento4 pagineClassification of Computers-1DENIS OKUMUNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of ComputerDocumento7 pagineTypes of ComputerAsma EmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Based On Principles of OperationDocumento11 pagineBased On Principles of OperationannusainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of ComputerDocumento8 pagineClassification of ComputerHabiba ShifaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1008171282044654types of ComputersDocumento1 pagina1008171282044654types of ComputersBrille Adrian FernandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Baluchistan University of Information Technology Engineering & Management Sciences QuettaDocumento11 pagineBaluchistan University of Information Technology Engineering & Management Sciences QuettaShokat AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Fanda MentalsDocumento148 pagineComputer Fanda MentalsJager JacksonNessuna valutazione finora
- Type of CoputerDocumento21 pagineType of CoputerMohit SainiNessuna valutazione finora
- ICT Basic Types of ComputerDocumento7 pagineICT Basic Types of ComputerMomina B KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of ComputerDocumento9 pagineClassification of ComputerSradhanjali JenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Introduction-1Documento25 pagineChapter 1 - Introduction-1bonsa tashomeNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Computers: The Analog Computer Is Almost An Extinct Type of Computer TheseDocumento4 pagineAnalog Computers: The Analog Computer Is Almost An Extinct Type of Computer TheseKundaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Charecterstics of ComputerDocumento9 pagineCharecterstics of ComputerSiva NemalipuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Jecyl PDocumento3 pagineJecyl PjecylpNessuna valutazione finora
- NotesDocumento26 pagineNotesDIVYANSHI PHOTO STATENessuna valutazione finora
- Types of ComputersDocumento3 pagineTypes of ComputersJohn Philip MalonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Puter TypesDocumento2 paginePuter TypesDipak KUmar SInghNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Computers Lecture 4Documento24 pagineIntroduction To Computers Lecture 4Nayela AkramNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Computers Prepared by AaDocumento46 pagineIntroduction To Computers Prepared by AaAqeelMeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 8 Computer Studies PDFDocumento3 pagineGrade 8 Computer Studies PDFKennedy LunguNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Computers: Efforts by - Himanshu Khanna Roll Number - 21722756Documento11 pagineTypes of Computers: Efforts by - Himanshu Khanna Roll Number - 21722756Himanshu KhannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Computers MCQ QuestionsDocumento18 pagineClassification of Computers MCQ QuestionsSuresh Khanal100% (5)
- Chapter 2Documento9 pagineChapter 2Jayaraj JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Difference Between Analog ComputerDocumento1 paginaDifference Between Analog Computertapas_bayen9388Nessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of ComputerDocumento8 pagineClassification of ComputerGiri BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 What Is Computer ?Documento43 pagineUnit 1 What Is Computer ?Apoorva ChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOINFORMATICSDocumento24 pagineBIOINFORMATICSMuthuraman ArNessuna valutazione finora
- Classfication of ComputersDocumento9 pagineClassfication of ComputersDaud BuyunguNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of ComputersDocumento2 pagineClassification of ComputersGHSNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT Ichapter1 (Introduction To Computer)Documento12 pagineUNIT Ichapter1 (Introduction To Computer)Vinutha SanthoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1: Introduction To ComputingDocumento123 pagineTopic 1: Introduction To ComputingKartel Gunter100% (1)
- Chapter One Introduction To Computer: of ComputersDocumento8 pagineChapter One Introduction To Computer: of ComputershaileNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of ComputerDocumento5 pagineClassification of ComputerkamranNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer ScienceDocumento16 pagineComputer Sciencesandesh spkNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Sheet 1.1 - Types of ComputerDocumento4 pagineActivity Sheet 1.1 - Types of ComputerLyssa BasNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of ComputerDocumento14 pagineTypes of Computerteferi GetachewNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4 Types of Computer in Our Society: 1. Analog ComputersDocumento2 pagine1.4 Types of Computer in Our Society: 1. Analog ComputersJhonna Sanchez CelestinoNessuna valutazione finora
- English IV It Lesson NotesDocumento45 pagineEnglish IV It Lesson NotesJoaquim CHICONessuna valutazione finora
- DF 1st ModelDocumento35 pagineDF 1st ModelKulkarni SushmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of A Computer.: 1. The System Unit. 2. Input Devices. 3. Output Devices. 4. Storage DevicesDocumento10 pagineParts of A Computer.: 1. The System Unit. 2. Input Devices. 3. Output Devices. 4. Storage DevicesMandillah S Eddie100% (1)
- Transfer Case Electrical RMDocumento51 pagineTransfer Case Electrical RMDaniel Canales75% (4)
- Case-Study - Decision Making Under UncertaintyDocumento21 pagineCase-Study - Decision Making Under UncertaintyMari GhviniashviliNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 12. Big Issues Lesson 12a. Reading. Pages 140-141: No Words TranslationDocumento4 pagineModule 12. Big Issues Lesson 12a. Reading. Pages 140-141: No Words TranslationLeonardo Perez AlegriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Yamaha r6 Yec Kit ManualDocumento2 pagineYamaha r6 Yec Kit ManualAlexander0% (1)
- TR189 Kathuria PDFDocumento168 pagineTR189 Kathuria PDFuqiNessuna valutazione finora
- Deva Surya - 19MF02Documento30 pagineDeva Surya - 19MF02SaravananNessuna valutazione finora
- Polynomial Transformations of Tschirnhaus, Bring and Jerrard4s++Documento5 paginePolynomial Transformations of Tschirnhaus, Bring and Jerrard4s++wlsvieiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Design A Roller Coaster ProjectDocumento4 pagineDesign A Roller Coaster Projectapi-3564628400% (1)
- Airbus A319-A320-A321 - Quick Reference HandbookDocumento113 pagineAirbus A319-A320-A321 - Quick Reference Handbookrafaelldalpra100% (9)
- Zetor Crystal 150 170 Tractor Operator Manual PDFDocumento234 pagineZetor Crystal 150 170 Tractor Operator Manual PDFAntonNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Principles of Remote SensingDocumento24 pagineBasic Principles of Remote Sensingfelipe4alfaro4salas100% (1)
- En LF Drivers 10nw76 8Documento3 pagineEn LF Drivers 10nw76 8ChrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Diwali Pujan BookletDocumento10 pagineDiwali Pujan Bookletman_ishkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Collage Lab PDFDocumento145 pagineCollage Lab PDFmaa siddhi92% (12)
- Disa Match: A Match You Can Count OnDocumento8 pagineDisa Match: A Match You Can Count OngNessuna valutazione finora
- PECI 405 ECPP 7th Sem CivilDocumento96 paginePECI 405 ECPP 7th Sem CivilYasaswi AkkirajuNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Years High and Low PointsDocumento7 pagine5 Years High and Low PointsNaresh Kumar VishwakarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Phytoremediation Acuatic PlantsDocumento120 paginePhytoremediation Acuatic PlantsFranco Portocarrero Estrada100% (1)
- Important Notice 38-2021 Dated 24-03-2021 Available Seats Foreign National Spon INI CET PG Courses July 2021Documento3 pagineImportant Notice 38-2021 Dated 24-03-2021 Available Seats Foreign National Spon INI CET PG Courses July 2021Priyobrata KonjengbamNessuna valutazione finora
- Feature Writing EnglishDocumento2 pagineFeature Writing EnglishAldren BababooeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Avionic ArchitectureDocumento127 pagineAvionic ArchitectureRohithsai PasupuletiNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuromuscular Diseases. ALSDocumento7 pagineNeuromuscular Diseases. ALSjalan_zNessuna valutazione finora
- CADS Revit Scia Engineer Link Best PracticesDocumento32 pagineCADS Revit Scia Engineer Link Best PracticestrevorNessuna valutazione finora
- Epilepsy Lecture NoteDocumento15 pagineEpilepsy Lecture Notetamuno7100% (2)
- Asyb 2020 2Documento295 pagineAsyb 2020 2KhangNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Documento6 pagineScience 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Jess Anthony Efondo100% (4)
- Lec 8-10Documento5 pagineLec 8-10osamamahmood333Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sotero 05activity EnvironmetnDocumento3 pagineSotero 05activity Environmetnbernadette soteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Annual Report 2022-23 (Eng.)Documento326 pagineAnnual Report 2022-23 (Eng.)Gaurav DurejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jib Crane Assembly ManualDocumento76 pagineJib Crane Assembly ManualRobert Cumpa100% (1)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialDa EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeDa EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (9)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosDa EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesDa EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Build Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionDa EverandBuild Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Analog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceDa EverandAnalog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceNessuna valutazione finora
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonDa EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesDa EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsDa EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- ARDUINO CODE: Mastering Arduino Programming for Embedded Systems (2024 Guide)Da EverandARDUINO CODE: Mastering Arduino Programming for Embedded Systems (2024 Guide)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionDa EverandPractical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Upcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)Da EverandUpcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionDa EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (543)
- Current Interruption Transients CalculationDa EverandCurrent Interruption Transients CalculationValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsDa EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Wearable Sensors: Fundamentals, Implementation and ApplicationsDa EverandWearable Sensors: Fundamentals, Implementation and ApplicationsEdward SazonovNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveDa EverandUnderstanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (16)