Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
9.2.26 - 983 - 20 PDF
Caricato da
LêXuânThắngDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
9.2.26 - 983 - 20 PDF
Caricato da
LêXuânThắngCopyright:
Formati disponibili
9.2.
26
AOAC Official Method 983.20
Mercury (Methyl) in Fish
and Shellfish
Gas Chromatographic Method
First Action 1983
Final Action 1988
A. Principle
Organic interferences are removed from homogenized material
by acetone wash followed by benzene wash. Protein-bound methyl
Hg is released by addition of HCl and extracted into benzene. Ben-
zene extract is concentrated and analyzed for CH
3
HgCl by GC.
B. Reagents
(a) Solvents.Acetone, benzene, and isopropanol are all dis-
tilled in glass (Burdick & Jackson Laboratories, Inc.; EM Science
OmniSolv reagents). (Note: Benzene is a possible carcinogen.)
(b) Hydrochloric acid solution (1 + 1).Add concentrated HCl
to equal volume of distilled or deionized H
2
O and mix. Extract HCl
solution 5 times with
1
4
its volume of benzene by shaking vigorously
15 s in separator. Discard benzene extracts. Solution may be mixed
in advance but must be extracted immediately before use.
(c) Carrier gas.GC quality ArCH
4
(95 + 5).
(d) Sodiumsulfate.Heat overnight in 600Cfurnace, cool, and
store in capped brown bottle. Line cap with Al foil to prevent con-
tamination from cap.
(e) Methyl mercuric chloride standard solutions.Keep tightly
stoppered. (1) Stockstandardsolution.1000gHg/mL. Weigh0.1252g
CH
3
HgCl into 100 mL volumetric flask. Dilute to volume with benzene.
(2) High intermediate standard solution.40g Hg/mL. Dilute 10.0 mL
stock solution to 250.0 mL with benzene. (3) Low intermediate standard
solution.2.0g Hg/mL. Dilute 10.0 mL high intermediate standard so-
lution to 200.0 mL with benzene. (4) Working standard solu-
tions.0.0100.30g Hg/mL. Prepare monthly by diluting with benzene
involumetric flasks as follows: Dilute 15mLof 2.0gHg/mLstandardto
100.0 mL, 10.0 mLto 100.0 mL, and 10.0 mLto 200.0 mLfor 0.30, 0.20,
and 0.10g Hg/mL, respectively. Dilute 20 mL of 0.10g Hg/mL stan-
dardto25.0mL, 10.0mLto25.0mL, 10.0mLto50.0mL, and10.0mLto
100.0 mL for 0.080, 0.040, 0.020, and 0.010g Hg/mL, respectively.
(f) Mercuric chloride column treatment solution.1000 ppm
(g/mL) HgCl
2
. Dissolve 0.1 g HgCl
2
in 100 mL benzene.
C. Apparatus
Wash all glassware with detergent (Micro Laboratory Cleaner, In-
ternational Products, POBox 70, Burlington, NJ 08601-0070, USA,
or equivalent) and rinse thoroughly with hot tap H
2
O followed by
distilled or deionized H
2
O.
(a) Centrifuge.Model UV (replacement Model PR-7000; In-
ternational Equipment Co.), or equivalent.
(b) Centrifuge tubes.50 mLcapacity with ground glass or Tef-
lon-lined stoppers.
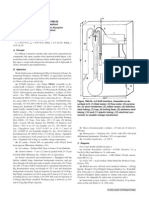
(c) Kuderna-Danish (K-D) concentrators.250 mL flask
(No. 570001, Kontes Glass Co.) and 10 mL graduated concentrator
tube (No. 570050, size 1025, Kontes Glass Co.).
(d) Snyder distilling column.Use No. 503100 size 0003
(Kontes Glass Co.) as is or modify Kontes No. 503000, size 121, in
either of 2 ways: (1) Shorten 3-section, 3-ball column to 2-section,
2-ball column by cutting off top at uppermost constriction. (2) Insu-
late 3-section, 3-ball column by wrapping glass wool around top sec-
tion and holding it in place with Al foil. Glass wool and foil must sur-
round only top section above top ball.
(e) Carborundum boiling chips.20 mesh, HCl-washed.
(f) Graduated cylinders.Class A, 25 mL capacity, with
ground-glass stopper (Kimble 20036, or equivalent).
(g) Transfer pipets.Disposable glass, Pasteur-type 5
3
4
in.
(15 cm) long (No. 13-678-6A, Fisher Scientific Co., or equivalent).
(h) Dropping pipets.5 mL capacity (No. 13-710B, Fisher Sci-
entific Co., or equivalent).
(i) Gas chromatograph.Hewlett Packard Model 5710A (re-
placed by HP-5890 series II) or equivalent, equipped with linear
63
Ni electron capture detector and 6 ft (1.8 m) 2 mm id silanized
glass column packed with 5% DEGS-PS on 100120 mesh
Supelcoport (Supelco, Inc., No. 1-1870). Pack column no closer
than 2.0 cm from injection and detector port nuts and hold pack-
ing in place with 2 cm high quality, silanized glass wool at both
ends. Install oxygen scrubber and molecular sieve dryer
(No. HGC-145, Analabs, Inc. or equivalent) between carrier gas
supply and column. Condition column according to manufac-
turers instructions as follows: Flush column 0.5 h with carrier
gas flowing at 30 mL/min at room temperature. Then heat 1 h at
100C. Next, heat column to 200C at programmed heating rate
of 4C/min and hold at 200C overnight. Do not connect column
to detector during this conditioning process. Maintain
30 mL/min carrier gas flowat all times during conditioning, treat-
ment, and use. Operating conditions: column 155C; injector
200C; detector 300C; carrier gas flow 30 mL/min; and recorder
chart speed 0.51.0 cm/min. Under these conditions and with
HgCl
2
column treatment procedure described below, CH
3
HgCl
peak will appear 23 min after sample injection.
D. Mercuric Chloride Column Treatment
5% DEGS-PS conditioned according to manufacturers instruc-
tions can be used to determine CH
3
HgCl only after treatment by
HgCl
2
solution, B(f). Treat column any time column has been heated
to 200C. Because columnperformance degrades withtime, also treat
column periodically during use. Performappropriate HgCl
2
treatment
procedures described below. Procedure (b) produces most stable
baseline and is recommended over procedure (c) for routine use.
(a) Following 200C column conditioning.If column has
just been conditioned overnight at 200C, use this procedure.
Adjust column temperature to 160C and connect detector.
When baseline is steady, treat column by injecting 20L HgCl
2
treatment solution 5 times at 510 min intervals. (Change in col-
umn performance may be monitored by injecting 5 L 0.010 g
Hg/mL standard solution before and between HgCl
2
treatment
solution injections.) During treatment procedure, large broad
peaks will elute. (CH
3
HgCl peak retention time will decrease
and peak height will increase.) Approximately 1
1
2
1
3
4
h after
last HgCl
2
treatment solution injection, a final large peak will
elute. (CH
3
HgCl peak height and retention time will be stable.)
This broad peak and CH
3
HgCl peak height stability signal com-
pletion of treatment process. Adjust column temperature to
155Cand wait for steady baseline; then column is ready for use.
(b) On day preceding extract analysis.If column has been
treated by procedure (a) or used at 155Cto analyze sample extracts,
column may be treated at end of working day for next days use as
follows: Lower column temperature to 115C and inject 20 L
HgCl
2
treatment solution one time. Broad peaks will elute between
11 and 15 h after HgCl
2
injection. Next working day, increase col-
2000 AOAC INTERNATIONAL
umn temperature to operating temperature. When baseline is steady
(ca 1530 min), column is ready for use.
(c) During extract analysis at 155C.If column has been used
at 155Cfor extract analysis and column performance has degraded
enough to require HgCl
2
treatment, increase column temperature to
160C, inject one 20 L aliquot of HgCl
2
treatment solution, and
monitor baseline. Large, broad peaks will elute 11
1
2
h after HgCl
2
injection, signaling completion of treatment process. Decrease col-
umn temperature to 155Cand wait for steady baseline; then column
is ready for use.
E. Extraction of Methyl Mercury Chloride
Performall operations, except weighing, in laboratory hood. Ac-
curately weigh 2 g homogenized test portion into 50 mL centrifuge
tube. Add 25 mL acetone, stopper, and shake vigorously 15 s. Re-
move stopper, cover with foil, and centrifuge 25 min at 2000 rpm.
Carefully decant and discard acetone. (Use dropping pipet to remove
acetone, if necessary.) Repeat 25 mL acetone wash step twice more.
Break up tissue with glass stirring rod before shaking, if necessary.
Add 20 mL benzene, stopper, and shake vigorously 30 s. Remove
stopper, cover with foil, and centrifuge 25 min at 2000 rpm. Care-
fully decant (or draw off with dropping pipet) and discard benzene.
Extraneous peaks in final GC analytical chromatograms indicate
that more vigorous shaking with acetone and benzene is required.
Add 10 mLHCl solution to centrifuge tube containing acetone
and benzene-washed test portion. Break up tissue with glass stir-
ring rod, and extract sample by adding 20 mL benzene and shak-
ing gently but thoroughly 2 min. Remove stopper, cover with
foil, and centrifuge 5 min at 2000 rpm. If emulsion forms, add
2 mL isopropanol and gently stir benzene layer to break emul-
sion, taking care not to disturb aqueous phase, and recentrifuge
Carefully transfer benzene layer to K-D concentrator, using
5 mL dropping pipet. Rinse centrifuge tube walls with 34 mL
benzene and transfer rinse to K-D concentrator. Repeat extrac-
tion step twice more, adding 20 mL benzene and shaking 1 min
each time. Combine all 3 benzene extracts in K-Dconcentrator.
Place 46 boiling chips in K-D concentrator, connect Snyder col-
umn, wet Snyder column bubble chambers with 34 drops of ben-
zene, and immediately place tube in steam bath or vigorously boiling
H
2
Obath. Evaporate so that 8 mL remains when cooled to roomtem-
perature. Cool. Disconnect concentrator tube and quantitatively trans-
fer solution to 25 mL glass-stoppered graduate using Pasteur-type
transfer pipet. Dilute to 20.0 mL with benzene and mix. Add 4 g
Na
2
SO
4
and mix again. Na
2
SO
4
must be added to 20 mLconcentrated
sample extract within10hof first acetone wash. Tightlystopperedex-
tracts may be held overnight at this point. Analyze by GC.
F. Chromatography
Verify that systemis operating properly by injecting 5Lvolumes
of 0.01 g Hg/mL working standard solution into chromatograph.
Difference between CH
3
HgCl peak heights for 2 injections should be
4%. Check detector linearity by chromatographing all 0.010.30g
Hg/mL working standard solutions.
Inject duplicate5Lvolumes (equivalent to0.5mgtest portion) of ex-
tract. Difference between CH
3
HgCl peak heights for 2 injections should
be 4%. Next, inject duplicate 5 L volumes of standard solution with
CH
3
HgCl concentration approximately equal to or slightly greater than
extract CH
3
HgCl concentration. Because column performance and peak
height slowlydecreasewithtime, calculateeachsampleconcentrationby
comparison to standard solution injected immediately after sample.
Calculate methyl Hg content of homogenate ing Hg/g (ppmHg) by
comparing average CH
3
HgCl peak height of duplicate sample injections
with average CH
3
HgCl peak height of duplicate standard injections.
g Hg/g (ppm) = (R/R) (C / C) 20
where R = average peak height of duplicate test solution injections;
R= average peak height of duplicate standard injections; C = g test
portion; C = concentration of Hg in CH
3
HgCl standard solution
(g Hg/mL).
Reference: JAOAC 66, 1121(1983).
CAS-7439-97-6 (mercury)
2000 AOAC INTERNATIONAL
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Stoichiometry Notes KEYDocumento17 pagineStoichiometry Notes KEYOnofre Algara Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Data Sheet for Emulsified Bituminous PrimerDocumento2 pagineTechnical Data Sheet for Emulsified Bituminous Primerhandhammer qatarNessuna valutazione finora
- ZeolitesDocumento35 pagineZeolitesRizwan Khan100% (2)
- Astm E1269 Standard Test Method For CP by DSCDocumento6 pagineAstm E1269 Standard Test Method For CP by DSCWMJNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.1.01 AOAC of Fi Cial Method 986.15 Ar Senic, Cad Mium, Lead, Se Le Nium, and Zinc in Hu Man and Pet FoodsDocumento3 pagine9.1.01 AOAC of Fi Cial Method 986.15 Ar Senic, Cad Mium, Lead, Se Le Nium, and Zinc in Hu Man and Pet FoodsLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- Torqueo Pikotek PDFDocumento4 pagineTorqueo Pikotek PDFjast111100% (1)
- 9.2.19 - 972 - 25 PDFDocumento1 pagina9.2.19 - 972 - 25 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- Flammables, Explosion Risks and DSEARDocumento10 pagineFlammables, Explosion Risks and DSEARTitash Mukherjee SenNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics of Methanol Production From Natural GasDocumento56 pagineEconomics of Methanol Production From Natural Gaspabel lema0% (1)
- 9.2.24 - 974 - 14Documento1 pagina9.2.24 - 974 - 14LêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.40 AOAC Official Method 993.14 Trace Elements in Waters and WastewatersDocumento11 pagine9.2.40 AOAC Official Method 993.14 Trace Elements in Waters and WastewatersLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.30 - 974 - 15Documento1 pagina9.2.30 - 974 - 15LêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.27 AOAC Official Method 988.11 Mercury (Methyl) in Fish and ShellfishDocumento2 pagine9.2.27 AOAC Official Method 988.11 Mercury (Methyl) in Fish and ShellfishLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.39 - 990 - 08Documento4 pagine9.2.39 - 990 - 08LêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.35 - 985 - 16Documento2 pagine9.2.35 - 985 - 16LêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.36 AOAC Official Method 973.36 Titanium in Cheese: Titanium Dioxide Standard Solution.-0.1 Mg/ml. AccuratelyDocumento1 pagina9.2.36 AOAC Official Method 973.36 Titanium in Cheese: Titanium Dioxide Standard Solution.-0.1 Mg/ml. AccuratelyLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.20 A - 997 - 15 PDFDocumento2 pagine9.2.20 A - 997 - 15 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.28 - 990 - 04Documento3 pagine9.2.28 - 990 - 04LêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.38 - 969 - 32 PDFDocumento1 pagina9.2.38 - 969 - 32 PDFLêXuânThắng100% (1)
- 9.2.23 - 977 - 15 PDFDocumento1 pagina9.2.23 - 977 - 15 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.22 - 971 - 21 PDFDocumento2 pagine9.2.22 - 971 - 21 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.08 - 973 - 34 PDFDocumento1 pagina9.2.08 - 973 - 34 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.14 - 973 - 35 PDFDocumento1 pagina9.2.14 - 973 - 35 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.16 - 979 - 17 PDFDocumento1 pagina9.2.16 - 979 - 17 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.1.04B - 9.1.04b PDFDocumento6 pagine9.1.04B - 9.1.04b PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.18 - 972 - 24 PDFDocumento1 pagina9.2.18 - 972 - 24 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.11 - 944 - 08 PDFDocumento5 pagine9.2.11 - 944 - 08 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.17 - 972 - 23 PDFDocumento1 pagina9.2.17 - 972 - 23 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.12 - 935 - 50 PDFDocumento1 pagina9.2.12 - 935 - 50 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.1.04 - 973 - 32 PDFDocumento2 pagine9.1.04 - 973 - 32 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.1.05 - 979 - 16 PDFDocumento1 pagina9.1.05 - 979 - 16 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.1.09 - 999 - 11 PDFDocumento3 pagine9.1.09 - 999 - 11 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.2.15 - 974 - 13 PDFDocumento1 pagina9.2.15 - 974 - 13 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.1.06 - 990 - 05 PDFDocumento2 pagine9.1.06 - 990 - 05 PDFLêXuânThắng100% (1)
- 9.1.07 - 971 - 20 PDFDocumento1 pagina9.1.07 - 971 - 20 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.1.08 - 999 - 10 PDFDocumento3 pagine9.1.08 - 999 - 10 PDFLêXuânThắngNessuna valutazione finora
- Stabilization and Anlysisng PropertiesDocumento14 pagineStabilization and Anlysisng PropertiesHarshaka Maduwatha JansNessuna valutazione finora
- UWO Chem 3300g Computer MethodsDocumento2 pagineUWO Chem 3300g Computer MethodsmejiasclaudiaNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF Cecil BrochureDocumento20 paginePDF Cecil Brochurechiralic100% (1)
- Manufacturing porcelain figures using binder jetting 3D printingDocumento8 pagineManufacturing porcelain figures using binder jetting 3D printingcesarNessuna valutazione finora
- React Rite Na-MBT50Documento2 pagineReact Rite Na-MBT50seditionaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Trifluoroacetic Acid - MSDS - 299537 PDFDocumento8 pagineTrifluoroacetic Acid - MSDS - 299537 PDFBigbearBigbearNessuna valutazione finora
- BP - 10 - SC - Pre Board - Set-2Documento1 paginaBP - 10 - SC - Pre Board - Set-2Manju MaliyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Combined Gas LawDocumento7 pagineCombined Gas LawAllenWORXNessuna valutazione finora
- L-5 Secondary TreatmentDocumento53 pagineL-5 Secondary Treatmentzubair k peerzadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Computational LaboratoryDocumento31 pagineComputational LaboratoryFrendick LegaspiNessuna valutazione finora
- T06002.006 Viva E System Onsite Training Workbook Eff Date 09-13-21Documento66 pagineT06002.006 Viva E System Onsite Training Workbook Eff Date 09-13-21Zitouni LamineNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive-A ReviewDocumento43 pagineAbrasive-A ReviewA.YusoffNessuna valutazione finora
- Ex 2disesl IndexDocumento6 pagineEx 2disesl IndexSalman AlshammariNessuna valutazione finora
- CurrentDocumento49 pagineCurrentTouati SaidNessuna valutazione finora
- Fat Digestion and Metabolism in RuminantsDocumento23 pagineFat Digestion and Metabolism in Ruminantsshahbaz zafarNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Notes on Semiconductor Theory and Electronics Engineering FundamentalsDocumento11 pagineReview Notes on Semiconductor Theory and Electronics Engineering FundamentalsFrance DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- Characterization of InclusionsDocumento8 pagineCharacterization of Inclusionsmahdisajjadi100% (1)
- Science Grade 5Documento8 pagineScience Grade 5quoc anh nguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Mineral Nutrition MycorrhizaDocumento34 pagineMineral Nutrition MycorrhizaZella PurnamaningtyasNessuna valutazione finora
- Refineria de Cartagena (Reficar) Refinery Expansion - Hydrocarbons TechnologyDocumento3 pagineRefineria de Cartagena (Reficar) Refinery Expansion - Hydrocarbons TechnologyGjorgeluisNessuna valutazione finora
- Elisa: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent AssayDocumento12 pagineElisa: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent AssayAmitNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil Pollution: Causes, Effects and Simple SolutionsDocumento7 pagineSoil Pollution: Causes, Effects and Simple SolutionsVon MorenNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch11 CastingProcessesDocumento102 pagineCh11 CastingProcessesFahmi PrayogiNessuna valutazione finora