Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
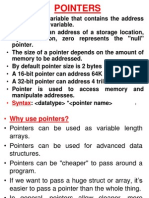
8 Pointers
Caricato da
yashbanwani2014Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
8 Pointers
Caricato da
yashbanwani2014Copyright:
Formati disponibili
C++ pointers
1
C++ pointers
Subject classification: this is a technology resource .
In C++, pointers are a primitive datatype that reference an object.
What is a pointer?
A pointer is a special kind of variable that stores the address in memory of another variable and can be used to
manipulate that variable. In general, whenever a variable is used in C++, it must exist somewhere in the host
computer's memory and pointers can store the location of a particular variable.
Pointers associate two pieces of information: (1) the memory address, which the "value" of the pointer itself, and (2)
the data type of the variable pointed to, which is the kind of variable located at that address.
Pointers can be dereferenced to access the value of the variable at the pointer's address. For example:
void f(int* p)
{
// The code "*p" takes the value of the data at location stored in p
int n = *p;
}
All the data stored in a program is stored in the computer's memory. For example, if a program has a global variable
named "numberOfEmployees" that variable has both a value, for example 120 employees, and an address, which is
the actual location in the computer's memory where the value is stored.
Declaring pointers
Declaring a pointer is similar to declaring a regular variable, although the name is preceded by an asterisk:
int *ptr;
struct coord *pCrd;
void *vp;
In the example above, ptr is a pointer to an integer. pCrd is a pointer to a structure named coord. vp is a void
pointer, which does not require a specific datatype.
Unlike references, pointers are not guaranteed to be initialized. As such, they should only be used when they are
known to point to an existing object.
C++ pointers
2
Arrays
Array is an collection of similar data types under same name. In C++, arrays are declared similar to the following:
int arr[25];
The above statement declares as static array of 25 elements, which can be accessed individually. Although arr
behaves as a pointer, its value cannot be changed as it references a specific region in memory.
Allocating variables
In C++, a new object, variable or array can be created using the new operator, and freed with the delete
operator.
int *ptr = new int;
/* ... */
delete ptr;
The new operator allocates an object from the heap and optionally initialize it. When you have finished using it,
you must delete it. Otherwise, the pointed memory is inaccessible and the result is memory leak.
Referencing variables
The & operator is used to reference an object. When using this operator on an object, you are provided with a
pointer to that object. This new pointer can be used as a parameter or be assigned to a variable.
Multi dimensional arrays
A multidimensional array allows nesting arrays:
int grid[3][3];
This allocates 3*3 elements in one memory block. Even though arrays behave similarly to pointers, a
multidimensional array is not a pointer-to-a-pointer, as shown below.
low address high address
grid
grid[0] grid[1] grid[2]
grid[0][0]grid[0][1]grid[0][2]grid[1][0]grid[1][1]grid[1][2]grid[2][0]grid[2][1]grid[2][2]
The objects grid, grid[0] and grid[0][0] is always at the same location (but different types) but the objects of pptr,
*pptr, **pptr is at different locations. When evaluating grid[0][0], The array grid (which is an int[3][3]) is first
converted to a pointer of type int(*)[3], taking the element at offset 0, and yields an object of int[3], then it is
converted to int* again and the element at offset 0 is taken, generating an object of type int& .
C++ pointers
3
Pointer to a pointer
A pointer contains a reference to another variable. It may also point to a pointer:
int **pptr;
pptr*pptr**pptr
For pptr[0][0], the address stored in pptr is taken and the address stored in that address is taken and it is the result of
the expression.
Where To Go Next
Topics in C++
Beginners Data Structures Advanced
Lesson 1: Introduction to C++ Lesson 8: Pointers Lesson 12: The STL
Lesson 2: Variables and User Input Lesson 9: Classes and Inheritance Lesson 13: STL Algorithms
Lesson 3: Simple Math Lesson 10: Templates 1
Lesson 4: Conditional Statements Lesson 11: Templates 2
Lesson 5: Loops
Lesson 6: Functions and Recursion
Lesson 7: More Functions
Part of the School of Computer Science
Article Sources and Contributors
4
Article Sources and Contributors
C++ pointers Source: http://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?oldid=746855 Contributors: Autumnfields, Erikgunby, Miklcct, Prohlep, Sigma 7, 7 anonymous edits
Image Sources, Licenses and Contributors
Image:Nuvola_apps_kcmprocessor.png Source: http://en.wikiversity.org/w/index.php?title=File:Nuvola_apps_kcmprocessor.png License: GNU Lesser General Public License Contributors:
Alno, Alphax, It Is Me Here, Mobius, Tothwolf, Ysangkok
License
Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported
//creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- BL3B User Manual PDFDocumento142 pagineBL3B User Manual PDFRandy VanegasNessuna valutazione finora
- Popular Tools CatalogDocumento24 paginePopular Tools CatalogCarbide Processors IncNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 React Redux React Router Es6 m7 SlidesDocumento19 pagine7 React Redux React Router Es6 m7 Slidesaishas11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Case Presentation - Bipolar Affective Disorder 2Documento73 pagineCase Presentation - Bipolar Affective Disorder 2Hemant's galaxy All is hereNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 18 - Introduction To PointersDocumento24 pagineLecture 18 - Introduction To PointersahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers in C++Documento20 paginePointers in C++Naveed IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Procedural vs OO Concepts in CDocumento29 pagineProcedural vs OO Concepts in CSantosh SutarNessuna valutazione finora
- PointerDocumento13 paginePointersarthakmalik5098Nessuna valutazione finora
- PointersDocumento35 paginePointerssoubhagyalaxmisamal2221Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers Unit 4th 2nd SemDocumento10 paginePointers Unit 4th 2nd SemBhanu Prakash ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.2 PointersDocumento14 pagine4.2 PointersKen MutaiNessuna valutazione finora
- PointersDocumento46 paginePointersbeshahashenafe20Nessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 9: Pointers, Virtual Functions and PolymorphismDocumento4 pagineCHAPTER 9: Pointers, Virtual Functions and PolymorphismdarshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers Guide for Dynamic Memory ManagementDocumento59 paginePointers Guide for Dynamic Memory ManagementEsubalew ChekolNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers and Dynamic Memory ManagementDocumento30 paginePointers and Dynamic Memory ManagementramandeepkaursainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Handout 6 CSM 1101Documento14 pagineHandout 6 CSM 1101Mohammad SulaimanNessuna valutazione finora
- C++ Pointers GuideDocumento16 pagineC++ Pointers GuideIt's MeNessuna valutazione finora
- MIT6 096IAP11 Lec05 PDFDocumento7 pagineMIT6 096IAP11 Lec05 PDFSuba ShniNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointer C NotesDocumento6 paginePointer C NotesMahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Programming fundamentals 2 Chapter 3:PointerDocumento14 pagineProgramming fundamentals 2 Chapter 3:PointerpushpanjaliNessuna valutazione finora
- C++ Important Topics For Placements.Documento5 pagineC++ Important Topics For Placements.baxila9033Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Basic Language Concepts of OOPDocumento196 pagineThe Basic Language Concepts of OOPKrishna KeshavNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture#01Documento25 pagineLecture#01KashanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cpps Mod5@Azdocuments - inDocumento23 pagineCpps Mod5@Azdocuments - inMunavalli Matt K SNessuna valutazione finora
- Review On Pointers and Dynamic ObjectsDocumento23 pagineReview On Pointers and Dynamic Objectsshrutipiet1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Pointer-1Documento43 pagineChapter 7 Pointer-1Abdullahi Bakar AbdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision on Pointers and Structures in c++Documento42 pagineRevision on Pointers and Structures in c++seadamoh80Nessuna valutazione finora
- PointersDocumento5 paginePointersAnonymous fqRan1Dd8Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-3 - PointerDocumento45 pagineChapter-3 - Pointerbeshahashenafe20Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1st ChapterDocumento22 pagine1st ChapterKaranpal Singh JulkaNessuna valutazione finora
- C PointersDocumento10 pagineC PointersshivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- CT-159 DATA STRUCTURES ALGORITHMS AND APPLICATIONS LECTURE 1Documento45 pagineCT-159 DATA STRUCTURES ALGORITHMS AND APPLICATIONS LECTURE 1MUHAMMADASHARIB SIDDIQUINessuna valutazione finora
- Linked List Data Structure GuideDocumento44 pagineLinked List Data Structure GuideDickson WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Assign 3 FullDocumento26 pagineAssign 3 FullKunalNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymorphism and pointers in CDocumento63 paginePolymorphism and pointers in CShakeel AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- What are Pointers and Structures in CDocumento11 pagineWhat are Pointers and Structures in Csaman rafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- Cin and Cout: - C++ Provides An Easier Way For Input and Output. - The Output: - The InputDocumento20 pagineCin and Cout: - C++ Provides An Easier Way For Input and Output. - The Output: - The InputJane ridriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers: of An Another Variable. by Convention, Zero Represents The "Null" Pointer. Memory To Be AddressedDocumento23 paginePointers: of An Another Variable. by Convention, Zero Represents The "Null" Pointer. Memory To Be Addressedlakshmigsr6610Nessuna valutazione finora
- 8 PointersDocumento33 pagine8 PointersRishab KashyapNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers and Virtual Functions Final 2Documento33 paginePointers and Virtual Functions Final 2Saakshi PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointer and Polymorphism in C++Documento23 paginePointer and Polymorphism in C++sahilkumar3570218Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IVDocumento35 pagineUnit IVDark soulNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers Q&ADocumento13 paginePointers Q&AriscomputersirNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointer and Array Review & Introduction To Data StructureDocumento39 paginePointer and Array Review & Introduction To Data Structurebryan chandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers in CDocumento33 paginePointers in CSakthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 PointersDocumento46 pagineChapter 3 Pointersnuniyat.gNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers and Introduction To Data StructuresDocumento22 paginePointers and Introduction To Data StructuresHEMANT KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 CPDocumento9 pagineUnit 4 CPJayanth KanumuriNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Pointers UpdatedDocumento52 pagine5 Pointers Updatedhana mahmoudNessuna valutazione finora
- C++ Plus Data Structures: Nell DaleDocumento46 pagineC++ Plus Data Structures: Nell Daleahmed ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- DSA Lab1Documento11 pagineDSA Lab1daniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers and StructuresDocumento11 paginePointers and Structuressaman rafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers N ClassesDocumento25 paginePointers N ClassesmwendwashyleenNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-3. Pointer & StructureDocumento18 pagineChapter-3. Pointer & StructureQuazi Hasnat IrfanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Four: PointersDocumento24 pagineChapter Four: Pointerssisay gmedhinNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers and Dynamic Objects: Mechanisms For Developing Flexible List RepresentationsDocumento44 paginePointers and Dynamic Objects: Mechanisms For Developing Flexible List RepresentationsElay Bee ÜNessuna valutazione finora
- Short Notes On C/C++Documento55 pagineShort Notes On C/C++Shivay ShivayNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers in CDocumento6 paginePointers in CNitin GodheyNessuna valutazione finora
- Geetanjali DalviDocumento17 pagineGeetanjali DalviPreeti ParyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Structures and Algorithms OverviewDocumento15 pagineData Structures and Algorithms OverviewmuradNessuna valutazione finora
- PointersDocumento16 paginePointersRuchita AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- POINTER1Documento70 paginePOINTER1k.kalaivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- C Programming Unit 4.1 PointersDocumento33 pagineC Programming Unit 4.1 PointersrishikaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Simple AmthDocumento3 pagine3 Simple Amthyashbanwani2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Conditional StatementsDocumento4 pagine4 Conditional Statementsyashbanwani2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- 13 STL AlgorithmsDocumento3 pagine13 STL Algorithmsyashbanwani2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To C++: Hello World!Documento5 pagineIntroduction To C++: Hello World!yashbanwani2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Variables and User InputDocumento5 pagine2 Variables and User Inputyashbanwani2014100% (1)
- 7 More FunctionsDocumento4 pagine7 More Functionsyashbanwani2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Templates Part 1Documento11 pagine10 Templates Part 1yashbanwani2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- The STL: The Standard Template LibraryDocumento5 pagineThe STL: The Standard Template Libraryyashbanwani2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Functions and RecursionDocumento7 pagine6 Functions and Recursionyashbanwani2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Templates Part 2Documento3 pagine11 Templates Part 2yashbanwani2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5 LoopsDocumento5 pagine5 Loopsyashbanwani2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- 9 Classes and InheritanceDocumento6 pagine9 Classes and Inheritanceyashbanwani2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- MIT6 096IAP11 Lec03 PDFDocumento66 pagineMIT6 096IAP11 Lec03 PDFCarlos Alberto Sosa TNessuna valutazione finora
- MIT6 096IAP11 Lec10Documento11 pagineMIT6 096IAP11 Lec10yashbanwani2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6.096 Introduction to C++ Flow of Control NotesDocumento9 pagine6.096 Introduction to C++ Flow of Control NotesAkash Kumar BhoiNessuna valutazione finora
- MIT6 096IAP11 Lec01 PDFDocumento9 pagineMIT6 096IAP11 Lec01 PDFKushNessuna valutazione finora
- MIT6 096IAP11 Lec05 PDFDocumento7 pagineMIT6 096IAP11 Lec05 PDFSuba ShniNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4 Notes: Arrays and StringsDocumento6 pagineLecture 4 Notes: Arrays and Stringsmanishbhardwaj8131Nessuna valutazione finora
- Object Oriented Programming in C++Documento8 pagineObject Oriented Programming in C++xob97Nessuna valutazione finora
- Memory ManagementDocumento77 pagineMemory Managementmanishbhardwaj8131Nessuna valutazione finora
- MIT6 096IAP11 Lec06Documento66 pagineMIT6 096IAP11 Lec06vert231Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 9 Notes: Advanced Topics I: 1 TemplatesDocumento7 pagineLecture 9 Notes: Advanced Topics I: 1 TemplatesRahul MaraviNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan 12 Climate ChangeDocumento5 pagineLesson Plan 12 Climate ChangeRey Bello MalicayNessuna valutazione finora
- ACM JournalDocumento5 pagineACM JournalThesisNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution BrochureDocumento4 pagineEvolution Brochurelucas28031978Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2: Lesson Plan Analysis, Revision and Justification - Kaitlin Rose TrojkoDocumento9 pagineAssignment 2: Lesson Plan Analysis, Revision and Justification - Kaitlin Rose Trojkoapi-408336810Nessuna valutazione finora
- KG ResearchDocumento257 pagineKG ResearchMuhammad HusseinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento2 pagineChapter 1Nor-man KusainNessuna valutazione finora
- Service: Audi A6 1998Documento256 pagineService: Audi A6 1998Kovács EndreNessuna valutazione finora
- Irc SP 65-2005 PDFDocumento32 pagineIrc SP 65-2005 PDFAjay Kumar JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Batool2019 Article ANanocompositePreparedFromMagn PDFDocumento10 pagineBatool2019 Article ANanocompositePreparedFromMagn PDFmazharNessuna valutazione finora
- List of DEA SoftwareDocumento12 pagineList of DEA SoftwareRohit MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Indra: Detail Pre-Commissioning Procedure For Service Test of Service Water For Unit 040/041/042/043Documento28 pagineIndra: Detail Pre-Commissioning Procedure For Service Test of Service Water For Unit 040/041/042/043AnhTuấnPhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Country Profile - NigerDocumento1 paginaCountry Profile - Nigernana kayNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of Benefits and Risk of Genetically ModDocumento29 pagineAssessment of Benefits and Risk of Genetically ModSkittlessmannNessuna valutazione finora
- Ford 30 V600Documento7 pagineFord 30 V60008088338Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cats - CopioniDocumento64 pagineCats - CopioniINES ALIPRANDINessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 Paired and Two Sample T TestDocumento18 pagineModule 3 Paired and Two Sample T TestLastica, Geralyn Mae F.Nessuna valutazione finora
- ROM Magazine V1i6Documento64 pagineROM Magazine V1i6Mao AriasNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Case StudyDocumento8 pagine2 Case Studysehrish khawerNessuna valutazione finora
- Fabm1 q3 Mod4 Typesofmajoraccounts FinalDocumento25 pagineFabm1 q3 Mod4 Typesofmajoraccounts FinalClifford FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Minimum Fees To Be Taken by CADocumento8 pagineMinimum Fees To Be Taken by CACA Sanjay BhatiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Music QuizDocumento3 pagineOnline Music QuizGiang VõNessuna valutazione finora
- Purp Com Lesson 1.2Documento2 paginePurp Com Lesson 1.2bualjuldeeangelNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Global Positioning System: Anil Rai I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi - 110012Documento19 pagineIntroduction To Global Positioning System: Anil Rai I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi - 110012vinothrathinamNessuna valutazione finora
- Galley cleaning hazards and controlsDocumento9 pagineGalley cleaning hazards and controlsRosalie RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Bonding in coordination compoundsDocumento65 pagineBonding in coordination compoundsHitesh vadherNessuna valutazione finora
- (V) 2020-Using Extensive Reading in Improving Reading Speed and Level of Reading Comprehension of StudentsDocumento7 pagine(V) 2020-Using Extensive Reading in Improving Reading Speed and Level of Reading Comprehension of StudentsMEYTA RAHMATUL AZKIYANessuna valutazione finora