Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
TALLER 2estructura Indices
Caricato da
SergioNovoa0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
135 visualizzazioni3 pagineCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
135 visualizzazioni3 pagineTALLER 2estructura Indices
Caricato da
SergioNovoaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
TALLER 2. CIENCIA DE MATERIALES. ESTRUCTURAS CRISTALINAS.
1. Calcule la densidad del aluminio fcc y del vanadio bcc.
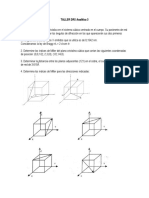
2. Dibuje los vectores unitarios [111],[110],[121] y [113].
3. Dibuje las siguientes direcciones en una celda BCC y enumere las coordenadas de posicin de los tomos cuyos centros
son cortados por cada direccin: [100],[110] y [111].
4. Calcule la densidad atmica lineal en tomos/mm para el iridio FCC que tiene una constante de red de 0.38389 nm, en
las direcciones 100],[110] y [111].
5. Calcule la densidad atmica planar en tomos/mm
2
para el cromo BCC en los planos (111), (001) y (110) si a = 0.2846
nm.
6. Calcule el volumen de la celda unitaria de la estructura cristalogrfica del zinc con la siguiente informacin HCP, a =
0.2665 nm y c = 0.4947 nm.
7. El hierro puro a 20 C es BCC y tiene un radio atmico de 0.124 nm. Calcule la constante de red y la longitud de la
diagonal ms larga.
8. Determine la distancia entre los planos cristalinos (110)
9. Calcule la densidad planar para los planos (010) y (020) en el polonio cubico simple que tiene un parmetro de red de
0.334 nm.
10. Calcule la densidad del hierro BCC que tiene un parmetro de red de 0.2866 nm.
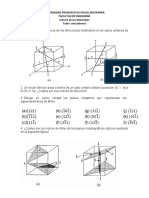
11. Determine los ndices de Miller en las siguientes figuras
12. Un difractograma para un elemento presenta picos de difraccin para ngulos 2 38.68, 55.71, 69.70, 82.55, 95.00 y
107.67. (la longitud de onda de la radiacin incidente es de 0,15405 nm). Determinar la estructura cristalina, el
parmetro de red e identifique el elemento.
13. El patrn de difraccin que se muestra en la figura fue realizado con rayos X cuya longitud de onda fue de 0,15418 nm.
Calcule la estructura cristalina, los ndices de los planos que producen cada pico y el parmetro de red.
14. A diffracted x-ray beam is observed from the (311) planes of aluminum at a 2 angle of 78.3 when x-rays of 0.15418 nm
wavelength are used. Calculate the lattice parameter of the aluminum.
15. Determine the planar density for BCC lithium in the (100), (110), and (111) planes.
16. Determine the Miller indices of the plane that passes through three points having the following coordinates.
(a) 0,0,1; 1,0,0; and 12,12,0
(b) 12,0,1; 12,0,0; and 0,1,0
(c) 1,0,0; 0,1,12; and 1,12,14
(d) 1,0,0; 0,0,14; and 12,1,0
17. Below are listed the atomic weight, density, and atomic radius for three hypothetical alloys. For each determine whether
its crystal structure is FCC, BCC, or simple cubic and then justify your determination.
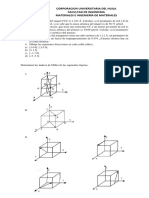
18. Determine the indices for the directions shown in the following cubic unit cell:
19. Determine the Miller indices for the planes shown in the following unit cell:
20. The metal rhodium has an FCC crystal structure. If the angle of diffraction for the (311) set of planes occurs at (first-order
reflection) when monochromatic x-radiation having a wavelength of 0.0711 nm is used, compute (a) the interplanar
spacing for this set of planes, and (b) the atomic radius for a rhodium atom..
21. Figure shows the first five peaks of the x-ray diffraction pattern for a element; monochromatic x-radiation having a
wavelength of 0.1542 nm was used. (a) Index (i.e., give h, k, and l indices) for each of these peaks. (b) Determine the
interplanar spacing for each of the peaks. C) determine the crystal structure and the element.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Caracterización química, morfológica y estructural de materialesDa EverandCaracterización química, morfológica y estructural de materialesNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller de Estructuras CristalinasDocumento7 pagineTaller de Estructuras CristalinasJean Pierre Leon Bueno OsorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller Cristalografía I 2021Documento4 pagineTaller Cristalografía I 2021Diego LemusNessuna valutazione finora
- Guia Ejercicios Estructura CristalinaDocumento4 pagineGuia Ejercicios Estructura CristalinaPandak On Merkén100% (1)
- Mecánica de la fractura y análisis de falla en metalesDa EverandMecánica de la fractura y análisis de falla en metalesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Taller de Estructuras CristalinasDocumento7 pagineTaller de Estructuras CristalinasDaniel SarriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unidad 1 Tarea 3Documento2 pagineUnidad 1 Tarea 3ironalejanNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller Sobre Estructuras y Geometrías CristalinasDocumento3 pagineTaller Sobre Estructuras y Geometrías CristalinasOscar Andres Pinzon GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Ejercicios Resueltos de Estructura Cristalina y DesnidadesDocumento15 pagine1 Ejercicios Resueltos de Estructura Cristalina y DesnidadesAron MasíasNessuna valutazione finora
- Problemario Tema 3 - Arreglo Atomico y Estruc CristalinaDocumento4 pagineProblemario Tema 3 - Arreglo Atomico y Estruc CristalinaluisalejandropiñapijalNessuna valutazione finora
- Práctica de Problemas #2Documento3 paginePráctica de Problemas #2Joel LazoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dispositivos ElectronicosDocumento8 pagineDispositivos ElectronicosAnthony Saavedra GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller Ciencia de Los Materiales 1er Corte PDFDocumento2 pagineTaller Ciencia de Los Materiales 1er Corte PDFAndres Camilo ChocontaNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller Ciencia de Los Materiales 1er CorteDocumento2 pagineTaller Ciencia de Los Materiales 1er Cortebrayan chocontaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1serie11 2Documento3 pagine1serie11 2Katherin SanzNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller Ciencia de Los Materiales. 3era UnidadDocumento1 paginaTaller Ciencia de Los Materiales. 3era UnidadSentencia 1994Nessuna valutazione finora
- Taller 6Documento3 pagineTaller 6sjdjd ddjdjfNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller Propiedades y Estructuras PDFDocumento2 pagineTaller Propiedades y Estructuras PDFNelsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Problemas Propuestos 2Documento5 pagineProblemas Propuestos 2Aru HuamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Segunda Lista PDFDocumento3 pagineSegunda Lista PDFGustavo GuillénNessuna valutazione finora
- Tarea de Ciencia e Ingeniería de Los MaterialesDocumento3 pagineTarea de Ciencia e Ingeniería de Los MaterialesFrancisco Alejandro Ramírez Díaz0% (1)
- Unidad 1Documento4 pagineUnidad 1ironalejanNessuna valutazione finora
- Practica DispoDocumento2 paginePractica DispoxxfolladorNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller Número 3 - MaterialesDocumento2 pagineTaller Número 3 - MaterialesNicolas Eduardo Gomes HerreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller N°1 Materiales Corte 2Documento2 pagineTaller N°1 Materiales Corte 2Jacobo NaderNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios Parametros de RedDocumento3 pagineEjercicios Parametros de RedCECIA MALQUI DIAZNessuna valutazione finora
- SOLIDIFICACIONDocumento3 pagineSOLIDIFICACIONMaria Fernanda Galvez GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Guía de EjerciciosDocumento5 pagineGuía de EjerciciosGabriel CNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller DRXDocumento3 pagineTaller DRXDANIELA ALARCÓN SILVANessuna valutazione finora
- Teller 3Documento2 pagineTeller 3Sofia RosasNessuna valutazione finora
- TalleresDocumento8 pagineTalleresFelipe Garcia67% (3)
- Practica 1 Ciencia de Los MaterialesDocumento5 paginePractica 1 Ciencia de Los MaterialesCarla Flores0% (1)
- Taller 3Documento1 paginaTaller 3Namy BriNessuna valutazione finora
- Materiales Industriales 2016-Trabajo Practico #1Documento3 pagineMateriales Industriales 2016-Trabajo Practico #1Fernando F CabezasNessuna valutazione finora
- PROBLEMARIO 1er DEP CyD A20Documento4 paginePROBLEMARIO 1er DEP CyD A20Ivan Carpio VilchisNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratorio de CristalografiaDocumento3 pagineLaboratorio de CristalografiaCésar Anthony Díaz EsquénNessuna valutazione finora
- Banco Intro Ducci Enc I A Material EsDocumento12 pagineBanco Intro Ducci Enc I A Material EsE HernándezNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller N°1 Materiales Corte 2Documento2 pagineTaller N°1 Materiales Corte 2juan david chavarrioNessuna valutazione finora
- Segundo Taller 2018-IDocumento1 paginaSegundo Taller 2018-IPaola MurilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Problemario 1 Parte No 1Documento3 pagineProblemario 1 Parte No 1Israel YllescasNessuna valutazione finora
- Asignación 3Documento2 pagineAsignación 3Santiago Salgado TrujilloNessuna valutazione finora
- TALLER Unidad I - Materiales No MetalicosDocumento2 pagineTALLER Unidad I - Materiales No MetalicosGabriel MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Clase 5. Ejercicio BDocumento1 paginaClase 5. Ejercicio BCarlos FrancisNessuna valutazione finora
- Propuestos de MaterialesDocumento2 paginePropuestos de MaterialesmariNessuna valutazione finora
- Serie 03 FMyM (Estruturas Cristalinas)Documento3 pagineSerie 03 FMyM (Estruturas Cristalinas)RebecaNessuna valutazione finora
- P1 - Estructuras CristalinasDocumento4 pagineP1 - Estructuras CristalinasAinoaNessuna valutazione finora
- Asignación 5 2020Documento3 pagineAsignación 5 2020Alida Moreno0% (2)
- Taller 2 - Cristalografía y Difracción de Rayos XDocumento2 pagineTaller 2 - Cristalografía y Difracción de Rayos XLUIS FERNANDO DÁVALOS CASTRONessuna valutazione finora
- Taller Cristalografia, Enlace Quimico, Teoria Atómica y DRX PDFDocumento7 pagineTaller Cristalografia, Enlace Quimico, Teoria Atómica y DRX PDFViviana Sanchez GambaNessuna valutazione finora
- Problemas Fisica Del Estado SolidoDocumento2 pagineProblemas Fisica Del Estado SolidomaikosNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios y CuestioDocumento4 pagineEjercicios y Cuestiojulio gutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Prob Tema 2Documento4 pagineProb Tema 2sebas LuqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Trabajo Práctico 1Documento4 pagineTrabajo Práctico 1Franco DemonariNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF Practica de Problemas 2 - CompressDocumento3 paginePDF Practica de Problemas 2 - CompressRomeo SolísNessuna valutazione finora
- EjerciciosDocumento17 pagineEjerciciosKevin Casanova MartínezNessuna valutazione finora
- Leoanfer - Taller 2 - Densidad Parámetros Red ÍndicesDocumento1 paginaLeoanfer - Taller 2 - Densidad Parámetros Red ÍndiceserNessuna valutazione finora
- CristalografiaDocumento13 pagineCristalografiaKevin Casanova MartínezNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller 3Documento3 pagineTaller 3Isabel ArdilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trabajo de PedregalDocumento42 pagineTrabajo de PedregalFreddy EspinozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Work Final - Cu - AndaluciteDocumento43 pagineWork Final - Cu - AndaluciteLuis Colunche ToctoNessuna valutazione finora
- Practica 5 MineDocumento8 paginePractica 5 MineCRISTHIAN GONZALES CATAYNessuna valutazione finora
- Minerales MetamorficosDocumento4 pagineMinerales MetamorficosAlex FigueroaNessuna valutazione finora
- Microestructuras y Celdas CristalinasDocumento6 pagineMicroestructuras y Celdas CristalinasFabianNessuna valutazione finora
- Informe Yacimientos MetamórficosDocumento14 pagineInforme Yacimientos MetamórficosCarlosArévaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Tarea 3 Defectos CristalinosDocumento8 pagineTarea 3 Defectos CristalinosSoyer SoyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Trabajo 2. Suelo Mineral.Documento15 pagineTrabajo 2. Suelo Mineral.Magnolia sanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Triptico VerdanaDocumento2 pagineTriptico VerdanaGustavoCastilloRoqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Esquistos VerdesDocumento8 pagineEsquistos VerdesJuan Daly PacoticonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Isomorfismo y PolimorfismoDocumento11 pagineIsomorfismo y PolimorfismoAlison Estafani Saldana Guevara0% (1)
- Shrinkage StopingDocumento14 pagineShrinkage StopingmisaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cristalografía-Jeshua Dominguez NolascoDocumento16 pagineCristalografía-Jeshua Dominguez NolascoJeshua DomínguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller 1. Fundamentos Procesos de ManufacturaDocumento3 pagineTaller 1. Fundamentos Procesos de ManufacturaLuis VargasNessuna valutazione finora
- Cap. 4 Imperfecciones Arreglo At.Documento26 pagineCap. 4 Imperfecciones Arreglo At.Javier Lizárraga VargasNessuna valutazione finora
- Estructura CristalinaDocumento85 pagineEstructura Cristalinalisbeth camachoNessuna valutazione finora
- JJJDocumento18 pagineJJJAgustin C-aNessuna valutazione finora
- 16-Yacimientos IOCG e IOADocumento74 pagine16-Yacimientos IOCG e IOAValentinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mineralogia SistematicaDocumento103 pagineMineralogia SistematicaRicardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Elaboración de Sistemas Cristalinos en 3DDocumento6 pagineElaboración de Sistemas Cristalinos en 3DFredy QuiñonezNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentación Planta de PelletDocumento80 paginePresentación Planta de PelletAlexis Montero Olivo100% (1)
- Minerales Corteza TerrestreDocumento25 pagineMinerales Corteza TerrestreSneakers CrewNessuna valutazione finora
- CristalografiaDocumento19 pagineCristalografiajossep cuadrosNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios Balance MetalurgicoDocumento4 pagineEjercicios Balance MetalurgicoJose Miguel Parco SaavedraNessuna valutazione finora
- LEY DE CORTE CuDocumento11 pagineLEY DE CORTE CuSantiago Urquizo RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Dise o de Plantas 1640255634Documento13 pagineDise o de Plantas 1640255634alpasemaNessuna valutazione finora
- La Niquelina o NicolitaDocumento2 pagineLa Niquelina o NicolitaFernando Mantari MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Mineralizacion Minera EscondidaDocumento6 pagineMineralizacion Minera EscondidaDiego Pereira CaresNessuna valutazione finora
- AluminosilicatosDocumento16 pagineAluminosilicatosLeo VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- 02-Explotación de MinasDocumento17 pagine02-Explotación de MinasRudy quispe vargasNessuna valutazione finora
- Resetea tu mente. Descubre de lo que eres capazDa EverandResetea tu mente. Descubre de lo que eres capazValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (196)
- Psicología oscura: Una guía esencial de persuasión, manipulación, engaño, control mental, negociación, conducta humana, PNL y guerra psicológicaDa EverandPsicología oscura: Una guía esencial de persuasión, manipulación, engaño, control mental, negociación, conducta humana, PNL y guerra psicológicaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (766)
- Recupera tu mente, reconquista tu vidaDa EverandRecupera tu mente, reconquista tu vidaValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (8)
- Cómo hacer que te pasen cosas buenas: Entiende tu cerebro, gestiona tus emociones, mejora tu vidaDa EverandCómo hacer que te pasen cosas buenas: Entiende tu cerebro, gestiona tus emociones, mejora tu vidaValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1875)
- La revolución de la glucosa: Equilibra tus niveles de glucosa y cambiarás tu salud y tu vidaDa EverandLa revolución de la glucosa: Equilibra tus niveles de glucosa y cambiarás tu salud y tu vidaValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (203)
- Yo Pude, ¡Tú Puedes!: Cómo tomar el control de tu bienestar emocional y convertirte en una persona imparable (edición revisada y expandida)Da EverandYo Pude, ¡Tú Puedes!: Cómo tomar el control de tu bienestar emocional y convertirte en una persona imparable (edición revisada y expandida)Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (7)
- El poder del optimismo: Herramientas para vivir de forma más positivaDa EverandEl poder del optimismo: Herramientas para vivir de forma más positivaValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (16)
- Tus Zonas Erroneas: Guía Para Combatir las Causas de la InfelicidadDa EverandTus Zonas Erroneas: Guía Para Combatir las Causas de la InfelicidadValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (1833)
- Resumen de Pensar rápido pensar despacio de Daniel KahnemanDa EverandResumen de Pensar rápido pensar despacio de Daniel KahnemanValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (64)
- Batidos Verdes Depurativos y Antioxidantes: Aumenta tu Vitalidad con Smoothie Detox Durante 10 Días Para Adelgazar y Bajar de Peso: Aumenta tu vitalidad con smoothie detox durante 10 días para adelgazar y bajar de pesoDa EverandBatidos Verdes Depurativos y Antioxidantes: Aumenta tu Vitalidad con Smoothie Detox Durante 10 Días Para Adelgazar y Bajar de Peso: Aumenta tu vitalidad con smoothie detox durante 10 días para adelgazar y bajar de pesoValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- La metamedicina. Cada síntoma es un mensaje: La curación a tu alcanceDa EverandLa metamedicina. Cada síntoma es un mensaje: La curación a tu alcanceValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (8)
- Cómo terminar lo que empiezas: El arte de perseverar, pasar a la acción, ejecutar los planes y tener disciplinaDa EverandCómo terminar lo que empiezas: El arte de perseverar, pasar a la acción, ejecutar los planes y tener disciplinaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- La violencia invisible: Identificar, entender y superar la violencia psicológica que sufrimos (y ejercemos) en nuestra vida cotidianaDa EverandLa violencia invisible: Identificar, entender y superar la violencia psicológica que sufrimos (y ejercemos) en nuestra vida cotidianaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Sistema nervioso y osteopatía: Nervios periféricos, meninges craneales y espinales, y sistema nervioso vegetativo (Color)Da EverandSistema nervioso y osteopatía: Nervios periféricos, meninges craneales y espinales, y sistema nervioso vegetativo (Color)Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (9)
- Influencia. La psicología de la persuasiónDa EverandInfluencia. La psicología de la persuasiónValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (14)
- Escritura terapéutica. El poder curativo de la expresión escritaDa EverandEscritura terapéutica. El poder curativo de la expresión escritaValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Una mente en calma: Técnicas para manejar los pensamientos intrusivosDa EverandUna mente en calma: Técnicas para manejar los pensamientos intrusivosValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (142)
- Cómo romper el ciclo de pensamientos negativosDa EverandCómo romper el ciclo de pensamientos negativosValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (274)
- Tu cerebro emocional: Saca partido de lo que sientes y transforma tu vidaDa EverandTu cerebro emocional: Saca partido de lo que sientes y transforma tu vidaValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Zensorialmente : Dejá que tu cuerpo sea tu cerebroDa EverandZensorialmente : Dejá que tu cuerpo sea tu cerebroNessuna valutazione finora
- Técnicas de resolución de problemas: En la vida diaria y profesionalDa EverandTécnicas de resolución de problemas: En la vida diaria y profesionalValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Liberación del trauma: Perdón y temblor es el caminoDa EverandLiberación del trauma: Perdón y temblor es el caminoValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)