Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Vlsi Lab 2
Caricato da
Vishal Iyer0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
65 visualizzazioni6 paginevlsi
Titolo originale
Vlsi lab 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentovlsi
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
65 visualizzazioni6 pagineVlsi Lab 2
Caricato da
Vishal Iyervlsi
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 6
SVKMS NMIMS
Mukesh Patel School of Technology Management & Engineering
Department of Electronics Engineering
Subject- VLSI
EXPERIMENT NO. 1
Aim:- a) Fabrication of IC PNP Transistor .Describe all the steps in the fabrication
b) Describe Lithography in detail
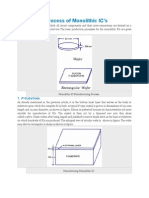
Fabrication of BJT
1. p-type substrate
The starting material for a vertical npnstructure is p-type substrate doped at 1016/cm3or less
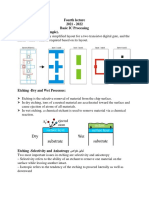
2. Oxide deposition (CVD)
Using a chemical process (CVD), oxide is deposited on the wafer surface
3. Patterning of first oxide
Photoresistspun on top of the oxide is exposed using the buried layer mask (mask #1)
The BL mask is usually generated automatically from other masks
Etching of first oxide
Using a wet etch, a window corresponding to the buried layer mask is opened in the oxide
Final Buried Layer Window
After the remaining PR is stripped, the deposited oxide has an opening etched in the location
specified by the buried layer mask
Buried Layer Implant
The buried layer is formed with a high density (dose) implant of n-type dopant, usually
Phosphorous
Some lateral diffusion of dopants takes place during the implant
Dopant is also introduced into the masking oxide
Final Buried Layer
After the masking oxide is removed (etched), the result is a highly doped buried layer region in
the original silicon substrate
Final epiLayer
Using epitaxialdeposition (similar to CVD), a layer of very high quality (crystalline) silicon is
deposited on the surface
Some diffusion of dopantsoccurs from the highly doped buried layer into the more lightly doped
epitaxiallayer
Photoresist (mask #2)
The resulting epitaxiallayer will form the collector region in the BJT, with the highly doped (low
R) buried layer forming an equipotentialregion under the device
Note that the buried layer is now completely enclosed in siliconmaterial
Isolation Implantation
A heavy p-type doping forms the p+isolation regions
The masking oxide absorbs dopant, preventing implantation between the isolation regions
Final isolated structure
After a long enough implant so that the isolation regions reach the underlying substrate, the
masking oxide is removed
Sinker mask exposure and Photoresist (mask #3)
Connection will be made to the buried layer (collector) using a sinker, an implantation of high
concentration and significant depth
Oxide and PR layers are exposed using a sinker mask(mask #3)
Final Sinker Structure
Depending on the implantation conditions and the thickness of the epiregion, the sinker may or
may not reach right down to the buriedlayer
Base Region Implantation
A p-type dopant(usually Boron) is implanted into the epilayer through the oxide window to form
the p-type base region
Final Base Region
(mask #5)
After implantation is complete, a p-type counterdopedbase region has been formed in the n-type
collector epi
Emitter Implant
A heavy n-type dopant(usually As) is implanted through the oxide window opening to form the
emitter
Control of this implant is critical to the BJTsoperation
Final Contact Cuts and Metal Deposition
Top view layout shows the various masks used to realize the basic structure
Cross section is duplicated to show correspondence
Buried layer and isolation masks can by generated automatically based on size of base region
and position of collector
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignDa EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendaleNessuna valutazione finora
- VLSI CMOS Fabrication TechnologyDocumento15 pagineVLSI CMOS Fabrication TechnologyRamanaButterflyNessuna valutazione finora
- Vlsi PDFDocumento81 pagineVlsi PDFShruthiNessuna valutazione finora
- VLSI Micro-Project Report Group A PDFDocumento14 pagineVLSI Micro-Project Report Group A PDFganesh SawantNessuna valutazione finora
- Fabrication of PN Junction DiodeDocumento11 pagineFabrication of PN Junction DiodeV.Harika.78% (9)
- N Channel, P Channel Fabrication by School of MicroelectronicsDocumento44 pagineN Channel, P Channel Fabrication by School of MicroelectronicsjouleNessuna valutazione finora
- Nmos and Cmos FabricationDocumento33 pagineNmos and Cmos FabricationmannsloveNessuna valutazione finora
- Fabrication Mod 2Documento16 pagineFabrication Mod 2albin shajanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2CMOSFabricationMNIT (DEc2006)Documento46 pagine2CMOSFabricationMNIT (DEc2006)Arjun YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Multi-Patterning Lithography - An Efficient Photolithography TechniqueDocumento29 pagineMulti-Patterning Lithography - An Efficient Photolithography TechniqueKrishna Saroja SankaNessuna valutazione finora
- ALD in Semiconductor ProcessingDocumento26 pagineALD in Semiconductor ProcessingWeiHsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon Credit BussinessDocumento2 pagineCarbon Credit BussinessVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Nmos Fabrication ProcessDocumento12 pagineNmos Fabrication ProcessMierul Asrap100% (17)
- BJT Fabrication 2018Documento13 pagineBJT Fabrication 2018عہۣۗثہۣۗمہۣۗان الہۣۗضہۣۗاحہۣۗيNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction of A Monolithic Bipolar TransistorDocumento6 pagineConstruction of A Monolithic Bipolar TransistorsampNessuna valutazione finora
- CMOS Fabrication: (With Extended Comments)Documento26 pagineCMOS Fabrication: (With Extended Comments)srivardhana7Nessuna valutazione finora
- VLSI Module-2 PPT For FabricationDocumento13 pagineVLSI Module-2 PPT For FabricationPhanindra ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit I Ic FabricationDocumento23 pagineUnit I Ic FabricationBhuvana VaradharajNessuna valutazione finora
- EE3402 Linear Integrated Circuits Reg 2021 Notes (Unit I)Documento20 pagineEE3402 Linear Integrated Circuits Reg 2021 Notes (Unit I)Monika GNessuna valutazione finora
- Operation and FabricationDocumento27 pagineOperation and Fabricationsaiteja kothapalliNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To IC FabricationDocumento7 pagineIntroduction To IC FabricationAbhishek DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Digital VLSI Design: Discipline/eee/agupta/advd/advd - HTMDocumento78 pagineAnalog Digital VLSI Design: Discipline/eee/agupta/advd/advd - HTMhkajaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Vlsi Part-Ii 1647682812Documento17 pagineVlsi Part-Ii 1647682812Noman Ali35Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fabrication of Silicon DiodeDocumento26 pagineFabrication of Silicon Diodeali974424Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fabrication of PNP TransistorDocumento32 pagineFabrication of PNP TransistorRahul RajNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT-1: TOPIC: MOS Process, NMOS Process, CMOS ProcessDocumento36 pagineUNIT-1: TOPIC: MOS Process, NMOS Process, CMOS ProcessashishNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To VLSI Fabrication Technologies: Emanuele BaravelliDocumento38 pagineIntroduction To VLSI Fabrication Technologies: Emanuele BaravelliNelarapuMaheshNessuna valutazione finora
- Mod 2a Fabrication & Design RulesDocumento73 pagineMod 2a Fabrication & Design RulesVijayalaxmi N CNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 IC Fabrication: Advantages of Integrated CircuitsDocumento13 pagineUnit 1 IC Fabrication: Advantages of Integrated CircuitsVerloves Love0% (1)
- Unit - I: Vlsi Fabrication TechniquesDocumento64 pagineUnit - I: Vlsi Fabrication TechniquesAnand KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 12 PDFDocumento14 pagineLec 12 PDFPrashant SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 01-Reviewing PolySi NMOS TechnoDocumento53 pagine01-Reviewing PolySi NMOS TechnoCyrille MagdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nmos FabricationDocumento4 pagineNmos FabricationAshadur RahamanNessuna valutazione finora
- NotesDocumento2 pagineNoteskoctyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2Documento33 pagineUnit 2Venky VellankiNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Semiconductor Fabrication Technology Prof. A. MasonDocumento5 pagineOverview of Semiconductor Fabrication Technology Prof. A. MasonPradeep BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- FEOL (Front End of Line: Substrate Process, The First Half of Wafer Processing)Documento17 pagineFEOL (Front End of Line: Substrate Process, The First Half of Wafer Processing)karthikNessuna valutazione finora
- Vlsi Design UNIT-1: Lecture-3Documento11 pagineVlsi Design UNIT-1: Lecture-3Erica WhiteheadNessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductor FabricationDocumento6 pagineSemiconductor FabricationSyed Raheel AdeelNessuna valutazione finora
- FALLSEM2023-24 BECE303L TH VL2023240100258 2023-04-28 Reference-Material-IDocumento28 pagineFALLSEM2023-24 BECE303L TH VL2023240100258 2023-04-28 Reference-Material-IKamali SiddharthanNessuna valutazione finora
- Step1:: 1. With Neat Sketches Explain The NMOS and PMOS Fabrication ProcedureDocumento6 pagineStep1:: 1. With Neat Sketches Explain The NMOS and PMOS Fabrication ProcedurehghgNessuna valutazione finora
- BiCMOS FabricationDocumento7 pagineBiCMOS FabricationMahabub Hossain100% (1)
- Unit 2 Fabrication ProcessDocumento8 pagineUnit 2 Fabrication Processbhupendra1977Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vlsi NotesDocumento11 pagineVlsi NotesShowcase MarathiNessuna valutazione finora
- NMOS Fabrication Steps - VLSIDocumento3 pagineNMOS Fabrication Steps - VLSISAMUDRA NAGNessuna valutazione finora
- Production Process of Monolithic ICDocumento5 pagineProduction Process of Monolithic ICAmanda Spence100% (2)
- BiCMOS Process FlowDocumento6 pagineBiCMOS Process FlowrupakothurNessuna valutazione finora
- VLSI Design (EE-402) LithographyDocumento31 pagineVLSI Design (EE-402) LithographyZahidullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4Documento43 pagineModule 4Sidharth GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fabrication Process: Kanada TechnologiesDocumento33 pagineFabrication Process: Kanada TechnologiesKarthigai ValliNessuna valutazione finora
- NMOS Fabrication: Step 1: Processing The SubstrateDocumento5 pagineNMOS Fabrication: Step 1: Processing The Substratechinthala santhosh srkNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec4.Integrated CircuitsDocumento6 pagineLec4.Integrated Circuitsahmed yuosifNessuna valutazione finora
- Cmos Process FlowDocumento25 pagineCmos Process FlowSHAIK MUSTHAFANessuna valutazione finora
- CMOS FabricationDocumento27 pagineCMOS FabricationspvenuNessuna valutazione finora
- Fabrication of FLOTOX: (EEPROM Cell)Documento12 pagineFabrication of FLOTOX: (EEPROM Cell)सुधांशु जनवाड़करNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5 - VLSI Design - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocumento12 pagineUnit 5 - VLSI Design - WWW - Rgpvnotes.intanishachaturvedi2025Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Digital Bicmos RealizationDocumento63 pagineAnalog Digital Bicmos RealizationSravana JyothiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bicmos Process Flow: Figure 5.2-1: Device Cross-Section of Bicmos Process Showing N+ Buried Layer ImplantDocumento6 pagineBicmos Process Flow: Figure 5.2-1: Device Cross-Section of Bicmos Process Showing N+ Buried Layer ImplantArun GopinathNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture CMOS NWELL and TwinTub ProcessDocumento33 pagineLecture CMOS NWELL and TwinTub Processilias ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Dasar Design CMOS TransistorDocumento49 pagineDasar Design CMOS Transistormaqbulloh darojatiNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.2.1 Bicmos Process Flow: NextDocumento5 pagine5.2.1 Bicmos Process Flow: NextamithbaluNessuna valutazione finora
- Microfabrication: Yash V. Kankal Roll No.Documento31 pagineMicrofabrication: Yash V. Kankal Roll No.yogesh_lonkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Cmos Fabrication Technology and Design RulesDocumento56 pagineChapter 2 Cmos Fabrication Technology and Design Rulesvanarajesh620% (1)
- MMIC Design, Part 2 - ProcessingDocumento23 pagineMMIC Design, Part 2 - ProcessingVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 PlacementDocumento39 pagine4 PlacementVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- MMIC Design, Part 3 - Packaging & TestingDocumento30 pagineMMIC Design, Part 3 - Packaging & TestingVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- RF Fundamentals, Part IDocumento19 pagineRF Fundamentals, Part IVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 FPGA Architecture 3Documento52 pagine3 FPGA Architecture 3Vishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- RF Fundamentals, Part IIDocumento28 pagineRF Fundamentals, Part IIVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- VESPA Portable Scalable and Flexible FPGA-BasedDocumento10 pagineVESPA Portable Scalable and Flexible FPGA-Based5030011067Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reco Questionnaire (Non-Working Students)Documento5 pagineReco Questionnaire (Non-Working Students)Vishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Robotic Manual CoverPagesDocumento4 pagineRobotic Manual CoverPagesVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Resume PacketDocumento35 pagineResume PacketVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Cadence TutorialDocumento25 pagineCadence TutorialVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee6304 Ym Lec 1Documento25 pagineEe6304 Ym Lec 1Vishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- EE6304 Test1 2015 FallDocumento12 pagineEE6304 Test1 2015 FallVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- STM32F429 DiscoveryDocumento11 pagineSTM32F429 Discoverymail87523Nessuna valutazione finora
- Block Diagram of Smart Card Sys. LCDDocumento1 paginaBlock Diagram of Smart Card Sys. LCDVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- 04-CCFP4.0 - OOP Using JavaDocumento42 pagine04-CCFP4.0 - OOP Using JavaVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 NewDocumento69 pagineUnit 4 NewVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- 03-CCFP4.0 - OOP Using JavaDocumento43 pagine03-CCFP4.0 - OOP Using JavaVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- International TranscriptsDocumento2 pagineInternational TranscriptsVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- RbiDocumento1 paginaRbiVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Us TipsDocumento12 pagineUs TipsVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- 05-CCFP4.0 - OOP Using JavaDocumento47 pagine05-CCFP4.0 - OOP Using JavaVamsi SomisettyNessuna valutazione finora
- DzireDocumento4 pagineDzireAshish JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 2Documento17 paginePresentation 2Vishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods and ConstructorsDocumento14 pagineMethods and ConstructorsVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon Credit ProblemsDocumento3 pagineCarbon Credit ProblemsVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Vliw ArchitectureDocumento14 pagineVliw ArchitectureVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- AwpDocumento15 pagineAwpVishal IyerNessuna valutazione finora
- CMOS Process StepsDocumento34 pagineCMOS Process Stepsvarunmunjal245Nessuna valutazione finora
- Photo Bay: Previous Process Surface Preparation PR Coating Soft Bake Alignmen T & Exposure Development PEB CleanDocumento53 paginePhoto Bay: Previous Process Surface Preparation PR Coating Soft Bake Alignmen T & Exposure Development PEB CleanMuhammad Muzammil SaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- Microfabrication SOPsDocumento5 pagineMicrofabrication SOPswesene derbeNessuna valutazione finora
- Littelfuse Thyristor Cross ReferenceDocumento30 pagineLittelfuse Thyristor Cross ReferenceSinisa KondicNessuna valutazione finora
- Lithography PresentationDocumento10 pagineLithography PresentationNarendra AchariNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Electronics Lithography and MaterialsDocumento273 pagineOverview of Electronics Lithography and MaterialsIvar KuusikNessuna valutazione finora
- Exposure Light Source: - High-Pressure Mercury Lamp - Excimer Laser - Short Wavelength - High Intensity - StableDocumento47 pagineExposure Light Source: - High-Pressure Mercury Lamp - Excimer Laser - Short Wavelength - High Intensity - StableMuhammad Muzammil SaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- Soft Lithography: Presented By: Summayya ShafiqueDocumento22 pagineSoft Lithography: Presented By: Summayya ShafiqueSummayya ShafiqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Atmel Standard PackagesDocumento31 pagineAtmel Standard PackagesTóth GézaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Lithography - IDocumento22 pagineChapter 5 Lithography - Isatyam singhalNessuna valutazione finora
- 18ME653 - Syllabus - CO - PODocumento4 pagine18ME653 - Syllabus - CO - PORameshkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 16 October 2017Documento21 pagine16 October 2017wulunzhe1208Nessuna valutazione finora
- SMT Package Dimension List (PCB Design)Documento290 pagineSMT Package Dimension List (PCB Design)QuickteckNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 - Fabrication ProcessesDocumento39 pagine4 - Fabrication ProcessesAugustte StravinskaiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus LithographyDocumento1 paginaSyllabus LithographyAbhi KuttusNessuna valutazione finora
- Euv Sources For Lithography PDFDocumento2 pagineEuv Sources For Lithography PDFChrisNessuna valutazione finora
- LIGA EtchingDocumento42 pagineLIGA EtchingTito Winnerson SitanggangNessuna valutazione finora
- CMOS FabricationDocumento38 pagineCMOS FabricationPrajeeth Babu KodruNessuna valutazione finora
- Silex Microsystems Full Corporate Presentation March 2020Documento51 pagineSilex Microsystems Full Corporate Presentation March 2020Chao-Shiun WangNessuna valutazione finora
- TN 423: Vlsi Circuits: Silicon WafersDocumento23 pagineTN 423: Vlsi Circuits: Silicon WafersBernard Mkumbwa Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- B - Fan Driver 35W LV BLDC Ir BP IDocumento2 pagineB - Fan Driver 35W LV BLDC Ir BP Ipradeep rawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductor Packaging and Testing ProcessDocumento36 pagineSemiconductor Packaging and Testing ProcessVinodkumar MhetreNessuna valutazione finora
- Nanolithography - Processing Methods PDFDocumento10 pagineNanolithography - Processing Methods PDFNilesh BhardwajNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To LITHOGRAPHYDocumento7 pagineIntroduction To LITHOGRAPHYAshrav GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- FSM Session PlanDocumento12 pagineFSM Session PlanNava KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- A Brief Introduction To MEMS and NEMSDocumento29 pagineA Brief Introduction To MEMS and NEMS9894786946Nessuna valutazione finora
- CZ Wafer ProcessDocumento20 pagineCZ Wafer ProcessRajkumari MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- LEAPER 48 DeviceListDocumento44 pagineLEAPER 48 DeviceListSomendra SinghNessuna valutazione finora