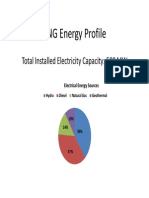
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Diana Fisher-Keynote TeachSDModel
Caricato da
kardraDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Diana Fisher-Keynote TeachSDModel
Caricato da
kardraCopyright:
Formati disponibili
10/12/2010
Learning and Teaching
System Dynamics Modeling
A 20 Year J ourney
Diana Fisher
Portland, Oregon USA
10/12/2010
Before 1990
A typical Modeling Exercise: Modeling Human Growth
THE QUESTION
What type of growth pattern is exhibited in the early years (pre-
adult) of an average person?
Age (years)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Weight (pounds)
21.6
27.2
31.9
36.4
40.0
45.9
51.4
57.3
62.1
68.3
Analysis:
1.Write the equation :
_______________________
2. a. Use your model to predict
the childs weight at 5.5 years and at
50 years.
b. How confident are you in
your answers?
10/12/2010
1990 NCCE Workshop
Analysis:
1.What is happening to the death rate over time? The population?
2.What are some of the limitations of this model?
Population
births deaths
kids per couple
death fraction
~
child bearing couples
couples fraction
10/12/2010
Getting Off the Ground
Purchased STELLA, started experimenting in
programming and in advanced algebra classes.
Wrote 2 in-district grants (one in 1990, other in 1991)
STACY
N
Project at Stanford (1991)
Meet Ed Gallaher (1991)
Systems Thinking in Education Conference (Tucson,
March 1992)
Franklin High School starts full year modeling class
Write NSF CC-STATDUS grant (awarded May 1993)
10/12/2010
Focus on Building Models
Old mental models and decision habits are deeply ingrained;
they do not change just because of a logical argument. J F
Coming to an understanding of systems must be a
participative experience. Computer modeling allows an
accelerated vicarious experience. immersion in such
active learning can change mental models.
Jay Forrester
10/12/2010
Early Models Student Model #1 (1993)
TEMP OF BODY
HEAT LOSS
AMBIENT TEMP
Ke
HALF TIME
AMOUNT OF CLOTHING WEIGHT
10/12/2010
Early Models Student Model #1 (1993)
Very simple model.
Problem with units.
Documentation, but no paper.
TEMP OF BODY
HEAT LOSS
AMBIENT TEMP
Ke
HALF TIME
AMOUNT OF CLOTHING WEIGHT
+
.5 .5
.693/HT
37
5
*
10/12/2010
Early Models Student Model #1 (1993)
10/12/2010
Student model #2 (1993)
CUBS
ADULTS
MATURATION
SURVIVING CUBS
DEATH RATE
SURVIVAL RATE
BIRTHRATE
NATURAL DEATHS
ACCIDENTAL HUMAN CAUSED
HUNTER CAUSED DEATHS
PROBLEM BEARS KILLED
CAUSE UNKNOWN
SENT TO ZOOS
TOTAL POPULATION
10/12/2010
Student model #2 (1993)
Dead buffalo syndrome.
CUBS
ADULTS
MATURATION
SURVIVING CUBS
DEATH RATE
SURVIVAL RATE
BIRTHRATE
NATURAL DEATHS
ACCIDENTAL HUMAN CAUSED
HUNTER CAUSED DEATHS
PROBLEM BEARS KILLED
CAUSE UNKNOWN
SENT TO ZOOS
TOTAL POPULATION
80 100
*.13
*
.3
A*.54*.654
+
*(+)
.007
.03
.05
.0006
.006
.02
10/12/2010
Student model #2 (1993)
10/12/2010
Teacher group model (NSF Grant 1993)
Nomads
Cattle
Land
Deaths
Births
Consumption
Rate
Birth
Desertification
Birth Rate
Death Rate
~
Food per
Nomad per Year
Cattle Density
Dead Cows
Support Factor
Medical Aid
Cow aid
10/12/2010
Teacher group model (NSF Grant 1993)
Nomads
Cattle
Land
Deaths
Births
Consumption
Rate
Birth
Desertification
Birth Rate
Death Rate
~
Food per
Nomad per Year
Cattle Density
Dead Cows
Support Factor
Medical Aid
Cow aid
7000
10000
971
.192
c/l
*
*
*
step(.24,50)
step(.19,75)
10/12/2010
Teacher group model (NSF Grant 1993)
Problem with units.
Complicated math,
hidden.
Nomads
Cattle
Land
Deaths
Births
Consumption
Rate
Birth
Desertification
Birth Rate
Death Rate
~
Food per
Nomad per Year
Cattle Density
Dead Cows
Support Factor
Medical Aid
Cow aid
If(ConRate>0.2*Cattle)
then(cattle*(.25+CowAid))
else(.05*Cattle)
CattleDensity*Cattle*.05*
(if(cattleDensity>.7)then 1 else 0)
CattleDensity*Land*.02*
(if(cattleDensity<.85)then 0 else 1)
FoodPerNomad(1+MedAid)
If(Cattle/Nomads<9)
then(.012*(Cattle/Nomads)^2.5)
else 3
10/12/2010
Help From Our Friends
Steve Peterson NSF grant speaker & mentor
Its not about the numbers.
George Richardson Workshops for core
team
Dimensionless multiplier, SD process,
Barry Richmond Workshops for core team
Models of non-physical processes, students share
learning
Regular attendance at ISDC (starting 1994)
Observing SD professionals & making connections
10/12/2010
How We Learned
Time to meet & talk core NSF training team
Cross-discipline, some rotating members.
Ed Gallaher, Tim J oy, Wayne Wakeland
SyM*Bowl -> SyM*Fest
Outline for a modeling paper
Regular attendance at CLE K-12 ST/SD Conference
Sharing ideas
Teaching each other
10/12/2010
SyM*Fest
Barry Richmond increases involvement
Reads some student papers
Presents to students
Software & T-shirts
Trains teachers
System
Citizen
10/12/2010
SYST&MS Project
Receive Intel Innovation in Teaching
Award/Grant (1996)
Start SYST&MS Project
Attract upper level students to Franklin High School
Expand number of modeling classes
3 first year classes, 1 second year class
Increase number of modeling teachers to three
10/12/2010
NSF CC-SUSTAIN Project
NSF CC-SUSTAIN grant awarded (1997)
Expand teacher SD training to other parts of US
Include some middle school teachers
Release time (1/2 time) to administer grant
Obstacles
Lack of comprehensive curriculum
Teachers need support after the workshop, but
very difficult to support remote locations
10/12/2010
Seedlings
Saplings
Harvestable Trees
Regeneration
Seedling Survivors
Maturing Period
Matured Trees
Harvested Trees
Natural Deaths
Natural Lifespan
Trees Planted
Manual Regeneration
Animal Consumption
Harvesting Rate
Consumption Rate
Planted Tree Survival Rate
Seedling Lifespan
Models Improve
Student Model (1999)
10/12/2010
Models Improve
Student Model (1999)
Consistent units.
Surprising leverage pt.
Seedlings
Saplings
Harvestable Trees
Regeneration
Seedling Survivors
Maturing Period
Matured Trees
Harvested Trees
Natural Deaths
Natural Lifespan
Trees Planted
Manual Regeneration
Animal Consumption
Harvesting Rate
Consumption Rate
Planted Tree Survival Rate
Seedling Lifespan
1.9e8
3.8e7
1.5e8
*
.25
.02
*
4
*
*
.5
-
*
5
20
550
10/12/2010
Models Improve
Student Model (1999)
Animal
consumptio
n
0.25 -> 0.05
Out of all the tested variables, animal consumption
proved to be the most viable leverage point. According to
our results, efforts to reduce animal consumption could
be the most important action taken to save forests, even
more important than lowering harvest rates.
10/12/2010
Student Reflection Franklin High School (1999)
10/12/2010
Move to Wilson High School
Two SD teachers move from Franklin to
Wilson High School
Two SD teachers remain at Franklin but do not
want to continue the effort to recruit students
SYST&MS Project dies at Franklin after one more
year
Wilson High School
Teaching SD and programming during the same
class period, until 2008.
New hire continues SD modeling class.
10/12/2010
SD Learning Continues
Delays, J ournals and auto-check Unit Consistency
Help from Debra Lyneis
10/12/2010
A quote from a student journal
Chinas one child policywas introduced to combat
overpopulation, butthe policy has led to selective
abortions which leads to gender imbalanced
generation There are also not enough young people to
sustain and support the economy built by a burgeoning
population. This could impact economic growth and
Chinas position as an emerging power. In addition, there
will likely be issues as a generation without siblings
comes of age.
Kate L. (age 15)
10/12/2010
SD Learning Continues
Delays, J ournals, auto-check Unit Consistency
Help from Debra Lyneis
Take WPI System Dynamics classes
Oscillations, segment dynamic hypothesis,
start model in equilibrium, extreme value
testing, systematic parameter testing, policy
testing required
10/12/2010
Student Thinking Improves
Systems in the news
10/12/2010
Student Thinking Improves
Systems in the news
10/12/2010
Student Models
Continue to Improve
10/12/2010
Hybrid Cars
Hybrid Inventory
Active Hybrid Vehicles
Order Fulfillment Becoming Obsolete
Actual Production
Hybrid Demand
Backlog
Average LIfespan of Car
New Demand
Perceived
Backlog
of Hybirds
Fulfilling Demand
Desired
Shipment Rate
Target
Delivery
Time
Gap Between Inventory
and Order Fulfillment
Unmet Demand
Change in Perception
Real and Perceived
Availability Gap
~
Effect of Price
on Demand
Normal Customer
Order Rate
Actual Customer
Order Rate
Delay in Availability Perception
Price of Oil
Changing Oil Price
~
Effect of Oil
Price on Demand
Normal Oil Price
Price of Hybrid
Normal Price of Hybrid
~
Effect of Backlog on Price
Ratio of Actual to Normal Price
~
Effect of Perceived
Backlog on Demand
Production
Capacity
Constructed
Capital
Constructing Startup
Normal Backlog
Closing
Time to Construct
Actual Lifespan
of Factory
Time to Startup
Ratio of Desired
Production to Capacity
~
Effect of Capacity Availability
on Construction Starts
~
Effect of Capcity
Availability on Closures
~
Effect of Ratio of Actual Production
to Capacity on Factory Life
Normal LIfespan
of Factory
Normal Hybrid
Inventory
~
Effect of Inventory Ratio
on Desired Production
Shipping Time
Supplying
Desired Production Hybrid Production
Desired Production
~
Effect of Price on
Desired Production
Normal Rate
of Construction
Ideal Utilization
Ideal Utilization
Change
Student Model (2007)
10/12/2010
Student Presentation J oseph Kibe
10/12/2010
Student Reflection
In other classes, I am often asked to posit logical
solutions to problems or am given the solutions reached
by other people. Using models of complex systems I can
test out my own theories and confirm those of others
instead of faithfully accepting them as fact.
Where other classes ask me to memorize, this one dares me to
explore.
Tommy H. (age 16)
10/12/2010
Students Care About
Local and World Problems
How do breaches affect airport security?
How Can We Improve the Blood Donation
Process in the United States?
How Devastating Is An Invasive Species?
What Could Bird Flu do to a Human Population?
How Much do Carbon Emissions Need to be
Reduced in Order to Stop Global Warming?
How Does Colony Collapse Disorder
Affect the Almond Industry?
Does Having More Children Keep People Poor?
How Can the United State's Social Security
Program Be Sustained?
10/12/2010
CC Modeling Systems
View Student Work
model diagram, paper, video presentation
Link System Dynamics to National Education Standards
Resources and Research
10/12/2010
Lessons Learned
Start somewhere ST .. SD
Always work toward a simulate-able model
George Richardson
Work in a group, if possible
Make the learning available to others
Barry Richmond
Learn the correct method for building models
Teachers can learn now in 9 months what it took me
20 years to learn - but they need the opportunity
10/12/2010
Lessons Learned
Kids can do this. They will amaze you!
Your children deserve to learn this in
school
Only you can make that happen
We need the help of Parents and the
informed public to promote the inclusion
of ST/SD in schools to make this happen.
It will not happen from within the schools
10/12/2010
Modeling Dynamic Feedback Systems:
A Different Way to Think
We cannot solve our
problems with the same
thinking we used when we
created them.Albert Einstein
10/12/2010
Thank You
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Ut Dallas Dissertation FormatDocumento4 pagineUt Dallas Dissertation FormatWhatShouldIWriteMyPaperOnCanada100% (1)
- University of Toronto Dissertation FormatDocumento4 pagineUniversity of Toronto Dissertation FormatCollegePaperWritingServicesUK100% (1)
- Iu Dissertation FormatDocumento6 pagineIu Dissertation FormatBuyPsychologyPapersRanchoCucamonga100% (1)
- Senior Thesis CornellDocumento7 pagineSenior Thesis Cornellaliciastoddardprovo100% (2)
- Common Mistakes First y CAEDocumento5 pagineCommon Mistakes First y CAERaquel RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Senior Thesis Paper SampleDocumento4 pagineSenior Thesis Paper SampleBuyPapersForCollegeCanada100% (2)
- Essay On Green EnvironmentDocumento5 pagineEssay On Green Environmentsbbftinbf100% (2)
- Koichi ScienceDocumento13 pagineKoichi ScienceCharlene AngacNessuna valutazione finora
- Ut Arlington Dissertation TemplateDocumento4 pagineUt Arlington Dissertation TemplateSecondarySchoolReportWritingSiouxFalls100% (1)
- Research Paper On FcatDocumento8 pagineResearch Paper On Fcatb0pitekezab2100% (1)
- s41599 020 0483 7 PDFDocumento9 pagines41599 020 0483 7 PDFAndreia SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Patzeltetal 2014Documento36 paginePatzeltetal 2014cstettinerNessuna valutazione finora
- All Lectures Open-Ended Questions + KeyDocumento15 pagineAll Lectures Open-Ended Questions + KeySally CampbellNessuna valutazione finora
- 377 Consumer SYLLABUSDocumento5 pagine377 Consumer SYLLABUSwaterloouNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis at The End of An EssayDocumento8 pagineThesis at The End of An Essaykatiefernandezkansascity100% (2)
- Thesis Statement On Standardized TestingDocumento4 pagineThesis Statement On Standardized Testinggjfs5mtv100% (2)
- Unc Graduate School Dissertation SubmissionDocumento7 pagineUnc Graduate School Dissertation SubmissionWriteMyPaperApaFormatUK100% (1)
- An Essay On My SchoolDocumento4 pagineAn Essay On My Schoolglzhcoaeg100% (2)
- Bio205 2015spring Fry 1 - Bio 205 Syllabus Evolution 2015Documento4 pagineBio205 2015spring Fry 1 - Bio 205 Syllabus Evolution 2015api-283084607Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ucsd Dissertation SubmissionDocumento4 pagineUcsd Dissertation SubmissionDoMyCollegePaperSingapore100% (1)
- Dissertation Got DeletedDocumento8 pagineDissertation Got DeletedHelpWithPaperSingapore100% (1)
- Welcoming Deaf Students Into STEM - Recommendations For University Science EducationDocumento8 pagineWelcoming Deaf Students Into STEM - Recommendations For University Science EducationDaniela SaitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Alternative Thesis FormatDocumento8 pagineAlternative Thesis Formatangelarobertswilmington100% (2)
- Senior Thesis UdelDocumento4 pagineSenior Thesis Udelrachelphillipsbillings100% (1)
- City University DissertationDocumento5 pagineCity University DissertationCollegePaperWritingServicesCanada100% (1)
- Bramesfeld Introduction-FINALDocumento86 pagineBramesfeld Introduction-FINALIosif CadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis UtkDocumento7 pagineThesis Utkfjn29rfk100% (2)
- Community Immersion Research PaperDocumento5 pagineCommunity Immersion Research Paperaflboetbe100% (1)
- Term Paper SolutionDocumento5 pagineTerm Paper Solutionc5h4drzj100% (1)
- Three Minute Thesis OntarioDocumento6 pagineThree Minute Thesis Ontarioafknmwhjn100% (1)
- Senior Thesis Paper ExamplesDocumento8 pagineSenior Thesis Paper Exampleskmxrffugg100% (1)
- Scientific Notation Lesson Plan 2Documento4 pagineScientific Notation Lesson Plan 2api-378960179100% (1)
- Undergraduate Dissertation Example TopicsDocumento7 pagineUndergraduate Dissertation Example TopicsPayingSomeoneToWriteAPaperUK100% (1)
- Bài tập tu vung IELTSDocumento4 pagineBài tập tu vung IELTSBl Mê Đu ĐamNessuna valutazione finora
- Itu SFL 2023-2024 Mock Proficiency - Session I (June 2023 Exam)Documento11 pagineItu SFL 2023-2024 Mock Proficiency - Session I (June 2023 Exam)kktcacc1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Senior Thesis UsfDocumento6 pagineSenior Thesis Usftonyastrongheartanchorage100% (2)
- Temporary ThesisDocumento7 pagineTemporary Thesisaflnxhshxlddxg100% (2)
- Udel Senior ThesisDocumento4 pagineUdel Senior ThesisMandy Brown100% (1)
- Undergraduate Dissertation GuidelinesDocumento6 pagineUndergraduate Dissertation GuidelinesWriteMyCustomPaperCanada100% (1)
- Problem Set1Documento4 pagineProblem Set1hanipaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dissertation Draft ExampleDocumento5 pagineDissertation Draft ExampleOnlinePaperWritingServiceDesMoines100% (1)
- Top 10 Sustainability Tips For Schools ETC ETCDocumento2 pagineTop 10 Sustainability Tips For Schools ETC ETCEfe TosluNessuna valutazione finora
- Coursework Science 2014Documento5 pagineCoursework Science 2014frebulnfg100% (2)
- Class 2Documento19 pagineClass 2api-129985624Nessuna valutazione finora
- Uconn Dissertation FormatDocumento5 pagineUconn Dissertation FormatBuyPapersOnlineForCollegeCanada100% (1)
- DCT DiscussionDocumento12 pagineDCT DiscussionNguyen Xuan TrieuNessuna valutazione finora
- PHD Thesis On Academic AchievementDocumento4 paginePHD Thesis On Academic Achievementgj9vq5z0100% (2)
- Practice Final Test Practice: Ae2 WritingDocumento4 paginePractice Final Test Practice: Ae2 WritingQỳnh ZanNessuna valutazione finora
- Undergraduate Dissertation Examples PDFDocumento6 pagineUndergraduate Dissertation Examples PDFWhoWillWriteMyPaperForMeCanada100% (1)
- Lessonplan 1-19-17Documento5 pagineLessonplan 1-19-17api-346184496Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sociology Honors Thesis ExamplesDocumento7 pagineSociology Honors Thesis Examplesjoyceknightjackson100% (1)
- American Sociological AssociationDocumento9 pagineAmerican Sociological AssociationShaziaNessuna valutazione finora
- Eng Project 3Documento12 pagineEng Project 3api-298566195Nessuna valutazione finora
- D.min DissertationDocumento8 pagineD.min DissertationPayToDoMyPaperCanada100% (1)
- Penjelasan Theory of IntelligenceDocumento19 paginePenjelasan Theory of IntelligenceMay JanuaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Question Paper Social Science Class 9 Cbse Term 2Documento6 pagineSample Question Paper Social Science Class 9 Cbse Term 2afmzmxkayjyosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ttu Graduate School Dissertation FormatDocumento5 pagineTtu Graduate School Dissertation FormatPayForAPaperUK100% (1)
- CVEN4705 Lec Week1 T32020Documento73 pagineCVEN4705 Lec Week1 T32020Cynthia OuyangNessuna valutazione finora
- 045 Lesson Plan Genetic DiversitiesDocumento4 pagine045 Lesson Plan Genetic DiversitiesbayangatkizzyNessuna valutazione finora
- Oliver Grasl-Business Model DynamicsDocumento48 pagineOliver Grasl-Business Model DynamicskardraNessuna valutazione finora
- Stochastic Hydrology: Indian Institute of ScienceDocumento40 pagineStochastic Hydrology: Indian Institute of SciencekardraNessuna valutazione finora
- Interactive Protection Using ATP Models PDFDocumento6 pagineInteractive Protection Using ATP Models PDFCarlos Lino Rojas AgüeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Pareto Distribution: X and 0, 0Documento6 paginePareto Distribution: X and 0, 0kardraNessuna valutazione finora
- Shunt Compensation On Ehv Transmission LineDocumento9 pagineShunt Compensation On Ehv Transmission LinekardraNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 KinerosDocumento117 pagine1 KineroskardraNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 Kalak KanawiDocumento21 pagine14 Kalak KanawikardraNessuna valutazione finora
- IEEE 33-Bus Test Distribution SystemDocumento2 pagineIEEE 33-Bus Test Distribution Systemkardra85% (20)
- 123 Bus DataDocumento7 pagine123 Bus DatakardraNessuna valutazione finora
- Jansen.M Harmonics PaperDocumento6 pagineJansen.M Harmonics PaperkardraNessuna valutazione finora
- Supplemental Lecture - Sensitivity AnalysesDocumento23 pagineSupplemental Lecture - Sensitivity AnalyseskardraNessuna valutazione finora
- Component Modeling: Power System StructureDocumento3 pagineComponent Modeling: Power System StructurekardraNessuna valutazione finora
- IEEE 30 Bus Distribution SystemDocumento5 pagineIEEE 30 Bus Distribution Systemkardra100% (1)
- TREND User GuideDocumento29 pagineTREND User GuidekardraNessuna valutazione finora
- Regional Ow-Duration Curves: Reliability For Ungauged BasinsDocumento13 pagineRegional Ow-Duration Curves: Reliability For Ungauged BasinskardraNessuna valutazione finora
- Subscripting in Vensim 2 - Introducing, Progressing Between, Mapping and Creating Subranges of SubscriptsDocumento41 pagineSubscripting in Vensim 2 - Introducing, Progressing Between, Mapping and Creating Subranges of SubscriptskardraNessuna valutazione finora
- 350 Quant QuestionsDocumento330 pagine350 Quant QuestionsKaustabh SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study:: The Enterprise Resource Planning ProjectDocumento6 pagineCase Study:: The Enterprise Resource Planning ProjecttulikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Supply, Delivery, Installation, Testing and Commissioning of Electrical Installation Works PDFDocumento151 pagineSupply, Delivery, Installation, Testing and Commissioning of Electrical Installation Works PDFkuldeep singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Chương 4Documento3 pagineChương 4Trần Khánh VyNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocumento21 pagineStandard Costing and Variance Analysisback2rahul100% (1)
- Final Report 2022Documento6 pagineFinal Report 2022AstridNessuna valutazione finora
- Chua Ping Hian v. Manas, G.R. No. 198867, 16 Oct 2019Documento15 pagineChua Ping Hian v. Manas, G.R. No. 198867, 16 Oct 2019James RonquilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 GST - ProblemsDocumento10 pagineChapter 5 GST - Problemsbalaji RNessuna valutazione finora
- ARTES IAP Full Proposal Cover Letter TemplateDocumento7 pagineARTES IAP Full Proposal Cover Letter Templateosama zamamNessuna valutazione finora
- Profit EquationDocumento1 paginaProfit EquationSaraNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Manuscript Template of AGRARIS 2021Documento17 pagineA. Manuscript Template of AGRARIS 2021Ahmad Fatikhul KhasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Advocacy Centre For Tenants Ontario v. Ontario Energy BoardDocumento24 pagineAdvocacy Centre For Tenants Ontario v. Ontario Energy BoardBrian HillNessuna valutazione finora
- MBTC and BPI RatiosDocumento11 pagineMBTC and BPI RatiosarianedangananNessuna valutazione finora
- Titan Earnings Call Transcript Q3 FY'22Documento17 pagineTitan Earnings Call Transcript Q3 FY'22alim shaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Strategy Notes Prof Kalim KhanDocumento94 pagineMarketing Strategy Notes Prof Kalim KhanPraveen PraveennNessuna valutazione finora
- Book AnswersDocumento138 pagineBook AnswersMartina Vassallo100% (1)
- Phan - Phuong Sourcing Strategy at BakeryDocumento49 paginePhan - Phuong Sourcing Strategy at BakeryNiraj Kumar0% (1)
- L16 Developing Pricing Strategies and ProgramsDocumento29 pagineL16 Developing Pricing Strategies and ProgramsAshish kumar ThapaNessuna valutazione finora
- BroilersDocumento23 pagineBroilersRooney YenoorNessuna valutazione finora
- MKTNG 1Documento1 paginaMKTNG 1BONGGO MARY GRACENessuna valutazione finora
- Post-Keynesian Economics An Introduction PDFDocumento24 paginePost-Keynesian Economics An Introduction PDFMoses AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- (B207A) Shaping Business OpportunityDocumento6 pagine(B207A) Shaping Business OpportunityUtkarsh SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Asset Purchase AgreementDocumento22 pagineAsset Purchase Agreementtom304467% (3)
- preboard-GEN EDDocumento22 paginepreboard-GEN EDALJa bherNessuna valutazione finora
- EM - Reviewer IIDocumento18 pagineEM - Reviewer IIGinalyn MateoNessuna valutazione finora
- BusinessplanDocumento13 pagineBusinessplanapi-288803730Nessuna valutazione finora
- Suggested Solutions To Chapter 8 Problems: NswerDocumento5 pagineSuggested Solutions To Chapter 8 Problems: NsweremilyNessuna valutazione finora
- SubsidiesDocumento5 pagineSubsidiesMahendra ChhetriNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Charging Models: Fixed PriceDocumento6 pagine1 Charging Models: Fixed Pricerajat_rathNessuna valutazione finora
- Bidding DocumentsDocumento82 pagineBidding DocumentsPalwasha GulNessuna valutazione finora