Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
2-9 Electronic Aids To Navigation
Caricato da
mingo622Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
2-9 Electronic Aids To Navigation
Caricato da
mingo622Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Electronic
Electronic
Aids to
Aids to
Navigation
Navigation
Kolegij: ENGLESKI JEZIK 2 Kolegij: ENGLESKI JEZIK 2
Profesor: Bisera Profesor: Bisera Plan Plan i i
Student: Student: Tin Tin
Priti Priti anac anac
Electronic
Electronic
Aids to
Aids to
Navigation
Navigation
terrestrial radio navigation systems
terrestrial radio navigation systems
satellite navigation systems
satellite navigation systems
radar navigation systems
radar navigation systems
Terrestrial Radio Navigation Systems
Terrestrial Radio Navigation Systems
Position is obtained by receiving
a radio signal from at least 3
different
coastal radiostations
(2 pairs). The signals are time delayed
and signal from each pair of stations when drawn on a chart
represents one hyperbolic line.
The intersections of 2 such lines
reveal the ship's position.
This is why this type of navigation is called
Hyperbolic navigation.
Because of different advantages and disadvantages and availability
these systems were often used in combination with one another or
other types of navigation.
The
best
known
terrestrial
radio navigation
systems:
DECCA
LORAN
OMEGA
Terrestrial
Terrestrial
Radio
Radio
Navigation
Navigation
Systems
Systems
DECCA developed in UK during WW2 for Allied military purposes. Decca
system was one of the few, if not the only, position fixing system available
to many mariners. It's accuracy depended on many factors including
weather, time of the day and propagation conditions.
It had a range of
400NM during the day and up to 250 NM during the night. DECCA stopped
transmitting in 2000.
LORAN -
was developed in America during the WW2.It worked on the
similar principles as DECCA,
using hyperbolic
lines,
except
it had a longer
range-1200 M.
It also suffered from the signal delay and propagation
problems. The latest known variant of this system is LORAN-C which is still
in use but has been in steep decline, with the satellite based Global
Positioning System (GPS) being the primary replacement. USA and Canada
ceased transmitting LORAN-C signals in 2010.
OMEGA-
was the first truly global
radio navigation system.
It enabled ships
and aircraft to determine their position by receiving very low frequency
(VLF) radio signals transmitted by a network of fixed terrestrial radio
beacons.
It was very inaccurate
so it was used for ocean navigation and in
combination with other radio navigation systems. It became operational
around 1971 and was shut down in 1997.
Satellite navigation systems
Satellite navigation systems
TRANSIT
TRANSIT
GPS
GPS
GLONASS
GLONASS
Galileo
Galileo
Compass
Compass
TRANSIT / NAVSAT
TRANSIT / NAVSAT
TRANSIT TRANSIT also known as NAVSAT was the first satellite also known as NAVSAT was the first satellite
navigation system to be used operationally. The system navigation system to be used operationally. The system
was primarily used by the U.S. Navy and later it was made was primarily used by the U.S. Navy and later it was made
available for civilian use as well. available for civilian use as well. It used lower number of It used lower number of
sat satt telites, elites, compared to GPS so the position could be compared to GPS so the position could be
obtained only every hour or more, obtained only every hour or more, depending on latitude. depending on latitude. It It
also had the distinct disadvantage that it generated two also had the distinct disadvantage that it generated two
possible locations for any given measurements very close possible locations for any given measurements very close
to each other, to each other, so it was hard to determine what is the real so it was hard to determine what is the real
position. position. In combination with OMEGA it produced a highly In combination with OMEGA it produced a highly
accurate global navigation system. accurate global navigation system. It ceased navigation It ceased navigation
service in 1996. service in 1996.
GPS
GPS
GPS GPS- - Global Positioning System is a system that Global Positioning System is a system that
provides location and time information in all provides location and time information in all
weather, anywhere on or near the Earth, where there weather, anywhere on or near the Earth, where there
is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS
satellites. It is maintained by the United States satellites. It is maintained by the United States
government and is freely accessible to anyone with a government and is freely accessible to anyone with a
GPS receiver. It is highly accurate and most widely GPS receiver. It is highly accurate and most widely
used satellite navigation system. used satellite navigation system.
GLONASS
GLONASS
GLONASS GLONASS- -currently the only alternative to the GPS. GLONASS is the currently the only alternative to the GPS. GLONASS is the
Russian sate Russian satel llite lite navigation system made available for civilian use in navigation system made available for civilian use in
2007. I t is very slightly less accurate than GPS, but more accur 2007. I t is very slightly less accurate than GPS, but more accurate on ate on
high latitudes. When used in combination with GPS it is faster high latitudes. When used in combination with GPS it is faster, , more more
accurate than each system used alone, because than it has over 5 accurate than each system used alone, because than it has over 50 0
sate satel llites lites available. That is why many new receivers support both GPS available. That is why many new receivers support both GPS
and GLONASS reception. I t is expected that future improvements w and GLONASS reception. I t is expected that future improvements will ill
achieve accuracy up to 0.6 meters or better by 2020. achieve accuracy up to 0.6 meters or better by 2020.
Gallileo Gallileo, , Compass and others Compass and others - - Gallileo Gallileo is future EU positioning is future EU positioning
system that will be completed by 2020. and aims to be more system that will be completed by 2020. and aims to be more
accurate than other sat accurate than other satt telite position systems. elite position systems. Compass is the Compass is the
future Chinese sat future Chinese satt telite position system. elite position system.
Radar
Radar
navigation
navigation
systems
systems
ARPA ARPA Automatic Radar Plotting Aid Automatic Radar Plotting Aid- - is an electronic computer system is an electronic computer system
that uses radar data to plot targets and calculate the tracked that uses radar data to plot targets and calculate the tracked object's object's
course, speed and closest point of approach (CPA), thereby knowi course, speed and closest point of approach (CPA), thereby knowing if ng if
there is a danger of collision with the other ship or landmass. there is a danger of collision with the other ship or landmass.
First ARPA units were standalone and were only an addition to th First ARPA units were standalone and were only an addition to the e
conventional radar unit. conventional radar unit.
Modern ARPA units are fully integrated with radar in one unit, Modern ARPA units are fully integrated with radar in one unit, with the with the
main operational advantage: both the radar and ARPA data are rea main operational advantage: both the radar and ARPA data are readily dily
comparable. comparable.
Today ARPA radars use modern types o Today ARPA radars use modern types of f rasterscan rasterscan displays which displays which
have many advantages such as: steady picture, colour and are day have many advantages such as: steady picture, colour and are daylight light
viewable due to increased brightness. viewable due to increased brightness.
Other
Other
electronic
electronic
navigation
navigation
aids
aids
ECDIS
ECDIS
-
-
electronic chart display
electronic chart display
AIS
AIS
-
-
Automatic identification System
Automatic identification System
-
-
used for identifying
used for identifying
and locating vessels by electronically exchanging data
and locating vessels by electronically exchanging data
with other nearby ships and AIS Base stations. AIS
with other nearby ships and AIS Base stations. AIS
information supplements marine radar, which continues
information supplements marine radar, which continues
to be the primary method of collision avoidance for
to be the primary method of collision avoidance for
water transport.
water transport.
RDF
RDF
-
-
Radio direction finder
Radio direction finder
-
-
still in use on coastal vessels
still in use on coastal vessels
and as a backup for GPS
and as a backup for GPS
Depth finders
Depth finders
Pitometer
Pitometer
log
log
-
-
used to measure a ship's speed relative to
used to measure a ship's speed relative to
the water.
the water.
References
References
1.Boris 1.Boris Pritchard Pritchard, ,Maritime Maritime English English 1, 1, kolska knjiga, Zagreb 1995. kolska knjiga, Zagreb 1995.
2. http://www. 2. http://www.jproc jproc.ca/ .ca/hyperbolic hyperbolic/ /
3. 3.
http:// http://msi msi. .nga nga. .mil mil/ /MSISiteContent MSISiteContent/ /StaticFiles StaticFiles/NAV_PUBS/RNM/310ch5.pdf /NAV_PUBS/RNM/310ch5.pdf
4. 4. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satellite_navigation http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satellite_navigation
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The SatNav Users Guide to Navigation and Mapping Using GPSDa EverandThe SatNav Users Guide to Navigation and Mapping Using GPSValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (2)
- Advanced Electronic Navigation SystemsDocumento19 pagineAdvanced Electronic Navigation SystemsAKANKSHA PANDEYNessuna valutazione finora
- Radar and ARPA Manual: Radar, AIS and Target Tracking for Marine Radar UsersDa EverandRadar and ARPA Manual: Radar, AIS and Target Tracking for Marine Radar UsersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- Notices To Mariners - Week01 - 2013Documento99 pagineNotices To Mariners - Week01 - 2013karaflass100% (3)
- Cumulative List of Notices to MarinersDocumento2 pagineCumulative List of Notices to MarinersResian Garalde Bisco100% (2)
- Radar - Arpa: Pablo, Marco I. Odonio, Ean Penamante, JerzonDocumento16 pagineRadar - Arpa: Pablo, Marco I. Odonio, Ean Penamante, JerzonAdrian Neil Pablo100% (2)
- Library Books AmendedDocumento4 pagineLibrary Books Amendedbittu692Nessuna valutazione finora
- Admiralty e NP FactsheetDocumento4 pagineAdmiralty e NP FactsheetVisveswaran Inbasekaran100% (1)
- Gps SystemDocumento21 pagineGps SystemRaishNessuna valutazione finora
- Boxing The CompassDocumento11 pagineBoxing The Compassjoeven64Nessuna valutazione finora
- How To Keep Your Charts Up-To-Date PDFDocumento56 pagineHow To Keep Your Charts Up-To-Date PDFMario disi100% (2)
- Vts Specific NotesDocumento10 pagineVts Specific NotesSatya Prakash Bhardwaj100% (1)
- Handbook For: Marine Radio CommunicationDocumento33 pagineHandbook For: Marine Radio CommunicationNoor M.S100% (3)
- 2-7 The Marine RadarDocumento11 pagine2-7 The Marine Radarmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- ADMIRALTY List of Radio Signals (ALRS)Documento2 pagineADMIRALTY List of Radio Signals (ALRS)Summer Davz100% (1)
- Bristish Admiralty Publications by United Kingdom Hydrographic OfficeDocumento4 pagineBristish Admiralty Publications by United Kingdom Hydrographic OfficeGS Dmps100% (2)
- Watch Keeping Contents of Bridge Procedures GuideDocumento13 pagineWatch Keeping Contents of Bridge Procedures GuideArnab Poddar100% (3)
- Gmdss Guide: Furuno Electric Co., LTDDocumento8 pagineGmdss Guide: Furuno Electric Co., LTDtibalinajadelene67% (3)
- SIX Objectives of Ships RouteingDocumento48 pagineSIX Objectives of Ships Routeingkalpesh100% (1)
- What Is Integrated Bridge System (IBS) On Ships PDFDocumento9 pagineWhat Is Integrated Bridge System (IBS) On Ships PDFstamatis100% (1)
- Chart Work PPT - 5TH Revision - Aug2021 Batch OnwardsDocumento63 pagineChart Work PPT - 5TH Revision - Aug2021 Batch OnwardsAjal Shajahan100% (2)
- Week 6 - AppraisalDocumento28 pagineWeek 6 - AppraisalVinz Vizen100% (2)
- Marine Radar PDFDocumento60 pagineMarine Radar PDFMarijaŽaperNessuna valutazione finora
- ROR Explained HandbookDocumento56 pagineROR Explained HandbookMelroyd Dsouza100% (1)
- Magnetic CompassDocumento36 pagineMagnetic CompassRajeewa Wickramahewage100% (1)
- SOLAS V Reg 19Documento5 pagineSOLAS V Reg 19ABDUL ALIMNessuna valutazione finora
- NavguideHDwithCorrectedCardinalMarks PDFDocumento184 pagineNavguideHDwithCorrectedCardinalMarks PDFMariana MichimotoNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Passage PlanningDocumento6 pagineWhat Is Passage PlanningKrishan Perera100% (2)
- NMD - Colreg 72Documento6 pagineNMD - Colreg 72NMD.Jr.1618100% (1)
- Research on West Philippine Sea Claims Under UNCLOSDocumento123 pagineResearch on West Philippine Sea Claims Under UNCLOSMarville Cullen EspagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ror FlowchartDocumento3 pagineRor Flowchartsuresh yadav100% (1)
- Ecdis NotesDocumento112 pagineEcdis Notesmhegden100% (2)
- Rule 22 - Visibility of Lights by JNWDocumento5 pagineRule 22 - Visibility of Lights by JNWArun Singh100% (1)
- Voyage Data RecorderDocumento42 pagineVoyage Data RecorderVivek GillNessuna valutazione finora
- Bridge Procedures Guide: Capt. B. K. Mohanty Dock Master Jawaharlal Nehru PortDocumento39 pagineBridge Procedures Guide: Capt. B. K. Mohanty Dock Master Jawaharlal Nehru Portpankaj kumar100% (6)
- GMDSS Guide: Global Maritime Distress and Safety System ExplainedDocumento52 pagineGMDSS Guide: Global Maritime Distress and Safety System Explainedtualpu100% (3)
- Ranging and Phasing ExplainedDocumento8 pagineRanging and Phasing ExplainedPraveen Kumar Rajarajacholan100% (1)
- IAMSARDocumento13 pagineIAMSARatinder1375% (4)
- Charts and PublicationsDocumento34 pagineCharts and PublicationsSamir Alshaar100% (1)
- Radar Presentation 01Documento30 pagineRadar Presentation 01cozdim100% (5)
- Survival Craft VHF 2Documento7 pagineSurvival Craft VHF 2Kunal SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Long-Range Identification and TrackingDocumento45 pagineLong-Range Identification and TrackingVivek GillNessuna valutazione finora
- Gmdss ManualDocumento808 pagineGmdss ManualNautika PSO PantoloanNessuna valutazione finora
- Shipborne Navigation Systems and EquipmentDocumento10 pagineShipborne Navigation Systems and EquipmentAbdel Nasser Al-sheikh YousefNessuna valutazione finora
- d947e43d-106a-42a6-8004-a777a6475728Documento63 pagined947e43d-106a-42a6-8004-a777a6475728Yamandeep Singh100% (1)
- Col Reg 1972Documento87 pagineCol Reg 1972Ran Oronce100% (2)
- LRITDocumento10 pagineLRITatinder13100% (2)
- Course Specs Nav II CHEDDocumento5 pagineCourse Specs Nav II CHEDReymarr HijaraNessuna valutazione finora
- GMDSS Questions: Question? A B C DDocumento9 pagineGMDSS Questions: Question? A B C DAboody AL-ghamdy100% (2)
- RADAR LEARNINGDocumento40 pagineRADAR LEARNING.cheng.100% (1)
- GMDSS GOC - CN - Ver.2019.05.1Documento124 pagineGMDSS GOC - CN - Ver.2019.05.1T Sumner100% (4)
- Admiralty Digital Publications ADP FactsheetDocumento6 pagineAdmiralty Digital Publications ADP FactsheetVisveswaran Inbasekaran100% (1)
- Admiralty List of Radio Signals (Alrs)Documento13 pagineAdmiralty List of Radio Signals (Alrs)Saurabh Madaan50% (10)
- 3.0 Plane Sailing Answers - FullDocumento16 pagine3.0 Plane Sailing Answers - FullUdhya Kumar50% (2)
- Mercator Sailing: Prepared By: Leonil Roderick E. RelonDocumento12 pagineMercator Sailing: Prepared By: Leonil Roderick E. RelonJasper AbrantesNessuna valutazione finora
- Marine Gyro-Compasses and Automatic Pilots: A Handbook for Merchant Navy OfficersDa EverandMarine Gyro-Compasses and Automatic Pilots: A Handbook for Merchant Navy OfficersValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Ship Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesDa EverandShip Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Marine Radio Operator Permit Manual: Pass Your Marine Operator Permit ExamDa EverandMarine Radio Operator Permit Manual: Pass Your Marine Operator Permit ExamNessuna valutazione finora
- Marine Electrical Systems Survey ChecklistDocumento18 pagineMarine Electrical Systems Survey Checklistmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- Marine Electrical Systems Survey ChecklistDocumento18 pagineMarine Electrical Systems Survey Checklistmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic PumpsDocumento62 pagineDynamic PumpsRaunaq AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- UNCLOS Legal FrameworkDocumento15 pagineUNCLOS Legal Frameworkmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- This Presentation Introduces : SAFEMED III Seminar On Marine Accident Investigation Data CollectionDocumento7 pagineThis Presentation Introduces : SAFEMED III Seminar On Marine Accident Investigation Data Collectionmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- MLC General Presentation and PrinciplesDocumento6 pagineMLC General Presentation and Principlesmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- IMO Code For ImplementationDocumento8 pagineIMO Code For Implementationmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ship Propeller Correction Method TestedDocumento12 pagineShip Propeller Correction Method Testedmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- MLC EU Flag State DirectiveDocumento9 pagineMLC EU Flag State Directivemingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Radica Jelic DomicDocumento9 pagine3 Radica Jelic Domicmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 03.legislative FrameworkDocumento22 pagine03.legislative Frameworkmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
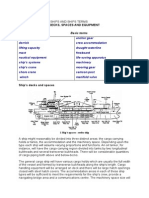
- Ship'S Decks, Spaces and Equipment: Unit 3Documento21 pagineShip'S Decks, Spaces and Equipment: Unit 3mingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2-15 Collision RulesDocumento9 pagine2-15 Collision Rulesmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maritime Security International and EU LegislationDocumento10 pagineMaritime Security International and EU Legislationmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2-12 Buoyage SystemsDocumento11 pagine2-12 Buoyage Systemsmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2-11 Astronomical NavigationDocumento9 pagine2-11 Astronomical Navigationmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2-11 Astronomical NavigationDocumento9 pagine2-11 Astronomical Navigationmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2-13 Safety at SeaDocumento12 pagine2-13 Safety at Seamingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2-10 at AnchorDocumento9 pagine2-10 at Anchormingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2-8 The Navigating BridgeDocumento7 pagine2-8 The Navigating Bridgemingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2-4 Arriving at A PortDocumento13 pagine2-4 Arriving at A Portmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2-7 The Marine RadarDocumento11 pagine2-7 The Marine Radarmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2-2 Under WayDocumento7 pagine2-2 Under Waymingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2-6 Sea Charts (Ecdis)Documento17 pagine2-6 Sea Charts (Ecdis)mingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ship Motions and Heavy Weather PrecautionsDocumento7 pagineShip Motions and Heavy Weather Precautionsmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Whole ErrorsDocumento314 pagine02 Whole Errorsmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2-5 Obtaining A Ship's PositionDocumento7 pagine2-5 Obtaining A Ship's Positionmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2-1 Leaving The DockDocumento8 pagine2-1 Leaving The Dockmingo622Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maritime Security Policy ISPS SOLASDocumento52 pagineMaritime Security Policy ISPS SOLASnamsungship140100% (1)
- Nurses Assigned in Covid-19 Isolation Facilities. in This ConnectionDocumento4 pagineNurses Assigned in Covid-19 Isolation Facilities. in This ConnectionDan HizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal Entry DiscussionDocumento8 pagineJournal Entry DiscussionAyesha Eunice SalvaleonNessuna valutazione finora
- Dislocating The Sign: Toward A Translocal Feminist Politics of TranslationDocumento8 pagineDislocating The Sign: Toward A Translocal Feminist Politics of TranslationArlene RicoldiNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept of Intestate SuccessionDocumento9 pagineConcept of Intestate SuccessionBodhiratan BartheNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF To Sas DatasetsDocumento6 paginePDF To Sas DatasetsSiri KothaNessuna valutazione finora
- Schumann Op15 No5 PsuDocumento1 paginaSchumann Op15 No5 PsuCedric TutosNessuna valutazione finora
- PeripheralDocumento25 paginePeripheralMans FansNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiration NotesDocumento2 pagineRespiration NotesBriana TaylorNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 XS DLX 15 - 11039691Documento22 pagine14 XS DLX 15 - 11039691Ramdek Ramdek100% (1)
- Reviewer in Intermediate Accounting IDocumento9 pagineReviewer in Intermediate Accounting ICzarhiena SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- HSG Anh 9 Thanh Thuy 2 (2018-2019) .Documento8 pagineHSG Anh 9 Thanh Thuy 2 (2018-2019) .Huệ MẫnNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic - Properties - Part 2 - by - AKansha - Karnwal - 1702453072953Documento68 paginePeriodic - Properties - Part 2 - by - AKansha - Karnwal - 1702453072953Saktipratik MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment: Bipolar DisorderDocumento2 pagineAssessment: Bipolar DisorderMirjana StevanovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1: Overview of Implementation of The NSTP (Activities)Documento3 pagineModule 1: Overview of Implementation of The NSTP (Activities)RonnelNessuna valutazione finora
- Creating Early Learning Environments PDFDocumento25 pagineCreating Early Learning Environments PDFkrisnahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lauritzen 1964Documento10 pagineLauritzen 1964Priyanka GandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Neutralization Titrations for Acid-Base AnalysisDocumento21 pagineApplication of Neutralization Titrations for Acid-Base AnalysisAdrian NavarraNessuna valutazione finora
- CFA三级百题 答案Documento163 pagineCFA三级百题 答案vxm9pctmrrNessuna valutazione finora
- EDU101 Solution FileDocumento2 pagineEDU101 Solution FileTahaNessuna valutazione finora
- First State of The Nation Address of ArroyoDocumento9 pagineFirst State of The Nation Address of ArroyoJennifer Sisperez Buraga-Waña LptNessuna valutazione finora
- Var, CaR, CAR, Basel 1 and 2Documento7 pagineVar, CaR, CAR, Basel 1 and 2ChartSniperNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcquillin Murphy ResumeDocumento1 paginaMcquillin Murphy Resumeapi-253430225Nessuna valutazione finora
- GST Project ReportDocumento29 pagineGST Project ReportHENA KHANNessuna valutazione finora
- PersonalDevelopment Q1 Module 2Documento7 paginePersonalDevelopment Q1 Module 2Stephanie DilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Plusnet Cancellation FormDocumento2 paginePlusnet Cancellation FormJoJo GunnellNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study 1Documento2 pagineCase Study 1Diana Therese CuadraNessuna valutazione finora
- Classic Failure FORD EdselDocumento4 pagineClassic Failure FORD EdselIliyas Ahmad KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Annex-4-JDVP Certificate of Learners MasteryDocumento1 paginaAnnex-4-JDVP Certificate of Learners MasteryZINA ARRDEE ALCANTARANessuna valutazione finora
- C++ Project On Library Management by KCDocumento53 pagineC++ Project On Library Management by KCkeval71% (114)
- Residential Water Piping Installation GuideDocumento28 pagineResidential Water Piping Installation GuideMunir RasheedNessuna valutazione finora