Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
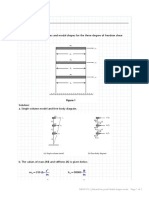
Statically Indeterminate Beams: Let Solve The Following Statically Indeterminate Beam (EI Constant)
Caricato da
Stângaciu Vlad AlexandruDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Statically Indeterminate Beams: Let Solve The Following Statically Indeterminate Beam (EI Constant)
Caricato da
Stângaciu Vlad AlexandruCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Gh.
Asachi Technical University of Iai Structural Statics Statically Determinate Structures
Department of Structural Mechanics Senior Lecturer Cezar Aanici, Dr. Eng.
- 1 -
STATICALLY INDETERMINATE BEAMS
Let solve the following statically indeterminate beam (EI = constant):
The equilibrium equation system for the chosen primary
system PS is (N0 2 unknowns M, M):
0 0
0 0
' M ' M "
" M ' M "
= + + =
= + + =
The main terms of the equations are:
1 1 2 10
1 1
2 3 3 3
l
m' m' l
dx l
EI EI EI EI
= = = =
1 1 2 10
1 1
2 3 3 3
l
m" m" l
" dx l
EI EI EI EI
= = = =
It is obvious that if EI =constant
" =
1 1 1 10
1 1
2 3 6 6
l l
m' m" m" m'
' " dx dx
EI EI
l
l
EI EI EI
= = = = =
= = =
The free terms of the equation system are:
( )
( )
( )
1 3
2 07 78 1 78
6
4
2 07 78 2 03 102 07 102 03 78
6
3 301
2 03 102
6
p
l
M m'
' dx .
EI EI
. . . .
.
EI
= = + +
+ + + + +
+ =
( )
( )
( )
1 3
2 07 102 1102
6
4
2 03 78 2 07 102 03 102 07 78
6
3 329
2 03 78
6
p
l
M m"
" dx .
EI EI
. . . .
.
EI
= = + +
+ + + + +
+ =
M' 'M'
'
M' M"
"
40 kN 20 kN
40 kN 20 kN
'=0 "=0
1
'
0.7 0.3
m'
r
e
a
l
l
o
a
d
c
a
s
e
1
1
0.7 0.3
m'
v
i
r
t
u
a
l
l
o
a
d
c
a
s
e
"
0.7 0.3
m" m"
M"=1
M"=1
1
SR SV
1
M'
M'=1
' "
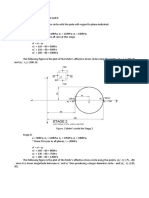
40 kN 20 kN
102 78
Mp
SR
P.S.
4 m 3 m 3 m
EI=const.
V'=26 V"=34
Gh. Asachi Technical University of Iai Structural Statics Statically Determinate Structures
Department of Structural Mechanics Senior Lecturer Cezar Aanici, Dr. Eng.
- 2 -
The free terms could also be solved using
the loading factors m and m,
respectively, as follows:
, and
6 6
l l
' m' " m"
EI EI
= =
where
M M
6R' 6R"
, and m' m"
l l
= =
and R
M
and R
M
are the reactive forces
given by the bending moment diagram
considered as a load for the primary
system.
6 6 1 1 1
78 3 7 3 78 4 5
10 10 2 3
1 1 1 2
24 4 3 4 102 3 3 1806
2 3 2 3
M
R'
m'
l
.
= = + + +
+ + + =
6 6 1 1 2
78 3 3 78 4 5
10 10 2 3
1 2 1 1
24 4 3 4 102 3 7 3 1974
2 3 2 3
M
R"
m"
l
.
= = + +
+ + + + =
Hence:
10 301 10 329
1806 , and 1974
6 6
' . " .
EI EI EI EI
= = = = - the same values.
Solving the equation system, the bending moments are as follows:
2 2
5460 , and 7140
" ' " ' " '
M ' . kNm M " . kNm
' " ' "
= = = =
.
102 78
R'M R"M
40 kN
20 kN
V'=24.32 kN V"=35.68 kN
M'=54.6 kNm M"=71.4 kNm
+
-
54.6 71.4
18.36
35.64
24.32
35.68
4.32
Qf
Mf
Gh. Asachi Technical University of Iai Structural Statics Statically Determinate Structures
Department of Structural Mechanics Senior Lecturer Cezar Aanici, Dr. Eng.
- 3 -
Let solve the following statically indeterminate beam with step variable stiffness:
The equilibrium equation system for the chosen
primary system PS is (N0 2 unknowns M, M):
0 0
0 0
' M ' M "
" M ' M "
= + + =
= + + =
Because the beam is geometrically and
mechanically symmetric the main terms of the
equations are equal, " = , Hence:
(
( )
0
2 2
0
0 0
1 3
2 11 2 07 07 2 1 07
4 6
1 4
2 07 2 03 2 07 03
6
1 1 2 45099
03 3 03
4 2 3 3
l l
m' m' m" m"
" dx dx
EI EI
. . .
EI
. . . .
EI
.
. .
EI EI
= = = =
= + + +
+ + + +
+ =
( )
( )
( )
0
2 2
0
0 0
1 3
2 07 03 1 03
4 6
1 4
2 07 03 2 03 07 07 03
6
1 3 11267
2 07 03 03 1
4 6
l l
m' m" m" m'
dx dx
EI EI
. . .
EI
. . . . . .
EI
.
. . .
EI EI
= = =
= + +
+ + + + +
+ + =
The free terms of the equation system are:
( )
(
) ( )
0
0
0 0
1 3
2 07 78 1 78
4 6
1 4
2 07 78 2 03 102 07 102
6
1 3 20785
03 78 2 03 102
4 6
p
l
M m'
' dx .
EI EI
. . .
EI
.
. .
EI EI
= = + +
+ + + +
+ + =
M' 'M'
M' M"
40 kN 20 kN
40 kN 20 kN
'=0 "=0
1
'
0.7 0.3
m'
1
1
0.7 0.3
m'
"
0.7 0.3
m" m"
M"=1
M"=1
1
SR SV
1
M'
M'=1
' "
40 kN 20 kN
102 78
Mp
SR
P.S.
4 m 3 m 3 m
V'=26 V"=34
EI0
4EI0 4EI0
' "
r
e
a
l
l
o
a
d
c
a
s
e
v
i
r
t
u
a
l
l
o
a
d
c
a
s
e
Gh. Asachi Technical University of Iai Structural Statics Statically Determinate Structures
Department of Structural Mechanics Senior Lecturer Cezar Aanici, Dr. Eng.
- 4 -
( ) (
) ( )
0 0
0 0
1 3 1 4
2 07 102 1 102 2 03 78 2 07 102
4 6 6
1 3 21965
03 102 07 78 2 03 78
4 6
p
l
M m"
" dx . . .
EI EI EI
.
. . .
EI EI
= = + + + +
+ + + =
The free terms could also be solved using the
loading factors m and m, respectively, as
follows:
, and
6 6
l l
' m' " m"
EI EI
= =
where
M M
6R' 6R"
, and m' m"
l l
= =
and R
M
and R
M
are the reactive forces given
by the reduced bending moment diagram
(proportionally with the bending stiffness)
considered as a load for the primary system.
6 1 1 1
195 3 7 3 78 4 5
10 10 2 3
1 1 1 2
24 4 3 4 255 3 3 20785
2 3 2 3
M
R' .
. .
= + + +
+ + + =
6 1 1 2
195 3 3 78 4 5
10 10 2 3
1 2 1 1
24 4 3 4 255 3 7 3 21965
2 3 2 3
M
R" .
. .
= + +
+ + + + =
Solving the equation system, the bending
moments are as follows:
2
6561 ,
" ' "
M ' . kNm
' "
= =
2
9695 .
' " '
M ' . kNm
' "
= =
' "
40 kN 20 kN
102 78
Mp
SR
102
78
V'=26 V"=34
R'M R"M
40 kN
20 kN
V'=22.87 kN V"=37.13 kN
M'=65.61 kNm M"=96.95 kNm
+
-
65.61 96.95
2.99
14.45
22.87
37.13
2.87
Qf
Mf
19.5
25.5
Gh. Asachi Technical University of Iai Structural Statics Statically Determinate Structures
Department of Structural Mechanics Senior Lecturer Cezar Aanici, Dr. Eng.
- 5 -
Let solve the following statically indeterminate beam
with linear voussoirs at the ends:
The equilibrium equation system for the chosen primary
system PS is (N0 2 unknowns M, M):
0 0
0 0
' M ' M "
" M ' M "
= + + =
= + + =
Because the beam is geometrically and
mechanically symmetric the main terms of the
equation system are equal, " = :
0 0 0
=
3 3 6
l l l
c' , " c" , c
EI EI EI
= =
where c=c, and c are voussoir influence coefficients
which depend on the voussoir type (linear, parabolic,
symmetrically disposed or not etc.) and length,
stiffness ratio between the moment of inertia in the
current span and the moment of inertia at the ends of the
beam, respectively, are given in specific tables, and the
values in this case are:
0
0
3
03 025
10 4
span
v
v
max
I
l I
. , n .
l I I
= = = = = =
and
0644 0832 c' c" . , c . = = = .
For the free terms, the following relationships are
used:
0 0
6 6
l l
' m' k' , " m" k",
EI EI
= =
where mk and mk depend on the load
characteristics (concentrated or distributed forces
etc.) and by the voussoirs type (linear, parabolic,
symmetrically disposed or not etc.) and its
mechanical properties as mentioned above and are
given in tables. For this particular case, two distinct
sets of values must be extracted because the beam
is loaded with two concentrated forces F
1
= 20
kN, and F
2
= 40 kN. Consequently, considering
valid the load superposition hypothesis, these
influences could be added as follows:
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
1 2
1 2
1 1 1 2
1 2
1 2
2 1 2 2
+
+
F F
F F
F F
F F
m' k' m' k' m' k' v Fl v F l
m" k" m" k" m" k" v Fl v F l
= = +
= = +
the coefficients v
i
Fi
being obtained by corresponding linear interpolation, and the final values are:
M' M"
40 kN 20 kN
40 kN 20 kN
'=0 "=0
1
'
0.7 0.3
m' =
1
m'
"
0.7 0.3
m" =m"
M"=1
1
SR = SV
1
M'=1
' "
40 kN 20 kN
102 78
Mp
SR
P.S.
4 m 3 m 3 m
V'=26 V"=34
40 kN
20 kN
V'=23.5 kN V"=36.5 kN
M'=62.08 kNm M"=87.08 kNm
+
-
62.08 87.08
8.42
22.42
23.5
36.5
3.5
Qf
Mf
EI0
4EI0
4EI0
' "
SR = SV
Gh. Asachi Technical University of Iai Structural Statics Statically Determinate Structures
Department of Structural Mechanics Senior Lecturer Cezar Aanici, Dr. Eng.
- 6 -
1 2
1 1
1 2
2 2
0292 0235
0235 0292
F F
F F
v . , v .
v . , v .
= =
= =
Hence,
0292 20 10 0235 40 10 15240
0235 20 10 0292 40 10 16380
m' k' . . .
m" k" . . .
= + =
= + =
and the free terms are:
0 0 0
0 0 0
254
15240
6 6
21965
16380
6 6
l l
' m' k' . ,
EI EI EI
l l .
" m" k" .
EI EI EI
= = =
= = =
Replacing all these values in the equation system, the ends bending moments are:
( )
( )
0
0
2 0
6 0
0
2 0
6
l
M ' c' M " c m' k'
EI M ' M "
M ' M " l
M ' c' M " c m" k"
EI
+ + =
+ + =
+ + =
+ + =
from which:
2 2
2 2
2 2 0644 1524 0832 1638
6208 kNm ,
4 4 0644 0644 0832
2 2 0644 1638 0832 1524
8708 kNm
4 4 0644 0644 0832
c" m' k' cm" k" . . . .
M ' .
c' c" c . . .
c' m" k" cm' k' . . . .
M " .
c' c" c . . .
= = =
= = =
Gh. Asachi Technical University of Iai Structural Statics Statically Determinate Structures
Department of Structural Mechanics Senior Lecturer Cezar Aanici, Dr. Eng.
- 7 -
Let solve the following statically indeterminate beams subjected to the shown support settlements.
a) Fully fixed beam subjected to an imposed unit rotation of a beam end
The equilibrium equation system for the chosen primary system PS is (N0 2 unknowns M, M):
1 1
0 1
k k ,settle
k
k k ,settle
k
' M ' M " ' R
" M ' M " " R
= + = +
= + = +
The main terms of the equation system are:
=
3 3 6
l l l
, " ,
EI EI EI
= =
Consequently, the equation system becomes:
1
1 1 1 0 1
3 6
1
1 0 0 0 0
6 3
k k ,settle
k
k k ,settle
k
l l
M ' M " ' R
EI EI l
l l
M ' M " " R
EI EI l
+ = + = + =
+ = + = + =
and bending moments are
4 2
and
ij ji
EI EI
M ' k M ' k
l l
= = = =
also known as rotation stiffness and transmitted rotation stiffness, respectively of a fully fixed beam
with a constant bending stiffness along the whole length.
'=1
"=0
l
EI=const.
'
M'=1
"
M"=1
'
M' M"
"
P.S.
i j
Gh. Asachi Technical University of Iai Structural Statics Statically Determinate Structures
Department of Structural Mechanics Senior Lecturer Cezar Aanici, Dr. Eng.
- 8 -
b) Fully fixed beam subjected to an imposed unit vertical displacement of a beam end
"=0
l
EI=const.
'
M'=1
"
M"=1
'
M' M"
"
P.S.
"=0
"=1
1/l 1/l
1/l 1/l
i j
The equilibrium equation system for the chosen primary system PS is (N0 2 unknowns M, M):
0 1
0 1
k k ,settle
k
k k ,settle
k
' M ' M " ' R
" M ' M " " R
= + = +
= + = +
The main terms of the equation system are:
=
3 3 6
l l l
, " ,
EI EI EI
= =
Consequently, the equation system becomes:
1 1
1 0 0 1
3 6
1 1
1 0 0 1
6 3
k k ,settle
k
k k ,settle
k
l l
M ' M " ' R
EI EI l l
l l
M ' M " " R
EI EI l l
+ = + = =
+ = + = + =
and bending moments are
2 2
6 6
and
ij ij
EI EI
M ' k M ' k
l l
= = = =
also known as translation stiffness of a fully fixed beam with a constant bending stiffness
along the whole length.
Gh. Asachi Technical University of Iai Structural Statics Statically Determinate Structures
Department of Structural Mechanics Senior Lecturer Cezar Aanici, Dr. Eng.
- 9 -
'=1
l
EI=const.
'
M'=1
'
M'
"
P.S.
i j
c) Fixed-hinged beam subjected to an imposed unit rotation of a beam end
The elastic equilibrium equation for the chosen
primary system PS is (N0 one unknown M):
1 1
k k ,settle
k
' M ' ' R = = +
Knowing that
3
l
EI
= ,
the equilibrium equation becomes:
1
1 11 0 1
3
k k ,settle
k
l
M ' ' R
EI l
= + = + =
and bending moment is:
3
ij
EI
M ' k
l
= =
also known as rotation stiffness of a fixed-hinged beam with a constant bending stiffness along the
whole length.
d) Fixed-hinged beam subjected to an imposed unit vertical displacement of a hinged end
The elastic equilibrium equation for the same
chosen primary system PS is (N0 one
unknown M):
1 1
1 1 0 1
k k ,settle
k
M ' ' R
l l
= + = =
replacing
3
l
EI
= , and solving for the
unknown bending moment M, the translation
stiffness is:
2
1 3
3
ij
l EI
M ' M ' k
EI l l
= = =
l
EI=const.
'
M'=1
'
M'
"
P.S.
"=0
"=1
1/l 1/l
i j
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ASYMPTOTES1Documento13 pagineASYMPTOTES1hanumateNessuna valutazione finora
- 6-Transformation of Stress & Strain (Jan2013)Documento49 pagine6-Transformation of Stress & Strain (Jan2013)Mohammad HanafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 - Exercise: y I W y C X I W W WDocumento2 pagineModule 2 - Exercise: y I W y C X I W W WTrigger DineshNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Vibration Solved ExamplesDocumento92 pagineMechanical Vibration Solved ExamplesZain Ahmed85% (13)
- AE 321 - Solution of Homework #4: 1. First construct Mohr's circle. At stresses at the given element are σDocumento8 pagineAE 321 - Solution of Homework #4: 1. First construct Mohr's circle. At stresses at the given element are σArthur DingNessuna valutazione finora
- EE203 Chapter 2 Solve ODE Using Power SeriesDocumento34 pagineEE203 Chapter 2 Solve ODE Using Power Series许凉发Nessuna valutazione finora
- Statically Determinate Arches: The Parabolic ArchDocumento0 pagineStatically Determinate Arches: The Parabolic ArchSarbu AlexandruNessuna valutazione finora
- Teknik Kekuatan BahanDocumento29 pagineTeknik Kekuatan BahanfayuangNessuna valutazione finora
- NFNMS 5Documento87 pagineNFNMS 5wanpudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Met 1Documento46 pagineMet 1Ahmed AbdelhamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Pair of Straight LinesDocumento18 paginePair of Straight Linesakashprabhakaran100% (2)
- Aplica/ia 3.1.: ϕ ϕ ϕ && &, , ϕ ⋅ − ⋅ x k l ϕ ⋅ + ⋅ x k lDocumento3 pagineAplica/ia 3.1.: ϕ ϕ ϕ && &, , ϕ ⋅ − ⋅ x k l ϕ ⋅ + ⋅ x k lCipar ClauNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Vibration Solved ExamplesDocumento84 pagineMechanical Vibration Solved ExamplesKajal Khan100% (2)
- Plastic Analysis of StructuresDocumento13 paginePlastic Analysis of StructuresAkshata Deshpande100% (1)
- Curve FittingDocumento37 pagineCurve FittingToddharris100% (4)
- Analysis of Frames Beams TrussesDocumento17 pagineAnalysis of Frames Beams TrussesRameez AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- ExcerciseDocumento3 pagineExcerciserigoxmufiNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Freq and Modal ShapesDocumento5 pagineNatural Freq and Modal ShapesHelen HerodicoNessuna valutazione finora
- CH6 PDFDocumento34 pagineCH6 PDFteknikpembakaran2013Nessuna valutazione finora
- Min 05037 Geo Technical EngineeringDocumento15 pagineMin 05037 Geo Technical EngineeringBhaskar ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Rotors - SolutionDocumento25 pagineTutorial Rotors - SolutionMuntoiaNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY2014F Buffler VW1Documento125 paginePHY2014F Buffler VW1Matthew BaileyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Two-Dimensional Problem SolutionDocumento51 pagineChapter 8 Two-Dimensional Problem Solutiongpskumar22Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Two-Dimensional Problem SolutionDocumento51 pagineChapter 8 Two-Dimensional Problem SolutionUNsha bee kom100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Two-Dimensional Problem SolutionDocumento51 pagineChapter 8 Two-Dimensional Problem SolutionJoseph Daguio JrNessuna valutazione finora
- Elementary Tutorial: Fundamentals of Linear VibrationsDocumento51 pagineElementary Tutorial: Fundamentals of Linear VibrationsfujinyuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuliah 5 Tegangan BDNGDocumento23 pagineKuliah 5 Tegangan BDNGBrian Halomoan Putra PardosiNessuna valutazione finora
- Continuous BeamsDocumento18 pagineContinuous Beamszdravac9220Nessuna valutazione finora
- Comp It Emg SolutionDocumento11 pagineComp It Emg Solutionpatelahmad952Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practise Problems Set03Documento5 paginePractise Problems Set03rohit kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- MEC 3611: Structural Mechanics: Lecture 3: REVIEWDocumento22 pagineMEC 3611: Structural Mechanics: Lecture 3: REVIEWhellolover0% (1)
- Solved Problems TOEDocumento5 pagineSolved Problems TOErameshbabu_1979Nessuna valutazione finora
- Beam BucklingDocumento45 pagineBeam BucklingSaleha QuadsiaNessuna valutazione finora
- E ∠ δ, …, E ∠δ δ, …, δ E, …, E: II. Classical Power System Model For Transient Stability AnalysisDocumento6 pagineE ∠ δ, …, E ∠δ δ, …, δ E, …, E: II. Classical Power System Model For Transient Stability AnalysisSyaloom Gorga NapitupuluNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems and Solutions Section 6.7 (6.53 Through 6.63) 6.53: W (X, T) L T Sin XDocumento13 pagineProblems and Solutions Section 6.7 (6.53 Through 6.63) 6.53: W (X, T) L T Sin Xsonti11Nessuna valutazione finora
- ChewMA1506-14 Ch8 PDFDocumento69 pagineChewMA1506-14 Ch8 PDFalibabawalaoaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modal AnalysisDocumento40 pagineModal AnalysisSumit Thakur100% (1)
- Worksheet - Regression and CorrelationDocumento1 paginaWorksheet - Regression and CorrelationElizabeth SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 D LectureDocumento36 pagine3 D LectureAisha AbuzgaiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Soils & Stresses Example. 1Documento6 pagineSoils & Stresses Example. 1hahaduNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 3 SolidDocumento3 pagineSheet 3 Solidmariam.ahmed03Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mathcad - Fresnel - SlitDocumento3 pagineMathcad - Fresnel - SlitAprilMalcolmPhdNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamics Response Spectrum AnalysisDocumento33 pagineDynamics Response Spectrum AnalysisAhmed Gad100% (1)
- Uncracked Section Example: QuestionsDocumento8 pagineUncracked Section Example: QuestionsRaju SkNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6Documento4 pagineChapter 6newrome76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Composite LaminatesDocumento11 pagineTheory of Composite LaminatespraveenpinnojiNessuna valutazione finora
- A Rectangular Steel Bar Having A CrossDocumento2 pagineA Rectangular Steel Bar Having A CrossHitesh PrajapatNessuna valutazione finora
- On The Sum of Left and Right Circulant Ma 2023 Linear Algebra and Its ApplicDocumento24 pagineOn The Sum of Left and Right Circulant Ma 2023 Linear Algebra and Its ApplicSasikalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise ProblemsDocumento20 pagineExercise ProblemsmustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Problem of Home WorkDocumento3 pagine1st Problem of Home WorkEsmael AdemNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 04 Nonlinear RegressionDocumento22 pagine06 04 Nonlinear RegressionJohn Bofarull GuixNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7INDITERMINATEDocumento7 pagineChapter 7INDITERMINATEHEWAN DEJENENessuna valutazione finora
- 114 119Documento9 pagine114 119Carlos Moran CepedaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Da EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Valutazione: 2.5 su 5 stelle2.5/5 (2)
- Normal Two-Dimensional Singularities. (AM-71), Volume 71Da EverandNormal Two-Dimensional Singularities. (AM-71), Volume 71Nessuna valutazione finora
- Difference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsDa EverandDifference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsNessuna valutazione finora
- FS OEM E90 Ambient Door Lighting Retrofit Kit - BMW 3-Series (E90 E92) ForumDocumento1 paginaFS OEM E90 Ambient Door Lighting Retrofit Kit - BMW 3-Series (E90 E92) ForumStângaciu Vlad AlexandruNessuna valutazione finora
- Online BMW Parts CatalogDocumento1 paginaOnline BMW Parts CatalogStângaciu Vlad AlexandruNessuna valutazione finora
- E92&E93 PDC RetrofitDocumento32 pagineE92&E93 PDC RetrofitStângaciu Vlad AlexandruNessuna valutazione finora
- Windows 7 G2 AIO 22in1 ESD en-US May 2015Documento2 pagineWindows 7 G2 AIO 22in1 ESD en-US May 2015Stângaciu Vlad Alexandru0% (1)
- Display Cuadruple de 7 SegmentosDocumento2 pagineDisplay Cuadruple de 7 SegmentosJose CastañedaNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 30 Minhaal Kalyan Chevron.8569Documento19 pagine13 30 Minhaal Kalyan Chevron.8569Rohan DangareNessuna valutazione finora
- Definitions and MCQs of Ninth Class Chemistry (Solution and Suspension)Documento6 pagineDefinitions and MCQs of Ninth Class Chemistry (Solution and Suspension)Sajid AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Vision System PlatformDocumento4 pagineVision System PlatformtnchsgNessuna valutazione finora
- CFD With Opensource Software: Non-Newtonian Models in Openfoam Implementation of A Non-Newtonian ModelDocumento19 pagineCFD With Opensource Software: Non-Newtonian Models in Openfoam Implementation of A Non-Newtonian ModelDino DinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Word - CH 12 Worksheet 2-2 - DocDocumento7 pagineMicrosoft Word - CH 12 Worksheet 2-2 - DocAhmad RezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Candela To Lumen Conversion CalculationDocumento11 pagineCandela To Lumen Conversion CalculationSimon CondorNessuna valutazione finora
- Accepted Manuscript: Food HydrocolloidsDocumento38 pagineAccepted Manuscript: Food HydrocolloidsIoana PeptănaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalysis Today: Anna Maria Venezia, Valeria La Parola, Leonarda Francesca LiottaDocumento11 pagineCatalysis Today: Anna Maria Venezia, Valeria La Parola, Leonarda Francesca LiottaLujy Al-SyoufNessuna valutazione finora
- ECOTherms Feed Water TanksDocumento4 pagineECOTherms Feed Water TanksFadzil NorNessuna valutazione finora
- DQE SimplifiedDocumento8 pagineDQE SimplifiedBen100% (1)
- Today's Objective:: Method of SectionsDocumento20 pagineToday's Objective:: Method of SectionsAtef NazNessuna valutazione finora
- Bond Fission, Types of Reagents-TtDocumento23 pagineBond Fission, Types of Reagents-TtdhanushNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasonic Testing - Wikipedia PDFDocumento26 pagineUltrasonic Testing - Wikipedia PDFKarthicWaitingNessuna valutazione finora
- Instruction Manual of RH 143Documento7 pagineInstruction Manual of RH 143minhankyaw75% (4)
- Non Destructive Testing of Pipelines State and Methods For Its RepairingDocumento19 pagineNon Destructive Testing of Pipelines State and Methods For Its RepairingCarlos MusellaNessuna valutazione finora
- En - 1999 01 07 - T - WL 21507 Ea Srbs in Polysius Vertical Roller Mill QuadropolDocumento2 pagineEn - 1999 01 07 - T - WL 21507 Ea Srbs in Polysius Vertical Roller Mill QuadropolmiteshmechNessuna valutazione finora
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council (Zimsec) : Advanced Level SyllabusDocumento72 pagineZimbabwe School Examinations Council (Zimsec) : Advanced Level Syllabusnyasha chanetsaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Causes and Effects of EarthquakesDocumento4 pagineThe Causes and Effects of EarthquakesKarma AkabaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 4Documento4 pagineTutorial 4Zarif ZufayriNessuna valutazione finora
- Au2-13, Deka2008Documento11 pagineAu2-13, Deka2008ht117Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ocean Engineering: Wen-Huai Tsao, Wei-Shien Hwang TDocumento10 pagineOcean Engineering: Wen-Huai Tsao, Wei-Shien Hwang T邱俊祥Nessuna valutazione finora
- ISO-8573!3!1999 - Métodos de Prueba - HumedadDocumento4 pagineISO-8573!3!1999 - Métodos de Prueba - Humedadj_jjerfNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Materials (UES012) School of Physics and Materials Science Tutorial Sheet No 1-2Documento1 paginaEngineering Materials (UES012) School of Physics and Materials Science Tutorial Sheet No 1-2Arpit Sachdeva100% (1)
- Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Microanalysis: Book ReviewDocumento1 paginaScanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Microanalysis: Book Review平Nessuna valutazione finora
- T 86 UDocumento1 paginaT 86 URenny DevassyNessuna valutazione finora
- Thickness Calculation of Cylindrical Shell and TubeDocumento1 paginaThickness Calculation of Cylindrical Shell and TubeThanhNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Technology Subject Code: CH2001Documento17 pagineChemical Technology Subject Code: CH2001U SANKAR TEJONessuna valutazione finora
- CompositeMaterials PHD Summary-2007Documento31 pagineCompositeMaterials PHD Summary-2007Ege menNessuna valutazione finora
- Sanyal Classification of Geothermal Systems 2005 PDFDocumento8 pagineSanyal Classification of Geothermal Systems 2005 PDFLevi OktaNessuna valutazione finora