Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Physical Chemistry For The Life Sciences
Caricato da
snowblindedDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Physical Chemistry For The Life Sciences
Caricato da
snowblindedCopyright:
Formati disponibili
EXERCISES 213
solubility of the protein to such an extent that the protein precipitates
from solution. Tis observation is called the salting-out efect and is
used widely by biochemists to isolate and purify proteins. Consider
the equilibrium PX
n
(s) 7 P
n+
(aq) + nX
(aq), where P
n+
is a
polycationic protein of charge +n and X
is its counter-ion. Use Le
Chateliers principle and the physical principles behind the Debye
Hckel theory to provide a molecular interpretation for the salting-in
and salting-out efects.
5.15 Te overall reaction for the active transport of Na
+
and K
+
ions
by the Na
+
/K
+
pump is
3 Na
+
(aq,inside) + 2 K
+
(aq,outside) + ATP
ADP + P
i
+ 3 Na
+
(aq,outside) + 2 K
+
(aq,inside)
At 310 K, D
r
G
for the hydrolysis of ATP is 31.3 kJ mol
1
. Given that
the [ATP]/[ADP] ratio is of the order of 100, is the hydrolysis of
1 mol ATP suf cient to provide the energy for the transport of Na
+
and K
+
according to the equation above? Take [P
i
] = 1.0 mol dm
3
.
5.16 Vision begins with the absorption of light by special cells in
the retina. Ultimately, the energy is used to close ligand-gated ion
channels, causing sizable changes in the transmembrane potential.
Te pulse of electric potential travels through the optical nerve
and into the optical cortex, where it is interpreted as a signal and
incorporated into the web of events we call visual perception (see
Chapter 13). Taking the resting potential as 30 mV, the temperature
as 310 K, permeabilities of the K
+
and Cl
ions as P
K
+ = 1.0 and P
Cl
= 0.45,
respectively, and the concentrations as [K
+
]
in
= 100 mmol dm
3
,
[Na
+
]
in
= 10 mmol dm
3
, [Cl
]
in
= 10 mmol dm
3
, [K
+
]
out
= 5 mmol dm
3
,
[Na
+
]
out
= 140 mmol dm
3
, and [Cl
]
out
= 100 mmol dm
3
, calculate the
relative permeability (Case study 5.1) of the Na
+
ion.
5.17 Is the conversion of pyruvate ion to lactate ion
CH
3
COCO
2
(aq) + NADH(aq) + H
+
(aq)
CH
3
CH
2
(OH)CO
2
(aq) + NAD
+
(aq)
a redox reaction?
5.18 Express the reaction in Exercise 5.17 as the diference of two
half-reactions.
5.19 Express the reaction in which ethanol is converted to
acetaldehyde (propanal) by NAD
+
in the presence of alcohol
dehydrogenase as the diference of two half-reactions and write
the corresponding reaction quotients for each half-reaction
and the overall reaction.
5.20 Express the oxidation of cysteine, HSCH
2
CH(NH
2
)COOH,
to cystine, HOOCCH(NH
2
)CH
2
SSCH
2
CH(NH
2
)COOH, as the
diference of two half-reactions, one of which is O
2
(g) + 4 H
+
(aq)
+ 4 e
2 H
2
O(l).
5.21 One of the steps in photosynthesis is the reduction of NADP
+
by
ferredoxin (fd) in the presence of ferredoxin:NADP oxidoreductase:
2 fd
red
(aq) + NADP
+
(aq) + 2 H
+
(aq) 2 fd
ox
(aq) + NADPH(aq).
Express this reaction as the diference of two half-reactions. How
many electrons are transferred in the reaction event?
5.22 From the biological standard half-cell potentials E
cell
(O
2
,H
+
,H
2
O)
= +0.82 V and E
cell
(NAD,H
+
,NADH) = 0.32 V, calculate the standard
potential arising from the reaction in which NADH is oxidized to
NAD
+
and the corresponding biological standard reaction Gibbs
energy.
5.23 Cytochrome c oxidase receives electrons from reduced
cytochrome c (cyt-c
red
) and transmits them to molecular oxygen,
with the formation of water. (a) Write a chemical equation for this
process, which occurs in an acidic environment. (b) Estimate the
values of E
cell
, D
r
G
, and K for the reaction at 25C.
5.24 A fuel cell develops an electric potential from the chemical
reaction between reagents supplied from an outside source. What is
the cell potential of a cell fuelled by (a) hydrogen and oxygen, each
at 1 bar and 298 K, and (b) the combustion of butane at 1.0 bar and
298 K?
5.25 Consider a hydrogen electrode in HBr(aq) at 25C operating
at 1.45 bar. Estimate the change in the electrode potential when the
solution is changed from 5.0 mmol dm
3
to 25.0 mmol dm
3
.
5.26 A hydrogen electrode can, in principle, be used to monitor
changes in the molar concentrations of weak acids in biologically
active solutions. Consider a hydrogen electrode in a solution of lactic
acid as part of an overall galvanic cell at 25C and 1 bar. Estimate the
change in the electrode potential when the concentration of lactic acid
in the solution is changed from 5.0 mmol dm
3
to 25.0 mmol dm
3
.
5.27 Write the cell reactions and electrode half-reactions for the
following cells:
(a) Pt(s) | H
2
(g, p
L
) | HCl(aq) | H
2
(g, p
R
) | Pt(s)
(b) Pt(s) | Cl
2
(g) | HCl(aq) | | HBr(aq) | Br
2
(l) | Pt(s)
(c) Pt(s) | NAD
+
(aq), H
+
(aq),NADH(aq) | | oxaloacetate
2
(aq),
H
+
(aq),malate
2
(aq) | Pt(s)
(d) Fe(s) | Fe
2+
(aq) | | Mn
2+
(aq), H
+
(aq) | MnO
2
(s) | Pt(s)
5.28 Write the Nernst equations for the cells in the preceding exercise.
5.29 Devise cells to study the following biochemically important
reactions. In each case state the value for n to use in the Nernst
equation.
(a) CH
3
CH
2
OH(aq) + NAD
+
(aq)
CH
3
CHO(aq) + NADH(aq) + H
+
(aq)
(b) ATP
4
(aq) + Mg
2+
(aq) MgATP
2
(aq)
(c) 2 cyt-c(red, aq) + CH
3
COCO
2
(aq) + 2 H
+
(aq)
2 cyt-c(ox, aq) + CH
3
CH(OH)CO
2
(aq)
5.30 Use the standard potentials of the electrodes to calculate the
standard potentials of the cells devised in Exercise 5.29.
5.31 Te permanganate ion is a common oxidizing agent. What is the
standard potential of the MnO
4
,H
+
/Mn
2+
couple at (a) pH = 6.00 and
(b) general pH?
5.32 State what you would expect to happen to the cell potential
when the following changes are made to the corresponding cells
in Exercise 5.27. Confrm your prediction by using the Nernst
equation in each case. (a) Te pressure of hydrogen in the lef-hand
compartment is increased. (b) Te concentration of HCl is increased.
(c) Acid is added to both compartments. (d) Acid is added to the
right-hand compartment.
5.33 State what you would expect to happen to the cell potential when
the following changes are made to the corresponding cells devised in
Exercise 5.29. Confrm your prediction by using the Nernst equation
in each case. (a) Te pH of the solution is raised. (b) A solution of
Epsom salts (magnesium sulfate) is added. (c) Sodium lactate is added
to the solution.
5.34 (a) Calculate the standard potential of the cell
Hg(l) | HgCl
2
(aq) | | TlNO
3
(aq) | Tl(s) at 25C. (b) Calculate
the cell potential when the molar concentration of the Hg
2+
ion
is 0.150 mol dm
3
and that of the Tl
+
ion is 0.93 mol dm
3
.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chapter 5 Org Chem AnswersDocumento19 pagineChapter 5 Org Chem Answersbilly100% (1)
- Bch341 Exam3 Expanded Spring2019Documento9 pagineBch341 Exam3 Expanded Spring2019Anonymous ffLrUFNessuna valutazione finora
- (Advanced Chemistry) Herbert August Laitinen, Walter E. Harris-Chemical Analysis - An Advanced Text and Reference-McGraw-Hill (1975) PDFDocumento627 pagine(Advanced Chemistry) Herbert August Laitinen, Walter E. Harris-Chemical Analysis - An Advanced Text and Reference-McGraw-Hill (1975) PDFarefNessuna valutazione finora
- A Green Method For Synthesis of Cyclohexanone Oxidation of Cyclohexanol Using Sodium HypochloriteDocumento6 pagineA Green Method For Synthesis of Cyclohexanone Oxidation of Cyclohexanol Using Sodium Hypochloritefleetfoxes886% (7)
- Problemas ICHO28 A ICHO24Documento40 pagineProblemas ICHO28 A ICHO24Leonardo FagundesNessuna valutazione finora
- EquilibriumDocumento9 pagineEquilibriumKashvi DevNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemistryDocumento6 pagineChemistryHajime Hikari100% (1)
- Which of The Following Statements About The Equivalence Point of An AcidDocumento10 pagineWhich of The Following Statements About The Equivalence Point of An AcidCorrine PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermochemistry, Equilibrium, Electrochemistry Review WorksheetDocumento5 pagineThermochemistry, Equilibrium, Electrochemistry Review WorksheetakshayddsbNessuna valutazione finora
- 7) EquilibriumDocumento3 pagine7) EquilibriumB9 Adi JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Sample Paper 1 AnswersDocumento7 pagineChemistry Sample Paper 1 AnswersprathishskaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM 224 Last Three ExptsDocumento8 pagineCHM 224 Last Three ExptsanoopNessuna valutazione finora
- EquilibriumDocumento6 pagineEquilibriumariasinghhh07Nessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Regular Question BankDocumento5 pagine12 Regular Question BankJava WalaNessuna valutazione finora
- SIS Sujet Principal-Chimie - FrancaisDocumento6 pagineSIS Sujet Principal-Chimie - FrancaisTerence YepdjouNessuna valutazione finora
- CHE 323 Electrochemisty Problem Set 3-16-17Documento2 pagineCHE 323 Electrochemisty Problem Set 3-16-17Zhu Chen ChuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment - EquilibriumDocumento5 pagineAssignment - EquilibriumYash KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- A2 Chemistry ExamzoneDocumento4 pagineA2 Chemistry ExamzoneSan SiddzNessuna valutazione finora
- VJC 2007Documento14 pagineVJC 2007sswee_1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Artigo 1Documento7 pagineArtigo 1Rafael AmaranteNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8:chemical Equilibrium: Short Question With AnswersDocumento5 pagineChapter 8:chemical Equilibrium: Short Question With AnswersMuhammad ShahzadNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQs For Class XII ChemistryDocumento29 pagineMCQs For Class XII Chemistryjkc collegeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 1051 Final Exam ReviewDocumento17 pagineChem 1051 Final Exam ReviewClaire Elizabeth SnowNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectrochemistryDocumento40 pagineElectrochemistryJithesh Parambath0% (1)
- Redox: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions: Pre-Lab DiscDocumento12 pagineRedox: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions: Pre-Lab DiscKaren LazoNessuna valutazione finora
- GENTELMEN EQUILIBRIUM (Red)Documento25 pagineGENTELMEN EQUILIBRIUM (Red)ewin TijaNessuna valutazione finora
- ExamDocumento6 pagineExampiyushdua01Nessuna valutazione finora
- GgdffhtdfydDocumento3 pagineGgdffhtdfydbokoka5233Nessuna valutazione finora
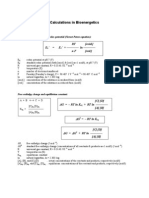
- Calculations in BioenergeticsDocumento4 pagineCalculations in BioenergeticsmanenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 12th Chemistry Solved Sample Paper 2Documento13 pagineClass 12th Chemistry Solved Sample Paper 2cbsestudymaterialsNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Chemistry23 24 sp10Documento14 pagine12 Chemistry23 24 sp10Babur HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Icho1986-1994p Technical and PhysicalDocumento38 pagineIcho1986-1994p Technical and PhysicalAlexandra AlgueraNessuna valutazione finora
- Final - Spring 2015 - Ghada & RonyDocumento14 pagineFinal - Spring 2015 - Ghada & Ronyreve amaneddineNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Chemistry 2010 Free-Response Questions Form B: The College BoardDocumento13 pagineAP Chemistry 2010 Free-Response Questions Form B: The College BoardDharul Handri PranawaNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set 1Documento3 pagineProblem Set 1supernerd4ever0% (1)
- Semester Exam 1 OutlinesDocumento4 pagineSemester Exam 1 OutlinesDWIKI KURNIYAWAN ARIYA PUTRANessuna valutazione finora
- Mock TestDocumento3 pagineMock Testariasinghhh07Nessuna valutazione finora
- HL ChemistryDocumento12 pagineHL ChemistryVithursan ThangarasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 1 06Documento51 pagineChemistry Form 6 Sem 1 06Ng Swee Loong Steven100% (2)
- 2007 ADocumento4 pagine2007 AAmiro MayraNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2013-2-1Documento9 pagineAssignment 2013-2-1Min Ko SoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Reactor ModelDocumento12 pagineReactor ModelTanuja ThanuNessuna valutazione finora
- 31 Prepare ThaiDocumento52 pagine31 Prepare ThaiHuyềnTrânCôngChúaNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ Prelims 2006Documento12 pagineMCQ Prelims 2006Sherman HoNessuna valutazione finora
- EquillibriumDocumento16 pagineEquillibriumparth ladaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Gene Chem ExamDocumento2 pagineGene Chem Examhiru mangoNessuna valutazione finora
- Code:SP/LV-2 Sample Paper: General InstructionsDocumento3 pagineCode:SP/LV-2 Sample Paper: General InstructionsKhogen MairembamNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.2.3 Redox and Electrode Potentials QPDocumento37 pagine5.2.3 Redox and Electrode Potentials QPUbayd HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Electro Chemistry AssaignmentDocumento11 pagineElectro Chemistry AssaignmentGadde Gopala KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetics of The Esterifieation of Palmitie Acid With Isobutyl AlcoholDocumento10 pagineKinetics of The Esterifieation of Palmitie Acid With Isobutyl AlcoholKemal MohammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Equilibrium and Acids BasesDocumento7 pagineChemical Equilibrium and Acids BasesGagan NdNessuna valutazione finora
- Examen Campinas InglesDocumento7 pagineExamen Campinas InglesSharon Laurente RamónNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 7 EquilibriumDocumento5 pagineCH 7 EquilibriumBriennaNessuna valutazione finora
- DPP 1 CT 1 ChemistryDocumento8 pagineDPP 1 CT 1 ChemistryRohan Patel0% (1)
- NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 EquilibriumDocumento19 pagineNCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 EquilibriumAnidhya TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Tests U4Documento14 paginePractice Tests U4hubbleman100% (1)
- 1977Documento2 pagine1977bobothebioguyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics 119 Ques!!!Documento27 pagineChemical Kinetics 119 Ques!!!elifnazNessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsDa EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNessuna valutazione finora
- Selected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionDa EverandSelected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook of Coordination Catalysis in Organic ChemistryDa EverandHandbook of Coordination Catalysis in Organic ChemistryNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Plotting Tutorial 29Documento1 paginaGraph Plotting Tutorial 29snowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Plotting Tutorial 28Documento1 paginaGraph Plotting Tutorial 28snowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Plotting Tutorial 30Documento1 paginaGraph Plotting Tutorial 30snowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Plotting Tutorial 31Documento1 paginaGraph Plotting Tutorial 31snowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Plotting Tutorial 32 PDFDocumento1 paginaGraph Plotting Tutorial 32 PDFsnowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Plotting Tutorial 30Documento1 paginaGraph Plotting Tutorial 30snowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Plotting Tutorial 25Documento1 paginaGraph Plotting Tutorial 25snowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Plotting Tutorial 5Documento1 paginaGraph Plotting Tutorial 5snowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Plotting Tutorial 2Documento1 paginaGraph Plotting Tutorial 2snowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Plotting Tutorial 10Documento1 paginaGraph Plotting Tutorial 10snowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Instructor'S Solutions Manual: Mcgraw-Hill TegrityDocumento1 paginaInstructor'S Solutions Manual: Mcgraw-Hill TegritysnowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Plotting Tutorial 13Documento1 paginaGraph Plotting Tutorial 13snowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Plotting Tutorial 4Documento1 paginaGraph Plotting Tutorial 4snowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Graph Plotting Tutorial 3Documento1 paginaGraph Plotting Tutorial 3snowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Plotting Graphs in L Tex Using Lyx and PgfplotsDocumento1 paginaPlotting Graphs in L Tex Using Lyx and PgfplotssnowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- DS510Documento2 pagineDS510snowblindedNessuna valutazione finora
- Richard A. Larson, Eric J. Weber - Reaction Mechanisms in Environmental Organic Chemistry-Lewis Publishers (1994)Documento442 pagineRichard A. Larson, Eric J. Weber - Reaction Mechanisms in Environmental Organic Chemistry-Lewis Publishers (1994)nhonducNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.7 The Periodic Table - Groups 2 and 7Documento84 pagine2.7 The Periodic Table - Groups 2 and 7Listiyaning TiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Project 333Documento15 pagineBiology Project 333rudraparaste66Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial On Electrolysis and Faraday's Law.: Prepared by Lawrence KokDocumento27 pagineTutorial On Electrolysis and Faraday's Law.: Prepared by Lawrence KokoscarbecNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 2122 General Chemistry IIDocumento11 pagineChem 2122 General Chemistry IINezuko ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- NEET 2020 Question Paper With Answer Key E4 F4 G4 H4Documento101 pagineNEET 2020 Question Paper With Answer Key E4 F4 G4 H4Sanket SawantNessuna valutazione finora
- Ozone DecompositionDocumento13 pagineOzone DecompositionLad SlasNessuna valutazione finora
- C4 Acid - and - Redox - Ox - NumbersDocumento24 pagineC4 Acid - and - Redox - Ox - Numbersdosibo2378Nessuna valutazione finora
- BC Cellular RespirationDocumento83 pagineBC Cellular RespirationPaul CriolloNessuna valutazione finora
- B.-Sc.-Hons.-Syllabus-for-the-session-2017-18-to-2020-21 JUDocumento61 pagineB.-Sc.-Hons.-Syllabus-for-the-session-2017-18-to-2020-21 JUGalib AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- O Simplified Procedure For Constructing Pourbaix Diagrams : E. D. Verink, JRDocumento14 pagineO Simplified Procedure For Constructing Pourbaix Diagrams : E. D. Verink, JRdayangmyraNessuna valutazione finora
- ASOE Chem - 2012 0 - 1 - 1Documento30 pagineASOE Chem - 2012 0 - 1 - 1sarahs2chowNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Research in Chemistry Education Bucat 2004Documento14 pagineApplied Research in Chemistry Education Bucat 2004Mauro VanNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Chemical ReactionsDocumento12 pagineTypes of Chemical ReactionsROn Arellano100% (2)
- PHYS SCI 2024 National ANNUAL TEACHING PLAN GRADE 12Documento8 paginePHYS SCI 2024 National ANNUAL TEACHING PLAN GRADE 12masibulele641Nessuna valutazione finora
- Galvanic Corrosion PDFDocumento16 pagineGalvanic Corrosion PDFdraj1875977Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit3 Stoichiometry QnsDocumento14 pagineUnit3 Stoichiometry QnsRanjan KathuriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 6Documento4 pagineLecture 6Abhijeet BhagavatulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment-3: Galvanic SeriesDocumento4 pagineExperiment-3: Galvanic SeriesChayon MondalNessuna valutazione finora
- Kestrelle OpinaldoDocumento55 pagineKestrelle OpinaldoVienne OpinaldoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mypchem Ch10answersDocumento3 pagineMypchem Ch10answersPikunoShuousNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Activity 7 ElectrochemistryDocumento8 pagineLab Activity 7 Electrochemistryjhunjhun zambranoNessuna valutazione finora
- TIFR 2012 Solved PaperDocumento17 pagineTIFR 2012 Solved PaperMohit SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Modern School, Baranagar Syllabus For Second Unit Test & Final Examination of Session: 2022 - 2023Documento6 pagineCentral Modern School, Baranagar Syllabus For Second Unit Test & Final Examination of Session: 2022 - 2023Binay ShawNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 12: Provincial ExaminationDocumento25 pagineChemistry 12: Provincial ExaminationCát TriệuNessuna valutazione finora
- Advances in BioleachingDocumento16 pagineAdvances in BioleachingYatharth AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- DocumentDocumento37 pagineDocumentpriya dharshiniNessuna valutazione finora