Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
HRSG Operating Man
Caricato da
Nicolae Marin100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
844 visualizzazioni49 pagineOp Manual
Titolo originale
Hrsg Operating Man
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoOp Manual
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
844 visualizzazioni49 pagineHRSG Operating Man
Caricato da
Nicolae MarinOp Manual
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 49
Projects and Customers Information:
Fujairah 2 Project Company
Additional Project Information
Project name: Fujairah II Country UAE
Revision History
Rev. Revision/Date Created by
Checked by
Approved by
Description
B 18/07/2008 Varatharaj N.Gobi MAXY Initial Issue
C 23/10/2008 Varatharaj N.Gobi N.Gobi Burner operating proce-
dure generally revised
D 20/02/2009 Varatharaj N.Gobi N.Gobi Generally Revised
Scale
Project Document Coding
FUJ/00/M/H------A30/OI/006 Rev.D
Responsible dept.
EHG
Created by
Varatharaj
Checked by
N.Gobi
Approved by
AJ R
Format
Word
Document Type
Selection Sheet
Document Status
Electronically Released
Originator Identification number
FUJ/00/M/H------A30/OI/006 Rev.D
Client
abcd
Power Turbo-Systems
Title, Subtitle
OPERATING PROCEDURE
Rev.
D
Date
20-02-2009
Lang.
EN
Sheet
1 of 49
abcd
EHG
ALSTOM Project India Limited
Document Number PB0048-19.02
THIS DOCUMENT IS THE PROPERTY OF ALSTOM PROJ ECTS INDIA LIMITED AND IS ONLY ALLOWED TO BE USED BY
EXPRESS PERMISSION & LICENCE FROM ALSTOM PROJ ECTS INDIA LIMITED
(1)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
DocumentType: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE NO.
INTRODUCTION.......................................................................................................................... 4
COMPLETION OF MAINTENANCE PRIOR TO OPERATION.................................................... 4
INITIAL FILLING.......................................................................................................................... 4
HP FILLING.................................................................................................................................. 5
PRE-OPERATIONAL EQUIPMENT CHECKS............................................................................. 6
START-UP FROM A COLD CONDITION.................................................................................... 6
START-UP FROM A WARM / HOT CONDITION........................................................................ 8
SUPPLEMENTARY FIRING SYSTEM....................................................................................... 10
SECURING TO A WARM LAY-UP CONDITION....................................................................... 11
SECURING TO DRAIN (WITHOUT NITROGEN BLANKETING).............................................. 11
CONTROLS AND INSTRUMENTATION................................................................................... 12
Controls ..................................................................................................................................... 12
Instrumentation ........................................................................................................................ 12
SAFETY VALVES...................................................................................................................... 12
EMERGENCY PROCEDURES .................................................................................................. 14
High Water Level ...................................................................................................................... 14
Low Water Level ....................................................................................................................... 15
Tube Failure .............................................................................................................................. 15
Loss of Feedwater Supply ....................................................................................................... 15
SUPPLEMENTARY FIRING SYSTEM OPERATING PRINCIPLES.22
(2)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
Document Type: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
TABLES:
Table 1 - Valve Alignment: High Pressure Section
Table 2 - HP Drum Level Setpoints
ENGINEERING DRAWINGS:
Piping & Instrumentation Diagram
Legend Sheet..... FUJ/00/M/H A30/FD/001
HP System .............................................................................. FUJ/00/M/H A30/FD/002
Blowdown Tank...................................................................... FUJ/00/M/H A30/FD/003
Gas Side.................................................................................. FUJ/00/M/H A30/FD/004
Burner Head Valve Train and Burner Head ......................... FUJ/00/M/H A30/FD/005
Diesel Oil Pumping set .......................................................... FUJ/00/M/H A30/FD/006
Cooling air skid and Fuel main valve trains ........................ FUJ/00/M/H A30/FD/007
Instrument , service air & Nitrogen system FUJ/00/M/H A30/FD/041
REFERENCE DOCUMENTS:
FUJ/00/M/H ..A30/LV/001 - Valve List
FUJ/00/M/H A30/LI/001 - Instrument List
FUJ/00/M/H A30/OI/006 - Operating Procedures
FUJ/01/B/H..A30/EI/004 Input Data for Functional and Logic Diagrams
FUJ/00/M/H A30/OI/001 Start-Up and Shut down curves
B
B
D
(3)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
DocumentType: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
4
INTRODUCTION
These procedures are intended to serve as a guide during the initial operating
stages of a Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG). They include the proper
operating sequences for the steam generator and auxiliary equipment furnished
by ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Refer to the Piping and Instrumentation Dia-
grams. The sequential procedures do not include detailed reference to equip-
ment not furnished by ALSTOM Projects India Ltd, such as the feed pumps, or
the gas turbine.
Because the steam generator is only one part of the power plant, and all equip-
ment must operate in unison, specific procedures and detailed values cannot be
included in this manual. As operating experience is gained and the controls are
fine-tuned, the characteristics and operating requirements of the unit will become
apparent.
Refer to manufacturer's instructions for further operating details for specific
equipment supplied by ALSTOM Projects India Ltd.
COMPLETION OF
MAINTENANCE PRIOR TO
OPERATION
Check the HRSG to make sure that all maintenance work has been completed,
all tools and debris have been removed, the hand hole plates and manhole cov-
ers have been installed and secured, and all access doors have been installed
and secured.
Check the safety valves to see that the gags have been removed, the lifting lev-
ers have been replaced, and the valves are not fouled or hung up. In addition,
check to ensure that the steam and feed water isolation valves are operational
ready to open according to procedures, drain and vent valves are all operational
ready to be preset according to procedures and as listed in the appropriate valve
alignment list.
Ensure all the components were installed after acid cleaning
The operator should understand the start up and shut down curves (PB0048-
01.04) prior to operating the HRSG.
D
(4)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
Document Type: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
5
INITIAL FILLING
This section describes the recommended procedure for fiIIing an empty HRSG
with water.
If the unit is hot, filling of a pressure level system with cold water should not be
initiated until the drum metal temperature for that pressure level has cooled to
within 56C (100F) of the incoming feedwater temperature. Filling should be
done slowly, with the feedwater 30% control valve at 10% open, to avoid severe
temperature strains. Otherwise, damage may result due to relatively cool water
coming into contact with heated pressure parts.
Also, since deposits of solids in a superheater can cause corrosion or inhibit heat
transfer, introduction of solids by carryover of boiler water from the drum during
filling, hydrostatic testing or chemical cleaning must be avoided.
Proceed as follows:
1. Prepare HP Feed water Pumps and plant feed piping for start-up.
2. Align all HRSG valves as shown under the column labeled START FROM
COLD on Tables 1.
3. Make sure all drain valves are closed.
4. Before starting the HP Feed water Pumps used in initial filling operation, feed
system control valve station should be positioned to allow for filling of the
boiler, including the following (Refer to Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams):
a. Close HP Feedwater Stop Valve (LAB96 AA051).
b. Open the HP Feedwater Bypass Fill Valve (LAB96 AA061) to allow for
filling.
c. Open the HP Feedwater Control Valve (30%) (HAC58 AA024) to allow
for filling
HP FILLING
5. Start the HP Feedwater Pump used for initial filling operations and open
(approximately 1/4 turns) the HP Drum Outlet Vent Valves (HAD52 AA201,
HAD52 AA202), the HP Economizer Vent Valves (HAC53 AA201, HAC53
AA202, HAC53 AA211, HAC53 AA212, HAC53 AA221, HAC53 AA222 HAC53
AA231, HAC53 AA232, HAC53 AA261, HAC53 AA262, HAC54 AA211,
HAC54 AA212, HAC54 AA221, HAC54 AA222, HAC54 AA231, HAC54
AA232, HAC54 AA201, HAC54 AA202, HAC55 AA211, HAC55 AA212,
HAC55 AA221, HAC55 AA222, HAC55 AA231, HAC55 AA232, HAC55
AA201, HAC55 AA202, HAC56 AA211, HAC56 AA212, HAC56 AA221,
HAC56 AA222, HAC56 AA231, HAC56 AA232, HAC56 AA201, HAC56
AA202, HAC57 AA211, HAC57 AA212, HAC57 AA221, HAC57 AA222,
HAC57 AA231, HAC57 AA232, HAC57 AA201, HAC57 AA202,
HAC58 AA201, HAC58 AA202, HAC58 AA211, HAC58 AA212)
and Feed Water Heater Vent valves ( HAC10 AA201, AA202,
AA203, AA204,AA208,AA209,AA210,AA211,AA212,AA213,AA214,AA215).
B
D
(5)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
DocumentType: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
6
6. Fill the HP Economizer and HP Evaporator until the Cold Start-up NWL has
been cleared in the HP Drum (see Table 2 for Drum Levels). DO NOT
OVERFILL THE DRUMS. Close the HP Economizer Vent Valves for each
section when all air has been displaced from that section. Close the HP Drum
Outlet Vent Valves when the HP Drum fill is complete.
7. After the drum fill is complete close HP Feedwater Control Valve (HAC58
AA024). Place all feed system control valve stations including associated
drum level controls in AUTO MODE.
All condensate / feed water pumps can be temporarily off-line while waiting for
pre-operation equipment checks and valve alignments prior to start-up. The
HRSG is now ready to be started using the procedure for START-UP FROM
A COLD CONDITION.
PRE-OPERATIONAL
EQUIPMENT CHECKS
Have all HRSG auxiliary equipment lined up for operation prior to allowing flow of
the gas turbine exhaust to the HRSG.
Prior to initial operation:
1. Make sure that:
a. All instrument valves should be lined up for service.
b. All drum level transmitter reference legs are filled.
c. All sample line valves should be closed.
d. All chemical and nitrogen feed valves should be closed.
e. All drain valves should be closed.
2. Open and close the following valves to ensure that water level gauges are
reading correctly:
a. HP Drum Level Indicator Drains (HAD50 AA243, HAD50 AA244).
b. HP Drum Level Control Unit Drains (HAD50 AA251, HAD50 AA252).
START-UP FROM A COLD
CONDITION
This section describes the recommended procedure for starting the HRSG from a
cold condition with no pressure in the HP boiler section. Proceed as follows:
1. Purge the HRSG in accordance with NFPA 85 dated 2004, Chapter 8.9.2
(Combustion Turbine Exhaust Systems) guidelines.
It is understood that purging is accomplished by using air at ambient tem-
peratures. The ambient air temperatures during a normal purge cycle will not
have any damaging effect on any of the HRSG components.
(6)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
Document Type: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
7
2. Align all HRSG valves as shown under the column labeled START FROM
COLD on Table 1.
NOTE: Some of the following procedures are redundant
to what is shown on Table 1. This is done to emphasize
the importance of performing these procedures.
3. Place the HP Desuperheater Spray Water Control Valve (LAE50 AA005,
LAE50 AA002) in AUTO. Place the HP Desuperheater Spraywater Power
Block Valve (LAE50 AA024, LAE50 AA001) in AUTO.
NOTE: Although desuperheating is not required except
at peak turbine load, it is good practice to have the con-
trol station available whenever the unit is operating.
4. Open and place the following Drain Valves in AUTO:
a. HP Superheater 1/2 Drain Isolation Valve (HAH52 AA202),
b. HP Superheater 3 Drain Isolation Valve (HAH51 AA202),
Allow any condensate in these sections to drain.
5. Prior to start up, reset the water level set points in the feedwater control sys-
tem to ensure that the water levels in the HP Drum is just above the Cold
Start-up NWL (see Table 2 for Drum Levels). Use the HP Evaporator (HAD50
AA209) Intermittent Blow-off Isolation Valves as necessary to reduce water
levels.
6. Close HP Feedwater Stop Valve (LAB96 AA051). Open the HP Feedwater
Stop Fill Valve (LAB96 AA061) and open the HP Feedwater 30% Control
Valve (HAC58 AA024) to allow for filling of the drum.
7. Open the HP Main Steam Outlet Stop Valve (LBA51 AA001, LBA51
AA002
#
)[Manual Valve] in order to warm up the piping downstream of
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd scope.
8. Open the HP Steam Startup Vent Isolation Valve (LBA51 AA211) and HP
steam Startup vent MOV (LBA51 AA212). This vent should be placed in
AUTO.
9. If needed, restart condensate / feedwater pumps and ensure that pumps are
running.
B
B
D
D
(7)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
DocumentType: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
8
10. Allow heated gas turbine exhaust flow to enter the HRSG by starting the gas
turbine (Flame On).
11. While the steam generator is being brought up to pressure, all cold steam
piping should be gradually heated and drained of condensate. The HP Steam
Startup Vent Valve (LBA51 AA211, LBA51 AA212) must stay opened to in-
sure a positive flow of steam which will reduce thermal expansion.
To warm the piping downstream of ALSTOM Projects India Ltds scope, open
a drain or vent downstream of ALSTOM Projects India Ltds scope to allow
the steam from the bypass valve to warm the piping. Ensure that all steam
piping downstream of the boiler piping is drained prior to admitting steam.
12. When a measurable HP steam flow is established (approximately 10% of full
flow), the HP steam section is on line and the HP Main Steam Outlet Stop
Valve (LBA51 AA001, LBA51 AA002
#
)[Manual Valve] may be opened and the
HP Startup Vent Valve (LBA51 AA211, LBA51 AA212) may be closed.
NOTE: During startup or steam startup vent operation
the HP systems steam flow can be obtained from the
HP Feedwater Flow Transmitters (HAC58 CF001 and
HAC58 CF002).
13. The water level set points in the feedwater control system for the HP Drum
will return to the normal operating water level settings automatically when
the respective system steam flow >10%.
Flowrates by Pressure Section (kg/s)
Normal unfired Op.
Setpoints
(Case 6)
Startup Setpoints
Section 100% <10 %
HP 110.66 11.066
14. Open the following continuous blowdown isolation valves:
a. HP Drum Continuous Blowdown Isolation Valve (LCQ61 AA001).
Blow down flow should be controlled with the following valves:
a. HP Drum Continuous Blowdown Metering Valve (LCQ61 AA002).
START-UP FROM A WARM
/ HOT CONDITION
This section describes the recommended procedure for starting the HRSG from a
Warm / Hot condition, which is when the HP Drum Pressure (HAD50 CP003) >
1.72 barg (2.74 bara). Proceed as follows:
B
D
D
(8)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
Document Type: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
9
1. Purge the HRSG in accordance with NFPA 85 dated 2004, Chapter 8.9.2 (Combus-
tion Turbine Exhaust Systems) guidelines.
It is understood that purging is accomplished by using air at ambient tempera-
tures. The ambient air temperatures during a normal purge cycle will not have
any damaging effect on any of the HRSG components.
2. Align all HRSG valves as shown under the column labeled START FROM
WARM on Table 1.
NOTE: Some of the following procedures are redundant
to what is shown on Table 1. This is done to emphasize
the importance of performing these procedures.
3. Place the HP Desuperheater Spray Water Control Valve (LAE50 AA005,
LAE50 AA002) in AUTO. Place the HP Desuperheater Spray water Power
Block Valve (LAE50 AA024, LAE50 AA001) in AUTO.
NOTE: Although desuperheating is not required except
at peak turbine load, it is good practice to have the con-
trol station available whenever the unit is operating.
4. Open and place the following Drain Valves in AUTO:
a. HP Superheater 1/2 Drain Isolation Valve (HAH52 AA202),
b. HP Superheater 3 Drain Isolation Valve (HAH51 AA202),
Allow any condensate in these sections to drain.
5. Prior to start up, reset the water level set points in the feedwater control sys-
tem to ensure that the water levels in the HP Drum is just above the Cold
Start-up NWL (see Table 2). Use the HP Evaporator (HAD50 AA209) Intermit-
tent Blow-off Isolation Valves as necessary to reduce water levels.
6. Open the HP Feedwater Stop Valve (LAB96 AA051).
7. Open the HP Main Steam Outlet Stop Valve (LBA51 AA001, LBA51
AA002
#
)[Manual Valve] in order to warm up the piping downstream of
ALSTOM Projects India Ltds scope.
8. Open the HP Steam Startup Vent Isolation Valve (LBA51 AA211) and the HP
steam Startup vent MOV (LBA51 AA212). This vent should be placed in
AUTO.
9. If needed, restart condensate / feedwater pumps and ensure that pumps are
running.
10. Allow heated gas turbine exhaust flow to enter the HRSG by starting the gas
turbine (Flame On).
B
D
(9)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
DocumentType: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
10
11. While the steam generator is being brought up to pressure, all colsteam
piping should be gradually heated and drained of condensate. The HP Steam
Startup Vent Valves (LBA51 AA211, LBA51 AA212) must stay opened to
insure a positive flow of steam, which will reduce thermal expansion.
To warm the piping downstream of ALSTOM Projects India Ltds scope, open
a drain or vent downstream of ALSTOM Projects India Ltds scope to allow
the steam from the bypass valve to warm the piping. Ensure that all steam
piping downstream of the boiler piping is drained prior to admitting steam.
12. When a measurable HP steam flow is established (approximately 10% of full
flow), the HP steam section is on line and the HP Main Steam Outlet Stop
Valve (LBA51 AA001, LBA51 AA002*)[Manual Valve] may be opened and the
HP Startup Vent Valves (LBA51 AA211, LBA51 AA212) may be closed.
NOTE: During startup or steam startup vent operation
the HP systems steam flow can be obtained from the
HP Feedwater Flow Transmitters (HAC58 CF001,
HAC58 CF002).
13. The water level set points in the feedwater control system for the HP Drum
will return to the normal operating water level settings automatically when
the respective system steam flow >10%.
Flowrates by Pressure Section (kg/s)
Normal Unfired Op.
Setpoints
(Case 6)
Startup Setpoints
Section 100% >10 %
HP 110.66 11.066
14. Open the following continuous blowdown isolation valves:
a. HP Drum Continuous Blowdown Isolation Valve (LCQ61 AA001).
Blowdown flow should be controlled with the following valves:
b. HP Drum Continuous Blowdown Metering Valve (LCQ61 AA002).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIRING
SYSTEM
This section describes the recommended procedure for start up and shut
down of the Supplementary Firing system and its auxiliaries. Please refer An-
nexure(08.0.0.1436.00, Part 8 Operating Principles) to this document for
operating principles of supplementary firing system.
B
D
D
(10)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
Document Type: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
11
SECURING TO A WARM
LAY-UP CONDITION
SECURING TO WARM LAY-UP CONDITION WITHIN 24 HOURS
IMMEDIATELY FOLLOWING THE GAS TURBINE SHUT DOWN.
This section describes the recommended procedure for securing the HRSG to a
warm lay-up condition. Proceed as follows:
1. Prevent the gas turbine exhaust flow to the HRSG by shutting down the Gas
Turbine to the HRSG.
2. Align all HRSG valves as shown under the column labeled SECURE TO
WARM on Table 1. In particular, ensure that the following valves are
closed:
a. HP Feed water Stop Valve (LAB96 AA051) and HP Feedwater
Fill Valve (LAB96 AA061).
b. HP Main Steam Outlet Stop Valve (LBA50 AA001, LBA50
AA002
#
)[Manual Valve].
c. HP Drum Continuous Blowdown Isolation Valve (LCQ61 AA001).
d. HP Feed Water Preheater Valves (LAA96 AA001,
AA002)[Manual Valve].
3. When the HP Drum Pressure (HAD50 CP003) falls below 1.72 barg (2.74
bara), the drum pressure may be allowed to decrease to atmospheric pressure
by opening the HP Steam Startup Vent Valve (LBA51 AA212) or a nitrogen
blanket may be maintained by opening the HP Nitrogen Stop Valve (HAD50
AA702).
SECURING TO DRAIN (WITHOUT
NITROGEN BLANKETING)
This section describes the recommended procedure for securing the HRSG with-
out nitrogen blanketing in order to drain the unit prior to performing maintenance.
Proceed as follows:
1. Prevent any gas turbine exhaust flow to the HRSG by shutting down the gas
turbine.
2. Align all HRSG valves as shown under the column labeled SECURE TO
DRAIN on Tables 1.
a. HP Feedwater Stop Valve (LAB96 AA051).
b. HP Main Steam Outlet Stop Valve (LBA51AA001, LBA51
AA002
#
)[Manual Valve].
c. HP Drum Continuous Blowdown Isolation Valve (LCQ61
AA001).
d. HP Feed Water Preheater Valves (LAA96 AA001,
AA002)[Manual Valve].
(11)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
DocumentType: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
12
3. When the HP Drum Pressure (HAD50 CP003) falls to 1.72 barg (2.73 bara),
open the HP Steam Startup Vent Valve (LBA50 AA212). These main steam
vent valves must be opened before the associated drum pressure falls any
lower to prevent a vacuum from developing that may cause leakage of the
drum man way gaskets.
4. When the HP Drum Pressure (HAD50 CP003) falls to 1.03 barg (2.04 bara),
open the HP Superheater 1/2 and HP Superheater 3 Drain Isolation Valves
(HAH52 AA201, HAH52 AA202, HAH51 AA201, HAH51 AA202). The drum
pressure may be allowed to decrease to atmospheric pressure.
5. The HRSG can be drained when it is completely cooled (when vapor no longer
escapes from the vents).
6. Open the vent valves and drain valves one heat exchanger section at a time to
avoid overloading the drain discharge system downstream of the HRSG.
Open the Blowdown Stop Valves if the blowdown lines are to be drained.
CONTROLS AND
INSTRUMENTATION
Controls
It is beyond the scope of this manual to discuss the design parameters and se-
lection criteria of control systems. Instead, we will review the steam generator
dynamics involved in tuning these systems and note problems we have found on
actual operating units. When we discuss steam generator control, we are actually
referring to the drum level controls; all other controls are supplied by others.
The drum level controls will regulate the rate of feedwater flow to maintain a
proper drum level throughout the operating range of the steam generator.
To get maximum benefit from a three-element system, feedwater flow should be
proportional to steam flow with reset action on drum level. This means that
pounds of feedwater entering should always equal pounds of steam leaving, with
periodic small corrections made to correct deviations from level set points. The
best drum level control is achieved through mass flow balance.
Instrumentation
Even the most sophisticated and well-tuned control systems do not take the
place of the judgment of an alert, motivated and trained operator. The only
means that an operator has to make his judgments is through adequate and cali-
brated instrumentation.
SAFETY VALVES
Safety valves serve to protect pressure vessels from overpressure. On superhea-
ter outlets they serve the additional purpose of protecting the superheater from
overheating in the event of a sudden interruption in steam consumption.
(12)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
Document Type: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
13
The total relieving capacity of the safety valves on a boiler cannot be less than the de-
sign steaming capacity. It is a Code requirement that one or more safety valves on
the steam drum be set at or below the design pressure of the unit. Any economizer
which can be isolated from the boiler must have its own safety valve. The discharge ca-
pacity of any superheater safety valve or valves can be included in the total relieving ca-
pacity of the boiler, provided there is no way to isolate the superheater. Valves are to be
designed to operate without chattering and to obtain full lift at no more than 3% above
their set pressure. Valves are to close within 4% of set pressure, but no less than 2% of
set pressure.
The popping point tolerance shall not exceed:
0.14 barg (2 psig) for pressures up to 4.83 barg (70 psig).
3% for pressures up to 20.68 barg (300 psig).
0.69 barg (10 psig) for pressures up to 68.95 barg (1000 psig).
1% for pressures over 68.95 barg (1000 psig).
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd recommends that all safety valves be lifted to check
popping pressure and blow down prior to annual maintenance outages. During
these outages, valves that leaked or had a tendency to simmer or chatter should
be disassembled and repaired. During valve testing, it is important to maintain
drum level at or below normal water level to prevent water damage to drum valve
seats and to prevent high solids boiler water from being drawn into superheaters.
Any time a valve is disassembled, its seat should be touched up with a lap and
1000 grit-lapping compound. If the seat is in poor shape, use a carborundum disc
first, then progressively finer grits.
The following are safety tips and helpful hints:
1. Never set safety valves by holding set pressure and lowering the popping
pressure setting with a wrench. This is extremely hazardous. Valve setting
changes should be made with the boiler pressure considerably lower than
set point. After the wrench adjustment is made the lifting gear should be
replaced and boiler pressure should be raised to the new popping point.
2. Ring locking pins can vibrate loose when a valve is relieving. The pins
should always be wired to each other except when one pin is removed to
make a ring adjustment.
3. Entrained water will cause excessive blowdown on drum valves. Set drum
valves with the drum water level a few inches below normal water level, if
possible.
4. A rule of thumb: Vent pipes should be 50 mm (2 inches) larger in diameter
than the valve discharge pipe.
5. The discharge pipe should extend no more than 350 mm (14 inches) into
the vent pipe from the bottom of the drip pan.
6. A safety valve seat can be damaged by debris and water, which enters the valve
body through the vent pipe. This debris is blown around when the valve lifts. Cover-
ing the vent pipe with a plastic bag can eliminate the problem.
(13)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
DocumentType: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
14
7. It is occasionally necessary to mount a vent pipe rigidly to the discharge
elbow. This should be done only when there is no alternative. Care should
be taken that the vent pipe is cut off square, not on the bias.
8. Do not exceed five pops on a valve. If more pops are required, allow valve
to cool before proceeding.
9. Do not make adjustments on first pop. Always evaluate the necessary ad-
justment from two pops.
10. When popping a valve, always have the cap and drop lever assembly in
place with a rope affixed. If the valve begins to chatter, it can be manually
popped before the seating surfaces are damaged.
11. Observe the popping pressure on a suitable gauge mounted in the prox-
imity of the valve being tested. A second gauge, preferably a dead weight
gauge, should be used to validate the calibration of the observed gauge.
EMERGENCY
PROCEDURES
High Water Level
Abnormally high water levels should be avoided, as it may lead to carry-over
and even priming.
In the event of a high water level, there will be a high drum level alarm. Pro-
ceed as follows:
1. Isolate the feedwater supply for the appropriate drum using the HP Fe-
edwater Control Valves (HAC58 AA004, HAC58 AA014 and HAC58
AA024) and HP Feedwater Stop Valve (LAB96 AA051) as required.
2. Blowdown the appropriate drum until the water level is at the normal level.
Use the HP Intermittent Blow-off Isolation Valve (HAD50 AA209) as re-
quired. The Intermittent Blow-off Valves may be used when the HRSG is
operating at any pressure in order to reduce the drum water level.
3. Isolate the steam outlet for the appropriate drum using the HP Main
Steam Outlet Stop Valve (LBA51 AA001, LBA50 AA002#)[Manual Valve] as
required. Open Superheater Drain Valves for appropriate drum using HP Su-
perheater Drain Isolation Valves (HAH52 AA202, HAH51 AA202) as appro-
priate.
4. If the HIGH HIGH HIGH alarm has not cleared within 2 minutes, initiate
trip of gas turbine.
5. Investigate the water conditions (alkalinity and solids).
B
(14)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
Document Type: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
15
Low Water Level
If the water level falls out of sight in the water gauge, due to failure of the fe-
edwater supply or neglect of the operator, appropriate action should be taken
at once. The only exception is in the case of momentary fluctuations that
might occur with extraordinary changes in load. Any decision to continue to
operate, even if only for a short time at a reduced rating, would have to be
made by someone in authority who is thoroughly familiar with the circum-
stances that led to the emergency and positively certain that the water level
can be restored immediately without damaging the boiler. In the absence of
such a decision:
1. Isolate the steam outlet for the appropriate drum using the HP Main
Steam Outlet Stop Valve (LBA51 AA001, LBA50 AA002
#
)[Manual Valve]
as required.
2. If the condition has not been stabilized and gas turbine trip has been initi-
ated, allow HRSG to cool so that it may be inspected for damage if re-
quired. After correcting the cause, the unit may be restarted.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to add water until the steam
generator has cooled down sufficiently to where the
drum metal temperatures are within 56C (100F) of the
feedwater temperature; otherwise, damage may result
due to relatively cool water coming in contact with
heated pressure parts.
Tube Failure
1. Immediately secure the gas turbine exhaust flow.
2. Secure unaffected sections of HRSG according to Securing to Warm
Lay-up Condition instructions.
3. Isolate and drain affected sections of HRSG according to Securing to
Drain instructions.
Loss of Feedwater Supply
The loss of feedwater supply is a rare occurrence in a properly maintained
steam plant. However, loss of the feedwater supply can happen and it is to
be treated as an extreme emergency.
A steady persistent drop in the steam drum level indicates problems with the
feed pump, feed pump recirculation control, steam generator feedwater valve
control or a tube leak. By quickly comparing system pressures and flows with
data taken at comparable loads during normal operation, the operators
should be able to identify the problem area.
(15)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
DocumentType: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
16
If feedwater flow is increasing relative to steam flow and the drum water
level is still falling, a tube leak can be assumed. Secure the gas turbine ex-
haust flow and proceed with tube failure emergency procedures (see Emer-
gency Procedures Tube Failure section for details).
For the HP Drum, an alarm will sound when the drum water goes to the low
level. At the low low HP Drum level the gas turbine exhaust flow should be
secured.
If the problem is with the feed pump or controls, restrict steam generator
steam flow to balance the ability of the crippled feedwater system to maintain
drum level.
If it is not possible to stabilize drum levels by reducing load, secure the gas
turbine exhaust flow and bottle up the steam generator, keeping all vents
closed. When the feedwater system is repaired, restart the unit as detailed
under the procedure titled Start-Up From A Warm Condition.
In any case, the first consideration must be the protection of the steam gen-
erator pressure parts from operation with low water.
As is true of any emergency situation with a steam plant, events do not al-
ways follow an orderly pattern. The procedures above may or may not fit the
pattern for every circumstance. The intent is to emphasize what should be
done in order to protect the steam generator and bring the plant back in op-
eration as soon as possible.
(16)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
Document Type: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
17
Table 1 Valve Alignment: High Pressure Section
VALVE TAG
DESIGNATION
VALVE DESCRIPTION
START
FROM
COLD
START
FROM
WARM
NORMAL
OPERATION
SECURE
TO
WARM
SECURE
TO
DRAIN
11LAA96 AA001 HP Feed Water Preheater inlet
Closed Closed Open Closed Closed
11LAA96 AA002 HP Feed Water Preheater Outlet
Closed Closed Open Closed Closed
11LAA96 AA251
11LAA96 AA252
HP Feed Water Preheater inlet
Line Drain Valves
Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAC10 AA201
11HAC10 AA202
11HAC10 AA203
11HAC10 AA204
11HAC10 AA208
11HAC10 AA209
11HAC10 AA210
11HAC10 AA211
11HAC10 AA212
11HAC10 AA213
11HAC10 AA214
11HAC10 AA215
HP Feed Water Preheater Vent
Valves
Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAC10 AA205
11HAC10 AA206
11HAC10 AA207
HP Feed Water Preheater Drain
Valves
Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11LAA96 AA253
11LAA96 AA254
HP Feed Water Preheater Outlet
Line Drain Valves
Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11LAB96AA051 HP Feedwater Stop Valve Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
Open / Auto Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
11LAB96AA061 HP Feedwater Stop BYPASS MOV
Valve
Open Open Open Open Open
11LAB96AA251
11LAB96AA252
11LAB96AA253
11LAB96AA254
HP Feedwater Inlet Drain Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAC53 AA241,
11HAC53 AA242,
11HAC53 AA251
HP Economizer 6 Drain Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
(17)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
DocumentType: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
18
11HAC53 AA201,
11HAC53 AA202,
11HAC53 AA211,
11HAC53 AA212,
11HAC53 AA221,
11HAC53 AA222,
11HAC53 AA231,
11HAC53 AA232,
11HAC53 AA261,
11HAC53 AA262
HP Economizer 6 Vent Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAC54 AA241,
11HAC54 AA242,
11HAC54 AA251
HP Economizer 5 Drain Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAC54 AA211,
11HAC54 AA212,
11HAC54 AA221,
11HAC54 AA222,
11HAC54 AA231,
11HAC54 AA232,
11HAC54 AA201,
11HAC54 AA202
HP Economizer 5 Vent Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAC55 AA241,
11HAC55 AA242,
11HAC55 AA251
HP Economizer 4 Drain Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAC55 AA211,
11HAC55 AA212,
11HAC55 AA221,
11HAC55 AA222,
11HAC55 AA231,
11HAC55 AA232,
11HAC55 AA201,
11HAC55 AA202
HP Economizer 4 Vent Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAC56 AA241,
11HAC56 AA242,
11HAC56 AA251
HP Economizer 3A/3B Drain
Valves
Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAC56 AA211,
11HAC56 AA212,
11HAC56 AA221,
11HAC56 AA222,
11HAC56 AA231,
11HAC56 AA232,
11HAC56 AA201,
11HAC56 AA202
HP Economizer 3A/B Vent Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAC57 AA241,
11HAC57 AA242,
11HAC57 AA251
HP Economizer 2 Drain Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
(18)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
Document Type: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
19
11HAC57 AA211,
11HAC57 AA212,
11HAC57 AA221,
11HAC57 AA222,
11HAC57 AA231,
11HAC57 AA232,
11HAC57 AA201,
11HAC57 AA202
HP Economizer 2 Vent Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAC58 AA241,
11HAC58 AA242,
11HAC58 AA251
HP Economizer 1 Drain Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAC58 AA201,
11HAC58 AA202,
11HAC58 AA211,
11HAC58 AA212
HP Economizer 1 Vent Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAC58 AA001,
11HAC58 AA011,
11HAC58 AA021,
11HAC58 AA005,
11HAC58 AA015,
11HAC58 AA025,
11HAC58 AA007
HP Feedwater CV Isolation Valves Open Open Open Open Open
11HAC58 AA261,
11HAC58 AA262,
11HAC58 AA263,
11HAC58 AA264
11HAC58 AA265,
11HAC58 AA266,
11HAC58 AA267,
11HAC58 AA268
HP Feedwater CV Drain Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed
11HAC58AA004,
11HAC58AA014,
11HAC58AA024
HP Feedwater Control Valve Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
Auto Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
11HAC58AA003
HP Feedwater CV Stop Valve Open Open Open Open Open
11LCQ61AA001 HP Drum Continuous Blowdown
Isolation MOV Valve
Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
Open / Auto Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
11LCQ61AA002 HP Drum Continuous Blowdown
Metering Valve
Open Open Open Open Open
11HAD50AA201 HP Evaporator Drain Isolation
Valve
Closed Closed Closed Closed Open
11HAD50AA202 HP Evaporator Drain Isolation
Valve
Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
(19)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
DocumentType: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
20
11HAD50AA208 HP Evaporator Intermittent Blowoff
Valve
Open Open Open Open Open
11HAD50AA209 HP Evaporator Intermittent Blowoff
Isolation Valve
Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
Closed / Auto Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
11HAD52AA201,
11HAD52AA202
HP Drum Outlet Vent Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAD50AA702 HP Nitrogen Feed Stop Valve Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed
11HAH51AA201 HP Superheater 3 Drain Isolation
Valve
Open Open Open Open Open
11HAH51AA202 HP Superheater 3 Drain Isolation
Valve
Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
Closed / Auto Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAH52AA201 HP Superheater 1/2 Drain Isolation
Valve
Open Open Open Open Open
11HAH52AA202 HP Superheater 1/2 Drain Isolation
Valve
Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
Closed / Auto Closed Closed /
Open*
11HAH51AA250,
11HAH51AA251
HP Superheater 2/3 Vent Valves Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed /
Open*
11LBA51AA211 HP Steam Startup Vent Isolation
Valve (M)
Closed Closed Closed / Auto Closed /
Open**
Closed /
Open**
11LBA51AA212 HP Steam Startup Vent MOV
Valve
Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
Closed / Auto Closed /
Open**
Closed /
Open**
11LAE50AA001,
11LAE50AA024
HP Desuperheater Spraywater
Power Block Valve
Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
Auto Closed Closed
11LAE50 AA201,
11LAE50 AA202,
11LAE50 AA203,
11LAE50 AA204
HP Desuperheater Spraywater
Drain Valves
Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed
11LAE50 AA003,
11LAE50 AA006
HP Desuperheater Spraywater CV
Isolation Valves
Open Open Open Open Open
11LAE50AA002,
11LAE50AA005
HP Desuperheater Spraywater
Control Valve
Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
Auto Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
11LBA51AA001,
11LBA51AA002
HP Steam Outlet Stop Valve Closed Closed Open Closed Closed
(20)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
Document Type: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
21
11LBA51AA222 HP DSH Outlet Drain ISV MOV Closed /
Auto
Closed /
Auto
Closed / Auto Closed Closed /
Open*
11LBA51 AA221 HP Steam Outlet Drain Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed
* Open applies to after the drum pressure falls below 0.5 barg (1.51 bara) and HRSG is completely
cooled (when vapor no longer escapes from the vents.).
** Open applies to after the drum pressure falls below 1.72 barg (2.74 bara).
#
Not Applicable to HRSG-21
Table 2 HP Drum Level Setpoints
Drum Level Setpoints for 1981 mm (78 inch) ID HP Drum
Cold Start-up Setpoints
[P
drum
<1.72 barg (2.73 bara)]
Normal Operating Setpoints
[P
drum
>55.4 barg (56.4bara)]
Level Value Level Value
HHH[MAX3] +330 mm (+13 in) HHH[MAX3] +330 mm (+13 in)
HH[MAX2] +279 mm (+11 in) HH[MAX2] +279 mm (+11 in)
H[MAX1] +228mm (+9 in) H[MAX1] +228mm (+9 in)
NWL -711 mm (-28 in) NWL +102 mm (+4 in)
L[MIN1] -762 mm (-30 in) L[MIN1] -102 mm (-4 in)
LL[MIN2] -813 mm (-32 in) LL[MIN2] -787 mm (-31 in)
LLL[MIN3] -864 mm (-34 in) LLL[MIN3] -864 mm (-34 in)
Levels are referenced to drum centerline.
Dimensions are in inches and millimeters.
Drum level setpoints will be determined based on drum pressure. An HP Drum
Pressure (HAD50 CP003) <1.72 barg (2.73 bara) will utilize Cold Startup Set-
points. An HP Drum Pressure between 1.72 barg (2.73 bara) and 55.4 barg
(56.4 bara) will utilize a linear function of determining the set points. An HP
drum pressure>55.4 barg (56.4 bara) will utilize Normal Operating setpoints.
Field tuning of startup setpoints is permissible.
D
(21)
ALSTOM Projects India Ltd. Item No.: 19.02
Contract Name: Fujairah II Rev. No.: D
Contract No.: PB0048 Date: 20 Feb 09
DocumentType: E
OPERATING PROCEDURE
22
ANNEXURE
SUPPLEMENTARY FIRING SYSTEM
OPERATING PRINCIPLES
(22)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 2/21
FIVES PILLARD
GRC DUAL FUEL FIRED INDUCT BURNER
(Refer to the P&I Diagrams N FUJ/00/M/H----A30/FD/005 &
FUJ/00/M/H----A30/FD/007)
1. SUBJECT 3
2. SAFETY DEVICES AND OPERATION SEQUENCES 3
2.1. Safety devices 3
2.1.1. GT/HRSG main safety devices 3
2.1.2. Measurement main safety devices 4
2.1.3. Burner safety devices 4
2.2. purge 7
2.2.1. HRSG (turbine) PURGE 7
2.2.2. Duct burner purge 7
2.3. Operator Interface 8
2.4. Cooling air fan sequences (switch-over logic) 9
2.5. AUGMENTING AIR FAN 9
2.6. DIESEL OIL BOOSTER PUMPS sequences (switch-over logic) 10
2.7. Diesel oil sequence 10
2.7.1. Prior to ignition: 10
2.7.2. Burner ignition sequence 11
2.7.3. Burner shut-down sequences 13
2.7.4. Diesel oil gun cleaning sequence 15
2.8. Natural gas sequence 16
2.8.1. Burner ignition sequence 16
2.8.2. Shut-Down NG burner head 19
2.9. Automatic change-over sequence 20
2.9.1. Change-over from natural gas to diesel oil 20
2.9.2. Change-over from diesel oil to natural gas 21
2.10. Interface between BMS and DCS (hardwired signals) 21
3. BURNER LOAD CONTROL 21
PART 8
OPERATING PRINCIPLES
C O N T E N T S
(23)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 3/21
FIVES PILLARD
1. SUBJECT
This technical instruction specifies the general operating conditions for a dual fuel fired GRC LOW NOx Induct
Burner installed in an exhaust gas duct, upstream to a Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG). The dual fuel
fired GRC LOW NOx Induct Burner consists of twelve (12) "GR" type Burner heads, mounted and firing
horizontally with natural gas (NG) or diesel oil (DO).
The operating mode is the post-combustion mode only.
The design code is NFPA 85, 2004 edition.
Additional client requirement:
The client has requested a remote burner start-up or shut-off from the DCS or from the BMS.
The igniters operate intermittently with each fuel; each igniter flame is detected by its own built-in flame detection
system.
Each "GR" type burner head flame is detected by 2 (UV) flame scanners both for NG and DO operation.
This document focuses on defining the control and operating principles of the heating equipment, and should
therefore be considered as an explanatory basic description for the purposes of design and manufacture of
automation equipment. It is not an operating manual, and should not be considered as a substitute for the
operating guide of the generator assembly, nor as instructions for commissioning of the generator assembly.
OPERATING PRINCIPLE
Post-combustion mode
The gas turbine and duct burner are in operation.
The duct burner increases the temperature of the gas turbine exhaust gas
Except during the light off, the burner is normally in operation with the 12 heads.
2. SAFETY DEVICES AND OPERATION SEQUENCES
2.1. SAFETY DEVICES
Burner ignition and shut-down sequences, and burner protection logic are ensured by a "fail-safe" programmable
logic controller (PLC).
To increase availability, the PLC is fitted with redundant CPU, redundant communication cards, redundancy of
discrete safety I/O cards (except for lamps) , redundant 24VDC power supplies, and each pressure safety device
(for DO, NG, cooling air and atomizing steam) is treated by the BMS in a 2 out of 3 voting logic system.
A manual fault reset on the BMS cabinet front faade is needed to allow a new burner ignition sequence after a
burner trip.
In the following safety devices description, a "valve position discrepancy" means that the limit switch(es) fitted to
the valve does not indicate the position -digital status- required regarding to the ON/OFF valve control signal.
2.1.1. GT/HRSG main safety devices
The protection logic system is to be made by DCS.
These safety devices shut-down the burner or prevent it from igniting; they are gathered via three logic
information (in a 2 out of 3 voting logic system):
(24)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 4/21
FIVES PILLARD
o Burner trip
This information must include the following safety devices:
Turbine running with sufficient load
Emergency stop
2.1.2. Measurement main safety devices
The protection logic system is to be made by CCS
The burner trip from the CCS must include the following devices:
DO flow (11HJF10 CF001) or pressure (11HJF10 CP001) transmitters bad signal (only when burners are
lightening with DO)
Atomizing steam pressure (11HJM10 CP001 and CP002) transmitters bad signal (only when burners are
lightening with DO)
NG flow (11HJG10 CF001), pressure (11HJG10 CP001) or temperature (11HJG10 CT001) transmitters
bad signal (only when burners are lightening with NG)
Augmenting air flow (11HJL10 CF001) transmitter bad signal
Cooling air pressure (11HJQ10 CP001) transmitter bad signal
2.1.3. Burner safety devices
The burner protection logic is ensured by the BMS supplied by Fives Pillard.
The burner safety devices consist of the following:
2.1.3.1. Ignition main safety devices
(refer to the P&I Diagram FUJ/00/M/H----A30/FD/007)
- Ignition gas shut-off valves position discrepancy of the main ignition gas line (11HJA10 CG081 & CG84),
- Ignition gas vent valve position discrepancy (11HJA10 CG082/CG083),
- Ignition gas purge valve position discrepancy (11HJA10 CG085),
- Loss of ignition gas pressure (11HJA10 CP801) checked after the opening of the ignition gas shut-off valves
(with 2 seconds time delay),
- Excess of ignition gas pressure (11HJA10 CP802) checked after the opening of the ignition gas shut-off
valves (with 2 seconds time delay).
These safety devices prevent all igniters and burner heads from igniting (with NG or DO) and generate:
A shut-down of burner heads igniting sequences,
A shut-down of do burner heads cleaning sequences,
An alarm signal if burner heads were firing with GN or DO,
A safety signal if burner heads were on light off sequence.
2.1.3.2. Ignition safety devices for each igniter
(refer to the P&I Diagram FUJ/00/M/H----A30/FD/005)
- Ignition gas individual shut-off valve position discrepancy of each igniter (CG081, lines HJA11 to HJA62),
- Igniter flame detected before ignition (ionization) (CR001, lines HJA11 to HJA62),
- Igniter flame not detected during ignition (ionization): (CR001, lines HJA11 to HJA62),
These safety devices prevent each igniter and associated burner head from igniting and generate:
An igniter shut-down,
A shut-down of DO burner head cleaning sequence,
An alarm signal if burner head was firing with NG or DO.
(25)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 5/21
FIVES PILLARD
2.1.3.3. Diesel oil main safety devices
(refer to the P&I Diagram FUJ/00/M/H----A30/FD/007)
- Loss of DO pressure at the inlet of main DO valve train (with 2 seconds time delay) obtained with a 2 out of 3
voting system between 11HJF10 CP801, CP802 and CP803 pressure switches (PSL)
- Loss of atomizing steam pressure of the main atomizing line, obtained with a 2 out of 3 voting system
between 11HJM10 CP801, CP802 and CP803 pressure switches (PSL),
- Loss of DO pressure downstream to the flow control valve, checked after the opening of the main shut-off
valve (with time delay to be adjusted during commissioning) obtained with a 2 out of 3 voting system between
11HJF10 CP804, CP805 and CP806 pressure switches (PSL),
- Excess of DO pressure downstream to the flow control valve, checked after the opening of the main shut-off
valve (with time delay to be adjusted during commissioning) obtained with a 2 out of 3 voting system between
11HJF10 CP807, CP808 and CP809 pressure switches (PSH)
- DO flow control valve (11HJF10 AA101)ignition position discrepancy (i.e. the valve is not positioned at its
ignition position prior to and during ignition of the first two burner heads) 11HJF10 CG082 ,
- DO accumulator isolating valve (11HJF10 AA152) position discrepancy (i.e. the valve is not closed before
ignition of the 1
st
burner head couple (11HJF10 CG083)
NOTE: an alarm signal is generated in case of closure of the valve after ignition of the 1
st
burner head couple.
- DO main shut-off valve (11HJF10 AA151) position discrepancy, 11HJF10 CG081,
- DO flow or DO pressure transmitters bad signal 11HJF10 CF001 or 11HJF10 CP001, safety device
generated in the CCS,
- Loss or excess of DO pressure during start-up under pressure control loop (threshold on the pressure
transmitter 11HJF10 CP001, safety device generated in the CCS),
- Loss of CCS watchdog,
- DO individual burner head shut-off valve closing position discrepancy
Concerning loss of NG safety devices when burner heads are firing with DO:
- NG vent valve (11HJG10 AA152) position discrepancy (.i.e. the limit switches fitted to this valve do not
indicate the opening position required when the burner is operated with DO) 11HJG10 CG083 & CG084,
- One NG main shut-off valve (11HJG10 AA151 or AA153) discrepancy (i.e. the limit switches fitted to this
valve do not indicate the closure position required) 11HJG10 CG082 or CG085.
These safety devices causes a burner shut-down (of the 12 burner heads) if DO was fired, or prevent it from
igniting with DO.
Note 1:
These safety devices are not active if the NG manual isolating valve (11HJG10 AA001) is closed
(11HJG10 CG080)
Note 2:
Upon condition there is no position discrepancy for NG main shut-off valves (11HJG10 AA151 or AA153)
and vent valve (11HJG10 AA152), one or more NG individual burner head shut-off valve closing position
discrepancy (closure position required) only generates an alarm.
2.1.3.4. Diesel oil safety devices for each burner head
There are 2 groups of safeties:
Group 1:
- DO individual burner head shut-off valve (AA151, lines HJF11 to HJF62) opening position discrepancy
(CG081, lines HHF11 to HHF62).
- Flame detected before ignition (CR001 or CR002 lines HJQ11 to HJQ62).
- Flame not detected after ignition (CR001 and CR002 lines HJQ11 to HJQ62).
Group 2 :
- Atomizing steam individual burner head manual valve (AA001 line HJM11 to HJM62) position discrepancy
(CG081, lines HJM11 to HJM62).
- Atomizing steam individual burner head automatic shut-off valve (AA151 line HJM11 to HJM62) position
discrepancy (CG082, lines HJM11 to HJM62).
- Cleaning individual burner head shut-off valve (AA152 line HJM11 to HJM62) position discrepancy (CG083,
lines HJM11 to HJM62).
(26)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 6/21
FIVES PILLARD
These 2 groups of safeties devices cause a shutdown of each considered head during DO firing, or prevent it
from igniting with DO.
Group 1 prevents to start the 1
st
couple heads and reset purge if problems occurred when purging or after
purging.
2.1.3.5. Natural gas main safety devices
- Loss of NG pressure at the inlet of main NG valve train (with 2 seconds time delay) obtained with a 2 out of 3
voting system between HJG10 CP801, CP802 and CP803 pressure switches (PSLL),
- Loss of NG pressure downstream to the flow control valve, checked after the opening of the main shut-off
valves (with time delay to be adjusted during commissioning) obtained with a 2 out of 3 voting system
between HJG10 CP804, CP805 and CP806 pressure switches (PSL),
- Excess of NG pressure downstream to the flow control valve checked after the opening of the main shut-off
valves (with time delay to be adjusted during commissioning) obtained with a 2 out of 3 voting system
between HJG10 CP807, CP808 and CP809 pressure switches (PSH),
- NG main shut-off valves (HJG10 AA151 & 153) position discrepancy for the upstream or downstream shut-
off valves (HJG10 CG082 & CG085) limit switches (ZSC),
- NG main vent valve (HJG10 AA152) position discrepancy (HJG10 CG083 & CG084) limit switches (ZSC &
ZSO),
- NG manual vent valve(HJG10 AA501) position discrepancy (HJG10 CG081) limit switch (ZSC),
- NG purge valve (HJG10 AA154) position discrepancy (HJG10 CG087) limit switch (ZSC),
- NG flow control valve (HJG10 AA101) position discrepancy (i.e. the valve is not positioned at its ignition
position prior to and during ignition of the first two heads) HJG10 CG086 limit switch (ZSC),
- NG flow transmitter HJG10 CF001 bad signal (safety device generated in the CCS),
- Loss or excess of NG pressure during start-up under pressure control (threshold on the pressure transmitter
HJG10 CP002, safety device generated in the CCS).
- NG individual burner head shut-off valve (AA151, line HJG11 to HJG62) closing position discrepancy
(CG081, line HJG11 to HJG62) limit switches (ZSC).
Concerning loss of DO safety devices when burner heads are firing with NG:
- A DO main shut-off valve closing position discrepancies (CG081 line HHF10) causes a burner shut-down (of
all burner heads in operation).
- The closing position discrepancy of one or more DO individual shut-off valve prevents the burner from igniting
with NG, generates an alarm signal and causes a burner shut-down (of all burner heads in operation) after a
time delay (5 minutes) if the burner was in operation with NG.
These safety devices cause a burner shut-down (of the 12 burner heads) during NG firing, or prevent it from
igniting with NG.
Note :
These safety devices are not active if the two DO booster pumps (HJF01 AP001 & AP002) are not
running.
2.1.3.6. Natural gas safety devices for each burner head
- NG individual burner head shut-off valve (AA151 line HJG11 to HJG62) opening position discrepancy
(CG081, line HJG11 to HJG62) limit switches (ZSC),
- Flame detected before ignition: CR001 or CR002 line HJQ11 to HJQ62,
- Flame not detected after ignition: CR001 and CR002 line HJQ11 to HJQ62,
These safety devices cause a shut-down of each considered burner head during NG firing, or prevent it from
igniting with NG.
2.1.3.7. Main safety devices
- Conditions see 2.1.1,
- Conditions see 2.1.2,
- Emergency shut-down,
(27)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 7/21
FIVES PILLARD
- Loss of instrument air pressure obtained with a 2 out of 3 voting system between HNX10 CP801, CP802 and
CP803 (see P&I Diagram No FUJ/00/M/H----A30/FD/007) pressure switches (PSLL),
- Loss of cooling air pressure, obtained with a 2 out of 3 voting system between HJQ10 CP801, CP802 and
CP803, line HJQ10 (with time delay to be adjusted during commissioning of the installation) (see P&I
Diagram No FUJ/00/M/H----A30/FD/007) pressure switches (PSL).
- Loss of augmenting air pressure, obtained with a 2 out of 3 voting system between HJL10 CP801, CP802
and CP803, line HJL10 (with time delay to be adjusted during commissioning of the installation) (see P&I
Diagram No FUJ/00/M/H----A30/FD/007) pressure switches (PSL).
These safety devices generate a burner shut-down (12 heads) or prevent it from igniting (with NG
or DO).
AFTER EACH SHUT DOWN CAUSED BY A SAFETY, THE BURNERS NEED TO BE ACKNOWLEDGED
(ON BMS PANEL OR BURNER LOCAL CONTROL BOX) AND RESTART LOCALLY.
IT IS IMPOSSIBLE TO START A TRIPPED BURNER FROM THE DCS.
2.2. PURGE
2.2.1. HRSG (turbine) PURGE
The HRSG purge sequence makes sure that the exhaust gas path of the process is free from gaseous or
suspended flammable matter prior to turbine ignition.
Purge conditions of the HRSG are performed by the DCS.
The turbine purge is made to ensure at least five (5) volume changes of the HRSG enclosure (total volume of the
physical boundary of ductwork from the inlet of turbine to portion of the HRSG where the combustion turbine
exhaust gas temperature is reduce to at least 56C below the lowest auto ignition temperature of the gas.
The augmenting air plenum and associated ductwork shall also be purge into the HRSG enclosure.
Prior to make the turbine purge, the operator must manually start the cooling air fan system.
As the cooling air flow through the augmenting air plenum is up to 25% of the full flow of the augmenting air, the
BMS end to the DCS "GT purge permissive". At this moment, the DCS can start the turbine purge.
A burner purge shall be accomplished before each 1
st
burner head couple ignition.
The burner purge control is made by the BMS. Information HRSG purge completed is send from the BMS to
the DCS to confirm that the burner purge has been realized according to NFPA 85 2004 requirements and to allow a
burner start.
2.2.2. Duct burner purge
The burner purge sequence makes sure that the exhaust gas path of the process is free from gaseous or
suspended flammable matter prior to burner ignition.
Purge may be performed once the safety devices and checks listed in . 2.1 have been carried out.
The purge conditions of the duct burner are performed by the GT. The gas turbine must therefore be operating at
insufficient load to ensure that the TEG rate is sufficient for adequate purging (combustion turbine exhaust gas at
not less then 25% of full load mass flow rate).
The burner purge is made to ensure at least eight (8) volume changes of the HRSG enclosure (total volume of
the physical boundary of ductwork downstream of burner + all steam generator pressure parts + flue gas path
downstream of HRSG to stack inlet).
The augmenting air plenum and associated ductwork shall also be purge into the HRSG enclosure.
As the cooling air flow through the augmenting air plenum is up to 25% of the full flow of the augmenting air, the
BMS send to the DCS "GT purge permissive". At this moment, the DCS can start the turbine purge.
A burner purge shall be accomplished before each 1
st
burner head couple ignition.
(28)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 8/21
FIVES PILLARD
The burner purge control is made by the BMS. Information HRSG purge completed is send from the BMS to
the DCS to confirm that the burner purge has been realized according to NFPA 85 2004 requirements and to allow a
burner start.
2.3. OPERATOR INTERFACE
The operator has, on the front door of the BMS cubicle (located into the air conditioned container) the following
items to start the sequences:
1 Emergency shut-down push button
1 push button "Failure reset"
1 push button "Lamp test"
1 push button "Horn reset"
1 illuminated push button "DO selection"
1 illuminated push button "NG selection"
1 three positions switch (with key) "BMS/Local/DCS"
1 Human Machine Interface (H.M.I.)
1 lamp "400 VAC power on"
1 lamp "230 VAC UPS 1 power on"
1 lamp "230 VAC UPS 2 power on"
1 lamp "110 VDC UPS power on"
1 lamp "24 VDC UPS power on Emergency stop"
1 lamp "24 VDC UPS power on BMS"
1 lamp "24 VDC UPS power on CCS"
1 lamp "Igniter fault"
1 lamp "Alarm"
1 lamp "Main flame fault"
1 lamp "Main failure"
1 lamp "Ignition gas valves discrepancy"
1 lamp "Ignition gas pressure fault"
1 lamp "cooling air system fault"
1 lamp "augmenting air fault"
1 alarm and safety horn
For DO sequences:
- 1 illuminated push button "Diesel oil burner stop "
- 1 illuminated push button "Diesel oil burner start-up"
- 1 lamp "Atomizing, cleaning, DO shut-off valves discrepancy"
- 1 lamp "DO pressure fault"
For the NG sequences:
- 1 illuminated push button "Natural gas burner stop "
- 1 illuminated push button " Natural gas burner start-up"
- 1 lamp "NG shut-off valves discrepancy"
- 1 lamp "NG pressure fault"
For CCS :
- 1 10" touch panel
Note 2:
Twelve local control boxes are also provided to allow local start, stop, cleaning sequences of each burner head.
Each local control box is fitted with:
1 push button "priority stop"
1 push button "Burner head start-up"
1 push button "Burner head stop"
1 push button "Burner head start-up cleaning sequence"
(29)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 9/21
FIVES PILLARD
1 push button "Lamp test"
1 lamp "Burner head in operation with NG"
1 lamp "Burner head in operation with DO"
1 lamp "Ready to start"
1 lamp "Burner head cleaning sequence in progress"
1 lamp "Igniter in operation"
Note 1: the fuel is selected with the two illuminated push buttons "Diesel oil selection" or "Natural gas selection"
on the BMS cubicle.
Note 2:
Lamps and push buttons on the BMS cubicle are provided to allow the burner start-up in case of a H.M.I.
failure.
2.4. COOLING AIR FAN SEQUENCES (SWITCH-OVER LOGIC)
The operator has, on the HMI dedicated to the BMS , the following items to start the cooling air fan sequences:
1 two position switch "Maintenance/Backup"
And for each fan:
1 Push button "Start fan"
1 Push button "Stop fan"
1 Lamp "Fan ON"
1 Lamp "Fan Fault"
Before transfer of TEG through the duct, the operator must check that all manual isolating valves on cooling air
lines are open and must start-up one cooling air fan to protect burner heads, burner igniters, and flame scanners.
When "Backup" mode is selected (which corresponds to the normal operation mode), one fan can be started
manually by the operator with the "Start fan" push button (if "BMS" or "LOCAL" is selected with the three position
switch on the BMS cubicle) or the fan no1 automatically from the BMS (when information "GT running" is
received from the DCS with "DCS" selected on the BMS cubicle).
In case of fan deficiency (electrical motor fault, loss of start response, loss of cooling air pressure, excess of
wrapping temperature, excess of bearing temperature) an alarm signal is generated and the second fan is
automatically started by the sequence.
When "Maintenance" mode is selected (on the BMS cubicle) regardless the choice "BMS" or "DCS", each fan
can be started and stopped manually by the operator and not automatically by the sequence.
2.5. AUGMENTING AIR FAN
The operator has, on the HMI dedicated to the BMS, the following items to start the augmenting air fan:
1 two position switch "Maintenance/Backup"
1 Push button "Start fan"
1 Push button "Stop fan"
1 Lamp "Fan ON"
1 Lamp "Fan Fault"
Before the burner light of, the operator must check that all manual isolating valves on augmenting air lines are
open and must start-up augmenting air fan.
When "Backup" mode is selected (which corresponds to the normal operation mode) the augmenting fan is
automatically start from the BMS when information "Burner start" is received from the DCS with "DCS" selected
on the BMS cubicle or when the operator start the burner from local panel with "Local" selected.
(30)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 10/21
FIVES PILLARD
When "Maintenance" mode is selected, regardless the choice "BMS" or "DCS", the fan is started and stopped
manually by the operator and not automatically by the sequence.
2.6. DIESEL OIL BOOSTER PUMPS SEQUENCES (SWITCH-OVER LOGIC)
The operator has, on the HMI dedicated to the BMS, the following items to start the cooling air fan sequences:
1 two position switch "Maintenance/Backup"
1 two position switch "pump selection"
And for each pump:
1 Push button "Start pump"
1 Push button "Stop pump"
1 Lamp "pump ON"
1 Lamp "pump Fault"
Before the burner light of with DO, the operator must check that all manual isolating valves on fuel oil lines are
open and must start-up one booster pump
When "Backup" mode is selected (which corresponds to the normal operation mode), the selected pump is
automatically started from the BMS when information "Burner start" is received from the DCS with "DCS"
selected on the BMS cubicle or when the operator start the burner from local panel with "Local" selected.
In case of pump deficiency (electrical motor fault, loss of start response, loss of DO feeder pump low pressure,
loss of DO downstream low pressure ) an alarm signal is generated and the second pump is automatically
started by the sequence.
When "Maintenance" mode is selected (on the BMS cubicle) regardless the choice "BMS" or "DCS", each pump
can be started and stopped manually by the operator and not automatically by the sequence.
2.7. DIESEL OIL SEQUENCE
When the GT is running and a burner head is not in operation, to prevent oil gun atomizing sets overheating that
would cause their damage, the burner gun is cooled with steam through the DO automatic cleaning valve (valve
AA152 line HJM11 to HJM62).
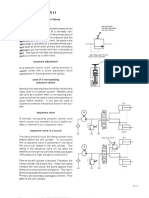
2.7.1. Prior to ignition:
- the operator must first check that:
All manual isolating valves on diesel oil, instrument air, steam line and cooling air lines are open,
All flexible hoses are correctly connected.
All DO guns are installed
All atomizing sets are installed
- "Diesel oil" operation must be selected with the associated illuminated push button, on the BMS cubicle.
Note:
If the dummy atomizing tips are not installed in the burner heads before boiler start-up: all burner heads
should be started-up in a reasonable time.
If the dummy atomizing tips are installed in the burner heads before boiler start-up: each atomizing set
should be installed in lieu of the dummy atomizing tip just before starting-up the burner heads.
After a burner head shut-down (voluntary or by fault) the burner should be re-started quickly or the
atomizing set replaced by a dummy atomizing tip.
(31)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 11/21
FIVES PILLARD
2.7.2. Burner ignition sequence
DO valves train particularity (see P&I Diagrams No FUJ/00/M/H----A30/FD/005 & FUJ/00/M/H----A30/FD/007):
The main DO valves train is supplied with 1 flow control valve (HJF10 AA101), 1 ignition pressure transmitter
(HJF10 CP001) and 1 flow transmitter (HJF10 CF001), line HJF10.
Each burner head piping is fitted with 1 DO shut-off valve (XSV AA151, lines HJF11 to HJF62), 1 atomizing shut-
off valve (XSV AA151, lines HJM11 to HJM62) and 1 cleaning shut-off valve (XSV AA152, lines HJM11 to
HJM62), allowing independent operation of each burner head.
The atomizing/purging piping is fitted with 2 pressure transmitter (HJM10 CP001 & CP002) and 1 pressure
control valve (HJM10 AA101).
Local start-up:
According to NFPA 85, 2004, "The start-up of the burner as a first-time function shall be accomplished
by the operator at the burner location who has a direct view of the burner.
So FIVES-PILLARD recommends that after a complete burner shut-down, first start-up for each couple of burner
head (not only the first couple of heads) should be done from the local control box by pressing the "Burner head
start-up" push button of one of the two local boxes associated to burner heads.
This recommendation is given for the following reasons:
- To make sure that each oil gun is installed in the head,
- To verify that there is no leak, in particular between the oil gun and the shut-off valve.
Remote start-up:
According to CLIENT request, it is possible to initiate the burner start-up from the BMS or from the DCS by
pressing the "DO burner start-up" push button. In such a case, all the couples of burner heads are automatically
started-up the one after the other.
The three position switch "BMS/Local/DCS" on the BMS cubicle, enables choice of the operating mode.
In local mode, each burner head couple ignition is locally started by the operator from the local boxes. There is
no order to manually start each burner heads couple but it is recommended to respect the requested order used
in automatic sequence.
The requested start-up order of the burner heads couples (in automatic sequence from the BMS or from the
DCS) is the following:
- Burner heads couple no XB31/XB32,
- Burner heads couple no XB41/XB42,
- Burner heads couple no XB21/XB22,
- Burner heads couple no XB51/XB52,
- Burner heads couple no XB11/XB22.
- Burner heads couple no XB61/XB62.
If the TEG characteristics are in accordance with the specified technical parameters for duct burner (mass flow
rate, no CO, sufficient O2 content, control is made by the DCS and information "Burner trip" sent to the BMS is
ON) the automation proceeds with starting ignition, under control of the safety devices, of burner heads nXB31
and XB32.
The lamp "Ready to start" of each burner head local panel is ON when safety devices and checks listed in . 2.1
and 2.2 have been carried out.
The "Burner head in operation with DO" lamp of the associated local boxes flashes during ignition and the burner
heads status is indicated on the H.M.I. in front of the BMS cabinet.
During ignition of the two first burner heads, the DO flow control valve HJF10-AA101 and the atomizing pressure
control valve HJM10-AA101 are forced on their ignition position.
T0 - Opening of upstream + downstream ignition gas shut-off valves HJA10-
AA151 and AA153
- Closure of ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Opening of ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
(32)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 12/21
FIVES PILLARD
T0 + 4'' - Energizing of ignition transformers HJA31-CE001 and HJA32-CE001
- Maintaining open the upstream + downstream ignition gas shut-off valves
HJA10-AA151 and AA153
- Maintaining close the ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Closure of ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
- Opening of the two burner heads ignition gas shut-off valves HAJ31-AA151
and HJA32 AA151
T0 + 10'' - De-energizing of ignition transformers HJA31-CE001 and HJA32-CE001
- Maintaining open upstream + downstream + burner heads ignition gas
shut-off valves HJA10-AA151, HJA10-AA153, HJA31-AA151 and HJA32
AA151
- Maintaining closed ignition gas vent and purge valves HJA10-AA152 and
HJA10-AA154
- Checking igniter flames by the 2 individual igniter flame ionization detection
HJA31-CR001 and HJA32- CR001
T0 + 16" + vidt - Maintaining open upstream + downstream + burner head ignition gas
shut-off valves HJA10-AA151, HJA10-AA153, HJA31-AA151 and HJA32
AA151
- Maintaining closed the ignition gas vent and purge valves HJA10-AA152 and
HJA10-AA154
- Opening of the DO main shut-off valve HJF10-AA151
- Opening of the two DO burner head shut-off valves HHF31-AA151
and HHF32-AA151
- Opening of the two burner head atomizing shut-off valves HJM31-AA151 and
HJM32- AA151
- Information "Taking into account of DO flow rate " is sent from BMS to CCS
T0 + 21" + vidt + FuT - Closure of upstream + downstream + burner head ignition gas shut-off valves
HJA10-AA151, HJA10-AA153, HJA31-AA151 and HJA32 AA151
- Opening of ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Maintaining closed ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
- Maintaining open the DO main shut-off valve HJF10-AA151 + DO burner
head shut-off valves HJF31-AA151 and HJF32-AA151
- Maintaining open the burner heads atomizing shut-off valves HJM31-AA151
and HJM32- AA151
- Checking main flames by individual flame detection HJQ31-CR001 or
HJQ31-CR002 and HJQ32-CR001 or HJQ32-CR002
- Maintaining information "Taking into account of DO flow rate" from BMS to CCS
T0 + 27" + vidt + FuT - Ignition of burner heads XB31 and XB32 is completed
- Maintaining information "Taking into account of DO flow rate" from BMS to
DCS
- DO ignition pressure loop is released in the CCS.
Note 1:
FuT = DO line filling-up time
FuT = 6 second for burner heads re-ignition without cleaning,
FuT = 20 seconds for burner heads re-ignition with cleaning.
During the first commissioning of the installation, FuT will be adjusted at the shortest time possible
vidt = steam line purging time
vidT = 0 second after the 1
st
DO couple ignited,
vidt = 60 seconds for 1
st
DO couple ignition.
During the first commissioning of the installation, vidt will be adjusted at the shortest time possible
The "Burner head in operation with DO" lamp of the associated local panels flashes during the burner light of and
switches to a permanently lit status when the burner is ignited. The burner head status is indicated on the H.M.I.
(33)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 13/21
FIVES PILLARD
Once ignition of burner heads XB31 and XB32 is completed, the operator (from the local box) or the automatic
sequence (initiated from BMS or DCS) proceeds with ignition start-up (under control of the safety devices) of the
other burner head couples, respecting the requested order (nXB41/XB42, XB21/XB22,.., XB61/XB62) with
equivalent actions on the associated local panels, valves and igniters.
Time between 2 burner heads couples ignition is at least 10 seconds.
Note 2:
During ignition:
If a fault appears during ignition (but main DO shut-off valves remained closed) of at least one burner
head of the first burner heads couple, the couple is tripped; the fault should be determined and
corrected. The burner light off is not allowed until the lamp "Ready to start" is off. The operator should
restart ignition sequence of the burner heads couple, with "Local" mode selected, by pressing the
"Burner head start-up" push button on the local panel,
If a fault appears during ignition (but main NG shut-off valves remained closed) of one or two head(s)
of a burner heads couple, with at least another head already in operation, only the head(s) faulty is
(are) stopped, the fault should be determined and corrected. The operator should restart ignition
sequence of the head(s), with "Local" mode selected, by pressing the "Burner head start-up" push
button on the local panel, after the end of the automatic burner light off sequence.
After ignition:
If a fault appears after ignition (after opening of the main ng shut-off valves) of a burner head, with at
least 2 other head already in operation in pressure control or with at least 8 other head already in
operation in flow control, only the faulty head is stopped, the failure should be determined and
corrected the burner ignition is not allowed until the lamp "ready to start" is off. The operator should
restart ignition sequence of the head(s), with "local" mode selected, by pressing the "burner head start-
up" push button on the local panel, if the automatic burner light off sequence is ended.
The normal burner operation is obtained with 12 burner heads firing simultaneously with DO or NG.
After ignition of the 12 burner heads is complete or after ignition of 8 burners head and the validation of
the flow control validation on the CCS HMI, NG flow control can modulate, but with n burner heads in
operation, the maximum load shall be limited to n x 8.33 %.
When 8 burner heads are in operation with the NG flow control loop released, loss of one head initiates
a shut-down sequence of the complete burner.
After ignition of the requested burner heads (8 to12 heads) when NG flow control loop is operational, if one or
two burner heads stop because of a safety device or of a voluntary shut-down (for maintenance), the DCS shall
automatically reduce the load according to the number of burner heads remaining in service.
The NG flow control loop will automatically distribute the load on the heads remaining in service.
After determination and correction of the fault, the operator should locally start up the remaining heads.
2.7.3. Burner shut-down sequences
Voluntary shut-down of one burner head:
The operator can shut-down each burner head (for maintenance) by pressing the associated "Burner head stop"
push-button on the local box. This action has priority regardless the choice "BMS/Local/DCS" given by the three
positions switch on the BMS cubicle.
After each voluntary shut-down of one head, excepted for the last one, the operator should start a cleaning
sequence of the associated DO gun (see . 2.7.4) by pressing the "Burner head start-up cleaning sequence"
push-button on the local panel.
The lamp "Burner cleaning sequence in progress" flashes slowly to inform the operator that the cleaning
sequence must be made.
For each head, the shut-off sequence is as follows:
- The associated DO and atomizing shut-off valves XSV AA151 lines HJF11 to HJF62 and HJM11 to HJM62
close
- The associated local "Burner head in operation with DO" lamp switches off.
For the complete burner:
(34)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 14/21
FIVES PILLARD
The complete voluntary shut-down of the burner can be realized by the operator by pressing the "DO burner
stop" push-button on the BMS panel or from the DCS.
The requested shut-down order of the burner heads couples (in automatic sequence from the BMS or from the
DCS, or to be respected by the operator in manual mode) is the following:
- Burner heads couple no XB61/XB62,
- Burner heads couple no XB11/XB12,
- Burner heads couple no XB51/XB52,
- Burner heads couple no XB21/XB22
- Burner heads couple no XB41/XB42,
- Burner heads couple no XB31/XB32.
After a complete voluntary shut-down of the burner, the BMS automatically proceeds with a cleaning sequence of
all burner heads (see . 2.7.4) excepted of the last one.
The time delay between each couple shut-down will be adjusted during the first commissioning in order to allow
complete cleaning sequence of each burner heads couple before shut-down of the last couple.
The complete shut-off sequence is as follows:
- Each DO burner head (XSV AA151 lines HJF11 to HJF62) and atomizing (XSV AA151 lines HJM11 to
HJM62) shut-off valves close,
- The DO main shut-off valve (HJF10- AA151) close,
- The DO accumulator isolating valve (HJF10- AA152) close,
- The DO flow control valve (HJF10- AA101) forced to its ignition position,
- All the local "Burner head in operation with DO" lamps switch off.
Note:
- If a general burner start-up occurs (from the BMS or from the DCS) during a complete voluntary shut-down
sequence, the shut-down sequence is automatically stopped and an ignition sequence restarts,
Safety shut-down:
After a safety shut-down of the complete burner, the cleaning sequence is forbidden.
In order to clean the DO guns, the operator should determine and correct the fault then should restart ignition of
at least one burner heads couple (after a boiler purge) before starting a cleaning sequence of each head.
A safety shut-down produces the same actions as the voluntary shut down.
The burner head fault is indicated on the H.M.I.
(35)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 15/21
FIVES PILLARD
2.7.4. Diesel oil gun cleaning sequence
After a voluntary shut-down of the complete burner, a cleaning sequence of each head (excepted of the last one)
is made by the BMS, except in the case of:
- DO burner head individual shut-off valve discrepancy stops or prevents the cleaning sequence of the
considered head,
- Atomizing pressure very low obtained with the 2 out of 3 voting system between PSL CP801, PSL CP802
and PSL CP803, line HJM10 (stops or prevents the cleaning sequence of the heads),
- Main safety devices (see . 2.1.3.7, stops or prevents the cleaning sequence of the heads),
- Individual igniter safeties (see . 2.1.3.5 and 2.1.3.6) stop or prevent the cleaning sequence of the
considered head.
The "Burner head cleaning sequence in progress" lamp(s) of the associated local panel(s) flash(es) rapidly
during cleaning sequence and the burner head status is indicated on the H.M.I.
T0 - Opening of upstream + downstream ignition gas shut-off valves HJA10-AA151 and
HJA10-AA153
- Closure of ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Opening of ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
T0 + 4'' - Energizing of burner head ignition transformer HJAxx-CE001
- Maintaining open upstream + downstream ignition gas shut off valves HJA10-AA151 and
HJA10-AA153
- Maintaining closed ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Closure of ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
- Opening of the burner head ignition gas shut-off valve HJAxx-AA151
T0 + 10'' - De-energizing of burner heads ignition transformer HJAxx-CE001
- Maintaining open upstream + downstream ignition gas shut-off valves HJA10-AA151 and
HJA10-AA153
- Maintaining open the burner head(s) ignition gas shut-off valves HJAxx-AA151
- Maintaining closed ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Maintaining closed the ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
- Checking igniter flames by the 2 individual igniter flame ionization detection HJAxx-CR001
T0 + 16'' - De-energizing of burner heads ignition transformer HJAxx-CE001
- Maintaining open upstream + downstream ignition gas shut-off valves HJA10-AA151 and
HJA10-AA153
- Maintaining open the burner head(s) ignition gas shut-off valves HJAxx-AA151
- Maintaining closed ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Maintaining closed the ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
- Checking igniter flames by the individual igniter flame ionization detection
HJAxx-CR001
- Opening of individual burner head atomizing shut-off valve HJMxx-AA151
- Opening of individual burner head cleaning shut-off valve HJMxx-AA152
T0 + 21'' + CT - Closure of upstream + downstream ignition gas shut-off valves HJA10-AA151 and HJA10-
AA153
- Closure of the burner head(s) ignition gas shut-off valve HJAxx-AA151
- Opening of ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Maintaining closed the ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
- Closure of individual burner head atomizing shut-off valve HJMxx-AA151
- Closure of individual burner head cleaning shut-off valve HJMxx-AA152
Note:
- CT = DO gun cleaning time; CT will be adjusted on site during the first commissioning of the
installation. CT will be as short as possible though at the same time making sure of an efficient
purging.
- During the cleaning sequence, a starting command from the local panel is priority. In this case,
the BMS makes the present sequence shorter and proceeds with burner head restarting.
(36)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 16/21
FIVES PILLARD
2.8. NATURAL GAS SEQUENCE
Prior to ignition :
- The operator must first check that all manual isolating valves on NG, instrument air and cooling air lines are
open,
- "Natural gas" operation must be selected with the associated illuminated push button, on the BMS cubicle.
When a burner head is not in operation with DO, to prevent oil gun atomizing sets overheating that would cause
their damage, a dummy atomizing tip should be installed in lieu of each DO gun atomizing set or the atomizing
shut of valve should be open in order to cooling the atomizing sets.
2.8.1. Burner ignition sequence
NG valves train particularity (see P&I Diagrams No FUJ/00/M/H----A30/FD/005 and FUJ/00/M/H----A30/FD/007):
The main NG valves train is supplied with 1 gas flow transmitter (HJG10-CF001), 1 gas pressure transmitter
(HJG10-CP001) and 1 gas temperature transmitter (HJG10-CT001) for gas flow correction, 1 upstream shut-off
valve (HJG10-AA151), 1 vent valve (HJG10-AA152), 1 downstream shut-off valve (HJG10-AA153), 1 gas flow
control valve (HJG10-AA101), 1 ignition gas pressure transmitter (HJG10-CP001).
Each burner head piping is fitted with 1 NG shut-off valve AA151, lines HJG11 to HJG62.
Local start-up:
According to NFPA 85, 2004 edition: "The start-up of the burner as a first-time function shall be accomplished
by the operator at the burner location who has a direct view of the burner.
So FIVES-PILLARD recommends that after a complete burner shut-down, first start-up for each couple of burner
head (not only the first couple of heads) should be done from the local control box by pressing the "Burner head
start-up" push button of one of the two local boxes associated to burner heads.
This recommendation is given for the following reasons:
To make sure that there is no problem on each burner head,
To verify that there is no leak.
Remote start-up:
According to CLIENT request, it is possible to initiate the burner start-up from the BMS or from the DCS by
pressing the "DO burner start-up" push button. In such a case, all the couples of burner heads are automatically
started-up the one after the other.
Even if ignition of the first couple of burner heads is done from the local control box, it remains possible to initiate
start-up of the other burner heads from the BMS or from the DCS. In such a case, start-up of the other heads is
done automatically as explained here after.
The three position switch "BMS/Local/DCS" on the BMS cubicle, enables choice of the operating mode.
In local mode, each burner head couple ignition is locally started by the operator from the local box. There is no
order to manually start each burner heads couple but it is recommended to respect the requested order used in
automatic sequence.
The requested start-up order of the burner heads couples (in automatic sequence from the BMS or from the
DCS, or to be respected by the operator in manual mode) is the following:
- Burner heads couple no XB31/XB32,
- Burner heads couple no XB41/XB42,
- Burner heads couple no XB21/XB22,
- Burner heads couple no XB51/XB52,
- Burner heads couple no XB11/XB22.
- Burner heads couple no XB61/XB62.
(37)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 17/21
FIVES PILLARD
In all cases, the start-up sequence is initiated by the operator by pressing a push button.
If the TEG characteristics are in accordance with the specified in the technical parameters for Duct burner (mass
flow rate, no CO, sufficient O2 content,..., control is made by the DCS and information "Burner trip" sent to the
BMS is ON the automation proceeds with starting ignition, under control of the safety devices, of burner heads n
XB31 and XB32.
The lamp "Ready to start" of each burner head local box is ON when safety devices and checks listed in . 2.1
and 2.2 have been carried out.
The "Burner head in operation with NG" lamp of the associated local panels flashes during ignition and the
burner heads status is indicated on the H.M.I. in front of the BMS cabinet.
During ignition of the two first burner heads, the NG flow control valve HJG10-AA101 is forced on its ignition
position.
T0 - Opening of upstream + downstream ignition gas shut-off valves HJA10-AA151 and
HJA10-AA153
- Closure of ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Opening of ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
T0 + 4'' - Energizing of ignition transformers HJA31-CE001 and HJA32-CE001
- Maintaining open the upstream + downstream ignition gas shut-off valves HJA10-
AA151 and HJA10-AA153
- Maintaining close the ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Closure of ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
- Opening of the two burner heads ignition gas shut-off valves HJA31-AA151 and
HJA32-AA151
T0 + 9" - De-energizing of ignition transformers HJA31-CE001 and HJA32-CE001
- Maintaining open the upstream + downstream ignition gas shut-off valves HJA10-
AA151 and HJA10-AA153
- Maintaining close the ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Maintaining close ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
- Maintaining close the two burner heads ignition gas shut-off valves HJA31-AA151 and
HJA32-AA151
- Checking igniter flames by the 2 individual igniter flame ionization detections
HJA31-CR001 and HJA32-CR001.
T0 + 13" - Maintaining open the upstream + downstream ignition gas shut-off valves HJA10-
AA151 and HJA10-AA153
- Maintaining close the ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Maintaining close ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
- Maintaining open the two burner's heads ignition gas shut-off valves HJA31-AA151
and HJA32-AA151
- Checking igniter flames by the 2 individual igniter flame ionization detections
HJA31-CR001 and HJA32-CR001.
- Opening of the main upstream shut-off valve HJG10-AA151
- Opening of the main downstream shut-off valve HJG10-AA153
- Closure of the main gas vent valve HJG10-AA152
- Opening of the purge valve HJG10-AA154
T0 + 17" - Maintaining open the upstream + downstream ignition gas shut-off valves HJA10-
AA151 and HJA10-AA153
- Maintaining close the ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Maintaining close ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
- Maintaining open the two burner's heads ignition gas shut-off valves HJA31-AA151
and HJA32-AA151
- Checking igniter flames by the 2 individual igniter flame ionization detections
HJA31-CR001 and HJA32-CR001.
- Maintaining open the main upstream shut-off valve HJG10-AA151
- Maintaining open the main downstream shut-off valve HJG10-AA153
- Maintaining closed the main gas vent valve HJG10-AA152
(38)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 18/21
FIVES PILLARD
- Closure of the purge valve HJG10-AA154
- Opening of the NG burner head shut off valves HJA31-AA151 and HJA32-AA151
- Information "Taking into account of NG flow rate" is sent from BMS to CCS
T0 + 21" - Closure of the upstream + downstream ignition gas shut-off valves HJA10-AA151 and
HJA10-AA153
- Opening of the ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Maintaining close the ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
- Maintaining open the main upstream shut-off valve HJG10-AA151
- Maintaining open the main downstream shut-off valve HJG10-AA153
- Maintaining closed the main gas vent valve HJG10-AA152
- Maintaining closed the purge valve HJG10-AA154
- Maintaining open the NG burner head shut off valves HJA31-AA151 and HJA32-
AA151
- Maintaining set the information "Taking into account of NG flow rate" from BMS to
CCS
- Checking of main flame detections of the two heads HJQ31-CR001 or HJQ31-CR002
and HJQ32-CR001 or HJQ32-CR002
T0 + 25" - Maintaining close the upstream + downstream ignition gas shut-off valves HJA10-
AA151 and HJA10-AA153
- Opening of the ignition gas vent valve HJA10-AA152
- Maintaining close the ignition gas purge valve HJA10-AA154
- Maintaining open the main upstream shut-off valve HJG10-AA151
- Maintaining open the main downstream shut-off valve HJG10-AA153
- Maintaining closed the main gas vent valve HJG10-AA152
- Maintaining closed the purge valve HJG10-AA154
- Maintaining open the NG burner head shut off valves HJA31-AA151 and HJA32-
AA151
- Maintaining set the information "Taking into account of NG flow rate" from BMS to
CCS
- Checking of main flame detections of the two heads HJQ31-CR001 or HJQ31-CR002
and HJQ32-CR001 or HJQ32-CR002
- Opening of the burners heads atomizing shut-off valves HJM31-AA151 and HJM32-
AA151 (for DO gun atomizing sets cooling)
T0 + 29" + T2 - Ignition of burner heads XB31 and XB32 is completed
- Holding information "Taking into account of NG flow rate" from BMS to CCS
- NG ignition pressure loop is released in CCS.
Note 1:
T2 time delay will be adjusted on site during the first commissioning of the installation,
The lamp "Burner head in operation with NG" of the local panel flashes during the light of and switches to
a permanently lit status when the burner head ignition is complete.
The burner head status is indicated on the H.M.I.
Once ignition of burner heads XB31 and XB32 is completed, the operator (from the local box) or the
automatic sequence (initiated from BMS or DCS) proceeds with ignition start-up (under control of the
safety devices) of the other burner head couples, respecting the requested order (nXB41/XB42,
XB21/XB22,.., XB61/XB62) with equivalent actions on the associated local panels, valves and igniters.
However, during ignition of the other burner head couples, the purge valve is maintained closed.
Time between 2 burner heads couples ignition is at least 10 seconds.
Ignition of the 2
nd
and other burner head couples is made under control of the NG ignition pressure loop, in
the CCS. The NG ignition pressure is given by the pressure transmitter PT CP002 line HJG10.
Once ignition of 12 burner heads is complete or after ignition of 8 burner heads and the validation of the
"flow control validation" selected from the HMI of the CCS, the NG flow control loop is operational.
The "Flow Control Validation" is necessary step because the requested NG flow to light-off the first couple
of burner heads is not high enough to be measured by the NG flow meter. Pressure control lighting-off
sequence is far more reliable.
(39)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 19/21
FIVES PILLARD
Note 2:
During ignition:
If a fault appears during ignition (but main NG shut-off valves remained closed) of at least one burner
head of the first burner heads couple, the couple is tripped; the fault should be determined and
corrected and 1 minute shall elapse before the next ignition is attempted (the lamp "Ready to start" is
off). The operator should restart ignition sequence of the burner head, with "Local" mode selected, by
pressing the "Burner head start-up" push button on the local panel,
If a fault appears during ignition (but main NG shut-off valves remained closed) of one or two head(s)
of a burner heads couple, with at least another head already in operation, only the head(s) faulty is
(are) stopped, the fault should be determined and corrected. The operator should restart ignition
sequence of the head(s), with "Local" mode selected, by pressing the "Burner head start-up" push
button on the local panel, after the end of the automatic burner light off sequence.
After ignition:
If a fault appears after ignition (after opening of the main ng shut-off valves) of a burner head, with at
least 2 other head already in operation in pressure control or with at least 8 other head already in
operation in flow control, only the faulty head is stopped, the failure should be determined and
corrected the burner ignition is not allowed until the lamp "ready to start" is off. The operator should
restart ignition sequence of the head(s), with "local" mode selected, by pressing the "burner head start-
up" push button on the local panel, if the automatic burner light off sequence is ended.
The normal burner operation is obtained with 12 burner heads firing simultaneously with DO or NG.
After ignition of the 12 burner heads is complete or after ignition of 8 burners head and the validation of
the flow control validation on the CCS HMI, NG flow control can modulate, but with n burner heads in
operation, the maximum load shall be limited to n x 8.33 %.
When 8 burner heads are in operation with the NG flow control loop released, loss of one head initiates
a shut-down sequence of the complete burner.
After ignition of the requested burner heads (8 to12 heads) when NG flow control loop is operational, if one or
two burner heads stop because of a safety device or of a voluntary shut-down (for maintenance), the DCS shall
automatically reduce the load according to the number of burner heads remaining in service.
The NG flow control loop will automatically distribute the load on the heads remaining in service.
After determination and correction of the fault, the operator should locally start up the remaining heads.
2.8.2. Shut-Down NG burner head
2.8.2.1. Voluntary shut down
The operator can shut-down each burner head (for maintenance) by pressing the associated "Burner head stop"
push-button on the local box. This action has priority regardless the choice "BMS/Local/DCS" given by the three
positions switch on the BMS cubicle.
For each head, the shut-off sequence is as follows:
- The associated NG shut-off valve XSV AA151 lines HJG11 to HJG62 close
- The associated local "Burner head in operation with NG" lamp switches off.
For the complete burner:
The complete voluntary shut-down of the burner can be realized by the operator by pressing the "NG burner
stop" push-button on the BMS panel or from the DCS.
The requested shut-down order of the burner heads couples (in automatic sequence from the BMS or from the
DCS, or to be respected by the operator in manual mode) is the following:
- Burner heads couple no XB61/XB62,
- Burner heads couple no XB11/XB12,
- Burner heads couple no XB51/XB52,
- Burner heads couple no XB21/XB22,
- Burner heads couple no XB41/XB42,
- Burner heads couple no XB31/XB32
(40)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 20/21
FIVES PILLARD
The complete shut-off sequence is as follows:
- Each NG burner head shut-off valves (XSV AA151 line HJG11 to HJG62) close,
- The NG main upstream shut-off valve (HJG10-AA151) close,
- The NG main downstream shut-off valve (HJG10-AA 153) close,
- The NG main vent valve (HJG10- AA152) open,
- The NG main purge valve (HJG10-AA154) close,
- The NG flow control valve (HJG10-AA101) forced on its ignition position,
- All the local "Burner head in operation with NG" lamps switch off.
Note:
If a general burner start-up occurs (from the BMS or from the DCS) during a complete voluntary shut-down
sequence, the shut-down sequence is automatically stopped and an ignition sequence restarts,
2.8.2.2. Safety shut-down
A safety shut-down produces the same actions as the voluntary shut down.
The burner head fault is indicated on the H.M.I.
2.9. AUTOMATIC CHANGE-OVER SEQUENCE
Refer to "Operating method of pressure control and flow control" document.
2.9.1. Change-over from natural gas to diesel oil
Before selecting a change-over from NG to DO, the operator must check that:
- All dummy atomizing tips (if they are mounted) have been replaced by atomizing sets on each DO gun,
- Each head is fitted with its DO gun,
- There is no leak, in particular between the oil gun and the shut-off valves.
The change-over sequence is selected by the operator by pressing the illuminated push button "DO selection" on
the BMS (if "BMS" was chosen on the three positions switch, on the BMS cubicle), or from the DCS (then the
order "DO selection" is sent by the DCS to the BMS; refer to interface signals between BMS and DCS).
After 5 minutes delay without at least one DO burner head in operation, the change-over sequence is invalidated
and the fuel choice remains "NG selection".
If the safety devices and checks (see . 2.1) have been carried out, one information "Priority to DO" is sent from
the BMS to the CCS so that the maximum NG load will be limited to 75% to take into account admission of DO.
The global burner thermal load will remain the same.
The operator proceeds with ignition of the 1
st
burner heads couple (XB31/XB32) with DO as described in . 2.7.2.
Each couple of burner heads is lit one after the other by the operator or automatically.
In case of deficiency during ignition of one burner head, the operator should determine and correct the fault
before locally starting the remaining head.
When ignition of the requested number of burner heads (10 or 12) with DO is completed, the NG load is
automatically reduced to reach the technical NG minimum while DO flow rate grows simultaneously to the
requested load.
The shut-down sequence of all NG burner heads couples is realized:
- Automatically by the BMS after a time delay (5 minutes, to be adjusted during commissioning),
- By the operator, after checking that the NG technical minimum flow rate is reached (on the CCS), with action
on push button "NG burner stop" from the BMS or from the DCS.
Then the automation proceeds with extinction of all NG burners couples according to . 2.8.2.
(41)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8 - OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 2009/01/12
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 5 - 21/21
FIVES PILLARD
2.9.2. Change-over from diesel oil to natural gas
Before selecting a change-over from DO to NG, the operator must check that:
- There is no problem on each burner head,
- There is no leak,..
The change-over sequence is selected by the operator by pressing the illuminated push button "NG selection" on
the BMS (if "BMS" was chosen on the three positions switch, on the BMS cubicle), or from the DCS (then the
order "NG selection" send by the DCS to the BMS; refer to interface signals between BMS and DCS).
After 5 minutes delay without at least one NG burner head in operation, the change-over sequence is invalidated
and the fuel choice remains "DO selection".
If the safety devices and checks (see . 2.1) have been carried out, one information " Priority to NG" is sent from
the BMS to the DCS so that the maximum DO load will be limited to 75% to take into account admission of NG.
The global burner thermal load will remain the same.
The operator proceeds with ignition of the 1
st
burner heads couple (XB31/XB32) with NG as described in . 2.8.1.
Each couple of burner heads is lit one after the other by the operator or automatically.
In case of deficiency during ignition of one burner head, the operator should determine and correct the fault
before locally starting the remaining head.
When ignition of the requested number of burner heads (depending on the load) with NG is completed, the DO
load is automatically reduced to reach the technical DO minimum while NG flow rate grows simultaneously to the
requested load.
The shut-down sequence of all DO burner heads couples is realized:
o Automatically by the BMS after a time delay (5 minutes, to be adjusted during commissioning),
by the operator, after checking that the DO technical minimum flow rate is reached (on the DCS) with action on
push button "DO burner stop" from the BMS or from the DCS).
Then the automation proceeds with extinction of all DO burner couples and an automatic cleaning sequence of
each burner heads couple takes place according to . 2.7.3. and 2.7.4.
2.10. INTERFACE BETWEEN BMS AND DCS (HARDWIRED SIGNALS)
- Refer to Signal Exchange List, Doc nFUJ/00/M/H----A30/IO/001
3. BURNER LOAD CONTROL
Refer to O&M MANUAL Part 8.3 "Burner Load Control Operating Principle".
Burner load control will be done by DCS.
The purpose of the burner control system is to follow power output required of the plant by giving a load signal
proportional to the difference between the required power output and to the set point selected by the operator.
The load control operation can be:
Automatic, depending on the difference between the requested power and the set point.
Manual, by action of the operator on the output signal of the controller.
The purpose of combustion control is to convert the signal from the load control into thermal output, in order to
ensure the steam flow rate required from the generator. The combustion control is based on the fuel flow rate
reading. The principle is to adjust the fuel flow according to the load required. The adjusting elements are the fuel
flow control valves FCV AA101 (lines HJG10 for NG or HJF10 for DO).
The control of the fuel flow is made by the CCS included in the BMS cabinet.
(42)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8.3 CONTROL OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 17/02/2009
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 1 - 1/7
FIVES PILLARD
GRC DUAL FUEL FIRED INDUCT BURNER
(Refer to the P&I Diagrams N PB0048-1C0015 & PB0048-1C0017)
1. SUBJECT 2
2. SUPPLEMENTARY FIRING LOAD CONTROL 3
2.1. CALCULATION OF THE LOAD UPPER LIMIT 3
2.2. LOAD CONTROL OPERATING MODE 3
3. COMBUSTION CONTROL 4
3.1. fuel gas control 4
3.1.1. FUEL GAS PRESSURE CONTROL 4
3.1.2. FUEL GAS FLOW CONTROL 4
3.2. DIESEL OIL CONTROL 5
3.2.1. DIESEL OIL PRESSURE CONTROL 5
3.2.2. DIESEL OIL FLOW CONTROL 6
4. DIESEL OIL HIGH PRESSURE CONTROL 6
5. ATOMIZING STEAM PRESSURE 7
PART 8.3
SUPPLEMENTARING FIRING CONTROL
OPERATING PRINCIPLE
C O N T E N T S
(43)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8.3 CONTROL OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 17/02/2009
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 1 - 2/7
FIVES PILLARD
1. SUBJECT
This technical instruction specifies the general control operating conditions for a dual fuel fired GRC LOW NOx
Induct Burner installed in an exhaust gas duct, upstream to a Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG). The
dual fuel fired GRC LOW NOx Induct Burner consists of twelve (12) "GR" type Burner heads, mounted and firing
horizontally with natural gas (NG) or diesel oil (DO).
The operating mode is the post-combustion mode only.
The design code is NFPA 85, 2004 edition.
Additional client requirement:
The client has requested a remote burner start-up or shut-off from the DCS or from the BMS.
The igniters operate intermittently with each fuel; each igniter flame is detected by its own built-in flame detection
system.
Each "GR" type burner head flame is detected by 2 (UV) flame scanners both for NG and DO operation.
This document focuses on defining the control and operating principles of the heating equipment, and should
therefore be considered as an explanatory basic description for the purposes of design and manufacture of
automation equipment. It is not an operating manual, and should not be considered as a substitute for the
operating guide of the generator assembly, nor as instructions for commissioning of the generator assembly.
OPERATING PRINCIPLE
Post-combustion mode
The gas turbine and duct burner are in operation.
The duct burner increases the temperature of the gas turbine exhaust gas (to 820C max.).
Except for start-up, the normal operating mode of the burner is with all the twelve burner heads. Moreover, in
order to increase the availability, the burner is allowed to operate with only height (8) burner heads
(44)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8.3 CONTROL OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 17/02/2009
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 1 - 3/7
FIVES PILLARD
2. SUPPLEMENTARY FIRING LOAD CONTROL
The supplementary firing load control is implemented on the DCS.
Purpose: maintaining constant the HRSG outlet steam flow
When the burner is off, or during the burner light off sequence, the load is forced to the minimum value
(20%).
Once the burner is operate with eight (8) heads, the BMS send to the DCS information "LOAD RELEASED
TO MODULATE". At this moment, the load can modulate from the minimum value (20%) to the high limit
value, calculated into the DCS depending to the GT load and the number of burner heads on.
2.1. CALCULATION OF THE LOAD UPPER LIMIT
The SF load HIGH limit value is calculated according to the bellowed formula:
(Ouput ot the curve) x (number of burner heads ignited)
12
2.2. LOAD CONTROL OPERATING MODE
- Automatic mode: the load is issue from the controller, depending on the difference between the reading
and the set point
- Manual mode:
o load modified by the operator intervening on the output signal from the controller of the DCS
(with the switch on the BMS cubicle on the position "DCS"
o load modified by the operator intervening on the output signal from Auto/Manual station of the
CCS (with the switch on the BMS cubicle on the position "BMS" or "LOCAL")
(45)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8.3 CONTROL OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 17/02/2009
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 1 - 4/7
FIVES PILLARD
3. COMBUSTION CONTROL
The purpose of combustion control is to convert the signal from the load control into thermal output, in order to
ensure the steam flow rate required from the generator. The combustion control is based on the fuel flow rate
measurement. The principle is to adjust the fuel flow according to the load required.
3.1. FUEL GAS CONTROL
Purpose:
maintaining constant the burner fuel gas pressure during the light off sequence of the burner
adjusting the fuel gas flow according to the power set point send by the DCS.
PRINCIPLE
As the burner if off, and until the light off of the first burner is ended, the gas fuel control valve is forced on the
light off opening position (controller on TRACK mode). When the first burner head is lighted off, the fuel gas
pressure control is allowed to modulate until the eighth burner head is lighted off. At this moment, the fuel gas
control is automatically switched from fuel gas pressure control to fuel gas flow control.
During the burner light off, the adjustment is proportional to the difference between the burner fuel
gas pressure measurement and the set point defined during the commissioning.
After the light off of the eighth burner head, the adjustment is proportional to the difference between
the gas flow measurement and the gas flow set point calculated by the CCS to ensure power demand
from the DCS.
3.1.1. FUEL GAS PRESSURE CONTROL
PRINCIPLE
The pressure controller adjust the fuel gas burner pressure control valve position; taking into account the
difference between the fuel gas burner pressure reading, and the set point set during the commissioning.
IMPLEMENTATION:
Fuel gas burner pressure reading (HJG10 CP002)
Pressure controller
Fuel gas flow control valve (HJG10 AA101)
FUEL GAS PRESSURE CONTROL OPERATING MODE
When the burner is off or during the light off of the first burner head: controller forced on track mode, output
value = fuel gas flow control valve start up value.
When the fuel gas control flow is released to modulate: controller forced on track mode, output value = fuel gas
flow controller output value.
Once the first burner head is ignited until the end of the light off of the 10
th
burner head : automatic remote mode;
the output depending of the difference between the fuel gas burner pressure and the pressure set point definite
during the commissioning.
Manual mode is not allowed.
3.1.2. FUEL GAS FLOW CONTROL
PRINCIPLE
(46)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8.3 CONTROL OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 17/02/2009
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 1 - 5/7
FIVES PILLARD
The flow controller adjust the fuel gas flow control valve position; taking into account the difference between the
fuel gas flow measurement (calculated with temperature and pressure correction) , and the set point calculated
by the CCS regarding the load signal send by the DCS.
IMPLEMENTATION:
Fuel gas flow reading (HJG10 CF001)
Fuel gas pressure reading (HJG10 CP001)
Fuel gas temperature reading (HJG10 CT001)
Flow controller
Fuel gas flow control valve (HJF10 AA101)
FUEL OIL FLOW CONTROL OPERATING MODE
When the burner is off or during the light off of the 10 first burner head: controller forced on track mode, output
value = fuel gas pressure controller output value.
When the fuel gas flow control is released to modulate: automatic remote mode: the output is depending of the
difference between the corrected fuel gas flow and the fuel gas flow set point calculated by the CCS according to
the load value send by the DCS.
3.2. DIESEL OIL CONTROL
Purpose:
maintaining constant the burner diesel oil pressure during the light off sequence of the burner
adjusting the diesel oil flow according to the power set point send by the DCS.
PRINCIPLE
As the burner if off, and until the light off of the first burner is ended, the diesel oil control valve is forced on the
light off opening position (controller on TRACK mode). When the first burner head is lighted off, the diesel oil
pressure control is allowed to modulate until the eighth burner head is lighted off. At this moment, the diesel oil
control is automatically switched from diesel oil pressure control to diesel oil flow control.
During the burner light off, the adjustment is proportional to the difference between the burner diesel
oil pressure measurement and the set point defined during the commissioning.
After the light off of the tenth burner head, the adjustment is proportional to the difference between
the diesel oil flow measurement and the diesel oil flow set point calculated by the CCS to ensure
power demand from the DCS.
3.2.1. DIESEL OIL PRESSURE CONTROL
PRINCIPLE
The pressure controller adjust the diesel oil burner pressure control valve position; taking into account the
difference between the diesel oil burner pressure reading, and the set point set during the commissioning.
IMPLEMENTATION:
Diesel oil burner pressure reading (HJF10 CP001)
Pressure controller
Diesel oil flow control valve (HJG10 AA101)
DIESEL OIL PRESSURE CONTROL OPERATING MODE
When the burner is off or during the light off of the first burner head: controller forced on track mode, output
value = diesel oil flow control valve start up opening.
(47)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8.3 CONTROL OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 17/02/2009
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 1 - 6/7
FIVES PILLARD
When the diesel oil control flow is released to modulate: pressure controller forced on track mode, output value
= diesel oil flow controller output value.
Once the first burner head is ignited until the end of the light off of the 10
th
burner head : automatic remote mode;
the output depending of the difference between the diesel oil burner pressure and the pressure set point definite
during the commissioning.
Manual mode is not allowed.
3.2.2. DIESEL OIL FLOW CONTROL
PRINCIPLE
The flow controller adjust the diesel oil flow control valve position; taking into account the difference between the
diesel oil flow reading, and the set point calculated by the CCS regarding the load signal send by the DCS.
IMPLEMENTATION:
Diesel oil flow reading (HJF10 CF001)
Flow controller
Diesel oil flow control valve (HJF10 AA101)
DIESEL OIL FLOW CONTROL OPERATING MODE
When the burner is off or during the light off of the 10 first burner head: controller forced on track mode, output
value = diesel oil pressure controller output value.
When the diesel oil flow control is released to modulate: automatic remote mode: the output is depending of the
difference between the diesel oil flow and the diesel oil flow set point calculated by the CCS according to the load
value send by the DCS.
4. DIESEL OIL HIGH PRESSURE CONTROL
PURPOSE
maintaining constant diesel oil pressure at the inlet of the Diesel oil general valve skid.
PRINCIPLE
The pressure controller adjust the diesel oil high pressure control valve position taking into account the difference
between diesel oil pressure reading (HJF10-CP001) and the local pressure set point define during the
commissioning.
The diesel oil HP control valve is a discharged valve; the diesel oil flow passed through the control valve has to
return to the diesel oil tank because for a matter of risk of diesel oil high temperature (which leads diesel oil
vaporization and HP booster pump cavitation), the return to the inlet of the HP booster pumps is not possible.
NOTA : When the two diesel oil pumps are not running, the controller is forced on tracking mode, output set to
the full opening value.
IMPLEMENTATION:
Diesel oil high pressure reading (HJF01 CP001)
Pressure controller
Diesel oil high pressure control valve (HJG01 AA101)
DIESEL OIL HIGH PRESSURE CONTROL OPERATING MODE
Manual mode : the diesel oil high pressure control valve opening is set by the operator intervening on the
output signal from the controller of the CCS (modification from the DCS is remote selected; modification from
the HMI on the BMS cubicle if local selected)
(48)
FUJAIRAH II O & M MANUAL
PART 8.3 CONTROL OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Date: 17/02/2009
08.0.0.1436.00
Rev. 1 - 7/7
FIVES PILLARD
Automatic mode : the diesel oil high pressure control valve opening is issued from the pressure controller,
depending of the difference between diesel oil pressure reading (HJF10-CP001) and the local pressure set
point definite during the commissioning.
5. ATOMIZING STEAM PRESSURE
PURPOSE
Adjusting the atomizing steam pressure at the inlet of the fuel valves skids.
PRINCIPLE
The atomizing pressure controller adjust the atomizing steam pressure control valve position taking into account
the difference between atomizing steam pressure reading (HJM10-CP001 or HJM10-CP002) and the calculated
pressure set point depending to the diesel oil pressure at the burner inlet..
NOTA 1 : There are two atomizing pressure measures (HJM10-CP001 & HJM10-CP002), the operator can
selected the active transmitter on the DCS or on the CCS HMI depending to the control place selected.
NOTA 2 : When all the burner heads are stopped, the atomizing control valve is forced on its start up value
IMPLEMENTATION:
Burner Diesel oil pressure measurement (HJF10 CP001)
Atomizing steam pressure measurement 1 (HJM10-CP001)
Atomizing steam pressure measurement 2 (HJM10-CP002)
Atomizing steam pressure measurement selector
Pressure controller
Atomizing pressure control valve (HJG01 AA101)
ATOMIZING PRESSURE CONTROL OPERATING MODE
Manual mode : not allowed
Automatic mode : the atomizing pressure control valve opening is issued from the pressure controller,
depending of the difference between atomizing pressure reading (HJF10-CP001) and the calculated set point.
Track mode: when all the burners head are stopped ,the pressure control valve is forced on its start up
opening value
(49)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- HRSG Operator Training ManualDocumento184 pagineHRSG Operator Training ManualXcdxtv100% (10)
- Shuaiba North HRSG ManualDocumento91 pagineShuaiba North HRSG Manualmartinp17171100% (7)
- Thermal Power Plant: Pre-Operational ActivitiesDa EverandThermal Power Plant: Pre-Operational ActivitiesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- Turbine Generator Operation ManualDocumento273 pagineTurbine Generator Operation ManualRizqi Priatna100% (1)
- Document Submission Status Feedwater SystemDocumento20 pagineDocument Submission Status Feedwater SystemMinh Hoang NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Steam TurbineDocumento64 pagineSteam TurbineLeelananda100% (6)
- Boiler Feed Pump Review PresentationDocumento29 pagineBoiler Feed Pump Review Presentationprmukkundi100% (8)
- HRSG StartupDocumento20 pagineHRSG Startupsujiv_sujiv1278100% (1)
- 220021enc Combined Cycle Power Plant OverviewDocumento27 pagine220021enc Combined Cycle Power Plant OverviewBalajirao Samatham100% (4)
- (Mech) Gland Steam SystemDocumento7 pagine(Mech) Gland Steam SystemThanh Son100% (1)
- Contoh CCPP Plant Operating Manual ProceduresDocumento163 pagineContoh CCPP Plant Operating Manual ProceduresDwi Mulyanti Dwimulyantishop100% (1)
- CCPPDocumento34 pagineCCPPphanindra100% (1)
- 02B HRSGDocumento50 pagine02B HRSGrseclen100% (2)
- SEC A Bekasi Design SpecDocumento20 pagineSEC A Bekasi Design Speccharleselitb92Nessuna valutazione finora
- HRSG Operator Training Manual PDFDocumento184 pagineHRSG Operator Training Manual PDFMohammed Yusuf100% (1)
- Steam Turbine InterlocksDocumento69 pagineSteam Turbine InterlocksSarah Frazier100% (2)
- Start-Up in Steps Siemens V94.2 Gas Turbine at KAPCODocumento13 pagineStart-Up in Steps Siemens V94.2 Gas Turbine at KAPCOFazalur Rehman Babar89% (19)
- Professional: October 2017 DR - Hans-Peter WolfDocumento34 pagineProfessional: October 2017 DR - Hans-Peter WolfJeeEianYann100% (2)
- O & M ManualDocumento131 pagineO & M Manualt_syamprasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Once Through BoilerDocumento9 pagineOnce Through Boilerbhuvi_patu12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Combined Cycle FundamentalsDocumento76 pagineCombined Cycle FundamentalsVinnu89% (9)
- Feasibility Study Report (1) ESPDocumento32 pagineFeasibility Study Report (1) ESPrajanarsuNessuna valutazione finora
- 600MW Training Manual of Boiler 20110326Documento94 pagine600MW Training Manual of Boiler 20110326chandhramohan100% (5)
- Air PreheaterDocumento11 pagineAir PreheaterSuresh Ramakrishnan100% (1)
- SuperCritical Boiler 1Documento45 pagineSuperCritical Boiler 1swatantar17100% (1)
- MHPS GT F ClassDocumento9 pagineMHPS GT F Classkp pkNessuna valutazione finora
- Combined Cycle PrinciplesDocumento43 pagineCombined Cycle PrinciplesFazalur Rehman Babar100% (1)
- Gek 107061Documento10 pagineGek 107061Anup MitraNessuna valutazione finora
- Turbine ManualDocumento399 pagineTurbine ManualSandeep Kumar100% (2)
- Part 1 Operation Manual of Steam TurbineDocumento157 paginePart 1 Operation Manual of Steam TurbineAshutosh Kushwaha75% (12)
- HRSG 2011 BrochureDocumento12 pagineHRSG 2011 BrochureAndry SetiawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Aes Chile Boiler Inspection 101 Nov - 2008Documento73 pagineAes Chile Boiler Inspection 101 Nov - 2008Hugo Alfredo Calderon Tapia100% (1)
- 2 - 1!01!02 - Basic Operation Concept For Turbine and Auxiliary Plant - r00Documento59 pagine2 - 1!01!02 - Basic Operation Concept For Turbine and Auxiliary Plant - r00Tiara Noir100% (2)
- Heat Recovery Steam Generator Operation ManualDocumento45 pagineHeat Recovery Steam Generator Operation ManualReyes Sanchez100% (1)
- Heat Recovery Steam GeneratorDocumento69 pagineHeat Recovery Steam GeneratorAayushi Agarwal100% (5)
- Lm6000 PF Plus Fact SheetDocumento2 pagineLm6000 PF Plus Fact SheetNivaldo GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- HRSG 01 Basic DesignDocumento40 pagineHRSG 01 Basic DesignPremadi SetyokoNessuna valutazione finora
- Commissioning of Combined Cycle Power PlantsDocumento30 pagineCommissioning of Combined Cycle Power Plantsa_mohid1780% (5)
- Ventilator ValveDocumento2 pagineVentilator ValveThiyagarajan Rajendran100% (1)
- Kawasaki Gas TurbineDocumento45 pagineKawasaki Gas Turbinepramasenja100% (2)
- Ger 3620n Heavy Duty Gas Turbine Operationg Maintenance ConsiderationsDocumento60 pagineGer 3620n Heavy Duty Gas Turbine Operationg Maintenance Considerationszomglolzscribd100% (3)
- HRSG PDFDocumento248 pagineHRSG PDFaztec20100% (11)
- Alstom New Designs PDFDocumento18 pagineAlstom New Designs PDF55312714100% (1)
- Steam Turbine - Q & A 1Documento104 pagineSteam Turbine - Q & A 1rahul_choubey_9100% (6)
- 02.SIPP-PP-07-M02 - IFC - 0 - Steam Turbine and Main Valves Installation ProcedureDocumento422 pagine02.SIPP-PP-07-M02 - IFC - 0 - Steam Turbine and Main Valves Installation ProcedureBadr MoutassarefNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimizing Duct Burner Performance Through MaintenanceDocumento10 pagineOptimizing Duct Burner Performance Through MaintenancePajooheshNessuna valutazione finora
- Piping Connection EquipmentDocumento19 paginePiping Connection EquipmentOmar TocmoNessuna valutazione finora
- Equipment List: Biturox Bitumen Blowing UnitDocumento10 pagineEquipment List: Biturox Bitumen Blowing UnitOsamah AdelNessuna valutazione finora
- 014 MS For General Scaffolding PDFDocumento33 pagine014 MS For General Scaffolding PDFfdfazfzNessuna valutazione finora
- FORM001 Inspect Report For Receiving MaterialDocumento1 paginaFORM001 Inspect Report For Receiving MaterialAndile CeleNessuna valutazione finora
- Concrete FoundationsDocumento8 pagineConcrete FoundationssakrakirfanNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction Security Plan SampleDocumento21 pagineConstruction Security Plan SampleKumar100% (15)
- 0100 Q-Pa 0003 DDocumento49 pagine0100 Q-Pa 0003 DNaved JattNessuna valutazione finora
- Laggan-Tormore Project: TOTAL E&P UK LimitedDocumento2 pagineLaggan-Tormore Project: TOTAL E&P UK LimitedApostolie IulianNessuna valutazione finora
- Waterproofing BldgsDocumento17 pagineWaterproofing BldgssakrakirfanNessuna valutazione finora
- YT-PF-Z-16-00202 Rev B Method Statement of GRPDocumento47 pagineYT-PF-Z-16-00202 Rev B Method Statement of GRPsethu1091100% (9)
- Hydro TestingDocumento26 pagineHydro TestingMahaveer SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- BAP-00-80-PE-0203-R R.2 Review and Approval Procedure - ASF 18.03.14Documento12 pagineBAP-00-80-PE-0203-R R.2 Review and Approval Procedure - ASF 18.03.14Jan Richardo GultomNessuna valutazione finora
- Part Number TW600: Installation, Operation, and MaintenanceDocumento20 paginePart Number TW600: Installation, Operation, and MaintenanceLuis AlbarracinNessuna valutazione finora
- Sulfur Process Technology136 - 111155Documento15 pagineSulfur Process Technology136 - 111155Ajay TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- LW22Documento2 pagineLW22Nicolae MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Propane Storage Tanks and Vaporizers ExplainedDocumento11 paginePropane Storage Tanks and Vaporizers ExplainedNicolae MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Welders TerminologyDocumento37 pagineWelders TerminologyNicolae Marin100% (2)
- Emcp 2Documento4 pagineEmcp 2Muhammad Ahsen100% (2)
- GeneratorsDocumento54 pagineGeneratorsNicolae Marin100% (1)
- ASHRAE Units PolicyDocumento22 pagineASHRAE Units PolicyNicolae MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- LW 7Documento1 paginaLW 7Nicolae MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Maria Deleanu Carte de BucateDocumento46 pagineMaria Deleanu Carte de BucateNicolae Marin0% (1)
- Introduction To Automatic SynchronizingDocumento12 pagineIntroduction To Automatic SynchronizingGavaskar GovindarajNessuna valutazione finora
- PropaneDocumento20 paginePropaneNicolae MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- IMPCO Training ManualDocumento145 pagineIMPCO Training ManualNicolae MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Refining Sector in KazakhstanDocumento8 pagineRefining Sector in KazakhstanVarun RockonNessuna valutazione finora
- HSEDocumento28 pagineHSENicolae Marin100% (1)
- Welders TerminologyDocumento37 pagineWelders TerminologyNicolae Marin100% (2)
- GeneratorsDocumento54 pagineGeneratorsNicolae Marin100% (1)
- OilandGas Tax Guide 2011 FINALDocumento498 pagineOilandGas Tax Guide 2011 FINALhundudeNessuna valutazione finora
- BETADocumento19 pagineBETANicolae MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformer Oil Regeneration SystemDocumento16 pagineTransformer Oil Regeneration SystemNicolae Marin100% (1)
- Gas ProcessingDocumento104 pagineGas ProcessingNicolae Marin100% (3)
- Trafic IncidentsDocumento17 pagineTrafic IncidentsNicolae MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Conversion RefineryDocumento1 paginaConversion RefineryNicolae MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- KEB FCCU ExpansionJoints PDFDocumento12 pagineKEB FCCU ExpansionJoints PDFhuangjlNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling of Non-Isothermal Fluid Catalytic Cracking Riser ReactorDocumento6 pagineModeling of Non-Isothermal Fluid Catalytic Cracking Riser ReactorEdgar Enrique Diaz MarquinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling VacuumDocumento128 pagineModeling VacuumNicolae MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Vendor Data Register: DOC. NO.: 09035-00-LST-VP-EL011-001 JOB NO.: 2009035Documento2 pagineVendor Data Register: DOC. NO.: 09035-00-LST-VP-EL011-001 JOB NO.: 2009035Nicolae MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipelines InterventionDocumento8 paginePipelines InterventionNicolae MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- FCC Emergency Interlock SystemDocumento3 pagineFCC Emergency Interlock SystemSALEHIBRAHIMNessuna valutazione finora
- Petroconsult Provides Engineering Services & Training for Oil & Gas IndustryDocumento18 paginePetroconsult Provides Engineering Services & Training for Oil & Gas IndustryNicolae MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Commercial Survey AUV: Valve AbbreviationsDocumento8 pagineCommercial Survey AUV: Valve AbbreviationsMario StrašniNessuna valutazione finora
- Keystone Butterfly Valve ParaSeal RangeDocumento16 pagineKeystone Butterfly Valve ParaSeal RangetungNessuna valutazione finora
- Slurry Pumping CalculationsDocumento4 pagineSlurry Pumping CalculationsSourav ChattopadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Tormene: L 5-10 X DNDocumento1 paginaTormene: L 5-10 X DNRoyer LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipeline Insulation Material Specs and QuantitiesDocumento1 paginaPipeline Insulation Material Specs and QuantitiesPriya TanejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Esquema de Tubos FabiusDocumento1 paginaEsquema de Tubos FabiusRobson BarrosNessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure Vessel - LSPDocumento4 paginePressure Vessel - LSPPengelana KehidupanNessuna valutazione finora
- Orifice Plate ReportDocumento1 paginaOrifice Plate ReportdsdeNessuna valutazione finora
- EvaporatorDocumento2 pagineEvaporatorDe JavuNessuna valutazione finora
- V S C Sec C Cte Ve Va: Pressure Control ValvesDocumento13 pagineV S C Sec C Cte Ve Va: Pressure Control Valvesfrederick alayonNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Pipe IsometricsDocumento2 pagineSample Pipe Isometricslinkinpark11129116Nessuna valutazione finora
- General HydraulicsDocumento60 pagineGeneral HydraulicsHector Sepulveda Orellana100% (1)
- SCX180 Catalog REV 01-08Documento32 pagineSCX180 Catalog REV 01-08Horea CordunianuNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Compressor Inlet Valve (Or Intake Valve - Unloader Valve)Documento6 pagineAir Compressor Inlet Valve (Or Intake Valve - Unloader Valve)anup_nairNessuna valutazione finora
- BOP Modifications GuideDocumento21 pagineBOP Modifications Guidecrd1990Nessuna valutazione finora
- p γ υ z H p γ υ z H: Problem 7Documento4 paginep γ υ z H p γ υ z H: Problem 7Ariel GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.expansion DevicesDocumento18 pagine4.expansion DevicesAbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Reinforced Branch Connection in A Piping System - Set-On TypeDocumento2 pagineReinforced Branch Connection in A Piping System - Set-On TypeRajendra LabadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Check Point 1250 Lista de PartesDocumento6 pagineCheck Point 1250 Lista de PartesRoberto Eduardo Salvador MonteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Schedule Serious Inspection Boiler Dan Esp Pt. Cahaya Fajar Kaltim Unit 2 Tahun 2019Documento3 pagineSchedule Serious Inspection Boiler Dan Esp Pt. Cahaya Fajar Kaltim Unit 2 Tahun 2019Nur Ali SaidNessuna valutazione finora
- Valve Drawing VSG2 PDFDocumento1 paginaValve Drawing VSG2 PDFGỗ MộcNessuna valutazione finora
- Backing Rings Data PDFDocumento1 paginaBacking Rings Data PDFAbhijeet SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- K FactorDocumento4 pagineK FactorSumanta BhayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Novenco Provision Ref Unit 081246 QPPDocumento1 paginaNovenco Provision Ref Unit 081246 QPPSady KanettiNessuna valutazione finora
- API Index ListDocumento18 pagineAPI Index ListRaja Ahsan AzanNessuna valutazione finora
- TSSA Fuels Safety High Pressure Piping Code, TSSA HPP-2017 November 2017Documento7 pagineTSSA Fuels Safety High Pressure Piping Code, TSSA HPP-2017 November 2017Manoj SaralayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Yanbu: Export Refinery ProjectDocumento7 pagineYanbu: Export Refinery ProjectJanakiraman MalligaNessuna valutazione finora
- NACA-RM-A52B13-The Effect of Bluntness On The Drag of Spherical-Tipped Truncated Cones of Fineness Ratio 3 at Mach Numbers 1.2 To 7.4Documento20 pagineNACA-RM-A52B13-The Effect of Bluntness On The Drag of Spherical-Tipped Truncated Cones of Fineness Ratio 3 at Mach Numbers 1.2 To 7.4dalfeNessuna valutazione finora
- Fil Sep Equipments Pvt. Ltd. Part ListDocumento1 paginaFil Sep Equipments Pvt. Ltd. Part ListAjay PrajapatiNessuna valutazione finora