Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Assignment of Research Methodology
Caricato da
Mohd MohsinDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Assignment of Research Methodology
Caricato da
Mohd MohsinCopyright:
Formati disponibili
ASSIGNMENT OF RESEARCH
METHODOLOGY
A PROJECT
in the subject of Research Methodology
SUBMITTED TO
UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI
FOR SEMESTER -III OF
MASTER OF COMMERCE
BY.
KHAN MOHD.MOHSIN
Roll No.(10)
Specialization: Business Management
UNDER THE GUIDANCE OF
Dr Vivek Deolankar
YEAR - 2014-15
DECLARATION BY THE STUDENT
I, Shri Khan Mohd. Mohsin, student of M. Com. Part-II Roll Number (10), at the
Department of Commerce, University of Mumbai do hereby declare that the project
titled, Assignement of Research Methodology submitted by me in the subject of
Research Methodology for Semester III during the academic year 2014-15, is based
on actual work carried out by me under the guidance and supervision of Dr Vivek
Deolankar
I further state that this work is original and not submitted anywhere else for any
other examination.
Date 29
Th
september 2014
Mumbai
Signature of Student
EVALUATION CERTIFICATE
This is to certify that the undersigned have assessed and evaluated the project on
Assignment of Research Methodology in the subject of Research Methodology
submitted by Kum/Smt/Shri Khan Mohd. Mohsin , student of M. Com. Part-II at the
Department of Commerce, University of Mumbai for Semester III during the
academic year 2014-15.
This project is original to the best of our knowledge and has been accepted for
Internal Assessment.
Internal Examiner External Examiner Director
Dr. Vivek Deolankar
University of Mumbai
Department of Commerce
Internal Assessment: Subject: Economics of Global Trade &
Finance
Name of Student Class Branch Roll
Number
First Name : MOHD MOHSIN
Fathers : MOHD MOIN
Surname : KHAN
M.COM
PART -II
Business
Managem
ent
10
Topic for the Project: Assignment of Research Methodology
Marks Awarded Signature
DOCUMENTATION
Internal Examiner
(Out of 10 Marks)
External Examiner
(Out of 10 Marks)
Presentation
(Out of 10 Marks)
Viva and Interaction
(Out of 10 Marks)
Total Marks
(Out of 40 Marks)
Contents
Q. N o. Particular Page
No.
1 What is research ?Explain in details characteristic of
research.
1-6
a) Need of research in business and social sciences.
Objectives of research.
7-15
2 What are the different types of research ? 16-20
a) Enumerate issue and problems in research. 21-23
3 As a customer, you wanted to buy a car in small
segment particularly without gear or automatic car.
How you will select ? What factors and which
company you will consider while doing a research
for automobile industry.
24-
a) How will you proceed for collecting the info/data
about the car. As a customer in all me
respects/specialty of car.
Question for the Assignment of Research Methodology
1. What is research ?Explain in details characteristic of research.
Need of research in business and social sciences.
Objectives of research.
2. What are the different types of research ? Enumerate issue and
problems in research.
3. As a customer, you wanted to buy a car in small segment
particularly without gear or automatic car. How you will select ?
What factors and which company you will consider while doing a
research for automobile industry.
How will you proceed for collecting the info/data about the car. As a
customer in all me respects/specialty of car.
1
CHAPTER 1
Question 1. What is research ?Explain in details characteristic of research.
a) Need of research in business and social sciences.
b) Objectives of research.
Answer 1.
MEANING OF RESEARCH
Research is a systematic investigation to search for new facts in any branch of
knowledge. Research helps to arrive at new conclusions. It enables to certain
problems.
Research is often referred to as scientific inquiry into a specific problem or
situation. This is because; the search for facts needs to be undertaken systematically
and not arbitrarily. The systematically approach to research enables the research to
search for facts in a rational manner and to arrive at logical conclusions, whereas,
the arbitrary approach attempts to find solutions to problems based on ones belief
and imagination.
Research comprises "creative work undertaken on a systematic basis in order to
increase the stock of knowledge, including knowledge of man, culture and society,
and the use of this stock of knowledge to devise new applications." It is used to
establish or confirm facts, reaffirm the results of previous work, solve new or
existing problems, support theorems, or develop new theories. A research project
may also be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of
instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior
projects, or the project as a whole.
The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are
2
documentation, discovery, interpretation, or the research and development (R&D) of
methods and systems for the advancement of humanknowledge. Approaches to
research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and
between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific,
humanities, artistic, economic, social, business, marketing, practitioner research, etc.
3
DEFINITIONS OF RESEARCH
According to the William C. Emory in the book Business Research Methods
defines Research is any organised inquiry designed and carried out to provide
information for solving a problem.
The Websters Dictionary states research is a careful critical inquiry or
examination in seeking facts or principles; diligent investigation in order to
ascertain something.
According to the V.Clover and H. Balsley define Research is the process of
systematically obtaining accurate answers to significant and pertinent questions
by the use of scientific method for gathering and interpreting information.
According to the James Black and Dean Champion state scientific research
consists of obtaining information through empirical observation that can be
used for the systematic development of logically related propositions attempting
to establish causal relations among variables.
According to a Pauline V. Young defines social research is a scientific
undertaking which, by means of logical and systematic techniques aims to:
Discover new facts or verify and test old facts,
Analyses their sequences, interrelationships and causal explanations,
Develop new scientific tools, concepts and theories, which would facilitate
reliable and valid study of human behaviour.
4
NATURE AND CHARACTERISTICS OF RESEARCH
a) Scientific Method:
Research uses scientific method to find facts or to provide solutions to specific
problems. The research needs to follow a systematic procedure to conduct
research. There is a set of procedures that have been tested over a period of time
and are thus suitable to use in research. This means each step in the research
procedure must follow the other.
Scientific research in any field of knowledge cannot be conducted in a
haphazard manner. Scientific research cannot be merely based on ones beliefs
and imagination. To get the best possible research results, the researcher needs
to adopt the scientific method of inquiry or investigation.
b) Objective and Logical:
The scientific research is objective and logical in nature. Research is based on
valid procedures and principles.There is a need to collect relevant, accurate and
objective data to investigate into the research problem. Researchers need to
make every possible effort to avoid bias in data collection. After collection of
objectives data, the researchers needs systematically process the data, analyse
and interpret it, and arrive at logical conclusions. Wherever required , the
researchers needs to systematically verify the findings and conclusions.
c) Applied and Basic Research:
5
The research can be broadly classified into two broad groups:
Applied Research
Basic Research
Applied Research is designed to solve practical problems of the modern world,
rather than to acquire knowledge for knowledges sake. The goal of applied
research is to improve the human condition. It is generally used to solve a
particular problem. For instance, a social research can be conducted to study the
problem of unemployment in rural areas, and based on the research findings;
appropriate measures can be taken by Government authorities to reduce the
problems of unemployment.
Basic or fundamental research is driven by a scientists curiosity or interest in
a scientific question. The main goal of basic research is to expand mans
knowledge. There is no obvious commercial value to the discoveries that result
from basic research. For instance, basic research can be undertaken to study the
origin of the universe. Basic research lays down the foundation for the applied
science that follows.
d) Empirical Nature of Research:
Research can be based on direct experience or observation by the research.
Empirical research is undertaken to study certain situations or events based on
experiments, observation and surveys. In empirical research, the researchers
develops a hypothesis and then collects data to prove it or disprove it.
e) Generalisation:
Research findings can be applied to larger population. A researcher can conduct
a research on a respondents that represent the universe. The sample of
respondents that represent the universe. The sample selection must be done
systematically so that it properly represents the whole population or the
universe. The research findings based on sample population can then be
generalized and applied to the whole universe. Therefore, generalization takes
place when research findings based on sample response are applied to whole
population.
6
f) Controlled nature of basic Research:
In real life experience there are many factors that affect an outcome. A single
event is often the result of several factors. When similar event is tested in
research, due to the boarder nature of factors, some factors are taken as
controlled factors while others are tested for possible effect. In pure sciences it
is easy to control certain factors because lab experiments are conducted.
However, it is difficult to perform controlled laboratory experiments in the case
of social science research, although to a limited extent laboratory experiments
are possible in social sciences as well.
g) Development of principles and theories:
A systematic research helps to develop new principles and theories. Such
principles and theories can be useful to several organisations to manage and
deal with people and things in a better way. The general laws or theories
developed through research may enable us to make reliable predictions of
events, which have not yet occurred.
h) Multipurpose Activity:
Research is multipurpose activity. It helps to discover new facts or verify old
facts. It helps not only to predict future events, it establishes causal relationships
between variables. It also helps to develop new scientific tools, concepts and
theories, which would facilitate reliable and valid study of human behaviour and
other aspects.
i) Manipulation of concepts:
The research tries to manipulate things, or concepts. The manipulation or
purposeful control things, or concepts is done with define purpose so as to
arrive at statements of generality. D. Slesinger and M. Stephenson in The
encyclopedia of social sciences define research as the manipulation of the
things, concepts or symbols for the purpose of generalizing to extend, correct or
verify knowledge, whether that knowledge aids in construction of theory or in
the practice of an art.
For instance, a researcher may manipulate the environment in a workplace such
7
as lighting, or layout or seating arrangement to find out its impact on the
productivity of the employees.
j) Quantitative and Qualitative Research:
Research undertaken to measures quantity or amount is called as quantitative
research. For instance, research undertaken to find out the number of
unemployed graduates or the number of unemployed in general. On the other
hand, research, which is undertaken to find out the reasons as to why employees
remain absent from work, or why people behave in certain manner. The
motivational research is an important type of qualitative research. Qualitative
research is especially important in the behavioural sciences where the main aim
is to find out the underlying motives of human behaviour.
k) Research a process:
Research is a systematic process. It involves a number of steps. The main steps
include:
Formulating the research problem or situation.
Development of a hypothesis.
Preparing the research design.
Determining sample design (in case of social research )
Collecting of data.
Analysis of data.
Testing of hypothesis.
Generalization and interpretation.
Preparation of report or thesis.
Follow-up of report.
8
NEED OF RESEARCH IN BUSINESS
Business organisations can gain significantly with the help of research. The research
and development to develop new products, improve the design and quality of
existing ones, and to reduce costs. The marketing research helps to solve marketing
9
problems relating to price, promotion, physical distribution, packaging, positioning,
and so on.
The need and importance of research in business is stated as follows:
I. Product Development:-
Through marketing research, a business firm can identify the customer
requirements, and therefore, it is possible to design new models or to modify
existing products to satisfy the customers.
For instance, through marketing research, a car manufacturing company may
find out that the customers look for features, after-sale-sale service, re-sale
value, right price, fuel efficiency, and so on. Accordingly, the product will be
designed and marketed. Also, with the help of research and development, the
car company would make every possible effort to develop the car with the best
possible features at the right prices depending upon the target customers.
II. Reduction in costs:-
Research in business helps a firm to reduce costs. The research may indicate the
areas where high costs are involved. It may be possible for the firm to cut down
the costs in certain areas. Therefore, cost-reduction will improve the overall
efficiency of the organization will be in a position to achieve higher returns at a
lower cost.
III. Marketing Mix decisions:-
Marketing research enables a firm to arrive at sound marketing-mix decision
with respect to product, price, promotion, and physical distribution.
a) Product decisions: As mentioned earlier, marketing research enables a firm
to design the right product to satisfy customer requirements.
b) Pricing decisions: Marketing research enables a firm to analyse
competitors pricing customers price sensitiveness,etc., and accordingly,
the firm can fix the right prices. For instance, if customers for a particular
product are not price sensitive, the firm may charge a higher price,
10
especially when it enjoys a good image in the market.
c) Promotion-mix Decisions: Marketing research may enable a firm to adopt
effective promotion-mix (publicity, advertising, sales promotion, etc). If
promotion-mix research is not conducted, the firm may give more emphasis
on certain elements of promotion-mix, thereby, ignoring the other elements.
d) Place Decisions: Marketing research may also enable the firm to take
appropriate place decisions, with reference to area of distribution, channel
selection, incentives to channel intermediaries, etc. For instance, the firm
may increase marketing efforts in those areas where it gets low sales, or if
the existing channels are not effective, it may select alternative channels,
etc.
IV. Customer Relationships:-
Marketing research may help the firm to develop good relations with its
customers, especially, the priority customers. Research can help the firm to
collect valuable inputs about the priority customers. Based on the inputs, the
firm can adopt various customer relationship techniques such as package of
loyalty incentives for customer suggestions, etc.
V. Dealer Relationship:-
Nowadays, dealer relationships are vital for the survival and success of a
business organization. Marketing research enables a business firm can get
feedback from the dealers regarding their expectations. Accordingly, the firm
may take appropriate decisions relating to dealers compensation and incentives
so as to maintain good relationship.
VI. Corporate Images:-
Nowadays, firms need to build, maintain, and enhance corporate image in the
minds of stakeholders- customers, dealers employees, and others. For instance,
consumer research may enables the firms to obtain feedback on customer
requirements and expectations, and accordingly the company would make the
right efforts to satisfy customer and develop good image in the minds of
11
customers.
VII. Competitive Advantage:-
Through research, a company can take proactive decisions, such as introduction
of new models, introduce price changes, undertake innovative promotional
schemes, as on. The proactive decisions can confer competitive advantage to the
firm. Based on competitors research, the firm can improve its market offering
vis-a vis that of the competitors, and thereby, enhance its competitive
advantage.
VIII. Human Resources Plans and Policies:-
Research may be undertaken to frame effective HR plans and policies in respect
of :
* Recruitment and selection
* Training to employees
* Performing Appraisal
* Compensation Plans, Etc.
IX. Financial Management:-
Research may be undertaken for efficient management of finance, Financial
management covers two broad areas :
* Sources of Funds
*Application of Funds
Proper research may enable a company to determine the best sources of funds,
and to ensure proper application of funds for working capital and fixed capital.
X. Market Expansion:-
With the help of marketing research inputs, the company can identify the
markets that have good potential. Accordingly, the marketers can enter in new
markets can be undertaken with the help of appropriate marketing activities,
such as promotional activities, such as promotional activities activities -
Publicity, advertising, salesmanship, sales-promotion, etc.
12
NEED OF RESEARCH IN SOCIAL SCIENCES
Social sciences refer to business, commerce, demography, psychology, sociology,
etc. Research in social sciences deals with the peoples behaviour in their different
roles, such as consumers, consultants, learners, leaders, teachers, trainers, employees,
executives, produce, parents, artists, advisiors, etc.
Nowadays, there is a growing need and importance of research in social sciences.
The research in social sciences provides workable solutions to economics and social
problems. The following points bring out the significance of research in social
sciences.
i. Modifies Social Behaviour:-
Social research studies social behaviour. Almost all our social problems could
be attributed to certain social behaviour of the members of the society. Social
research collects relevant data on social behaviour, analyses it and
recommendations are listed. Based on the recommendations of social
researchers, steps can be taken by the concerned authorities to modify the
societal behaviour.
ii. Development of Methodology:-
Development of methodology to deal with social issues is one of the
contributions of social research. For instance, organisations face the problem of
executive stress, lack of concern for ethics, poor leadership styles, employee
absenteeism and turnover, etc. To overcome such problems, certain
methodology needs to be developed. Social research enables the organisations
to develop appropriate methodology to study, analyse, and to take suitable
action to overcome the problems.
With reference to the above context, the methodology would involve the
13
following steps:
a. Identifications of the problem
b. Preparation of research design
c. Designing a questionnaire
d. Collecting of data
e. Processing of data
f. Analysis and interpretation of data
g. Recommendation
h. Reporting to higher authorities for suitable action.
iii. Social Development:-
Social research contributes to societal development. Social development can be
measured in terms of literacy, life expectancy, and other social development
indicators. Research can be undertaken to improve social development
standards of the society. For instance, social research can be undertaken to
improve social research can be conducted to improve literacy in a particular
state, the researchers may study the measures adopted by highly literate states,
and accordingly make recommendations to use such measures so as to improve
the literacy rate in low literacy states.
For instance the life expectancy in the Mumbai city is about 57 years according
to one study conducted in 2009.Experts say the reasons for Mumbai faring
poorly on the life expectancy parameter is because around 60% of the citys
population lives in slums in unhygienic conditions. Government and the local
authorities need to take suitable measures to improve hygenic standards in
slums, reduction in pollution levels, and so on.
iv. Social Welfare:-
Government organisations can be undertake social research to enhance social
welfare of the society. Research can help to design suitable package of measures
to reduce income inequalities, to reduce poverty and unemployment, to
overcome the problems of social evils such as drug addiction, abuse of alcohol,
gambling, and so on.
14
For instance, to reduce inequalities of income, Govt. Adopts progressive
taxation, unemployment allowance, pension to poor senior citizens and
handicapped persons, and so on.
v. Formulation of New Theories:-
Social research helps to formulate new theories. The existing theories can be
reevaluated and modified with help of social research. For instance, social
research has enable to develop several theories enables business and non
business organisations to design suitable packages for uplifting the social
behaviour of their members.
vi. Social Planning and control:-
Social research is a tool for social planing and control. Any constructive action
needs to be planned for effective implementation so as to achieve the desired
outcome. Also, the research may indicate suitable controls measures to correct
deviations as and when the deviations occur.
vii. Economic Planning:-
Social science research can be of immense use in economic planning in a given
society. Economic planning requires basic data on the various aspects of our
society and economy, resources endowment and the needs, hopes and problems
of the people, etc. Economic planning is undertaken to achieve certain
objectives such as:
* To bring about regional development.
* To make optimum use of available resources.
* To bring out self-reliance.
* To generate employment,etc.
viii. Prediction of Events in Society:-
Research can be undertaken to predict future events in the society and their
impact.
For instance, research may be undertaken to find out the incidence of poverty
and its impact on the society. The findings of such research would not only
15
indicate the causes of poverty and its current and possible future impact on the
society and on the nation. Such research may make the concerned authorities to
take appropriate measures to reduce the incidences of poverty, thereby, reducing
the negative consequences for the society.
OBJECTIVES OF RESEARCH
Researchers undertake research with definite objectives. Some of the important
purposes or objectives of research are briefly stated as follows:
1. To find solutions to problems:
Research can be undertaken to find solution to solve specific problems. For
instances, an organisation may initiate research to find solution to the declining
sales of their products in the market. An educational institutions can undertake
research to find out the causes of low attendance or poor results.
A government organisations may undertake research to solve the problem of
water scarcity in a particular area or district or to ascertain the impact of slums
on the quality of life in a particular city, and such other research activities. The
researches enables to find appropriate solutions to specific problems, which in
turn helps to improve the quality of performance in various organisations or
institutions.
2. To verify and test existing laws or theories:
Research may be undertaken to verify and test existing laws or theories. Such
verification and testing of existing theories helps to improve the knowledge and
ability to handle situations and events. This is true when the existing theories
16
may not be sufficient or relevant to handle certain situations and events, and
therefore, though research, improvements or modifications can be made in the
existing laws or theories.
3. To obtain information:
Research is undertaken to obtain information, which may not be easily obtained
during the ordinary course of functioning of an institution or an organisation.
For instance, marketing research may be undertaken to understand the changes
in consumer behaviour. A firm may undertake product research to bring about
improvement or modification in the existing product on the basis of feedback
obtained from consumers, dealers and others.
4. To extend knowledge:
Researchers undertaken research to extend the existing knowledge in physical
sciences (such as physics, chemistry, mathematics, etc) as well as in social
sciences (like sociology, management, psychology, etc) The knowledge can be
enhanced by undertaking research in general and by fundamental research in
particular.
5. To establish generalizations and general laws:
Research can be undertaken to establish generalizations and general laws in a
particular society. In other words, statements of generality can be stated through
research. The AIDA (attention, interest,desire,and action) model, the law odf
demand and supply, the law of gravitation, etc. Have been developed through
observation, experimentation, and other methods of research.
6. To predict events:
Research may be undertaken to predict future course of events. For instance,
research may be undertaken to find out the impact of growing unemployment of
educated youth on the social life of the social life of the social life of the society
in future. The findings of such research would not only indicate the possible
impact, but also would make the concerned authorities to take appropriate
measures to reduce unemployment, to reduce the growth of population, and to
17
overcome the negative consequences, as and when they take place.
7. To analyses inter-relationships:
Research may be undertaken to analyse inter-relationships between variables, so
as to derive causal explanations, which in turn would enable to have a better
understanding of our society and the universe in which we live. Researchers
often develop hypotheses and test them to analyse the causal relationship
between variables.
For Example, a researcher may study causal relationship between advertising
and sales, i.e. to find out whether or not advertising causes (results) higher sales.
8. To develop new tools and concepts:
Research helps to develop new tools and concepts for a better study of an
unknown phenomenon. For this purpose, exploratory research is undertaken to
achieve new insights into such phenomenon.
9. To develop new principles and theories:
A systematic research helps to develop new principles and theories. Such
principles and theories can be useful to several organisations to manage and
deal with people and things in a better way. The general laws or theories
developed through research may enable us to make reliable predictions of
events, which have not yet occurred.
10. To develop innovative ideas:
Research may be undertaken to generate innovative ideas for the welfare of
mankind. For instance, research may enables an organisation to develop
innovative ideas in respect of :
* New and improved products.
* Improved organisation structure.
* Better technology.
* New sources of raw materials, etc.
18
Question 2 What are the different types of research ? Enumerate issue and
problems in research.
The research activities can be classified into different categories. Some of the main
types of research are follows:
I. Basic Research:
19
Basic research is also called as pure of fundamental research. It is undertaken to
develop a theory or a body of knowledge. The main goal of basic research is to
expand mans knowledge. In basic research, there is no commercial angle. For
instance, basic research lays down the foundation for the applied science that
follows.
In basic research, there is no commercial angle. There is no obvious commercial
value to the discoveries that result basic research. In almost all countries, pure
research is mainly carried out by universities and institutes financed by the
government.
Basic research advances fundamental knowledge about the world it focuses on
refuting or supporting theories that explain observed phenomena. Pure research
is the source of most new scientific ideas and ways of thinking about the world.
It can be exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory; however, explanatory research
is the most common.
Basic research generates new ideas, principles, and theories, which may not be
immediately utilized. However, the new theories or ideas form the basis
progress and development in different fields. For instance, todays computers
does not exists without research in pure mathematics conducted over a century
ago, for which there was no known practical application at the time. Basic
research rarely helps practitioners directly with their everyday concerns;
nevertheless, it stimulates new ways of thinking that have the potential to
revolutionize and dramatically improve how practitioners deal with the future.
II. Applied Research:
Applied Research is a scientific study design to solve the practical problems,
rather than merely acquiring knowledge. Applied research is used to find
everyday problems and develop innovative technologies.
Psychologists working in human factors or organisations undertake applied
research. The goal of applied research is to improve human condition. It
generally used to handle a particular situation or to solve a particular problems.
For instance, a social research scholar may undertake research to find out job
20
satisfaction of college teachers affiliated to University of Mumbai. The research
findings can be applied by colleges or the University to improve the level of job
satisfaction of the teachers. Also, a research can be undertaken to study the job
satisfaction of nurses in Govt. Hospitals vis-a-vis private hospitals in the city of
Mumbai. The research findings can be used by Govt. Hospitals and private
hospitals to improve the job satisfaction levels of the nurses.
The applied research can be undertaken by business organisations as well. For
instance, a business organisation may undertake applied research to find out the
causes of poor sales of a particular brand in the market. The research findings
can be used to design necessary measures to overcome the problem of poor
sales.
III. Descriptive Research:
Descriptive research or statistical research provides data about the population or
universe being studied. But it can only describe the who, what, when, where,
and how of a situation. It does not describes what caused a particular situation.
Therefore, descriptive research is used when the objective is to provide a
systematic descriptive that is an factual and accurate as possibles. It provides
the number of times something occurs, or frequency of occurrence. It lends
itself to statistical calculations such as determining a average number of
occurrences or central tendencies. The two most commonly types of descriptive
research methods include observation method and survey method.
One of its major limitations is that it cannot help determine what causes a
specific behaviour, motivation, or occurrence. It cannot establish a cause-effect
relationship between variables.
The descriptive research provides facts of a particular events or situation. It give
description of the sate of affairs, as the exists of a particular event or situation.
The researcher has no control over the situation or event. He can only report
what has happened or what is happening. For instance, a researcher may report
on absenteeism in a particular organisations or several organisations in a
particular industry or even in different industries. Details can be given for a
particular period- in terms of the total number of absentees, the number of days
21
which employees are they remained absent, the department or section in which
there is absenteeism, the class of employees who remain absent most, and such
other details. The research will not indicate why the employees remained
absent.
IV. Analytical Research:
Analytical Research is undertaken to collect facts or data, or the facts or data
may be readily available. The researchers attempts critically evaluate such facts
or data so as to arrive at conclusions. This type of research may establish the
cause and effect relationship. The researchers may provide necessary
recommendations to improve or solve the problem or to handle certain
situations or event.
A research may be conducted to find out the relationship between advertising
and sales. The marketed sold the product in two periods say Period I (January to
March ) and Period II (April to June ). The marketer increases advertising in
Period II. The sales data indicate increase in sales in Period II. The marketer
may like to know through causal or analytical research whether or not
advertising has caused the increase in sales during Period II.
The analytical research helps to understand the causes-effect relationship
between variables. It is also helps to focus on those variables that have greater
positive effect, and to eliminate certain variables that have negative effect on the
situation.
V. Empirical Research:
Empirical research can be define as research based on experimentation or
observation Empirical research is a way of gaining knowledge by means of
direct an indirect observation or experience or experiment. Such research is
conducted to test hypothesis.
The word Empirical means information gained by experience observation, or
experiment. The central theme in scientific methods is that all evidence must be
empirical which means it is based on evidence. In scientific method the word
empirical refers to the use of working hypothesis that can be tested using
22
observation and experiment.
Research design varies by field and by the question being investigated. Many
researchers combine qualitative and quantitative forms of analysis to better
answer questions which cannot be studied in laboratory settings, particularly in
the social sciences.
VI. Qualitative Research:
Qualitative Research is a method of inquiry employed in many disciplines,
especially in the social sciences. Qualitative researchers aim to gather an
in-depth understanding of human behaviour and the reasons that govern such
behavior. The qualitative method investigates the why and how of decision
making, not just what, where, and when. Hence, smaller but focused samples
are often used than large samples.
For instance,a research undertaken to find out the reasons as to why employees
remain absent from work or why people behave in certain manner. The
motivational research is an important type of qualitative research. Qualitative
research is especially important in the behavioural sciences where the main
aims is to find out the underlying motive of human behaviour.
VII. Quantitative Research:
Quantitative research is Explaining phenomena by collecting numerical data
that are analyzed using mathematically based methods. The objective of
quantitative research is to develop and employ mathematical models, theories
and/or hypotheses pertaining to phenomena. The process of measurement is
central to quantitative research because it provides the fundamental connection
between empirical observation and mathematical expression of quantitative
relationships.
The research asks a specific, narrow question and collects a sample of
numerical data from the respondents. The researchers analyzes the data with the
help of statistics. The analyzed data may provide unbiased result that can be
generalized to some larger population. Qualitative research, on the other hand,
asks broad questions and collects data from participants. The researcher looks
23
for the themes and describes the information in themes and patterns exclusive to
that set of participants.
VIII. Other Types of Research:
Research can be classified into various other types such as:
Field research or laboratory research.
One- time research or multi-period research.
Conclusion-oriented research or decision-oriented research.
Historical research or current-situation research.
24
ISSUES AND PROBLEMS IN RESEARCH
There are certain issues that affect the effectiveness of research. The issues are
relating to objectivity of data collection, ethical issues, and so on. The issues create
problems for the researcher to collect correct accurate and reliable data.
The problems in research are as follows:
There are certain limitations or difficulties in the use of scientific method in social
sciences. The main limitations are as follows:
1. Problem of accuracy:
Social science deal with human beings- their behaviour, and social life. The
human behaviour cannot be predicated with accuracy. This is because; human
behaviour is subject to change depending upon the situation,the nature of the
person, and other factors. Therefore, scientific method in social sciences cannot
predict with accuracy the behaviour of human beings.
2. Problem of Uniformity:
Human behaviour is not uniform. Different persons different behaviour
differently under certain situations. In other world all people do not behave in te
same manner in similar situations. Also, one may behave differently in similar
situation at different times. Therefore, scientific method in social sciences has
the problem of generating uniformity in the behaviour of different human beings
under similar situations.
25
3. Problem of Bias:
The scientific method in social sciences is affected by the problem of bias on
the part of the researcher. Some researchers may be biased in scientific method.
They may draw conclusions subjectively depending upon their likes, dislikes,
feeling and emotions. In other worlds there is a problem of objectivity in using
the scientific method in social sciences as compared to physical sciences.
4. Problem of sampling:
In social sciences, the researcher uses a particular sample of respondents to
understand the behaviour of human being in a given situation. However, there
are problems in sampling. In the other words, the selected sample of
respondents may not represent the universe, and as such, even if the study
conducted with the use of scientific method, may not bring objectives results.
5. Problem of respondents:
In social sciences, scientific method may not provide objectives responses from
the respondents. Some respondent may deliberately give wrong responses so as
to please the researcher or to get away with the interviews as quickly as possible.
Even in the case of observation, the respondents may be conscious of being
observed, and therefore, they may behave differently than otherwise.
6. Problem of verification:
The physical phenomena may be known directly through senses, but the social
phenomena are known only symbolically through words representing such as
social phenomena, i.e. Culture, customs, tradition, values, and other subjective
aspects of social life. Therefore, it is difficult to verify the conclusions drawn
from social science research.
7. Problem of Laboratory Experiments:
In most physical sciences, it is possible to undertake controlled laboratory
experiments. However, it is difficult to perform controlled laboratory
experiments in the case of social science research, although to a limited extent
laboratory experiments are possible in social science as well. As social sciences
26
develop, a number of human problems may be hopefully be brought within the
reach of laboratory experiments.
8. Issues relating to Practical Significance:
At times, the research may be undertaken for name sake or just for the purpose
of recognition. For instance, academic research may be undertaken to get M.phil
or PhD Degree. A number of research programmes undertaken by academicians
in India and hardly serves any practical significance.
9. Ethical issues relating to Research Process:
There are various ethical issues in research. Some of the ethical issues in
research are conducted with the research process. The ethical issues relating to
the research process are concerned with research design, sample size, data
collection, data processing, data analysis and interpretation, and so on. However,
the ethical issues relating to research process can be avoided by systematic
planning for research and by following ethical norms in conducting the
research.
10. Issues relating to Plagiarism:
There are also issues relating to Plagiarism. Plagiarism is the copying the
published work of another person and ones own or without proper permission
and acknowledgment.|
Therefore, one should not copy, paraphrase or translate anything from elsewhere
without stating the source of the original text.
27
Question 3 As a customer, you wanted to buy a car in small segment
particularly without gear or automatic car. How you will select ? What factors
and which company you will consider while doing a research for automobile
industry.
How will you proceed for collecting the info/data about the car. As a customer
in all me respects/specialty of car.
Answer 2
28
In research of a buying a automatic car in small segment there are following several
factors which are going to effect this research are as follows:-
First The budget of the customer.
Types of car like in this case small car
There are following list of the car which are set in the small automatic or without
gear car segment.
Maruti Suzuki Celerio
Maruti Suzuki Ritz
Hyundai Grand i10
Mahindra e2o
Honda Brio
These are following car which i am going to serve of these car for research and
compare there features and rate technology, looks and colors etc.
29
First car which described is Maruti Suzuki Pvt ltd car Celerio and Ritz both the car
are automatic transmissions and which are as follows:-
Maruti Suzuki Celerio VXi AT
Price: 4.44 lakhs
Ex-showroom, New Delhi
The specification chart is as below
Length (mm)
3600
Width (mm)
1600
Height (mm)
1560
Seating Capacity (Person)
5
Displacement (cc)
998
Fuel Type
Petrol
Max Power (bhp@rpm)
67 @ 6000
30
Max Torque (Nm@rpm)
90 @ 3500
Mileage (ARAI) (kmpl)
23.1
Alternate Fuel
Not Applicable
Transmission Type
Automatic
No of gears (Gears)
5
Drive-train
FWD
Air Conditioner
Manual
Power Windows
Front & Rear
Seat Upholstery
Fabric
And next car is Maruti Suzuki Ritz Vxi AT BS-IV
Maruti Suzuki Ritz Vxi AT BS-IV
Price: 5.76 lakhs
Ex-showroom, New Delhi
31
The specification chart is as below
Length (mm) 3775
Width (mm) 1680
Height (mm) 1620
Seating Capacity (Person) 5
Displacement (cc) 1197
Fuel Type Petrol
Max Power (bhp@rpm) 85 @ 6000
Max Torque (Nm@rpm) 113 @ 4500
Mileage (ARAI) (kmpl) 17.1
Alternate Fuel Not Applicable
Transmission Type Automatic
No of gears (Gears) 4
Drive-train FWD
Air Conditioner Manual
Power Windows Front & Rear
Seat Upholstery Fabric
Central Locking Remote
The next car is from Hyundia i10 Sportz AT 1.2 Kappa VTVT
32
Hyundai i10 Sportz AT1.2 Kappa VTVT
Price: 5.68 lakhs
Ex-showroom, New Delhi
The specification chart of as below
Length (mm)
3765
Width (mm)
1660
Height (mm)
1520
Seating Capacity (Person)
5
Displacement (cc)
1197
Fuel Type
Petrol
Max Power (bhp@rpm)
79 @ 6000
Max Torque (Nm@rpm)
112 @ 4000
Mileage (ARAI) (kmpl)
16.95
33
Alternate Fuel
Not Applicable
Transmission Type
Automatic
No of gears (Gears)
4
Drive-train
FWD
Air Conditioner
Manual
Power Windows
Front & Rear
Seat Upholstery
Fabric
Central Locking
Remote
The next car is Mahindra e2o T0
Mahindra e2o T0
Price: 5.96 lakhs
34
Ex-showroom, New Delhi
The specification chart of as below
Length (mm)
3280
Width (mm)
1514
Height (mm)
1560
Seating Capacity (Person)
4
Displacement (cc)
Fuel Type
Electric
Max Power (bhp@rpm)
25 @ 3750
Max Torque (Nm@rpm)
53 @ 3400
Mileage (ARAI) (kmpl)
Alternate Fuel
ELECTRIC
Transmission Type
No of gears (Gears)
Drive-train
Air Conditioner
Automatic Climate Control
Power Windows Fonts&Rear
Seat Upholstery Fabric
Central Locking
The Last car is Honda Brio VXAT
35
Honda Brio VXAT
Price: 6 lakhs
Ex-showroom, New Delhi
The specification chart of as below
Length (mm) 3610
Width (mm) 1680
Height (mm) 1500
Seating Capacity (Person) 5
Displacement (cc) 1198
Fuel Type Petrol
Max Power (bhp@rpm) 87 @ 6000
Max Torque (Nm@rpm) 109 @ 4500
Mileage (ARAI) (kmpl) 18.9
36
Alternate Fuel Not Applicable
Transmission Type Automatic
No of gears (Gears) 5
Drivetrain FWD
Air Conditioner Manual
Power Steering
Power Windows Front & Rear
Central Locking Remote
Anti-Lock Braking System
Airbags 2 (Driver & Co-Driver)
Seat Upholstery Fabric
37
There is a comparing chart of all company
Basic of
compare
Maruti
Suzuki
Celerio
Maruti
Suzuki Ritz
Hyundai
i10
Mahindra
e2o
Honda Brio
Length
(mm)
3600 3775 3765 3280 3610
Width
(mm)
1600 1680 1660 1514 1680
Height
(mm)
1560 1620 1520 1560 1500
Seating
Capacity
(Person)
5 5 5 4 5
Displaceme
998 1197 1197 1198
38
nt (cc)
Fuel Type Petrol Petrol Petrol Electric Petrol
Max Power
(bhp@rpm)
67 @ 6000 85 @ 6000 79 @ 6000 25 @ 3750 87 @ 6000
Max Torque
(Nm@rpm)
90 @ 3500 113 @ 4500 112 @ 4000 53 @ 3400
109 @
4500
Mileage
(ARAI)
(kmpl)
23.1 17.1 16.95 18.9
Alternate
Fuel
Not
Applicable
Not
Applicable
Not
Applicable
ELECTRIC
Not
Applicable
Transmissio
n Type
Automatic Automatic Automatic Automatic
No of gears
(Gears)
5 4 4 5
Drivetrain FWD FWD FWD FWD
Air
Conditioner
Manual Manual Manual
Automatic
Climate
Control
Manual
Power
Steering
Front &
Rear
Front &
Rear
Front &
Rear
Fonts&Rear
Power
Windows
Fabric Fabric Fabric
Fabric Front &
Rear
Central
Remote Remote Remote
39
Locking
Airbags
2 (Driver &
Co-Driver)
Seat
Upholstery
Fabric
Price Rate
Ex-showroo
m New
Delhi
4.44
Lakhs
5.76
Lakhs
5.68
Lakhs
5.96
Lakhs
6.lakhs
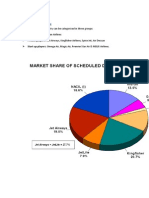
At this Comparison we find Out Two model for our consult these are Maruti Suzuki
Ritz And Honda Brio both car is Look sporty and mileage of the car are enjoyable
And i go for buy a car Maruti Suzuki Ritz and going to purchase.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Solid Waste Management PDFDocumento3 pagineSolid Waste Management PDFGanga Dhar Chaudhary0% (1)
- The Statistical Distribution of The Maxima of A Random Function by Cartwright and Longuet HigginsDocumento22 pagineThe Statistical Distribution of The Maxima of A Random Function by Cartwright and Longuet Higginsadaniliu13Nessuna valutazione finora
- BrochureDocumento12 pagineBrochureAhmedul HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Land Contamination and Case Study of Bajos de Haina, Dominican RepublicDocumento10 pagineLand Contamination and Case Study of Bajos de Haina, Dominican RepublicChang Shen ChangNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Mining Concepts and Techniques by Jiawei HanDocumento4 pagineData Mining Concepts and Techniques by Jiawei HanSandeep H SNessuna valutazione finora
- Fazaia College of Education For Women: Assignment of Software EngineeringDocumento7 pagineFazaia College of Education For Women: Assignment of Software EngineeringFarhat NaseemNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Question Paper Jan 2000 Unit-6Documento10 pagineChem Question Paper Jan 2000 Unit-6Shahariar HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Assignment 1Documento13 pagineDigital Assignment 1Gunasekhar PatchigollaNessuna valutazione finora
- Term Paper Fin441 1Documento31 pagineTerm Paper Fin441 1SAIMA SALAMNessuna valutazione finora
- Argumentative Essay Inb 490Documento13 pagineArgumentative Essay Inb 490FARHAN TANJIM AHMED 1712304630100% (1)
- Assignemnt - No - 7a - Operational AmplifierDocumento5 pagineAssignemnt - No - 7a - Operational AmplifierSudeep NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- North South University: School of Business Marketing Research (Mkt470)Documento41 pagineNorth South University: School of Business Marketing Research (Mkt470)Sadman Shabab RatulNessuna valutazione finora
- Nagavara Ramarao Narayana MurthyDocumento21 pagineNagavara Ramarao Narayana MurthyRobert AyalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Airtel ReportDocumento66 pagineAirtel Reportsadika123100% (1)
- Sales Assignment 2Documento4 pagineSales Assignment 2drarpitabasakNessuna valutazione finora
- Fair & Lovely AdvertisingDocumento2 pagineFair & Lovely Advertisingwubder7002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Crop Physiology Final PDFDocumento113 pagineCrop Physiology Final PDFPushp Lata100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Traffic Analysis TechniquesDocumento48 pagineChapter 8 - Traffic Analysis TechniquesAhmad Daher67% (3)
- Role of Twitter in PoliticsDocumento4 pagineRole of Twitter in PoliticsMariaMehmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdul Monem LimitedDocumento19 pagineAbdul Monem LimitedসামিউলইসলামNessuna valutazione finora
- Cover LetterDocumento2 pagineCover LetterciprianNessuna valutazione finora
- 9-Depletion of Natural ResourcesDocumento6 pagine9-Depletion of Natural Resourcesaps07Nessuna valutazione finora
- BUET MATH 157 Questions of Batch-11Documento3 pagineBUET MATH 157 Questions of Batch-11Shahariar HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Electronic CommerceDocumento35 pagineIntroduction To Electronic CommerceshubhamNessuna valutazione finora
- MIST MSC-CE SyllabusDocumento16 pagineMIST MSC-CE SyllabusSajidNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Language Processing AssignmentDocumento3 pagineNatural Language Processing AssignmentkuymanchoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To VissimDocumento24 pagineIntroduction To VissimaldojudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Personal Reflection - f5Documento24 paginePersonal Reflection - f5andrew_yardy2623Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sales Management Assignment - AJ PDFDocumento8 pagineSales Management Assignment - AJ PDFRamanan PillaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Pollution Air PollutionDocumento3 pagineEnvironmental Pollution Air PollutionCallie Jia LiNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 6Documento10 pagineExperiment 6JohnMarlo DammayNessuna valutazione finora
- Fieldwork ReportDocumento9 pagineFieldwork ReportWong Kiong LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Engineering Reading AssignmentDocumento1 paginaSoftware Engineering Reading AssignmentHawa IddrisuNessuna valutazione finora
- Plagiarism: Giving Credit Where Credit Is Due!Documento29 paginePlagiarism: Giving Credit Where Credit Is Due!Wnz NaiveNessuna valutazione finora
- Land Pollution in The PhilippinesDocumento2 pagineLand Pollution in The PhilippinesMelanie Christine Soriano Pascua50% (2)
- Reason and ImpartialityDocumento10 pagineReason and ImpartialityRr NgayaanNessuna valutazione finora
- CODE 187: CICM in Action A (Justice, Peace, Indigenous and Interreligious Dialogue) Final Learning ResourcesDocumento3 pagineCODE 187: CICM in Action A (Justice, Peace, Indigenous and Interreligious Dialogue) Final Learning ResourcesAngelo ValdezNessuna valutazione finora
- Stats ch12 PDFDocumento28 pagineStats ch12 PDFVivek AnandhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Executive Summary: Term Paper-Licensing JaquarDocumento28 pagineExecutive Summary: Term Paper-Licensing JaquarSabrina AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Antennas Military OKDocumento80 pagineAntennas Military OKgiandomenico camisascaNessuna valutazione finora
- Course 1 Module 03 Extra ProblemsDocumento2 pagineCourse 1 Module 03 Extra Problemshari1zzzNessuna valutazione finora
- Impacts of Indian Drama Serials On BangladeshiDocumento10 pagineImpacts of Indian Drama Serials On BangladeshiMaria Smith100% (1)
- Digital Logic Gates - PagesDocumento11 pagineDigital Logic Gates - PagesJhon Errol L. BorlagdanNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To VISSIMDocumento43 pagineIntroduction To VISSIMDavid SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- EEM - Assignment 2 During QuaramtineDocumento2 pagineEEM - Assignment 2 During Quaramtineshreya mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Alchemist (Bengali) PDFDocumento54 pagineThe Alchemist (Bengali) PDFAniket Ray67% (6)
- Reduce Water PollutionDocumento14 pagineReduce Water Pollutionapi-308622215Nessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Equations:: Cagayan State University-Carig CampusDocumento4 pagineDifferential Equations:: Cagayan State University-Carig CampusJulia MacugayNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 04 - Context Free LanguageDocumento21 pagineChapter 04 - Context Free LanguageprincejiNessuna valutazione finora
- Depletion of Natural ResourcesDocumento6 pagineDepletion of Natural ResourcesHaseeb MoledinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Automobile Emissions: An Overview: Cars and PollutionDocumento4 pagineAutomobile Emissions: An Overview: Cars and PollutionJordi-Joan Castillo GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bus 172Documento5 pagineBus 172api-538674995Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rapid Rural Appraisal: A Quick and Innovative ApproachDocumento10 pagineRapid Rural Appraisal: A Quick and Innovative ApproachMd.Anwar HossainNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rebuttal ParagraphDocumento1 paginaThe Rebuttal ParagraphdoubleeemanNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Proposal: (Synopsis) 1. Area / Specialization of The Research WorkDocumento26 pagineResearch Proposal: (Synopsis) 1. Area / Specialization of The Research WorkSsahil Khan100% (3)
- Winkler Method For Dissolved Oxygen AnalysisDocumento5 pagineWinkler Method For Dissolved Oxygen AnalysisAngeli FacunNessuna valutazione finora
- TT Golden RatioDocumento3 pagineTT Golden RatioRommel Samonte AlonzagayNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Methodology MbaDocumento99 pagineResearch Methodology MbaAjin RkNessuna valutazione finora
- Project On Methods and Techniques of Data Collection: in Partial Fulfillment of Requirement For The SubjectDocumento37 pagineProject On Methods and Techniques of Data Collection: in Partial Fulfillment of Requirement For The SubjectVandanaNessuna valutazione finora
- SLM - B Com, BBA-Research Methodology - 0Documento116 pagineSLM - B Com, BBA-Research Methodology - 0Ramees KpNessuna valutazione finora
- KDD Market Report 2Documento1 paginaKDD Market Report 2Mohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- RJ Collage Oc ProjectDocumento18 pagineRJ Collage Oc ProjectMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Questionnaire of The Assignment For The Research MDocumento50 pagineQuestionnaire of The Assignment For The Research MMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- KDD Market ReportDocumento3 pagineKDD Market ReportMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- 0 BorktxDocumento11 pagine0 BorktxMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Small Car IndustryDocumento33 pagineIndian Small Car IndustryparagmasleNessuna valutazione finora
- Humanresources 2Documento10 pagineHumanresources 2Mohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- IT ScribdDocumento12 pagineIT Scribdbijal_voraNessuna valutazione finora
- Password mk9580939030.: Mohd - Mohsin.khan2 Id of My Skype and Password mk8237368070, and Microsoft Id IsDocumento1 paginaPassword mk9580939030.: Mohd - Mohsin.khan2 Id of My Skype and Password mk8237368070, and Microsoft Id IsMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Scan 4Documento1 paginaScan 4Mohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Aviation IndustryDocumento10 pagineIntroduction To Aviation IndustryMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Industry AnalysisDocumento8 pagineIndustry AnalysisMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Aviation IndustryDocumento25 pagineIndian Aviation IndustryMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Mohd Mohsin KhanDocumento1 paginaMohd Mohsin KhanMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer BehaviourDocumento196 pagineConsumer BehaviourMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bertoli: Consumer Marketing India (PVT) LTD Stock Record Mohd - Mohsin.Khan (Shabi) Classico E-Tra Virgin E-Tra LightDocumento2 pagineBertoli: Consumer Marketing India (PVT) LTD Stock Record Mohd - Mohsin.Khan (Shabi) Classico E-Tra Virgin E-Tra LightMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Markerting India (PVT) LTDDocumento8 pagineConsumer Markerting India (PVT) LTDMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Figaro Purchase RecordDocumento1 paginaFigaro Purchase RecordMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Figaro Purchase RecordDocumento1 paginaFigaro Purchase RecordMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Figaro Daily ReportcDocumento15 pagineFigaro Daily ReportcMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Markerting India (PVT) LTDDocumento8 pagineConsumer Markerting India (PVT) LTDMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Figaro: Consumer Marketing India (PVT) LTD Stock Record Name of S.O. Mohd. Mohsin. KhanDocumento2 pagineFigaro: Consumer Marketing India (PVT) LTD Stock Record Name of S.O. Mohd. Mohsin. KhanMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- TrainDocumento2 pagineTrainMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Rs-1/-Extra On Recharge Below Than Rs - 50Documento1 paginaRs-1/-Extra On Recharge Below Than Rs - 50Mohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Histrocial Development of OBDocumento35 pagineHistrocial Development of OBMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Question For The Assignment For Thhje EntrepreneurshDocumento12 pagineQuestion For The Assignment For Thhje EntrepreneurshMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- A Broad Definition of Research Is Given by MartynDocumento1 paginaA Broad Definition of Research Is Given by MartynMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Ahmed Raza KhanDocumento7 pagineAhmed Raza KhanMohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Rs-1/-Extra On Recharge Below Than Rs - 50Documento1 paginaRs-1/-Extra On Recharge Below Than Rs - 50Mohd MohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- David LaChapelle - Photo Numero Collector Magazine - 03.2009Documento10 pagineDavid LaChapelle - Photo Numero Collector Magazine - 03.2009GabrieladeSennaNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes of Failure of Housing ProjectsDocumento7 pagineCauses of Failure of Housing Projectschill007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Barangay Ambassador: Republic of The Philippines Province of Benguet Municipality of TublayDocumento3 pagineBarangay Ambassador: Republic of The Philippines Province of Benguet Municipality of TublayKathlyn Ablaza100% (1)
- Counseling OutlineDocumento11 pagineCounseling Outlinesjanvie100% (1)
- Chapter-5 Radha S Quest For Love in Mistress'Documento21 pagineChapter-5 Radha S Quest For Love in Mistress'chandra ramNessuna valutazione finora
- Frued - Case StudyDocumento2 pagineFrued - Case StudyEric Thaddeus100% (4)
- HJHJBBBBDocumento6 pagineHJHJBBBBSupri GunNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Exam Math in The Modern WorldDocumento3 pagineMidterm Exam Math in The Modern WorldGregorio Gamboa Maniti II67% (3)
- Rubric Case Study 2 Group 2Documento3 pagineRubric Case Study 2 Group 2Abang BulanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Philosophy of Protective RelayingDocumento14 pagineThe Philosophy of Protective RelayingDev SwainNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Your Road, Man?Documento232 pagineWhat Is Your Road, Man?Oana AndreeaNessuna valutazione finora
- EOM Lecture Notes-1 PDFDocumento16 pagineEOM Lecture Notes-1 PDFChris MarvinNessuna valutazione finora
- Way of The Cobalt Soul - UpdateDocumento2 pagineWay of The Cobalt Soul - Updateckok95469Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rise of The DEO PDFDocumento22 pagineRise of The DEO PDFMarcia Matos0% (1)
- Critical Review of Roland Robertson's BEYOND THE DISCOURSE OF GLOBALIZATIONDocumento3 pagineCritical Review of Roland Robertson's BEYOND THE DISCOURSE OF GLOBALIZATIONAndrei ColteaNessuna valutazione finora
- Annotated Bibliography - Final RevisedDocumento6 pagineAnnotated Bibliography - Final Revisedapi-251911613Nessuna valutazione finora
- Taking The Lead With Autocad MepDocumento59 pagineTaking The Lead With Autocad MepThanh Van LeNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide of Key Ideas For Unit 3 KeyDocumento5 pagineStudy Guide of Key Ideas For Unit 3 Keyapi-236114955Nessuna valutazione finora
- Jose Prager - Name & SignDocumento7 pagineJose Prager - Name & SignFreddie666100% (4)
- Guidebook Machine Learning Basics PDFDocumento16 pagineGuidebook Machine Learning Basics PDFNguyen Duc AnhNessuna valutazione finora
- You, Me and Us Respectful Relationships Education Program: Training ManualDocumento257 pagineYou, Me and Us Respectful Relationships Education Program: Training ManualWomen's Health West100% (1)
- Sma 2100 Discrete MathematicsDocumento4 pagineSma 2100 Discrete MathematicsJoseph NjugunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Seeing Jesus in The PoorDocumento2 pagineSeeing Jesus in The PoorLadiesofCharityUSANessuna valutazione finora
- Book ReviewDocumento7 pagineBook ReviewAkshayMusaleNessuna valutazione finora
- CHE331 Note Set 1Documento6 pagineCHE331 Note Set 1Amauche OgeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Unique Selling Point The Emotional Selling Point and The TrueDocumento20 pagineThe Unique Selling Point The Emotional Selling Point and The Truesam1702Nessuna valutazione finora
- Thirty Alawāt For Easing That Which Has Been Decreed: Inspired To Shaykh Abd Al-Ghanī B.Shaykh Al-Ja FarīDocumento6 pagineThirty Alawāt For Easing That Which Has Been Decreed: Inspired To Shaykh Abd Al-Ghanī B.Shaykh Al-Ja FarīSouvenir Tas Blacu Solo100% (1)
- Meditation Practice Manual v4-3Documento36 pagineMeditation Practice Manual v4-3Karma Arnab100% (1)
- An Useful Methodological Syngery Combining CDA and Corpus Linguistics To Examine Discourses of Refugees and Asylum Seekers in The UK PressDocumento35 pagineAn Useful Methodological Syngery Combining CDA and Corpus Linguistics To Examine Discourses of Refugees and Asylum Seekers in The UK PressAnneleen MalesevicNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study: BhopalDocumento2 pagineCase Study: BhopalShaqi_aprilNessuna valutazione finora