Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
IDQ Learning
Caricato da
Pradeep KothakotaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
IDQ Learning
Caricato da
Pradeep KothakotaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
General:
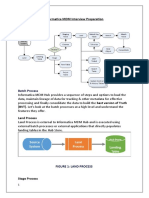
n standard Data Profiling and Data Quality projects, can anyone please clarify in what sequence in the project
lifecycle one would use Data Explorer, Data Quality and Data Director?
My understanding is
1) Data Profiling - For discovering the data and potential anomalies.
2) Data Quality - Outputs from data profiling stage implemented as data quality rules.
3) Data Director - Used to correct the data based on the DQ output. Can this tool be used to correct the data on
the source system directly?
Implementation logic mentioned by Robert is exactly correct. However I would like to add some more additional
points which makes you even clearer regarding the IDQ process in ETL flow.
The outcome of Exception management process is to clean up any database table of bad records (outliers). The output of
the Exception management process should be a clean database table that can be sourced directly into the ETL flow and is
expected to be of high data quality. When you design a process flow for Exception management, you cannot directly use
the bad records table itself as the source in the ETL flow. You need to create a separate process to copy data into the
actual source table from the bad table using the "status code" column information. There is no inherent process to change
data in bad table and have it automatically update the Source table.
The status codes column of the exception table have the following meaning:
UPDATE = 20
REPROCESS = 21
ACCEPT = 22
MERGED = 23
REMERGED = 24
EXTRACTED = 25
REJECT = 26
Hope this helps.
I recently got Analyst access and I'm just browsing through different options. I need help on Scorecard as of
now.
1. I did a sample profile for 200 rows from relational DB as source. When I run the scorecard on this profile, I
expect results for these 200 rows only. But in turn it runs scores on complete table I believe and so it takes hell
lot of time to generate scorecard. Any workaround on this to use only 200 rows for generating scorecard?
2. Can scorecard be run on the background?
3. Can scorecard be viewed by team members who do not have access to Analyst using hyperlink or
something like this?
1. Scorecards by default runs on the complete data set of the physical data object used to create profile. To run
the scorecard on only the required 200 records, follow the steps below:
Create an Logical Data Object (LDO) using developer client such that the output of LDO is only the required 200 records.
Create a profile on LDO.
Create a scorecard on the profile created above.
2. Scorecard runs on the DIS process if DIS is not enabled for "Lanuch Jobs as Separate Process".
Alternatively, you can execute the profile using the command "infacmd ps execute". This command could be
run through a script which executes in background on an operating system
Refer to Command Reference Guide for more details on the command.
3. You can configure scorecard notification settings so that the Analyst tool sends emails when specific metric
scores or metric group scores move across thresholds or remain in specific score ranges, such as
Unacceptable, Acceptable, and Good.
Notification Email message has an option for "ObjectURL" - A hyperlink to the scorecard. You need to provide
the username and password to access the object.
Refer to the Data Explorer User Guide for more details on the scorecard notifications and other details.
Domain:
The Informatica domain is the administrative unit for the Informatica environment. The domain is a
collection of nodes that represent the machines on which the application services run. When you install
the Informatica services on a machine, you install all files for all services.
Informatica has a service-oriented architecture that provides the ability to scale services and to share
resources across multiple machines. The Informatica domain is the primary unit for management and
administration of services.
The Informatica domain can contain one or more nodes. Multiple application services can run on each
node. The application service types that you can run depend on the Informatica license key generated for
your organization. When you plan the domain, you must consider the number of nodes needed in the
domain. You also must consider the types of application services the domain requires and the number of
application services that run on each node.
You must verify that each machine in the domain meets the system requirements to run the installer and
to run the application services. You must also verify that the port numbers that you specify during
installation are available on the machines where you install the Informatica services (How to check
whether ports are available or not?)
The domain requires a relational database to store configuration information and user account privileges
and permissions
You must verify that the databases have the disk space required by the Informatica domain and the
application services.
An Informatica domain is a collection of nodes and services. A node is the logical representation of a machine in a
domain. Services for the domain include the Service Manager that manages all domain operations and a set of
application services that represent server-based functionality.
The following image shows an installation on multiple machines:
For more information about the Informatica domain, see the Informatica Administrator Guide.
Nodes
Gateway node
A gateway node is any node that you configure to serve as a gateway for the domain. One node acts as
the gateway at any given time. That node is called the master gateway. A gateway node can run
application services, and it can serve as a master gateway node. The master gateway node is the entry
point to the domain.
The Service Manager on the master gateway node performs all domain operations on the master
gateway node. The Service Managers running on other gateway nodes perform limited domain
operations on those nodes.
(What are those limited domain tasks?)
Worker nodes
A worker node is any node not configured to serve as a gateway. A worker node can run application
services, but it cannot serve as a gateway. The Service Manager performs limited domain operations on
a worker node.
Service Manager
The Service Manager in the Informatica domain supports the domain and the application services. The
Service Manager runs on each node in the domain.
The Service Manager manages the following areas on each node in the domain:
Domain support
The Service Manager performs operations on each node to support the domain. Domain operations
include authentication, authorization, and logging. The domain operations that the Service Manager
performs on a node depend on the type of node. For example, the Service Manager running on the
master gateway node performs all domain operations on that node. The Service Manager running on
another gateway node or a worker node performs limited domain operations on that node.
Application service support
The Service Manager on each node starts the application services configured to run on that node. It
starts and stops application services based on requests from Informatica clients.
Application Services
Application services represent server-based functionality. After you complete the installation, you
create application services based on the license key generated for your organization. When you create
an application service, you designate a node to run the service process. The service process is the
run-time representation of a service running on a node. The service type determines how many service
processes can run at a time.
If you have the high availability option, you can run an application service on multiple nodes. If you
do not have the high availability option, configure each application service to run on one node.
Some application services require databases to store information processed by the application
service. When you plan the Informatica domain, you also need to plan the databases required by
each application service.
License Key
The license key controls the application services and the functionality that you can use.
Informatica Clients
The clients make requests to the Service Manager or to application services.
S
.
N
Client
Name
Cli
ent
Ty Usage
Metadata
Stores in
will be run
by
Com
ment
o pe
1
Informati
ca
Develop
er
Thi
ck
to create and run data objects,
mappings, profiles, workflows, and
virtual databases
Model
repository
Data
Integration
Service
2
PowerC
enter
Client
Thi
ck
use to define sources and targets,
create transformations and build
mappings, and create workflows to
run mappings
PowerCente
r repository
PowerCent
er
Integration
Service
3
Data
Transfor
mation
Studio
Thi
ck
you use to design and configure Data
Transformation projects
Data
Transformati
on
repository
directory
Data
Transform
ation
Engine
4
Analyst
tool we
b
to analyze, cleanse, integrate, and
standardize data in an enterprise
Model
repository
Data
Integration
Service
Analy
st
Servic
e runs
5
Data
Analyzer
we
b
to run reports to analyze
PowerCenter metadata
Data
Analyzer
repository
Data
Analyzer
application
6
Jaspers
oft we
b
use to run PowerCenter Repository
Reports and Metadata Manager
Reports
Reporting
and
Dashboard
s Service
7
Metadat
a
Manage
r
we
b
to browse and analyze metadata
from disparate metadata repositories
Metadata
Manager
repository
Metadata
Manager
Service
8
Web
Services
Hub
Console
we
b
use to manage the web services you
create in PowerCenter
Web
Services
Hub
Service
Application services:
Analyst Service
The Analyst Service is an application service that runs the Analyst tool in the Informatica domain. The
Analyst Service manages the connections between service components and the users that have access
to the Analyst tool.When you run profiles, scorecards, or mapping specifications in the Analyst tool, the
Analyst Service connects to the Data Integration Service to perform the data integration jobs. When you
work on Human tasks in the Analyst tool, the Analyst Service connects to the Data Integration Service to
retrieve the task data from the Human task database.
When you view, create, or delete a Model repository object in the Analyst tool, the Analyst Service
connects to the Model Repository Service to access the metadata. When you view data lineage analysis
on scorecards in the Analyst tool, the Analyst Service sends the request to the Metadata Manager
Service to run data lineage.
Note: When you create the Analyst Service, you do not associate it with any relational databases.
Associated Services
The Analyst Service connects to other application services within the domain.When you create the
Analyst Service, you can associate it with the following application services:
Data Integration Services
You can associate up to two Data Integration Services with the Analyst Service. The Analyst Service
manages the connection to the Data Integration Service that enables users to perform data preview,
mapping specification, scorecard, and profile jobs in the Analyst tool. The Analyst Service also manages
the connection to the Data Integration Service that you configure to run Human tasks. When you create
the Analyst Service, you provide the name of the Data Integration Services. You can associate the
Analyst Service with the same Data Integration Service for all operations.
Metadata Manager Service
The Analyst Service manages the connection to the Metadata Manager Service that runs data lineage for
scorecards in the Analyst tool. When you create the Analyst Service, you can provide the name of the
Metadata Manager Service.
Model Repository Service
The Analyst Service manages the connection to the Model Repository Service for the Analyst tool. The
Analyst tool connects to the Model Repository Service to create, update, and delete Model repository
objects in the Analyst tool. When you create the Analyst Service, you provide the name of the Model
Repository Service
Content Management Service
The Content Management Service is an application service that manages reference data. A reference
data object contains a set of data values that you can search while performing data quality operations on
source data. The Content Management Service also compiles rule specifications into mapplets. A rule
specification object describes the data requirements of a business rule in logical terms. The Content
Management Service uses the Data Integration Service to run mappings to transfer data between
reference tables and external data sources. The Content Management Service also provides
transformations, mapping specifications, and rule specifications with the following types of reference data:
Address reference data
Identity populations
Probabilistic models and classifier models
Reference tables
Associated Services
The Content Management Service connects to other application services within the domain. When you
create the Content Management Service, you can associate it with the following application services:
Data Integration Service
The Content Management Service uses the Data Integration Service to run mappings to transfer data
between reference tables and external data sources. When you create the Content Management Service,
you provide the name of the Data Integration Service. You must create the Data Integration Service and
Content Management Service on the same node.
Model Repository Service
The Content Management Service connects to the Model Repository Service to store metadata for
reference data objects in the Model repository. When you create the Content Management Service, you
provide the name of the Model Repository Service.
You can associate multiple Content Management Services with a Model Repository Service. The Model
Repository Service identifies the first Content Management Service that you associate as the master
Content Management Service. The master Content Management Service manages the data files for the
probabilistic models and classifier models in the Model repository.
(What are probabilistic models and classifier models?)
Required Databases
The Content Management Service requires a reference data warehouse in a relational database. When
you create the Content Management Service, you must provide connection information to the reference
data warehouse.
Create the following database before you create the Content Management Service:
Reference data warehouse
Stores data values for the reference table objects that you define in the Model repository. When you add
data to a reference table, the Content Management Service writes the data values to a table in the
reference data warehouse. You need a reference data warehouse to manage reference table data in
the Analyst tool and the Developer tool.
Data Integration Service
The Data Integration Service is an application service that performs data integration jobs for the Analyst
tool, the Developer tool, and external clients.
When you preview or run data profiles, SQL data services, and mappings in the Analyst tool or the
Developer tool, the client tool sends requests to the Data Integration Service to perform the data
integration jobs.
When you run SQL data services, mappings, and workflows from the command line program or an
external client, the command sends the request to the Data Integration Service.
Associated Services
The Data Integration Service connects to other application services within the domain. When you create
the Data Integration Service, you can associate it with the following application service:
Model Repository Service
The Data Integration Service connects to the Model Repository Service to perform jobs such as running
mappings, workflows, and profiles. When you create the Data Integration Service, you provide the name
of the Model Repository Service.
Required Databases
The Data Integration Service can connect to multiple relational databases. The databases that the service
can connect to depend on the license key generated for your organization. When you create the Data
Integration Service, you provide connection information to the databases. Create the following databases
before you create the Data Integration Service:
Data object cache database
Stores cached logical data objects and virtual tables. Data object caching enables the Data Integration
Service to access pre-built logical data objects and virtual tables. You need a data object cache database
to increase performance for mappings, SQL data service queries, and web service requests.
Profiling warehouse
Stores profiling information, such as profile results and scorecard results. You need a profiling warehouse
to perform profiling and data discovery.
Human task database
Stores metadata for Human tasks that run in workflows. The metadata identifies users and groups who
work on the Human task instances in the Analyst tool. The metadata contains user and group names and
specifies the range of exceptions records or clusters in each task instance. You need a Human task
database to perform exception management.
Metadata Manager Service
The Metadata Manager Service is an application service that runs the Metadata Manager web client in
the Informatica domain. The Metadata Manager Service manages the connections between service
components and the users that have access to Metadata Manager.
When you load metadata into the Metadata Manager warehouse, the Metadata Manager Service
connects to the PowerCenter Integration Service. The PowerCenter Integration Service runs workflows in
the PowerCenter repository to read from metadata sources and load metadata into the Metadata
Manager warehouse.
When you use Metadata Manager to browse and analyze metadata, the Metadata Manager Service
accesses the metadata from the Metadata Manager repository.
Associated Services
The Metadata Manager Service connects to other application services within the domain. When you
create the Metadata Manager Service, you can associate it with the following application services:
PowerCenter Integration Service
When you load metadata into the Metadata Manager warehouse, the Metadata Manager Service
connects to the PowerCenter Integration Service. The PowerCenter Integration Service runs workflows in
the PowerCenter repository to read from metadata sources and load metadata into the Metadata
Manager warehouse. When you create the Metadata Manager Service, you provide the name of the
PowerCenter Integration Service.
PowerCenter Repository Service
The Metadata Manager Service connects to the PowerCenter Repository Service to access
metadata objects in the PowerCenter repository. The PowerCenter Integration Service uses the
metadata objects to load metadata into the Metadata Manager warehouse. The metadata objects include
sources, targets, sessions, and workflows. The Metadata Manager Service determines the associated
PowerCenter Repository Service based on the PowerCenter Integration Service associated with the
Metadata Manager Service.
Required Databases
The Metadata Manager Service requires a Metadata Manager repository in a relational database. When
you create the Metadata Manager Service, you must provide connection information to the database.
Create the following database before you create the Metadata Manager Service:
Metadata Manager Repository
Stores the Metadata Manager warehouse and models. The Metadata Manager warehouse is a
centralized metadata warehouse that stores the metadata from metadata sources. Models define the
metadata that Metadata Manager extracts from metadata sources. You need a Metadata Manager
repository to browse and analyze metadata in Metadata Manager.
Model Repository Service
The Model Repository Service is an application service that manages the Model repository. The Model
repository stores metadata created by Informatica clients and application services in a relational
database to enable collaboration among the clients and services.
When you access a Model repository object in the Developer tool, the Analyst tool, the Administrator
tool, or the Data Integration Service, the client or service sends a request to the Model Repository
Service. The Model Repository Service process fetches, inserts, and updates the metadata in the Model
repository database tables.
Note: When you create the Model Repository Service, you do not associate it with other application
services.
Required Databases
The Model Repository Service requires a Model repository in a relational database. When you create the
Model Repository Service, you must provide connection information to the database. Create the following
database before you create the Model Repository Service:
Model repository
Stores metadata created by Informatica clients and application services in a relational database to enable
collaboration among the clients and services. You need a Model repository to store the design-time and
run-time objects created by Informatica clients and application services.
PowerCenter Integration Service
The PowerCenter Integration Service is an application service that runs workflows and sessions for the
PowerCenter Client. When you run a workflow in the PowerCenter Client, the client sends the requests to
the PowerCenter Integration Service. The PowerCenter Integration Service connects to the PowerCenter
Repository Service to fetch metadata from the PowerCenter repository, and then runs and monitors the
sessions and workflows.
Note: When you create the PowerCenter Integration Service, you do not associate it with any relational
databases.
Associated Services
The PowerCenter Integration Service connects to other application services within the domain. When you
create the PowerCenter Integration Service, you can associate it with the following application service:
PowerCenter Repository Service
The PowerCenter Integration Service requires the PowerCenter Repository Service. The PowerCenter
Integration Service connects to the PowerCenter Repository Service to run workflows and sessions.
When you create the PowerCenter Integration Service, you provide the name of the PowerCenter
Repository Service.
PowerCenter Repository Service
The PowerCenter Repository Service is an application service that manages the PowerCenter repository.
The PowerCenter repository stores metadata created by the PowerCenter Client and application services
in a relational database. When you access a PowerCenter repository object in the PowerCenter Client or
the PowerCenter Integration Service, the client or service sends a request to the PowerCenter Repository
Service. The PowerCenter Repository Service process fetches, inserts, and updates metadata in
the PowerCenter repository database tables.
Note: When you create the PowerCenter Repository Service, you do not associate it with other
application services.
Required Databases
The PowerCenter Repository Service requires a PowerCenter repository in a relational database. When
you create the PowerCenter Repository Service, you must provide connection information to the
database. Create the following database before you create the PowerCenter Repository Service:
PowerCenter repository
Stores metadata created by the PowerCenter Client in a relational database. You need a PowerCenter
repository to store objects created by the PowerCenter Client and to store objects that are run by the
PowerCenter Integration Service.
Reporting Service
The Reporting Service is an application service that runs the Data Analyzer application in the
Informatica domain. The Reporting Service manages the connections between service components and
the users that have access to Data Analyzer. The Reporting Service stores metadata for schemas,
metrics and attributes, queries, reports, user profiles, and other objects in the Data Analyzer
repository. When you run reports for a data source, the Reporting Service uses the metadata in the Data
Analyzer repository to retrieve the data for the report and to present the report.
Associated Services
The Reporting Service connects to other application services within the domain. When you create the
Reporting Service, you can associate it with the following application services:
PowerCenter Repository Service
The Reporting Service connects to the PowerCenter Repository Service when you use Data Analyzer to
run PowerCenter Repository Reports. When you create the Reporting Service, you can provide the
name of the PowerCenter Repository Service as the reporting source.
Metadata Manager Service
The Reporting Service connects to the Metadata Manager Service when you use Data Analyzer to run
Metadata Manager Reports. When you create the Reporting Service, you can provide the name of the
Metadata Manager Service as the reporting source.
Required Databases
The Reporting Service requires a Data Analyzer repository in a relational database. When you create the
Reporting Service, you must provide connection information to the database. Create the following
database before you create the Reporting Service:
Data Analyzer repository
Stores metadata for schemas, metrics and attributes, queries, reports, user profiles, and other objects.
You need a Data Analyzer repository to create and run reports in Data Analyzer.
Reporting and Dashboards Service
The Reporting and Dashboards Service is an application service that runs the JasperReports
application in the Informatica domain.
The Reporting and Dashboards Service stores metadata for PowerCenter Repository Reports and
Metadata Manager Reports in the Jaspersoft repository. You use the PowerCenter Client or Metadata
Manager to run the reports. When you run the reports, the Reporting and Dashboards Service uses the
metadata in the Jaspersoft repository to retrieve the data for the report and to present the report.
JasperReports is an open source reporting library that users can embed into any Java application.
JasperReports Server builds on JasperReports and forms a part of the Jaspersoft Business Intelligence
suite of products.
Associated Services
The Reporting and Dashboards Service connects to other application services within the domain.After
you create the Reporting and Dashboards Service, you can associate it with the following application
services:
PowerCenter Repository Service
The Reporting and Dashboards Service connects to the PowerCenter Repository Service when you use
JasperReports to run PowerCenter Repository Reports. After you create the Reporting and Dashboards
Service, you can provide the name of the PowerCenter Repository Service as the reporting source.
Metadata Manager Service
The Reporting and Dashboards Service connects to the Metadata Manager Service when you use
JasperReports to run Metadata Manager Reports. After you create the Reporting and Dashboards
Service, you can provide the name of the Metadata Manager Service as the reporting source.
Required Databases
The Reporting and Dashboards Service requires a Jaspersoft repository in a relational database. When
you create the Reporting and Dashboards Service, you must provide connection information to the
database.Create the following database before you create the Reporting and Dashboards Service:
Jaspersoft repository
Stores metadata for PowerCenter Repository Reports and Metadata Manager Reports. You need a
Jaspersoft repository to use JasperReports Server to run PowerCenter Repository Reports and Metadata
Manager Reports.
Search Service
The Search Service is an application service that manages search in the Analyst tool and Business
Glossary Desktop.
By default, the Search Service returns search results from a Model repository, such as data objects,
mapping specifications, profiles, reference tables, rules, and scorecards. The Search Service can also
return additional results. The results can include related assets, business terms, and policies. The results
can include column profile results and domain discovery results from a profiling warehouse. In addition,
you can perform a search based on patterns, data types, unique values, or null values.
Note: When you create the Search Service, you do not associate it with any relational databases.
Associated Services
The Search Service connects to other application services within the domain.
When you create the Search Service, you can associate it with the following application services:
Analyst Service
The Analyst Service manages the connection to the Search Service that enables and manages searches
in the Analyst tool. The Analyst Service determines the associated Search Service based on the Model
Repository Service associated with the Analyst Service.
Data Integration Service
The Search Service connects to the Data Integration Service to return column profile and domain
discovery search results from the profiling warehouse associated with the Data Integration Service. The
Search Service determines the associated Data Integration Service based on the Model Repository
Service.
Model Repository Service
The Search Service connects to the Model Repository Service to return search results from a Model
repository. The search results can include data objects, mapping specifications, profiles, reference tables,
rules, and scorecards. When you create the Search Service, you provide the name of the Model
Repository Service.
Web Services Hub
The Web Services Hub Service is an application service in the Informatica domain that exposes
PowerCenter functionality to external clients through web services.
The Web Services Hub Service receives requests from web service clients and passes them to the
PowerCenter Integration Service or PowerCenter Repository Service. The PowerCenter Integration
Service or PowerCenter Repository Service processes the requests and sends a response to the Web
Services Hub. The Web Services Hub sends the response back to the web service client.
Note: When you create the Web Services Hub Service, you do not associate it with any relational
databases
Associated Services
The Web Services Hub Service connects to other application services within the domain. When you
create the Web Services Hub Service, you can associate it with the following application services:
PowerCenter Integration Service
The Web Services Hub Service connects to the PowerCenter Integration Service to send requests from
web service clients to the PowerCenter Integration Service. The Web Services Hub Service determines
the associated PowerCenter Integration Service based on the PowerCenter Repository Service.
PowerCenter Repository Service
The Web Services Hub Service connects to the PowerCenter Repository Service to send requests from
web service clients to the PowerCenter Repository Service. When you create the Web Services Hub
Service, you provide the name of the PowerCenter Repository Service.
Databases:
Domain configuration repository - INFA_DOMAIN
Must have permissions to create and drop tables, indexes, and views, and to select, insert, update, and
delete data from tables
The domain stores configuration and user information in a domain configuration repository.
Data Analyzer repository
The Data Analyzer repository stores metadata for schemas, metrics and attributes, queries, reports, user
profiles, and other objects for the Reporting Service.
You must specify the Data Analyzer repository details when you create a Reporting Service.
Data object cache repository:
The data object cache database stores cached logical data objects and virtual tables for the Data
Integration Service. You specify the data object cache database connection when you create the Data
Integration Service
Human task repository:
The Data Integration Service stores metadata for Human tasks in the Human task database. Before you
create the Human task database, set up a database and database user account for the Model repository
You specify the Human task database connection when you create the Data Integration Service.
Jaspersoft repository:
The Jaspersoft repository stores reports, data sources, and metadata corresponding to the data source.
You must specify the Jaspersoft repository details when you create the Reporting and Dashboards
Service.
Metadata Manager Repository:
Metadata Manager repository contains the Metadata Manager warehouse and models. The Metadata
Manager warehouse is a centralized metadata warehouse that stores the metadata from metadata
sources. Specify the repository details when you create a Metadata Manager Service
Model repository:
Informatica services and clients store data and metadata in the Model repository. Before you create the
Model Repository Service, set up a database and database user account for the Model repository.
PowerCenter repository:
A PowerCenter repository is a collection of database tables containing metadata. A PowerCenter
Repository Service manages the repository and performs all metadata transactions between the
repository database and repository clients.
Profiling warehouse:
The profiling warehouse database stores profiling and scorecard results. You specify the profiling
warehouse connection when you create the Data Integration Service
Note: Ensure that you install the database client on the machine on which you want to run the Data
Integration Service.
Reference data warehouse:
The reference data warehouse stores the data values for reference table objects that you define in a
Model repository. You configure a Content Management Service to identify the reference data warehouse
and the Model repository.
You associate a reference data warehouse with a single Model repository. You can select a common
reference data warehouse on multiple Content Management Services if the Content Management
Services identify a common Model repository. The reference data warehouse must support mixed-case
column names.
Note: Ensure that you install the database client on the machine on which you want to run the Content
Management Service.
Service Manager Log Files
The installer starts the Informatica service. The Informatica service starts the Service Manager for the
node. The Service Manager generates log files that indicate the startup status of a node. Use these
files to troubleshoot issues when the Informatica service fails to start and you cannot log in to
Informatica Administrator. The Service Manager log files are created on each node.
catalina.out:
Log events from the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) that runs the Service Manager.
For example, a port is available during installation, but is in use when the Service Manager starts. Use
this log to get more information about which port was unavailable during startup of the Service Manager.
The catalina.out file is in the /tomcat/logs directory.
node.log:
Log events generated during the startup of the Service Manager on a node. You can use this log to
get more information about why the Service Manager for a node failed to start.
For example, if the Service Manager cannot connect to the domain configuration database after 30
seconds, the Service Manager fails to start.
The node.log file is in the /tomcat/logs directory.
Configure Informatica Environment Variables
You can configure Informatica environment variables to store memory, domain, and location settings
Configure INFA_JAVA_OPTS as a system variable.
Informatica uses a maximum of 512 MB of system memory
-Xmx1024m
configure INFA_DOMAINS_FILE as a system variable
INFA_DOMAINS_FILE variable to the path and file name of the domains.infa file
Use INFA_HOME to designate the Informatica installation directory
If you enable secure communication for the domain, set the INFA_TRUSTSTORE variable with the directory that contains
the truststore files for the SSL certificates
The directory must contain truststore files named infa_truststore.jks and infa_truststore.pem.
You must set the INFA_TRUSTSTORE variable if you use the default SSL certificate provided by Informatica or a certificate
that you provide
The following table describes the database connections that you must create before you create the
associated application services
Database Connection Description
Data object cache database To access the data object cache, create
the data object cache connection for the
Data Integration Service.
Human task database To store Human task metadata, create
the human task database connection for
the Data Integration Service.
Profiling warehouse database To create and run profiles and
scorecards, create the profiling
warehouse database connection for the
Data Integration Service.
To create and run profiles and
scorecards, select this instance of the
Data Integration Service when you
configure the run-time properties of the
Analyst Service.
Reference data warehouse To store reference data, create the
reference data warehouse connection for
the Content management service
Configuring IDQ:
Create 3 databases:
INFA_MRS - For Model Repository Database.
INFA_PROWHS - Profiling warehouse database
INFA_ANLSTG Analyst stage database
Created INFA_HUMAN user for Human Task database.
Created INFA_SQL_PROP user for SQL Properties as part of Data Integration service.
INFA_REF/INFA_REF:
Create database INFA_REF for Reference Database. After that need to create connection in Admin
Console, need to create content management service.
Logon to Infa admin console
Create 6 connections to point to above databases
Create new model repository service use infa_mrs database
It will create content and it may take some time.
Create new data integration service
Here we need to point to Model repository service that we have created in above step.
Below window, Gave Administrator /Administrator as user name/pwd.
Selected Human Task Service Module and Profiling Service Module. Did not select others.
Selected Human Task Service and Profiling Service. Did not select others.
Create new analyst service
Setting up IDQ Analyst Tool:
Logon to Infa 9 admin console using user ID and Password
Go to Analyst Service
You will see URL for Analyst tool
Click on the link and give user ID, password if asks
From Actions menu, click new project
Select Project and from Actions Menu, create New Folder
Click on Folder, Now to import the file customer_OrgA csv file, click on the Actions Menu and New Flat
file
Import the csv file
To import table, click on the Actions Menu and New Table
http://WIN-A4ZOPLLNM64:8085/analyst/
http://WIN-A4ZOPLLNM64:8085/analyst/
Administrator/Administrator
Creating a profile in Informatica Analyst:
Creating reference table in Informatica Analyst:
Setting up Infa Developer:
Property Description
User name Database user name.
Password Password for the user name.
Connection String for metadata
access
Connection string to import physical data objects. Use the following
connection string: jdbc:informatica:oracle://<host>:
1521;SID=<sid>
Connection String for data access Connection string to preview data and run mappings. Enter
dbname.world from the TNSNAMES entry.
Code Page Database code page.
Environment SQL Optional. Enter SQL commands to set the database environment when
you connect to the database. The Data Integration Service executes the
connection environment SQL each time it connects to the database.
Transaction SQL Optional. Enter SQL commands to set the database environment when
you connect to the database. The Data Integration Service executes the
transaction environment SQL at the beginning of each transaction.
Retry Period This property is reserved for future use.
Parallel Mode Optional. Enables parallel processing when loading data into a table in
bulk mode. Default is disabled.
SQL Identifier Character The type of character used to identify special characters and reserved
SQL keywords, such as WHERE. The Data Integration Service places
the selected character around special characters and reserved SQL
keywords. The Data Integration Service also uses this character for the
Support Mixed-case Identifiers property.
Support Mixed-case Identifiers When enabled, the Data Integration Service places identifier characters
around table, view, schema, synonym, and column names when
generating and executing SQL against these objects in the connection.
Use if the objects have mixed-case or lowercase names. By default, this
option is not selected.
Creating a Connection
In the Administrator tool, you can create relational database, social media, and file systems connections.
1. In the Administrator tool, click the Domain tab.
2. Click the Connections view.
3. In the Navigator, select the domain.
4. In the Navigator, click Actions > New >
Connection. The New Connection dialog box
appears.
5. In the New Connection dialog box, select the connection type, and then click
OK. The New Connection wizard appears.
6. Enter the connection properties.The connection properties that you enter depend
on the connection type. Click Next to go to the next page of the New Connection
wizard.
7. When you finish entering connection properties, you can click Test Connection to
test the connection.
8. Click Finish.
Informatica contains the following components:
1. Application clients. A group of clients that you use to access underlying Informatica
functionality. Application clients make requests to the Service Manager or application
services.
2. Application services. A group of services that represent server-based functionality.
An Informatica domain can contain a subset of application services. You configure the
application services that are required by the application clients that you use.
3. Repositories. A group of relational databases that store metadata about objects and
processes required to handle user requests from application clients.
4. Service Manager. A service that is built in to the domain to manage all domain
operations. The Service Manager runs the application services and performs domain
functions including authentication, authorization, and logging.
Application Client Application Services Repositories
Data Analyzer Reporting Service Data Analyzer repository
Informatica
Reporting &
Dashboards
Reporting and Dashboards Service Jaspersoft repository
Informatica Analyst Analyst Service
Data Integration Service
Model Repository Service
Search Service
Model repository
Informatica Data Director
for Data Quality
Data Integration Service
Informatica Data Director Service
Human task database
Informatica Developer - Analyst Service
- Content Management Service
- Data Integration Service
- Model Repository Service
Model repository
Metadata Manager - Metadata Manager Service
- PowerCenter Integration Service
- PowerCenter Repository Service
- Metadata Manager
repository
- PowerCenter repository
PowerCenter Client - PowerCenter Integration Service
- PowerCenter Repository Service
PowerCenter repository
Web Services Hub Console - PowerCenter Integration Service
- PowerCenter Repository Service
- Web Services Hub
PowerCenter repository
The following application services are not accessed by an Informatica application client:
PowerExchange Listener Service. Manages the PowerExchange Listener for bulk data movement
and change data capture. The PowerCenter Integration Service connects to the PowerExchange
Listener through the Listener Service.
PowerExchange Logger Service. Manages the PowerExchange Logger for Linux, UNIX, and Windows
to capture change data and write it to the PowerExchange Logger Log files. Change data can originate
from DB2 recovery logs, Oracle redo logs, a Microsoft SQL Server distribution database, or data sources
on an i5/OS or z/OS system.
SAP BW Service. Listens for RFC requests from SAP BI and requests that the PowerCenter Integration
Service run workflows to extract from or load to SAP BI.
RFC. Purpose. Communication between applications in different systems in the SAP environment
includes connections between SAP systems as well as between SAP systems and non-SAP systems.
Remote Function Call (RFC) is the standard SAP interface for communication between SAP systems.
Feature Availability
Informatica products use a common set of applications. The product features you can use depend on your product license.
The following table describes the licensing options and the application features available with each option:
Licensing
Option
Informatica Developer Features Informatica Analyst Features
Data Explorer
-
Profiling that includes using the enterprise
discovery profile and discovering primary key,
foreign key, and functional dependency.
-
Curate inferred profile results
-
Scorecarding
-
Profiling including enterprise discovery
-
Scorecarding
-
Use discovery search to find where data and metadata
exist in the profiling repositories
-
Curate inferred profile results
-
Create and run profiling rules
-
Reference table management
Data Quality
-
Create and run mappings with all transformations
-
Create and run rules
-
Profiling
-
Scorecarding
-
Export objects to PowerCenter
-
Profiling
-
Scorecarding
-
Reference table management
-
Create profiling rules
-
Run rules in profiles
-
Bad and duplicate record management
Data Services
-
Create logical data object models
-
Create and run mappings with Data Services
transformations
-
Create SQL data services
-
Create web services
-
Export objects to PowerCenter
-
Reference table management
Data Services
and Profiling
Option
-
Create logical data object models
-
Create and run mappings with Data Services
transformations
-
Create SQL data services
-
Create web services
-
Export objects to PowerCenter
-
Create and run rules with Data Services
transformations
-
Profiling
-
Reference table management
Informatica Analyst
Use to analyze, cleanse, standardize, profile, and score data in an enterprise
Column and rule profiling, scorecarding, and bad record and duplicate record management,
You can also manage reference data and provide the data to developers in a
data quality solution
Data Quality and Profiling
Profile data. Profiling reveals the content and structure of your data. Profiling is a key step in
any data project as it can identify strengths and weaknesses in your data and help you define
your project plan.
Create scorecards to review data quality. A scorecard is a graphical representation of the
quality measurements in a profile.
Standardize data values. Standardize data to remove errors and inconsistencies that you find
when you run a profile. You can standardize variations in punctuation, formatting, and
spelling. For example, you can ensure that the city, state, and ZIP code values are consistent.
Parse records. Parse data records to improve record structure and derive additional
information from your data. You can split a single field of freeform data into fields that contain
different information types. You can also add information to your records. For example, you can
flag customer records as personal or business customers.
Validate postal addresses. Address validation evaluates and enhances the accuracy and
deliverability of your postal address data. Address validation corrects errors in addresses and
completes partial addresses by comparing address records against reference data from
national postal carriers. Address validation can also add postal information that speeds mail
delivery and reduces mail costs.
Find duplicate records. Duplicate record analysis compares a set of records against each
other to find similar or matching values in selected data columns. You set the level of similarity
that indicates a good match between field values. You can also set the relative weight fixed to
each column in match calculations. For example, you can prioritize surname information over
forename information.
Create and run data quality rules. Informatica provides pre-built rules that you can run or edit
to suit your project objectives. You can create rules in the Developer tool.
Collaborate with Informatica users. The rules and reference data tables you add to the
Model repository are available to users in the Developer tool and the Analyst tool. Users can
collaborate on projects, and different users can take ownership of objects at different stages of a
project.
Export mappings to PowerCenter. You can export mappings to PowerCenter to reuse the
metadata for physical data integration or to create web services.
Informatica Analyst Tutorial
Creates projects and folders, creates profiles and rules, scores data, and creates reference tables
Errors:
Mapping service associated with the Analyst service is disabled or is not available. Recycle the
Mapping service in the Administrator tool.
Below module was set to false, now made it to true in admin console. And
recycled Repository service, Data Int service and Analyst service.
No data domains in the data domain glossary. This error has come while
creating Quick profile in Discovery workspace.
Tried creating reference table in Informatica Analyst tool:
Got the error: cannot create reference table
Solution:
https://mysupport.informatica.com/message/40554#40554
Login to informatica administator console. click on the analyst service.go to action on right
hand side. the click on audit table > create. Once the audit table is created the analyst
service can create the reference table.
I could not find this option, I feel content management service is required to create reference
tables from Analyst. So need to create Reference Data Warehouse and Content
Management service.
Created Content management service. After that got the below error: Audit Tables do not
exist.
Solution: Open Actions (Left side)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Informatica Data Quality Study GuideDocumento106 pagineInformatica Data Quality Study GuideSugguna ViswanadthNessuna valutazione finora
- SAS Programming Guidelines Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesDa EverandSAS Programming Guidelines Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Informatica Data Quality PDFDocumento44 pagineInformatica Data Quality PDFAjay SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- IDQ NotesDocumento5 pagineIDQ Notesravi_405Nessuna valutazione finora
- IBM InfoSphere DataStage A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDa EverandIBM InfoSphere DataStage A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- IdqDocumento2 pagineIdqPriyanka Sinha100% (1)
- Managing Data in Motion: Data Integration Best Practice Techniques and TechnologiesDa EverandManaging Data in Motion: Data Integration Best Practice Techniques and TechnologiesNessuna valutazione finora
- IDQ ReferenceDocumento31 pagineIDQ ReferenceRaman DekuNessuna valutazione finora
- Master data management Complete Self-Assessment GuideDa EverandMaster data management Complete Self-Assessment GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- HOL Informatica DataQuality 9.1Documento48 pagineHOL Informatica DataQuality 9.1vvmexNessuna valutazione finora
- Idq9 0 1Documento199 pagineIdq9 0 1adminolej100% (3)
- Core architecture data model A Clear and Concise ReferenceDa EverandCore architecture data model A Clear and Concise ReferenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Informatica ETL Interview Questions SolutionsDocumento2 pagineInformatica ETL Interview Questions SolutionsShashank SauravNessuna valutazione finora
- Logical data model A Clear and Concise ReferenceDa EverandLogical data model A Clear and Concise ReferenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Informatica MDM QuestionsDocumento3 pagineInformatica MDM Questionssrikanthv_14Nessuna valutazione finora
- Getting Started with Greenplum for Big Data AnalyticsDa EverandGetting Started with Greenplum for Big Data AnalyticsNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Profiling With Informatica Data QualityDocumento5 pagineData Profiling With Informatica Data QualityusermaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Metadata Definitions - V01Documento12 pagineMetadata Definitions - V01Tanuj KukretiNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Data Architecture A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandBig Data Architecture A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- DataStage MatterDocumento81 pagineDataStage MatterEric SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Lake Architecture Strategy A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDa EverandData Lake Architecture Strategy A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Datawarehousing - Etl Project Life CycleDocumento2 pagineDatawarehousing - Etl Project Life CycleShiva CHNessuna valutazione finora
- The Data Model Resource Book: Volume 3: Universal Patterns for Data ModelingDa EverandThe Data Model Resource Book: Volume 3: Universal Patterns for Data ModelingNessuna valutazione finora
- Informatica MDM Training 2Documento80 pagineInformatica MDM Training 2ravinder pal singhNessuna valutazione finora
- 89 Talend Interview Questions For Experienced 2018 - Real Time ScenarioDocumento3 pagine89 Talend Interview Questions For Experienced 2018 - Real Time ScenariobharathNessuna valutazione finora
- MIcro Design - ABC Framework Ver 1.3Documento26 pagineMIcro Design - ABC Framework Ver 1.3Anup Mukhopadhyay100% (1)
- Semantic Data Model A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandSemantic Data Model A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Informatica ResumeDocumento7 pagineInformatica ResumeSrikanth GogikarNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Modeling PrinciplesDocumento21 pagineData Modeling PrinciplesNag Dhall100% (1)
- Data Governance Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandData Governance Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Project ArchitectureDocumento7 pagineProject ArchitectureGondrala Balaji100% (1)
- Top 25 ETL Testing Interview QuestionsDocumento6 pagineTop 25 ETL Testing Interview QuestionsKancharlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Address Doctor With IDQDocumento7 pagineAddress Doctor With IDQzipzapdhoomNessuna valutazione finora
- Informatica IICS Interview QuestionsDocumento33 pagineInformatica IICS Interview QuestionsN ShaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Talend Open Studio For Data Integration: User GuideDocumento452 pagineTalend Open Studio For Data Integration: User GuideFirdaousNessuna valutazione finora
- ETL Process Definitions and DeliverablesDocumento4 pagineETL Process Definitions and Deliverableszia003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ab Initio - Introductory - Course - IDocumento92 pagineAb Initio - Introductory - Course - IMesha MalliNessuna valutazione finora
- IICS Asha24Documento3 pagineIICS Asha24Raja PappireddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Informatica MDM Interview PreparationDocumento35 pagineInformatica MDM Interview PreparationBharadwaj Karri100% (1)
- MDM Interview QuestionsDocumento5 pagineMDM Interview Questionspurnachandra42625% (4)
- Informatica ScenariosDocumento18 pagineInformatica ScenariosRaghu Nath100% (1)
- Datastage ScenariosDocumento34 pagineDatastage ScenariosNaresh Kumar100% (1)
- Introduction To Informatica Data Quality: Deloitte Consulting LLPDocumento23 pagineIntroduction To Informatica Data Quality: Deloitte Consulting LLPRakshit RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Datastage InterviewDocumento161 pagineDatastage Interviewmukesh100% (1)
- Data Quality and Preprocessing Concepts ETLDocumento64 pagineData Quality and Preprocessing Concepts ETLRahul PanthriNessuna valutazione finora
- Top 50 Tableau Real-Time Interview Questions and Answers PDFDocumento11 pagineTop 50 Tableau Real-Time Interview Questions and Answers PDFPandian NadaarNessuna valutazione finora
- ETL Healthcare Insurence Project DocumentDocumento40 pagineETL Healthcare Insurence Project DocumentRaamNessuna valutazione finora
- DataStage Best Practises 1Documento41 pagineDataStage Best Practises 1a_sachanNessuna valutazione finora
- Datastage Interview QuestionsDocumento18 pagineDatastage Interview QuestionsGanesh Kumar100% (1)
- Datawarehousing Interview QuestionsDocumento14 pagineDatawarehousing Interview Questionselena75% (4)
- Data Stage Interview QuestionsDocumento15 pagineData Stage Interview QuestionsManoj SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Informatica Error HandlingDocumento7 pagineInformatica Error HandlingVikas Sinha100% (1)
- DAR Implementation in HPServerDocumento4 pagineDAR Implementation in HPServerPradeep KothakotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Using Pushdown OptimizationDocumento18 pagineUsing Pushdown OptimizationPradeep KothakotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Teradata Client ANSI TERADATA ModesDocumento2 pagineTeradata Client ANSI TERADATA ModesPradeep KothakotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Informatica V9 Sizing GuideDocumento9 pagineInformatica V9 Sizing GuidePradeep Kothakota0% (1)
- Infa PWX OraclecdcDocumento18 pagineInfa PWX OraclecdcPradeep KothakotaNessuna valutazione finora
- INFA NotesDocumento161 pagineINFA NotesPradeep KothakotaNessuna valutazione finora
- WF Run Stats GuaravDocumento2 pagineWF Run Stats GuaravPradeep KothakotaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Join Vs Database JoinDocumento21 pagineA Join Vs Database JoinPradeep KothakotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Building A Scalable Meraki SolutionDocumento7 pagineBuilding A Scalable Meraki SolutionSergio VargasNessuna valutazione finora
- Sum UpgradeDocumento22 pagineSum UpgradeNarendra ChoudaryNessuna valutazione finora
- HGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGDocumento3 pagineHGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGrajashreeNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.6 Creating and Operating POSIX ThreadsDocumento12 pagine4.6 Creating and Operating POSIX ThreadsAlpha PlacardNessuna valutazione finora
- PAN-OS v8 Release NotesDocumento60 paginePAN-OS v8 Release NotesAlberto HuamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Qcsuper - Ims - Registration Capture Sample - Buscar Con GoogleDocumento2 pagineQcsuper - Ims - Registration Capture Sample - Buscar Con GoogleffdseerNessuna valutazione finora
- EV Whitepaper - PST Migration With Enterprise Vault 11Documento60 pagineEV Whitepaper - PST Migration With Enterprise Vault 11SteveNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Editor v. 1.1.1: Giuliana Pitança AlcántaraDocumento31 pagineCourse Editor v. 1.1.1: Giuliana Pitança AlcántaraEdmund LeongNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Safety: Name: - DateDocumento1 paginaComputer Safety: Name: - DateLarbi Nadia100% (1)
- Advance Compliance Reporting: Setting Up (1J2)Documento10 pagineAdvance Compliance Reporting: Setting Up (1J2)JimmyNessuna valutazione finora
- KPD 702 - Advanced Web ProgrammingDocumento6 pagineKPD 702 - Advanced Web ProgrammingShakirinah AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- TOPIC 2 Part 1 Machine Instructions and ProgramsDocumento16 pagineTOPIC 2 Part 1 Machine Instructions and ProgramsQuang MinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Class MethodsDocumento7 pagineTest Class Methodsvarun.chintatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cum Pio Midwife Clinic Management System 1Documento36 pagineCum Pio Midwife Clinic Management System 1jessrylmae belzaNessuna valutazione finora
- MixedDocumento12 pagineMixedzihadNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Security 1.0 Modules 11 - 12 - Intrusion Prevention Group Exam AnswersDocumento13 pagineNetwork Security 1.0 Modules 11 - 12 - Intrusion Prevention Group Exam AnswersBrali Dioulson NguemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Online World in Crisis Management S2 - RobihDocumento1 paginaEffect of Online World in Crisis Management S2 - RobihrobihNessuna valutazione finora
- SAD ProjectDocumento18 pagineSAD ProjectjordyNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manager 7.2 - Installation and Configuration - VIII - Managed System Config - Java SystemDocumento6 pagineSolution Manager 7.2 - Installation and Configuration - VIII - Managed System Config - Java SystemRockey MoseNessuna valutazione finora
- DMDW SyllabusDocumento2 pagineDMDW Syllabushellrider22Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tel-Track SatelliteDocumento7 pagineTel-Track SatelliteVavariroyashe MambanjeNessuna valutazione finora
- Palo Alto Networks Stallion Autumn SeminarDocumento20 paginePalo Alto Networks Stallion Autumn Seminarmasterlinh2008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco 700-765 Free Practice Exam & Test Training - ITExams - Com Page1Documento6 pagineCisco 700-765 Free Practice Exam & Test Training - ITExams - Com Page1Dark HorizonNessuna valutazione finora
- APPS 2 Customizing The Document LibraryDocumento40 pagineAPPS 2 Customizing The Document LibrarylementreeNessuna valutazione finora
- PCNSA Exam - Free Questions and Answers - ITExams - Com-15Documento2 paginePCNSA Exam - Free Questions and Answers - ITExams - Com-15amrulariffi.mppuitmsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Intrusion Policy Report: Modified by Admin Last Modified 2017-01-15 18:56:52 (UTC)Documento312 pagineIntrusion Policy Report: Modified by Admin Last Modified 2017-01-15 18:56:52 (UTC)dadavahidNessuna valutazione finora
- O & M Manual TemplateDocumento11 pagineO & M Manual Templatesooriya_82Nessuna valutazione finora
- W2-Csol 540 - The Bangladesh Bank HeistDocumento6 pagineW2-Csol 540 - The Bangladesh Bank Heistapi-694098467Nessuna valutazione finora
- Forum Sentry: Deployment Architecture ConceptsDocumento10 pagineForum Sentry: Deployment Architecture ConceptsKay AdeNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Indra Saputra, Senin, 19 Juni 23Documento2 pagineDr. Indra Saputra, Senin, 19 Juni 23Vedo RivedoNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Outlook Guide to Success: Learn Smart Email Practices and Calendar Management for a Smooth Workflow [II EDITION]Da EverandMicrosoft Outlook Guide to Success: Learn Smart Email Practices and Calendar Management for a Smooth Workflow [II EDITION]Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessDa EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Data Engineering: Plan and Build Robust Data SystemsDa EverandFundamentals of Data Engineering: Plan and Build Robust Data SystemsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Sweet Spot UX: Communicating User Experience to Stakeholders, Decision Makers and Other HumansDa EverandSweet Spot UX: Communicating User Experience to Stakeholders, Decision Makers and Other HumansValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (5)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveDa EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNessuna valutazione finora
- Python for Beginners: A Crash Course Guide to Learn Python in 1 WeekDa EverandPython for Beginners: A Crash Course Guide to Learn Python in 1 WeekValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (7)
- Microservices Patterns: With examples in JavaDa EverandMicroservices Patterns: With examples in JavaValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Microsoft Word Guide for Success: From Basics to Brilliance in Achieving Faster and Smarter Results [II EDITION]Da EverandMicrosoft Word Guide for Success: From Basics to Brilliance in Achieving Faster and Smarter Results [II EDITION]Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Microsoft Teams Guide for Success: Mastering Communication, Collaboration, and Virtual Meetings with Colleagues & ClientsDa EverandMicrosoft Teams Guide for Success: Mastering Communication, Collaboration, and Virtual Meetings with Colleagues & ClientsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Ultimate Snowflake Architecture for Cloud Data Warehousing: Architect, Manage, Secure, and Optimize Your Data Infrastructure Using Snowflake for Actionable Insights and Informed Decisions (English Edition)Da EverandUltimate Snowflake Architecture for Cloud Data Warehousing: Architect, Manage, Secure, and Optimize Your Data Infrastructure Using Snowflake for Actionable Insights and Informed Decisions (English Edition)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Agile Project Management: Scrum for BeginnersDa EverandAgile Project Management: Scrum for BeginnersValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (7)
- Microsoft Excel Guide for Success: Transform Your Work with Microsoft Excel, Unleash Formulas, Functions, and Charts to Optimize Tasks and Surpass Expectations [II EDITION]Da EverandMicrosoft Excel Guide for Success: Transform Your Work with Microsoft Excel, Unleash Formulas, Functions, and Charts to Optimize Tasks and Surpass Expectations [II EDITION]Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Excel 2023 for Beginners: A Complete Quick Reference Guide from Beginner to Advanced with Simple Tips and Tricks to Master All Essential Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, Charts, Tools, & ShortcutsDa EverandExcel 2023 for Beginners: A Complete Quick Reference Guide from Beginner to Advanced with Simple Tips and Tricks to Master All Essential Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, Charts, Tools, & ShortcutsNessuna valutazione finora
- Learn Power BI: A beginner's guide to developing interactive business intelligence solutions using Microsoft Power BIDa EverandLearn Power BI: A beginner's guide to developing interactive business intelligence solutions using Microsoft Power BIValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Designing Data-Intensive Applications: The Big Ideas Behind Reliable, Scalable, and Maintainable SystemsDa EverandDesigning Data-Intensive Applications: The Big Ideas Behind Reliable, Scalable, and Maintainable SystemsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (6)
- Optimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesDa EverandOptimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesNessuna valutazione finora
- Excel Formulas That Automate Tasks You No Longer Have Time ForDa EverandExcel Formulas That Automate Tasks You No Longer Have Time ForValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Microsoft PowerPoint Guide for Success: Learn in a Guided Way to Create, Edit & Format Your Presentations Documents to Visual Explain Your Projects & Surprise Your Bosses And Colleagues | Big Four Consulting Firms MethodDa EverandMicrosoft PowerPoint Guide for Success: Learn in a Guided Way to Create, Edit & Format Your Presentations Documents to Visual Explain Your Projects & Surprise Your Bosses And Colleagues | Big Four Consulting Firms MethodValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Microsoft Power Platform A Deep Dive: Dig into Power Apps, Power Automate, Power BI, and Power Virtual Agents (English Edition)Da EverandMicrosoft Power Platform A Deep Dive: Dig into Power Apps, Power Automate, Power BI, and Power Virtual Agents (English Edition)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Science Beginners Crash Course: Coding Data, Python, Algorithms & HackingDa EverandComputer Science Beginners Crash Course: Coding Data, Python, Algorithms & HackingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (12)
- Scrum: Understanding Scrum at a Deeper Level and Mastering Agile Project ManagementDa EverandScrum: Understanding Scrum at a Deeper Level and Mastering Agile Project ManagementValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Master Your Data with Power Query in Excel and Power BI: Leveraging Power Query to Get & Transform Your Task FlowDa EverandMaster Your Data with Power Query in Excel and Power BI: Leveraging Power Query to Get & Transform Your Task FlowValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Learn Power BI - Second Edition: A comprehensive, step-by-step guide for beginners to learn real-world business intelligenceDa EverandLearn Power BI - Second Edition: A comprehensive, step-by-step guide for beginners to learn real-world business intelligenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Kubernetes: The Updated Guide to Master Kubernetes for EveryoneDa EverandKubernetes: The Updated Guide to Master Kubernetes for EveryoneValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (3)
- Artificial Intelligence in Practice: How 50 Successful Companies Used AI and Machine Learning to Solve ProblemsDa EverandArtificial Intelligence in Practice: How 50 Successful Companies Used AI and Machine Learning to Solve ProblemsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (38)































































































![Microsoft Outlook Guide to Success: Learn Smart Email Practices and Calendar Management for a Smooth Workflow [II EDITION]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/728320983/198x198/d544db3174/1715524985?v=1)






![Microsoft Word Guide for Success: From Basics to Brilliance in Achieving Faster and Smarter Results [II EDITION]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/728320756/198x198/6f19793d5e/1715525026?v=1)





![Microsoft Excel Guide for Success: Transform Your Work with Microsoft Excel, Unleash Formulas, Functions, and Charts to Optimize Tasks and Surpass Expectations [II EDITION]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/728318885/198x198/86d097382f/1715431156?v=1)














